在前一篇博客滴滴插件化框架VirtualAPK原理解析(一)之插件Activity管理
中VirtualAPK是如何对Activity进行管理的,本篇博客,我们继续来学习这个框架,这次我们学习的是如何去管理Service。
Freedom框架,我个人手写的0反射插件化框架
Service工作原理分析
说道如何对Service进行插件化,肯定得先了解Service的工作过程,不然何谈插件化?所以我们先一起学习Service的工作原理。
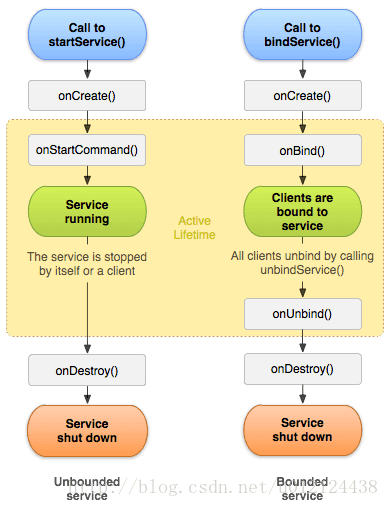
Service分为两种形式:以startService启动的服务和用bindService绑定的服务;其实这两种方法的启动都是大同小异,所以这里,我们以bindService为例分析进行分析即可。
bindService的启动是通过Context类的bindService方法完成的,这个方法需要三个参数:第一个参数代表想要绑定的Service的Intent,第二个参数是一个ServiceConnetion,我们可以通过这个对象接收到Service绑定成功或者失败的回调;第三个参数则是绑定时候的一些FLAG,当然如果你对Service还不是很了解的话,可以看官方的training文档http://developer.android.com/intl/zh-cn/guide/components/services.html
Context的具体实现在ContextImpl类,ContextImpl中的bindService方法直接调用了bindServiceCommon方法
private boolean bindServiceCommon(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags,
UserHandle user) {
IServiceConnection sd;
if (conn == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("connection is null");
}
if (mPackageInfo != null) {
sd = mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher(conn, getOuterContext(),
mMainThread.getHandler(), flags);
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Not supported in system context");
}
validateServiceIntent(service);
try {
IBinder token = getActivityToken();
if (token == null && (flags&BIND_AUTO_CREATE) == 0 && mPackageInfo != null
&& mPackageInfo.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion
< android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.ICE_CREAM_SANDWICH) {
flags |= BIND_WAIVE_PRIORITY;
}
service.prepareToLeaveProcess();
int res = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().bindService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), getActivityToken(),
service, service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver()),
sd, flags, user.getIdentifier());
if (res < 0) {
throw new SecurityException(
"Not allowed to bind to service " + service);
}
return res != 0;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
return false;
}
}
通过代码,其实你会发现最后是通过ActivityManagerNative借助AMS进而完成Service的绑定过程,这里需要提及一下sd变量,这个变量的类型是IServiceConnection,这个IServiceConnection与IApplicationThread是相同的,都是ActivityThread给AMS提供的用来与之进行通信的Binder对象;这个接口的实现类为LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher
接下来我们看ActivityManagerNative的bindService方法
public int bindService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token,
Intent service, String resolvedType,
IServiceConnection connection, int flags, int userId) {
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("bindService");
// Refuse possible leaked file descriptors
if (service != null && service.hasFileDescriptors() == true) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("File descriptors passed in Intent");
}
synchronized(this) {
return mServices.bindServiceLocked(caller, token, service, resolvedType,
connection, flags, userId);
}
}
bindService中调用了ActivityServices类的bindServiceLocked方法:
int bindServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection, int flags,
String callingPackage, int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
final ProcessRecord callerApp = mAm.getRecordForAppLocked(caller);
// 省略部分代码
ServiceLookupResult res =
retrieveServiceLocked(service, resolvedType, callingPackage,
Binder.getCallingPid(), Binder.getCallingUid(), userId, true, callerFg);
// 省略部分代码
ServiceRecord s = res.record;
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
// ... 省略部分代码
mAm.startAssociationLocked(callerApp.uid, callerApp.processName,
s.appInfo.uid, s.name, s.processName);
AppBindRecord b = s.retrieveAppBindingLocked(service, callerApp);
ConnectionRecord c = new ConnectionRecord(b, activity,
connection, flags, clientLabel, clientIntent);
IBinder binder = connection.asBinder();
ArrayList<ConnectionRecord> clist = s.connections.get(binder);
// 对connection进行处理, 方便存取,略
clist.add(c);
if ((flags&Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE) != 0) {
s.lastActivity = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
