代码下载地址:http://www.zuidaima.com/share/1774096228535296.htm
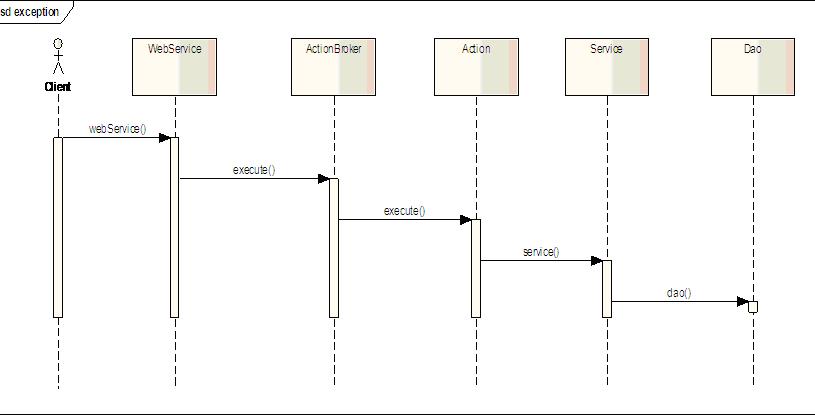
应用项目大致的体系结构:
该异常处理框架满足的要求:
- 完整的异常组织结构
- 异常的统一处理
- 可配置,受管式,方便使用
完整的异常组织结构:
- 用户可以方便的定义自己的异常,但所有UncheckedException需要继承BaseAppRuntimeException,所有的checked Exception可以继承BaseAppException,或者需要抛出且不需要check时用WrapperredAppException封装后抛出
- 合理地使用checked异常
- Exception有唯一的error code,这样用户报告异常后,可以根据异常号找到相应Exception,把exception直接显示给用户也没有太大的意义,如何纪录exception那就是下文讲到的ExceptionHandler的职责了。
- 如果是第三方包括jdk中的异常,需要封装成BaseAppException或者BaseAppRuntimeException后抛出
统一的异常处理
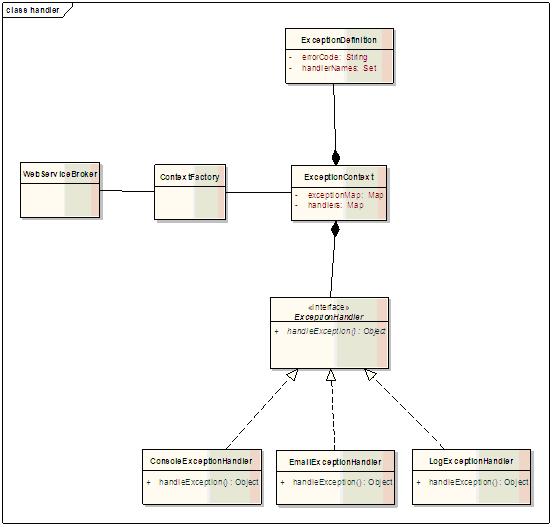
异常统一在框架中进行处理,不需要在上层应用的代码中去处理抛出的异常。为了尽量捕捉到所有的异常,将异常处理放在了ActionBroker中,这样凡是action以后抛出的异常都可以捕捉到,因为webservice只是简单的调用action类的方法,一般不会出现异常。当我们捕捉到异常后,需要进行异常处理,定义了ExceptionHandler接口,用接口抽象出异常处理类的具体实现。
USFContextFactory: 创建ExceptionContext的工厂
- package com.ldd0.exception.context;
- public class CoreContextFactory {
- private static CoreContextFactory instance;
- private volatile ExceptionContext exceptionContext;
- private Object exceptionContextLock = new Object();
- private CoreContextFactory() {
- }
- public static synchronized CoreContextFactory getInstance() {
- if (null == instance) {
- instance = new CoreContextFactory();
- }
- return instance;
- }
- public ExceptionContext getExceptionContext() {
- ExceptionContext tempExpContext = exceptionContext;
- if (tempExpContext == null) {
- synchronized (exceptionContextLock) {
- tempExpContext = exceptionContext;
- if (tempExpContext == null)
- exceptionContext = tempExpContext = new ExceptionContext();
- }
- }
- return tempExpContext;
- }
- }
ExceptionContext: 存放全局的exception信息
- package com.ldd600.exception.context;
- import java.util.ArrayList;
- import java.util.Collection;
- import java.util.Collections;
- import java.util.HashMap;
- import java.util.List;
- import java.util.Map;
- import java.util.Set;
- import org.springframework.util.Assert;
- import com.ldd600.exception.base.BaseAppRuntimeException;
- import com.ldd600.exception.base.ConfigException;
- import com.ldd600.exception.base.handler.ExceptionHandler;
- import com.ldd600.exception.config.ExceptionDefinition;
- public class ExceptionContext {
- private Map<Class<?>, ExceptionDefinition> exceptionMap;
- private Map<String, ExceptionHandler> handlers = new HashMap<String, ExceptionHandler>();
- ExceptionContext() {
- exceptionMap = new HashMap<Class<?>, ExceptionDefinition>();
- }
- public boolean containsException(Class<?> expClazz) {
- return (exceptionMap.containsKey(expClazz));
- }
- public void addExceptionHander(Class<?> expClazz, Class<? extends ExceptionHandler> handlerClazz) {
- try {
- ExceptionDefinition definition = getRealExceptionDefinition(expClazz);
- if (null == definition) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException(expClazz.getName() + "not in the context, please configure or add it to the context first!!");
- }
- ExceptionHandler handler = handlers.get(handlerClazz.getName());
- if (null == handler) {
- handler = handlerClazz.newInstance();
- handlers.put(handlerClazz.getName(), handler);
- }
- definition.getHandlerNames().add(handlerClazz.getName());
- } catch (Exception ex) {
- throw new ConfigException("Add exception handler to context failure!", ex);
- }
- }
- public void addExceptionHandler(Class<?> expClazz, String errorCode, Class<? extends ExceptionHandler> handlerClazz) {
- Assert.hasLength(errorCode, expClazz + " errorCode must not be null or empty string!");
- ExceptionDefinition definition = getRealExceptionDefinition(expClazz);
- if(null == definition) {
- definition = new ExceptionDefinition(errorCode);
- exceptionMap.put(expClazz, definition);
