转载请表明出处:http://write.blog.csdn.net/postedit/23692439
一般进入APP都有欢迎界面,基本都是水平滚动的,今天和大家分享一个垂直滚动的例子。
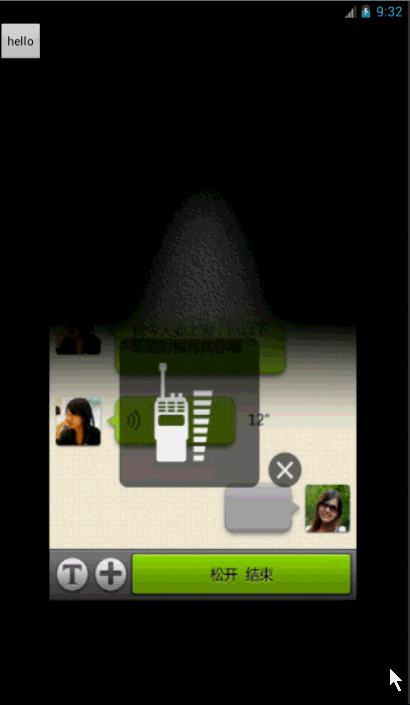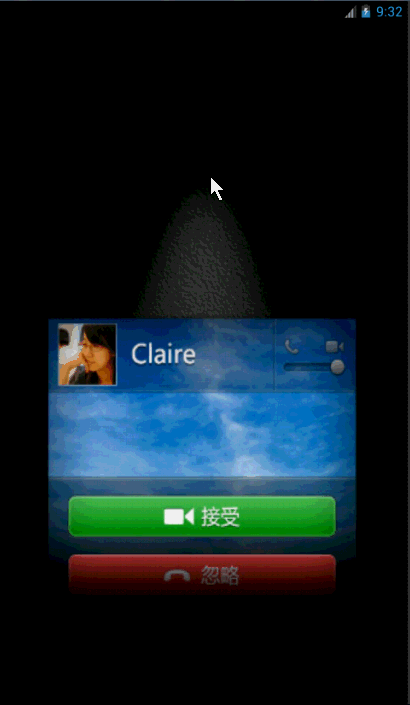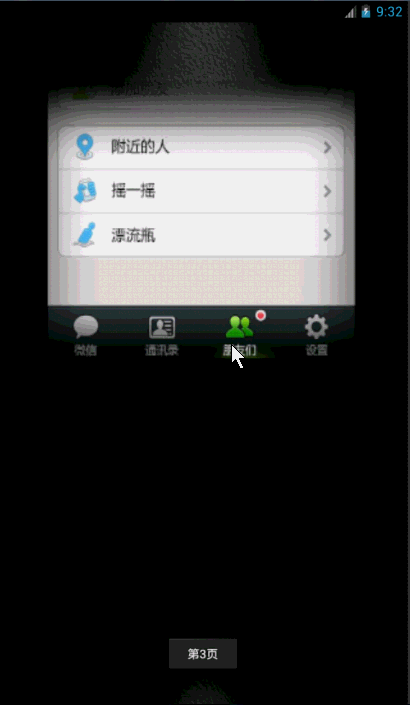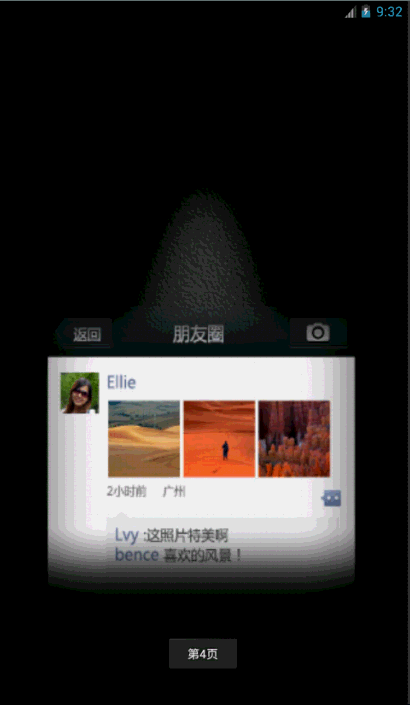
先来看看效果把:
1、首先是布局文件:
- <com.example.verticallinearlayout.VerticalLinearLayout xmlns:android=“http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android”
- xmlns:tools=“http://schemas.android.com/tools”
- android:id=“@+id/id_main_ly”
- android:layout_width=“match_parent”
- android:layout_height=“fill_parent”
- android:orientation=“vertical”
- android:background=“#fff” >
- <RelativeLayout
- android:layout_width=“fill_parent”
- android:layout_height=“fill_parent”
- android:background=“@drawable/w02” >
- <Button
- android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
- android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
- android:text=“hello” />
- </RelativeLayout>
- <RelativeLayout
- android:layout_width=“fill_parent”
- android:layout_height=“fill_parent”
- android:background=“@drawable/w03” >
- <Button
- android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
- android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
- android:layout_centerInParent=“true”
- android:background=“#fff”
- android:text=“hello” />
- </RelativeLayout>
- <RelativeLayout
- android:layout_width=“fill_parent”
- android:layout_height=“fill_parent”
- android:background=“@drawable/w04” >
- <Button
- android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
- android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
- android:layout_centerInParent=“true”
- android:text=“hello” />
- </RelativeLayout>
- <RelativeLayout
- android:layout_width=“fill_parent”
- android:layout_height=“fill_parent”
- android:background=“@drawable/w05” >
- <Button
- android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
- android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
- android:layout_centerInParent=“true”
- android:text=“hello” />
- </RelativeLayout>
- </com.example.verticallinearlayout.VerticalLinearLayout>
<com.example.verticallinearlayout.VerticalLinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/id_main_ly"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:background="#fff" >
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:background="@drawable/w02" >
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="hello" />
</RelativeLayout>
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:background="@drawable/w03" >
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:background="#fff"
android:text="hello" />
</RelativeLayout>
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:background="@drawable/w04" >
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:text="hello" />
</RelativeLayout>
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:background="@drawable/w05" >
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:text="hello" />
</RelativeLayout>
</com.example.verticallinearlayout.VerticalLinearLayout>2、主要看自定义的Layout了
- package com.example.verticallinearlayout;
- import android.content.Context;