if (bringUpServiceLocked(s, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false) != null) {
return 0;
}
}
// 与BIND_AUTO_CREATE不同的启动FLAG,原理与后续相同,略
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
return 1;
}
首先通过retrieveServiceLocked方法获取到了intent匹配到的需要bind到的Service组件res;然后把ActivityThread传递过来的IServiceConnection使用ConnectionRecord进行了包装,方便接下来使用;最后如果启动的FLAG为BIND_AUTO_CREATE,那么调用bringUpServiceLocked开始创建Service
private final String bringUpServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, int intentFlags, boolean execInFg,
boolean whileRestarting) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
// 省略代码
final boolean isolated = (r.serviceInfo.flags&ServiceInfo.FLAG_ISOLATED_PROCESS) != 0;
final String procName = r.processName;
ProcessRecord app;
if (!isolated) {
app = mAm.getProcessRecordLocked(procName, r.appInfo.uid, false);
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
try {
app.addPackage(r.appInfo.packageName, r.appInfo.versionCode, mAm.mProcessStats);
// 1. important !!!
realStartServiceLocked(r, app, execInFg);
return null;
} catch (TransactionTooLargeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception when starting service " + r.shortName, e);
}
}
} else {
app = r.isolatedProc;
}
// Not running -- get it started, and enqueue this service record
// to be executed when the app comes up.
if (app == null) {
// 2. important !!!
if ((app=mAm.startProcessLocked(procName, r.appInfo, true, intentFlags,
"service", r.name, false, isolated, false)) == null) {
bringDownServiceLocked(r);
return msg;
}
if (isolated) {
r.isolatedProc = app;
}
}
// 省略代码
return null;
}
如果Service所在的进程已经启动,那么直接调用realStartServiceLocked方法来真正启动Service组件;如果Service所在的进程还没有启动,那么先在AMS中记下这个要启动的Service组件,然后通过startProcessLocked启动新的进程。
先看Service进程已经启动的情况,realStartServiceLocked方法:
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException {
// 省略代码
boolean created = false;
try {
synchronized (r.stats.getBatteryStats()) {
r.stats.startLaunchedLocked();
}
mAm.ensurePackageDexOpt(r.serviceInfo.packageName);
app.forceProcessStateUpTo(ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE);
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.repProcState);
r.postNotification();
created = true;
} catch (DeadObjectException e) {
mAm.appDiedLocked(app);
throw e;
} finally {
// 省略代码
}
requestServiceBindingsLocked(r, execInFg);
//省略代码
}
调用了app.thread的scheduleCreateService方法,这是一个IApplicationThread对象,它是App所在进程提供给AMS的用来与App进程进行通信的Binder对象,这个Binder的Server端在ActivityThread的ApplicationThread类
public final void scheduleCreateService(IBinder token,
ServiceInfo info, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, int processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
CreateServiceData s = new CreateServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.info = info;
s.compatInfo = compatInfo;
sendMessage(H.CREATE_SERVICE, s);
}
这里发送一个消息给ActivityThread的H这个Handler,H类收到这个消息之后,直接调用了ActivityThread类的handleCreateService方法
private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) {
// If we are getting ready to gc after going to the background, well
// we are back active so skip it.
unscheduleGcIdler();
LoadedApk packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
data.info.applicationInfo, data.compatInfo);
Service service = null;
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();
service = (Service) cl.loadClass(data.info.name).newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate service " + data.info.name
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
try {
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Creating service " + data.info.name);
ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, packageInfo);
context.setOuterContext(service);
Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app,
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault());
service.onCreate();
mServices.put(data.token, service);
try {
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// nothing to do.