- }
- addExceptionHander(expClazz, handlerClazz);
- }
- public void addExceptionHandlers(Class<?> expClazz, Class<? extends ExceptionHandler> handlerClazzes) {
- for(Class<? extends ExceptionHandler> handlerClazz : handlerClazzes) {
- addExceptionHander(expClazz, handlerClazz);
- }
- }
- public void removeExceptionHandler(Class<?> expClazz, Class<? extends ExceptionHandler> handlerClazz) {
- Assert.isTrue(containsException(expClazz));
- String handlerName = handlerClazz.getName();
- getExceptionDefinition(expClazz).getHandlerNames().remove(handlerName);
- Collection<ExceptionDefinition> definitons = exceptionMap.values();
- boolean isClearHandler = true;
- for (ExceptionDefinition expDefinition : definitons) {
- if (expDefinition.getHandlerNames().contains(handlerName)) {
- isClearHandler = false;
- break;
- }
- }
- if (isClearHandler) {
- handlers.remove(handlers.get(handlerName));
- }
- }
- public void setExceptionDefinition(Class<?> expClazz, ExceptionDefinition definition) {
- exceptionMap.put(expClazz, definition);
- }
- public ExceptionDefinition getExceptionDefinition(Class<?> expClazz) {
- if (containsException(expClazz)) {
- return exceptionMap.get(expClazz);
- } else if (BaseAppRuntimeException.class.isAssignableFrom(expClazz.getSuperclass())) {
- return getExceptionDefinition(expClazz.getSuperclass());
- } else {
- return null;
- }
- }
- public ExceptionDefinition getRealExceptionDefinition(Class<?> expClazz) {
- return exceptionMap.get(expClazz);
- }
- public List<ExceptionHandler> getExceptionHandlers(Class<?> expClazz){
- ExceptionDefinition definition = getExceptionDefinition(expClazz);
- if (null != definition) {
- Set<String> handlerNames = definition.getHandlerNames();
- List<ExceptionHandler> handlerList = new ArrayList<ExceptionHandler>(handlerNames.size());
- for (String handlerName : handlerNames) {
- ExceptionHandler handler = handlers.get(handlerName);
- handlerList.add(handler);
- }
- List<ExceptionHandler> resultHandlerList = new ArrayList<ExceptionHandler>(handlerList);
- return resultHandlerList;
- } else {
- return Collections.<ExceptionHandler> emptyList();
- }
- }
- public String getErrorCode(Class<?> expClazz){
- ExceptionDefinition definition = getExceptionDefinition(expClazz);
- if (null != definition) {
- return definition.getErrorCode();
- } else {
- return "";
- }
- }
- }
ExceptionDefinition: Exception信息单元
- package com.ldd0.exception.config;
- import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
- import java.util.Set;
- public class ExceptionDefinition {
- private String errorCode;
- private Set<String> handlerNames = new LinkedHashSet<String> ();
- ExceptionDefinition() {
- }
- public ExceptionDefinition(String errorCode) {
- this.errorCode = errorCode;
- }
- public String getErrorCode() {
- return errorCode;
- }
- public void setErrorCode(String errorCode) {
- this.errorCode = errorCode;
- }
- public Set<String> getHandlerNames() {
- return handlerNames;
- }
- }
ExceptionDefiniton定义了和某个exception相关的具体信息,根据exception的class name可以从exceptionContext中的exceptionMap得到指定的exception的相关信息,这些信息是在系统初始化时读取到exceptionContext中的。并且避免了exception handler的重复初始化。
可配置,受管式,方便使用
采取两种配置方式,exception的相关信息比如它的errorCode, exceptionHandlers可以配置在外部的xml文件中,也可以用annotation标注。对于exception的处理是有继承性质的,如果某个exception没有在exceptionContext中注册,就使用它的父类的配置信息。如果无任何父类在exceptionContext中注册,就使用默认机制进行处理。
XML 方案:
因为spring2.0支持自定义schema功能,我们可以方便地采用自己的schema只要实现NamespaceHandler和BeanDefinitionPaser,后面一个比较重要,可以将自定义xml文件中的相关类注册到spring的上下文中,成为spring bean。
Xml schema:
- <xsd:complexType name="exceptionType">
- <xsd:sequence>