- import android.util.AttributeSet;
- import android.util.DisplayMetrics;
- import android.util.Log;
- import android.view.MotionEvent;
- import android.view.VelocityTracker;
- import android.view.View;
- import android.view.ViewGroup;
- import android.view.WindowManager;
- import android.widget.Scroller;
- public class VerticalLinearLayout extends ViewGroup
- {
- /**
- * 屏幕的高度
- */
- private int mScreenHeight;
- /**
- * 手指按下时的getScrollY
- */
- private int mScrollStart;
- /**
- * 手指抬起时的getScrollY
- */
- private int mScrollEnd;
- /**
- * 记录移动时的Y
- */
- private int mLastY;
- /**
- * 滚动的辅助类
- */
- private Scroller mScroller;
- /**
- * 是否正在滚动
- */
- private boolean isScrolling;
- /**
- * 加速度检测
- */
- private VelocityTracker mVelocityTracker;
- /**
- * 记录当前页
- */
- private int currentPage = 0;
- private OnPageChangeListener mOnPageChangeListener;
- public VerticalLinearLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs)
- {
- super(context, attrs);
- /**
- * 获得屏幕的高度
- */
- WindowManager wm = (WindowManager) context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
- DisplayMetrics outMetrics = new DisplayMetrics();
- wm.getDefaultDisplay().getMetrics(outMetrics);
- mScreenHeight = outMetrics.heightPixels;
- // 初始化
- mScroller = new Scroller(context);
- }
- @Override
- protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
- {
- super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
- int count = getChildCount();
- for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i)
- {
- View childView = getChildAt(i);
- measureChild(childView, widthMeasureSpec,mScreenHeight);
- }
- }
- @Override
- protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b)
- {
- if (changed)
- {
- int childCount = getChildCount();
- // 设置主布局的高度
- MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) getLayoutParams();
- lp.height = mScreenHeight * childCount;
- setLayoutParams(lp);
- for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++)
- {
- View child = getChildAt(i);
- if (child.getVisibility() != View.GONE)
- {
- child.layout(l, i * mScreenHeight, r, (i + 1) * mScreenHeight);// 调用每个自布局的layout
- }
- }
- }
- }
- @Override
- public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event)
- {
- // 如果当前正在滚动,调用父类的onTouchEvent
- if (isScrolling)
- return super.onTouchEvent(event);
- int action = event.getAction();
- int y = (int) event.getY();
- obtainVelocity(event);
- switch (action)
- {
- case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
- mScrollStart = getScrollY();
- mLastY = y;
- break;
- case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
- if (!mScroller.isFinished())
- {
- mScroller.abortAnimation();
- }
- int dy = mLastY - y;
- // 边界值检查
- int scrollY = getScrollY();
- // 已经到达顶端,下拉多少,就往上滚动多少
- if (dy < 0 && scrollY + dy < 0)
- {
- dy = -scrollY;
- }
- // 已经到达底部,上拉多少,就往下滚动多少
- if (dy > 0 && scrollY + dy > getHeight() - mScreenHeight)
- {
- dy = getHeight() - mScreenHeight - scrollY;
- }
- scrollBy(0, dy);
- mLastY = y;
- break;
- case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
- mScrollEnd = getScrollY();
- int dScrollY = mScrollEnd - mScrollStart;
- if (wantScrollToNext())// 往上滑动
- {