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to create service " + data.info.name
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
1.使用ClassLoader加载并通过反射创建Service 对象
2.创建ContextImpl ,并绑定Service
3.makeApplication创建Application
4.service.attach方法将创建的Application和ContextImpl 和service进行绑定
5.service.onCreate()方法进行service的创建
虽然都是通过ClassLoader通过反射创建,但是Activity却把创建过程委托给了Instrumentation类,而Service则是直接进行。
ActivityThread里面的handleCreateService方法成功创建出了Service对象,并且调用了它的onCreate方法;到这里我们的Service已经启动成功。scheduleCreateService这个Binder调用过程结束,代码又回到了AMS进程的realStartServiceLocked方法。
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException {
// 省略代码
boolean created = false;
try {
synchronized (r.stats.getBatteryStats()) {
r.stats.startLaunchedLocked();
}
mAm.ensurePackageDexOpt(r.serviceInfo.packageName);
app.forceProcessStateUpTo(ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE);
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.repProcState);
r.postNotification();
created = true;
} catch (DeadObjectException e) {
mAm.appDiedLocked(app);
throw e;
} finally {
// 省略代码
}
requestServiceBindingsLocked(r, execInFg);
// 省略代码
}
scheduleCreateService这个binder调用之后,执行了一个requestServiceBindingsLocked方法
private final boolean requestServiceBindingLocked(ServiceRecord r,
IntentBindRecord i, boolean execInFg, boolean rebind) {
if (r.app == null || r.app.thread == null) {
// If service is not currently running, can't yet bind.
return false;
}
if ((!i.requested || rebind) && i.apps.size() > 0) {
try {
bumpServiceExecutingLocked(r, execInFg, "bind");
r.app.forceProcessStateUpTo(ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE);
r.app.thread.scheduleBindService(r, i.intent.getIntent(), rebind,
r.app.repProcState);
if (!rebind) {
i.requested = true;
}
i.hasBound = true;
i.doRebind = false;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG, "Crashed while binding " + r);
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
又通过IApplicationThread这个Binder进行了一次IPC调用,我们跟踪ActivityThread类里面的ApplicationThread的scheduleBindService方法,发现这个方法不过通过Handler转发了一次消息,真正的处理代码在handleBindService里面:
private void handleBindService(BindServiceData data) {
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);
if (DEBUG_SERVICE)
Slog.v(TAG, "handleBindService s=" + s + " rebind=" + data.rebind);
if (s != null) {
try {
data.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(s.getClassLoader());
data.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
try {
if (!data.rebind) {
IBinder binder = s.onBind(data.intent);
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().publishService(
data.token, data.intent, binder);
} else {
s.onRebind(data.intent);
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
}
ensureJitEnabled();
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(s, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to bind to service " + s
+ " with " + data.intent + ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
}
要Bind的Service在这里完成了绑定,绑定之后又通过ActivityManagerNative这个Binder进行一次IPC调用,我们查看AMS的publishService方法,这个方法又调用了publishServiceLocked方法
void publishServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG, "PUBLISHING " + r
+ " " + intent + ": " + service);
if (r != null) {
Intent.FilterComparison filter
= new Intent.FilterComparison(intent);
IntentBindRecord b = r.bindings.get(filter);
if (b != null && !b.received) {
b.binder = service;
b.requested = true;
b.received = true;
for (int conni=r.connections.size()-1; conni>=0; conni--) {
ArrayList<ConnectionRecord> clist = r.connections.valueAt(conni);
for (int i=0; i<clist.size(); i++) {
ConnectionRecord c = clist.get(i);
if (!filter.equals(c.binding.intent.intent)) {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(
TAG, "Not publishing to: " + c);
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(
TAG, "Bound intent: " + c.binding.intent.intent);
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(
TAG, "Published intent: " + intent);
continue;
}
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG, "Publishing to: " + c);
try {
c.conn.connected(r.name, service);
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Failure sending service " + r.name +
" to connection " + c.conn.asBinder() +
" (in " + c.binding.client.processName + ")", e);
}
}
}
}
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, mDestroyingServices.contains(r), false);
}
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}
这里终于到IServiceConnection的用处了,在bindServiceLocked方法里面,这个IServiceConnection放到了一个ConnectionRecord的List中存放在ServiceRecord里面,这里所做的就是取出已经被Bind的这个Service对应的IServiceConnection对象,然后调用它的connected方法;我们说过,这个IServiceConnection也是一个Binder对象,它的Server端在LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher里面。接下来是LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher的connected方法
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
if (mActivityThread != null) {
mActivityThread.post(new RunConnection(name, service, 0));
} else {
doConnected(name, service);
}
}
无论哪种判断,都会走到doConnected方法中
public void doConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
ServiceDispatcher.ConnectionInfo old;
ServiceDispatcher.ConnectionInfo info;
synchronized (this) {
if (mForgotten) {
// We unbound before receiving the connection; ignore
// any connection received.