- <xsd:element name="level" default="error" minOccurs="0">
- <xsd:simpleType>
- <xsd:restriction base="xsd:string">
- <xsd:enumeration value="error" />
- <xsd:enumeration value="warning" />
- <xsd:enumeration value="info" />
- <xsd:enumeration value="confirmation" />
- </xsd:restriction>
- </xsd:simpleType>
- </xsd:element>
- <xsd:element name="handler" maxOccurs="unbounded">
- <xsd:simpleType>
- <xsd:restriction base="xsd:string" />
- </xsd:simpleType>
- </xsd:element>
- </xsd:sequence>
- <xsd:attribute name="errorCode">
- <xsd:simpleType>
- <xsd:restriction base="xsd:string">
- <xsd:whiteSpace value="preserve" />
- <xsd:pattern value="LDD600-+\d{1,5}.*" />
- </xsd:restriction>
- </xsd:simpleType>
- </xsd:attribute>
- <xsd:attribute name="class" type="xsd:string" use="required" />
- </xsd:complexType>
Annotation方案:
JDK1.5以上就有了annotation,可以简化我们的配置,使得配置信息和代码联系在一起,增加了代码的可读性。如何在spring中注册自定义的annotation和用annotation标注的class,可以参考文章2和文章: 。对于每个注册了的class用ExceptionalAnnotationBeanPostProcessor来parse具体的annotation信息(对于annotation的parse方法还会在以后继续改进)。
- package com.ldd600.exception.processor;
- import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
- import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
- import com.ldd600.exception.annotation.Exceptional;
- import com.ldd600.exception.base.BaseAppException;
- import com.ldd600.exception.base.BaseAppRuntimeException;
- import com.ldd600.exception.config.ExceptionDefinition;
- import com.ldd600.exception.context.ExceptionContext;
- import com.ldd600.exception.context.CoreContextFactory;
- public class ExceptionalAnnotationBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
- public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
- if(bean instanceof BaseAppRuntimeException || bean instanceof BaseAppException) {
- Exceptional exceptional = bean.getClass().getAnnotation(Exceptional.class);
- if(null != exceptional) {
- ExceptionContext ctx = CoreContextFactory.getInstance().getExceptionContext();
- if(!ctx.containsException(bean.getClass())) {
- ExceptionDefinition expDefinition = new ExceptionDefinition(exceptional.errorCode());
- ctx.setExceptionDefinition(bean.getClass(), expDefinition);
- }
- ctx.addExceptionHandlers(bean.getClass(), exceptional.handlers());
- return null;
- }
- }
- return bean;
- }
- public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
- return bean;
- }
- }
结果测试:
- package com.ldd600.exception.test;
- import org.jmock.Expectations;
- import org.jmock.Mockery;
- import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
- import com.ldd600.exception.action.BusinessAction;
- import com.ldd600.exception.base.BaseAppException;
- import com.ldd600.exception.base.BaseAppRuntimeException;
- import com.ldd600.exception.base.ConfigException;
- import com.ldd600.exception.base.handler.ConsoleHandler;
- import com.ldd600.exception.context.CoreContextFactory;
- import com.ldd600.exception.dto.DefaultRequest;
- import com.ldd600.exception.dto.DefaultResponse;
- import com.ldd600.exception.dto.Request;
- import com.ldd600.exception.dto.Response;
- import com.ldd600.exception.webservice.ActionBrokerImpl;
- public class ExceptionTest extends DependencyInjectionExceptionTestCase {
- Mockery context = new Mockery();
- ActionBrokerImpl broker = new ActionBrokerImpl();
- final Request request = new DefaultRequest();
- final Response response = new DefaultResponse();
- @Override
- protected String[] getConfigLocations() {
- return new String[] { "applicationContext.xml" };
- }
- public void testExceptionThrow() {
- final BusinessAction<Response, Request> action = context
- .mock(BusinessAction.class);