- if (shouldScrollToNext())
- {
- mScroller.startScroll(0, getScrollY(), 0, mScreenHeight - dScrollY);
- } else
- {
- mScroller.startScroll(0, getScrollY(), 0, -dScrollY);
- }
- }
- if (wantScrollToPre())// 往下滑动
- {
- if (shouldScrollToPre())
- {
- mScroller.startScroll(0, getScrollY(), 0, -mScreenHeight - dScrollY);
- } else
- {
- mScroller.startScroll(0, getScrollY(), 0, -dScrollY);
- }
- }
- isScrolling = true;
- postInvalidate();
- recycleVelocity();
- break;
- }
- return true;
- }
- /**
- * 根据滚动距离判断是否能够滚动到下一页
- *
- * @return
- */
- private boolean shouldScrollToNext()
- {
- return mScrollEnd - mScrollStart > mScreenHeight / 2 || Math.abs(getVelocity()) > 600;
- }
- /**
- * 根据用户滑动,判断用户的意图是否是滚动到下一页
- *
- * @return
- */
- private boolean wantScrollToNext()
- {
- return mScrollEnd > mScrollStart;
- }
- /**
- * 根据滚动距离判断是否能够滚动到上一页
- *
- * @return
- */
- private boolean shouldScrollToPre()
- {
- return -mScrollEnd + mScrollStart > mScreenHeight / 2 || Math.abs(getVelocity()) > 600;
- }
- /**
- * 根据用户滑动,判断用户的意图是否是滚动到上一页
- *
- * @return
- */
- private boolean wantScrollToPre()
- {
- return mScrollEnd < mScrollStart;
- }
- @Override
- public void computeScroll()
- {
- super.computeScroll();
- if (mScroller.computeScrollOffset())
- {
- scrollTo(0, mScroller.getCurrY());
- postInvalidate();
- } else
- {
- int position = getScrollY() / mScreenHeight;
- Log.e(”xxx”, position + “,” + currentPage);
- if (position != currentPage)
- {
- if (mOnPageChangeListener != null)
- {
- currentPage = position;
- mOnPageChangeListener.onPageChange(currentPage);
- }
- }
- isScrolling = false;
- }
- }
- /**
- * 获取y方向的加速度
- *
- * @return
- */
- private int getVelocity()
- {
- mVelocityTracker.computeCurrentVelocity(1000);
- return (int) mVelocityTracker.getYVelocity();
- }
- /**
- * 释放资源
- */
- private void recycleVelocity()
- {
- if (mVelocityTracker != null)
- {
- mVelocityTracker.recycle();
- mVelocityTracker = null;
- }
- }
- /**
- * 初始化加速度检测器
- *
- * @param event
- */
- private void obtainVelocity(MotionEvent event)
- {
- if (mVelocityTracker == null)
- {
- mVelocityTracker = VelocityTracker.obtain();
- }
- mVelocityTracker.addMovement(event);
- }
- /**
- * 设置回调接口
- *
- * @param onPageChangeListener
- */
- public void setOnPageChangeListener(OnPageChangeListener onPageChangeListener)
- {
- mOnPageChangeListener = onPageChangeListener;
- }
- /**
- * 回调接口
- *
- * @author zhy
- *
- */
- public interface OnPageChangeListener
- {
- void onPageChange(int currentPage);
- }
- }
package com.example.verticallinearlayout;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.DisplayMetrics;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.VelocityTracker;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.view.WindowManager;
import android.widget.Scroller;
public class VerticalLinearLayout extends ViewGroup
{
/**
* 屏幕的高度
*/
private int mScreenHeight;
/**
* 手指按下时的getScrollY
*/
private int mScrollStart;
/**
* 手指抬起时的getScrollY
*/
private int mScrollEnd;
/**
* 记录移动时的Y
*/
private int mLastY;
/**
* 滚动的辅助类
*/
private Scroller mScroller;
/**
* 是否正在滚动
*/
private boolean isScrolling;
/**
* 加速度检测
*/
private VelocityTracker mVelocityTracker;