return;
}
old = mActiveConnections.get(name);
if (old != null && old.binder == service) {
// Huh, already have this one. Oh well!
return;
}
if (service != null) {
// A new service is being connected... set it all up.
mDied = false;
info = new ConnectionInfo();
info.binder = service;
info.deathMonitor = new DeathMonitor(name, service);
try {
service.linkToDeath(info.deathMonitor, 0);
mActiveConnections.put(name, info);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// This service was dead before we got it... just
// don't do anything with it.
mActiveConnections.remove(name);
return;
}
} else {
// The named service is being disconnected... clean up.
mActiveConnections.remove(name);
}
if (old != null) {
old.binder.unlinkToDeath(old.deathMonitor, 0);
}
}
// If there was an old service, it is not disconnected.
if (old != null) {
mConnection.onServiceDisconnected(name);
}
// If there is a new service, it is now connected.
if (service != null) {
mConnection.onServiceConnected(name, service);
}
}
这里我们知道了onServiceConnected方法是在哪里进行的回调。
到这里,Service所在进程已经存在的情况已经分析完毕,如果Service所在进程不存在,那么会调用startProcessLocked方法创建一个新的进程,并把需要启动的Service放在一个队列里面;创建进程的过程通过Zygote fork出来,进程创建成功之后会调用ActivityThread的main方法,在这个main方法里面间接调用到了AMS的attachApplication方法,在AMS的attachApplication里面会检查刚刚那个待启动Service队列里面的内容,并执行Service的启动操作;之后的启动过程与进程已经存在的情况下相同
如何对Service进行插件化?
通过对Service的工作原理的分析,我们知道Service通过Context类完成启动,接着通过ActivityMnagaerNative进入AMS,最后又通过IApplicationThread这个Binder IPC到App进程的Binder线程池,然后通过H转发消息到App进程的主线程,最终完成组件生命周期的回调
Activity与Service组件最大的不同点在于,Activity组件可以与用户进行交互;这一点意味着用户的行为会对Activity组件产生影响,对我们来说最重要的影响就是Activity组件的生命周期;用户点击按钮从界面A跳转到界面B,会引起A和B这两个Activity一系列生命周期的变化。而Service组件则代表后台任务,除了内存不足系统回收之外,它的生命周期完全由我们的代码控制,与用户的交互无关。
Activity组件的生命周期受用户交互影响,而这种变化只有Android系统才能感知,因此我们必须把插件的Activity交给系统管理,才能拥有完整的生命周期;但Service组件的生命周期不受外界因素影响,那么自然而然,我们可以手动控制它的生命周期,既然Service的生命周期可以由我们自己控制,那么我们可以有更简单的方案实现它的插件化。
可以通过手动控制Service组件的生命周期实现Service的插件化
Service的生命周期相当简单:整个生命周期从调用 onCreate() 开始起,到 onDestroy() 返回时结束。对于非绑定服务,就是从startService调用到stopService或者stopSelf调用。对于绑定服务,就是bindService调用到unbindService调用;
1.如果以startService方式启动插件Service,直接回调要启动的Service对象的onStartCommand方法即可;如果用stopService或者stopSelf的方式停止Service,只需要回调对应的Service组件的onDestroy方法。
2.如果用bindService方式绑定插件Service,可以调用对应Service对应的onBind方法,获取onBind方法返回的Binder对象,然后通过ServiceConnection对象进行回调统计;unBindService的实现同理。
VirtualAPK是如何实现Service插件化的
VirtualAPK中使用了一种代理分发的方法,注册一个真正的Service组件ProxyService,让这个Service承载一个真正的Service组件所具备的能力(进程优先级等);当启动插件的服务比如PluginService的时候,我们统一启动这个ProxyService,当这个ProxyService运行起来之后,再在它的onStartCommand等方法里面进行分发,执行PluginService的onStartCommond等对应的方法
1.注册代理Service
上面说道,我们需要一个货真价实的Service组件来承载进程优先级等功能,因此需要在AndroidManifest.xml中声明一个或多个这样的Sevice,打开VirtualAPK的代码,我们发现也确实这样的:
<!-- Local Service running in main process -->
<service android:name="com.didi.virtualapk.delegate.LocalService" />
<!-- Daemon Service running in child process -->
<service android:name="com.didi.virtualapk.delegate.RemoteService" android:process=":daemon">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="${applicationId}.intent.ACTION_DAEMON_SERVICE" />
</intent-filter>
</service>
可以发现,VirtualAPK注册了两个Service ,一个本进程的Service,一个是跨进程的Service
2.Hook IActivityManager,拦截startService等调用过程
要手动控制Service组件的生命周期,需要拦截startService,stopService等调用,并且把启动插件Service全部重定向为启动ProxyService(保留原始插件Service信息);这个拦截过程需要Hook ActvityManagerNative,还记得我们前面说VirtualAPK通过动态代理的方式Hook ActvityManagerNative方法吗?