- final BeanFactory beanFactory = context.mock(BeanFactory.class);
- assertThrowing(new Closure() {
- public void run() throws Throwable {
- context.checking(new Expectations() {
- {
- allowing(beanFactory).getBean("action");
- will(returnValue(action));
- one(action).execute(request, response);
- will(throwException(new BaseAppException()));
- }
- });
- broker.setExceptionHandler(new ConsoleHandler());
- broker.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
- broker.execute("action", request, response);
- }
- }, BaseAppException.class);
- }
- public void testExceptionalAutoLoad() throws BaseAppException {
- final BeanFactory beanFactory = context.mock(BeanFactory.class);
- final BusinessAction<Response, Request> action = context
- .mock(BusinessAction.class);
- context.checking(new Expectations() {
- {
- allowing(beanFactory).getBean("action");
- will(returnValue(action));
- one(action).execute(request, response);
- will(throwException(new ConfigException()));
- }
- });
- broker.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
- broker.execute("action", request, response);
- assertEquals(CoreContextFactory.getInstance().getExceptionContext()
- .getErrorCode(ConfigException.class), "LDD600-00002");
- context.assertIsSatisfied();
- }
- public void testRuntimeException() {
- final BusinessAction<Response, Request> action = context
- .mock(BusinessAction.class);
- final BeanFactory beanFactory = context.mock(BeanFactory.class);
- assertThrowing(new Closure() {
- public void run() throws Throwable {
- context.checking(new Expectations() {
- {
- allowing(beanFactory).getBean("action");
- will(returnValue(action));
- one(action).execute(request, response);
- will(throwException(new BaseAppRuntimeException()));
- }
- });
- broker.setExceptionHandler(new ConsoleHandler());
- broker.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
- broker.execute("action", request, response);
- }
- }, BaseAppRuntimeException.class);
- // test config
- assertEquals(CoreContextFactory.getInstance().getExceptionContext()
- .getErrorCode(BaseAppRuntimeException.class), "LDD600-00001");
- // test handler
- assertFalse(response.isSuccess());
- assertEquals(response.getErrorCode(), CoreContextFactory.getInstance()
- .getExceptionContext().getErrorCode(
- BaseAppRuntimeException.class));
- context.assertIsSatisfied();
- }
- public void testCheckedException() {
- final BusinessAction<Response, Request> action = context
- .mock(BusinessAction.class);
- final BeanFactory beanFactory = context.mock(BeanFactory.class);
- assertThrowing(new Closure() {
- public void run() throws Throwable {
- context.checking(new Expectations() {
- {
- allowing(beanFactory).getBean("action");
- will(returnValue(action));
- one(action).execute(request, response);
- will(throwException(new ExceptionFaker()));
- }
- });
- broker.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
- broker.execute("action", request, response);
- }
- }, ExceptionFaker.class);
- // test config
- assertEquals(CoreContextFactory.getInstance().getExceptionContext()
- .getErrorCode(ExceptionFaker.class), "LDD600-00003");
- // test handler
- assertFalse(response.isSuccess());
- assertEquals(response.getErrorCode(), CoreContextFactory.getInstance()
- .getExceptionContext().getErrorCode(
- ExceptionFaker.class));
- context.assertIsSatisfied();
- }
- }
参考资料:
文章1:http://www.onjava.com/pub/a/onjava/2006/01/11/exception-handling-framework-for-j2ee.html
文章2:http://sannotations.sourceforge.net/
本文源代码:源代码下载
来源:http://blog.csdn.net/yaerfeng/article/details/25100239






















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