/**
* 记录当前页
*/
private int currentPage = 0;
private OnPageChangeListener mOnPageChangeListener;
public VerticalLinearLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs)
{
super(context, attrs);
/**
* 获得屏幕的高度
*/
WindowManager wm = (WindowManager) context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
DisplayMetrics outMetrics = new DisplayMetrics();
wm.getDefaultDisplay().getMetrics(outMetrics);
mScreenHeight = outMetrics.heightPixels;
// 初始化
mScroller = new Scroller(context);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
{
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int count = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i)
{
View childView = getChildAt(i);
measureChild(childView, widthMeasureSpec,mScreenHeight);
}
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b)
{
if (changed)
{
int childCount = getChildCount();
// 设置主布局的高度
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) getLayoutParams();
lp.height = mScreenHeight * childCount;
setLayoutParams(lp);
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++)
{
View child = getChildAt(i);
if (child.getVisibility() != View.GONE)
{
child.layout(l, i * mScreenHeight, r, (i + 1) * mScreenHeight);// 调用每个自布局的layout
}
}
}
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event)
{
// 如果当前正在滚动,调用父类的onTouchEvent
if (isScrolling)
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
int action = event.getAction();
int y = (int) event.getY();
obtainVelocity(event);
switch (action)
{
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
mScrollStart = getScrollY();
mLastY = y;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
if (!mScroller.isFinished())
{
mScroller.abortAnimation();
}
int dy = mLastY - y;
// 边界值检查
int scrollY = getScrollY();
// 已经到达顶端,下拉多少,就往上滚动多少
if (dy < 0 && scrollY + dy < 0)
{
dy = -scrollY;
}
// 已经到达底部,上拉多少,就往下滚动多少
if (dy > 0 && scrollY + dy > getHeight() - mScreenHeight)
{
dy = getHeight() - mScreenHeight - scrollY;
}
scrollBy(0, dy);
mLastY = y;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
mScrollEnd = getScrollY();
int dScrollY = mScrollEnd - mScrollStart;
if (wantScrollToNext())// 往上滑动
{
if (shouldScrollToNext())
{
mScroller.startScroll(0, getScrollY(), 0, mScreenHeight - dScrollY);
} else
{
mScroller.startScroll(0, getScrollY(), 0, -dScrollY);
}
}
if (wantScrollToPre())// 往下滑动
{
if (shouldScrollToPre())
{
mScroller.startScroll(0, getScrollY(), 0, -mScreenHeight - dScrollY);
} else
{
mScroller.startScroll(0, getScrollY(), 0, -dScrollY);
}
}
isScrolling = true;
postInvalidate();
recycleVelocity();
break;
}
return true;
}
/**
* 根据滚动距离判断是否能够滚动到下一页
*
* @return
*/
private boolean shouldScrollToNext()
{
return mScrollEnd - mScrollStart > mScreenHeight / 2 || Math.abs(getVelocity()) > 600;
}
/**
* 根据用户滑动,判断用户的意图是否是滚动到下一页
*
* @return
*/
private boolean wantScrollToNext()
{
return mScrollEnd > mScrollStart;
}
/**
* 根据滚动距离判断是否能够滚动到上一页
*
* @return
*/
private boolean shouldScrollToPre()
{
return -mScrollEnd + mScrollStart > mScreenHeight / 2 || Math.abs(getVelocity()) > 600;
}
/**
* 根据用户滑动,判断用户的意图是否是滚动到上一页
*
* @return
*/
private boolean wantScrollToPre()
{
return mScrollEnd < mScrollStart;