hookSystemServices是在PluginManager中实现的
private void prepare() {
Systems.sHostContext = getHostContext();
this.hookInstrumentationAndHandler();
this.hookSystemServices();
}
private void hookSystemServices() {
try {
Singleton<IActivityManager> defaultSingleton = (Singleton<IActivityManager>) ReflectUtil.getField(ActivityManagerNative.class, null, "gDefault");
IActivityManager activityManagerProxy = ActivityManagerProxy.newInstance(this, defaultSingleton.get());
// Hook IActivityManager from ActivityManagerNative
ReflectUtil.setField(defaultSingleton.getClass().getSuperclass(), defaultSingleton, "mInstance", activityManagerProxy);
if (defaultSingleton.get() == activityManagerProxy) {
this.mActivityManager = activityManagerProxy;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
首先拿到ActivityManagerNative中的gDefault对象,该对象返回的是一个Singleton,然后拿到其mInstance对象,即IActivityManager对象(可以理解为和AMS交互的binder的client对象)对象。
然后通过动态代理的方式,替换为了一个代理对象。
ActivityManagerProxy.java
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if ("startService".equals(method.getName())) {
try {
return startService(proxy, method, args);
} catch (Throwable e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Start service error", e);
}
} else if ("stopService".equals(method.getName())) {
try {
return stopService(proxy, method, args);
} catch (Throwable e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Stop Service error", e);
}
} else if ("stopServiceToken".equals(method.getName())) {
try {
return stopServiceToken(proxy, method, args);
} catch (Throwable e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Stop service token error", e);
}
} else if ("bindService".equals(method.getName())) {
try {
return bindService(proxy, method, args);
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else if ("unbindService".equals(method.getName())) {
try {
return unbindService(proxy, method, args);
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else if ("getIntentSender".equals(method.getName())) {
try {
getIntentSender(method, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else if ("overridePendingTransition".equals(method.getName())){
try {
overridePendingTransition(method, args);
} catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
try {
// sometimes system binder has problems.
return method.invoke(this.mActivityManager, args);
} catch (Throwable th) {
Throwable c = th.getCause();
if (c != null && c instanceof DeadObjectException) {
// retry connect to system binder
IBinder ams = ServiceManager.getService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
if (ams != null) {
IActivityManager am = ActivityManagerNative.asInterface(ams);
mActivityManager = am;
}
}
Throwable cause = th;
do {
if (cause instanceof RemoteException) {
throw cause;
}
} while ((cause = cause.getCause()) != null);
throw c != null ? c : th;
}
}
可以看到在ActivityManagerProxy中,对startService等将所有的Service操作进行拦截,然后调用了自己内部的相应方法,我们先看startService方法
3.拦截startService方法
private Object startService(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
IApplicationThread appThread = (IApplicationThread) args[0];
Intent target = (Intent) args[1];
ResolveInfo resolveInfo = this.mPluginManager.resolveService(target, 0);
if (null == resolveInfo || null == resolveInfo.serviceInfo) {
// is host service
return method.invoke(this.mActivityManager, args);
}
return startDelegateServiceForTarget(target, resolveInfo.serviceInfo, null, RemoteService.EXTRA_COMMAND_START_SERVICE);
}
1.mPluginManager.resolveService方法通过Intent 过滤出要启动的插件Service的ResolveInfo
public ResolveInfo resolveService(Intent intent, int flags) {
for (LoadedPlugin plugin : this.mPlugins.values()) {
ResolveInfo resolveInfo = plugin.resolveService(intent, flags);
if (null != resolveInfo) {
return resolveInfo;
}
}
return null;
}
这个方法最终会到LoadedPlugin的resolveService方法中
public ResolveInfo resolveService(Intent intent, int flags) {
List<ResolveInfo> query = this.queryIntentServices(intent, flags);
if (null == query || query.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
ContentResolver resolver = this.mPluginContext.getContentResolver();
return chooseBestActivity(intent, intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(resolver), flags, query);
}
然后会调用queryIntentServices
public List<ResolveInfo> queryIntentServices(Intent intent, int flags) {
ComponentName component = intent.getComponent();
List<ResolveInfo> resolveInfos = new ArrayList<ResolveInfo>();
ContentResolver resolver = this.mPluginContext.getContentResolver();
for (PackageParser.Service service : this.mPackage.services) {
if (service.getComponentName().equals(component)) {
ResolveInfo resolveInfo = new ResolveInfo();
resolveInfo.serviceInfo = service.info;
resolveInfos.add(resolveInfo);
} else if (component == null) {
// only match implicit intent
for (PackageParser.ServiceIntentInfo intentInfo : service.intents) {
if (intentInfo.match(resolver, intent, true, TAG) >= 0) {
ResolveInfo resolveInfo = new ResolveInfo();
resolveInfo.serviceInfo = service.info;
resolveInfos.add(resolveInfo);
break;
}
}
}
}
return resolveInfos;
}
如果要启动的Intent中含有component信息,则根据component来匹配,否则component为null的话,则根据intentInfo进行匹配
回到ActivityManagerProxy的startService方法中,如果null == resolveInfo,则表明不是插件里的Service,否则调用startDelegateServiceForTarget
private ComponentName startDelegateServiceForTarget(Intent target, ServiceInfo serviceInfo, Bundle extras, int command) {
Intent wrapperIntent = wrapperTargetIntent(target, serviceInfo, extras, command);
return mPluginManager.getHostContext().startService(wrapperIntent);
}
还记得我们说要将启动的PluginService先替换成ProxyService么,这个动作就是在wrapperTargetIntent方法中完成的
private Intent wrapperTargetIntent(Intent target, ServiceInfo serviceInfo, Bundle extras, int command) {
// fill in service with ComponentName
target.setComponent(new ComponentName(serviceInfo.packageName, serviceInfo.name));
String pluginLocation = mPluginManager.getLoadedPlugin(target.getComponent()).getLocation();
// start delegate service to run plugin service inside
boolean local = PluginUtil.isLocalService(serviceInfo);
Class<? extends Service> delegate = local ? LocalService.class : RemoteService.class;
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setClass(mPluginManager.getHostContext(), delegate);
intent.putExtra(RemoteService.EXTRA_TARGET, target);
intent.putExtra(RemoteService.EXTRA_COMMAND, command);
intent.putExtra(RemoteService.EXTRA_PLUGIN_LOCATION, pluginLocation);
if (extras != null) {
intent.putExtras(extras);
}
return intent;
}
这个方法主要做了以下步骤:
1.给target的Intent设置Component
target.setComponent(new ComponentName(serviceInfo.packageName, serviceInfo.name));
2.获取要启动的插件service的插件路径
String pluginLocation = mPluginManager.getLoadedPlugin(target.getComponent()).getLocation();
3.判断目标service是本地的还是跨进程的
boolean local = PluginUtil.isLocalService(serviceInfo);
Class<? extends Service> delegate = local ? LocalService.class : RemoteService.class;
4.替换intent为启动代理的Service的intent,并将启动真正插件的Service的intent保存到RemoteService.EXTRA_TARGET参数中,携将command保存到EXTRA_COMMAND_START_SERVICE,以及插件apk路径保存到EXTRA_PLUGIN_LOCATION中。
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setClass(mPluginManager.getHostContext(), delegate);
intent.putExtra(RemoteService.EXTRA_TARGET, target);
intent.putExtra(RemoteService.EXTRA_COMMAND, command);
intent.putExtra(RemoteService.EXTRA_PLUGIN_LOCATION, pluginLocation);
if (extras != null) {
intent.putExtras(extras);
}
接下来就是启动代理service啦
private ComponentName startDelegateServiceForTarget(Intent target, ServiceInfo serviceInfo, Bundle extras, int command) {
Intent wrapperIntent = wrapperTargetIntent(target, serviceInfo, extras, command);
return mPluginManager.getHostContext().startService(wrapperIntent);
}
接下来就会到LocalService中了,直接来到onStartCommand方法
if (null == intent || !intent.hasExtra(EXTRA_TARGET) || !intent.hasExtra(EXTRA_COMMAND)) {
return START_STICKY;
}
Intent target = intent.getParcelableExtra(EXTRA_TARGET);
int command = intent.getIntExtra(EXTRA_COMMAND, 0);
if (null == target || command <= 0) {
return START_STICKY;
}
如果启动不是插件的service,那就原来咋样就咋样,否则就根据传入的command来走相应的步骤,首先是EXTRA_COMMAND_START_SERVICE
case EXTRA_COMMAND_START_SERVICE: {
ActivityThread mainThread = (ActivityThread)ReflectUtil.getActivityThread(getBaseContext());
IApplicationThread appThread = mainThread.getApplicationThread();
Service service;
if (this.mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().isServiceAvailable(component)) {
service = this.mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().getService(component);
} else {
try {
service = (Service) plugin.getClassLoader().loadClass(component.getClassName()).newInstance();
Application app = plugin.getApplication();
IBinder token = appThread.asBinder();
Method attach = service.getClass().getMethod("attach", Context.class, ActivityThread.class, String.class, IBinder.class, Application.class, Object.class);
IActivityManager am = mPluginManager.getActivityManager();
attach.invoke(service, plugin.getPluginContext(), mainThread, component.getClassName(), token, app, am);
service.onCreate();
this.mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().rememberService(component, service);
} catch (Throwable t) {
return START_STICKY;
}
}
service.onStartCommand(target, 0, this.mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().getServiceCounter(service).getAndIncrement());
break;
}
如果这个插件service之前已经创建过了,已经缓存在ComponentsHandler中的mServices中,则不再重复创建
if (this.mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().isServiceAvailable(component)) {
service = this.mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().getService(component);
}
如果之前没有进行创建过,则通过ClassLoader加载这个service,反射调用service的attach方法,传入相应的参数,然后手动调用service的onCreate方法,并将这个service添加到缓存中,这样service的创建就完成了。
else {
try {
service = (Service) plugin.getClassLoader().loadClass(component.getClassName()).newInstance();
Application app = plugin.getApplication();
IBinder token = appThread.asBinder();
Method attach = service.getClass().getMethod("attach", Context.class, ActivityThread.class, String.class, IBinder.class, Application.class, Object.class);
IActivityManager am = mPluginManager.getActivityManager();
attach.invoke(service, plugin.getPluginContext(), mainThread, component.getClassName(), token, app, am);
service.onCreate();
this.mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().rememberService(component, service);
} catch (Throwable t) {
return START_STICKY;
}
}
当然上面的这段代码,其实思路就是来源于系统源码,他参照了系统是如何创建Service对象的,这个代码就是在ActivityThread类的handleCreateService完成,代码如下
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();
service = (Service) cl.loadClass(data.info.name).newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate service " + data.info.name
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
try {
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Creating service " + data.info.name);
ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, packageInfo);
context.setOuterContext(service);
Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app,
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault());
service.onCreate();
mServices.put(data.token, service);
try {
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// nothing to do.
}
}
4.拦截stopService方法
stopService方法与startService大同小异,最终都会到LocalService的onStartCommand方法中
case EXTRA_COMMAND_STOP_SERVICE: {
Service service = this.mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().forgetService(component);
if (null != service) {
try {
service.onDestroy();
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Unable to stop service " + service + ": " + e.toString());
}
} else {
Log.i(TAG, component + " not found");
}
break;
}
其实stopService方法十分简单,就是从ComponentsHandler中将对应的Service 从集合中移除,然后调用其service.onDestroy()方法
5.bindService方法
private Object bindService(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Intent target = (Intent) args[2];
ResolveInfo resolveInfo = this.mPluginManager.resolveService(target, 0);
if (null == resolveInfo || null == resolveInfo.serviceInfo) {
// is host service
return method.invoke(this.mActivityManager, args);
}
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
PluginUtil.putBinder(bundle, "sc", (IBinder) args[4]);
startDelegateServiceForTarget(target, resolveInfo.serviceInfo, bundle, RemoteService.EXTRA_COMMAND_BIND_SERVICE);
mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().remberIServiceConnection((IBinder) args[4], target);
return 1;
}
这里将IBinder存入了一个Bundle中,这个IBinder就是我们前面分析源码时候提及的IServiceConnection类,然后同样是通过startDelegateServiceForTarget,然后又是来到LocalService的onStartCommand方法中
case EXTRA_COMMAND_BIND_SERVICE: {
ActivityThread mainThread = (ActivityThread)ReflectUtil.getActivityThread(getBaseContext());
IApplicationThread appThread = mainThread.getApplicationThread();
Service service = null;
if (this.mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().isServiceAvailable(component)) {
service = this.mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().getService(component);
} else {
try {
service = (Service) plugin.getClassLoader().loadClass(component.getClassName()).newInstance();
Application app = plugin.getApplication();
IBinder token = appThread.asBinder();
Method attach = service.getClass().getMethod("attach", Context.class, ActivityThread.class, String.class, IBinder.class, Application.class, Object.class);
IActivityManager am = mPluginManager.getActivityManager();
attach.invoke(service, plugin.getPluginContext(), mainThread, component.getClassName(), token, app, am);
service.onCreate();
this.mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().rememberService(component, service);
} catch (Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
}
try {
IBinder binder = service.onBind(target);
IBinder serviceConnection = PluginUtil.getBinder(intent.getExtras(), "sc");
IServiceConnection iServiceConnection = IServiceConnection.Stub.asInterface(serviceConnection);
iServiceConnection.connected(component, binder);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
break;
}
来到这里,前半部分还是和startService一样,去创建Service并调用其onCreate方法,不同的是下面这部分
try {
IBinder binder = service.onBind(target);
IBinder serviceConnection = PluginUtil.getBinder(intent.getExtras(), "sc");
IServiceConnection iServiceConnection = IServiceConnection.Stub.asInterface(serviceConnection);
iServiceConnection.connected(component, binder);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
我们知道通过bindService的方式,还有一个ServiceConnection回调的问题,这里就是将之前保存的IServiceConnection取出来,然后手动调用其connected方法,完成这个回调的过程,具体可以参考AMS的如下源码部分:
void publishServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
if (r != null) {
Intent.FilterComparison filter
= new Intent.FilterComparison(intent);
IntentBindRecord b = r.bindings.get(filter);
if (b != null && !b.received) {
b.binder = service;
b.requested = true;
b.received = true;
for (int conni=r.connections.size()-1; conni>=0; conni--) {
ArrayList<ConnectionRecord> clist = r.connections.valueAt(conni);
for (int i=0; i<clist.size(); i++) {
ConnectionRecord c = clist.get(i);
if (!filter.equals(c.binding.intent.intent)) {
continue;
}
try {
c.conn.connected(r.name, service);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
}
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, mDestroyingServices.contains(r), false);
}
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}
7.unbindService
unbindService的套路也是基本一致,我们只看LocalService就可以了
case EXTRA_COMMAND_UNBIND_SERVICE: {
Service service = this.mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().forgetService(component);
if (null != service) {
try {
service.onUnbind(target);
service.onDestroy();
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Unable to unbind service " + service + ": " + e.toString());
}
} else {
Log.i(TAG, component + " not found");
}
break;
}
也是非常简单,取出service,手动调用 service.onUnbind()和service.onDestroy()方法即可
到此,整个VirtualAPK框架的Service就基本分析完毕了,细心的你或许会发现在ActivityManagerProxy中还hook了一个stopServiceToken方法,这个方法主要用于一些特殊的Service,比如IntentService,其stopSelf是由自身调用的,最终会调用mActivityManager.stopServiceToken方法,这个方法最后还是走代理stopService的逻辑。
























 1056
1056











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