}
@Override
public void computeScroll()
{
super.computeScroll();
if (mScroller.computeScrollOffset())
{
scrollTo(0, mScroller.getCurrY());
postInvalidate();
} else
{
int position = getScrollY() / mScreenHeight;
Log.e("xxx", position + "," + currentPage);
if (position != currentPage)
{
if (mOnPageChangeListener != null)
{
currentPage = position;
mOnPageChangeListener.onPageChange(currentPage);
}
}
isScrolling = false;
}
}
/**
* 获取y方向的加速度
*
* @return
*/
private int getVelocity()
{
mVelocityTracker.computeCurrentVelocity(1000);
return (int) mVelocityTracker.getYVelocity();
}
/**
* 释放资源
*/
private void recycleVelocity()
{
if (mVelocityTracker != null)
{
mVelocityTracker.recycle();
mVelocityTracker = null;
}
}
/**
* 初始化加速度检测器
*
* @param event
*/
private void obtainVelocity(MotionEvent event)
{
if (mVelocityTracker == null)
{
mVelocityTracker = VelocityTracker.obtain();
}
mVelocityTracker.addMovement(event);
}
/**
* 设置回调接口
*
* @param onPageChangeListener
*/
public void setOnPageChangeListener(OnPageChangeListener onPageChangeListener)
{
mOnPageChangeListener = onPageChangeListener;
}
/**
* 回调接口
*
* @author zhy
*
*/
public interface OnPageChangeListener
{
void onPageChange(int currentPage);
}
}注释还是相当详细的,我简单描述一下,Action_down时获得当前的scrollY,然后Action_move时,根据移动的距离不断scrollby就行了,当前处理了一下边界判断,在Action_up中再次获得scrollY,两个的scrollY进行对比,然后根据移动的距离与方向决定最后的动作。
3、主Activity
- package com.example.verticallinearlayout;
- import android.app.Activity;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.widget.Toast;
- import com.example.verticallinearlayout.VerticalLinearLayout.OnPageChangeListener;
- public class MainActivity extends Activity
- {
- private VerticalLinearLayout mMianLayout;
- @Override
- protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
- {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
- mMianLayout = (VerticalLinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.id_main_ly);
- mMianLayout.setOnPageChangeListener(new OnPageChangeListener()
- {
- @Override
- public void onPageChange(int currentPage)
- {
- // mMianLayout.getChildAt(currentPage);
- Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, “第”+(currentPage+1)+“页”, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
- }
- });
- }
- }
package com.example.verticallinearlayout;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.Toast;
import com.example.verticallinearlayout.VerticalLinearLayout.OnPageChangeListener;
public class MainActivity extends Activity
{
private VerticalLinearLayout mMianLayout;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mMianLayout = (VerticalLinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.id_main_ly);
mMianLayout.setOnPageChangeListener(new OnPageChangeListener()
{
@Override
public void onPageChange(int currentPage)
{
// mMianLayout.getChildAt(currentPage);
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "第"+(currentPage+1)+"页", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
}
}
为了提供可扩展性,还是定义了回调接口,完全可以把这个当成一个垂直的ViewPager使用。
总结下:
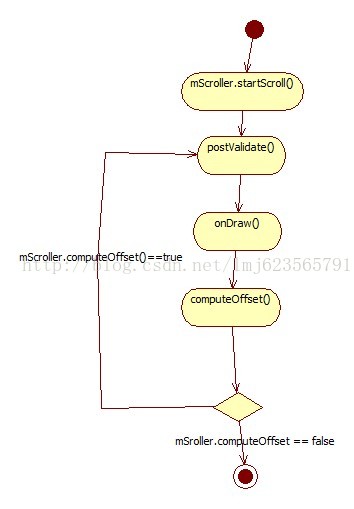
Scroller这个辅助类还是相当好用的,原理我简单说一下:每次滚动时,让Scroller进行滚动,然后调用postInvalidate方法,这个方法会引发调用onDraw方法,onDraw方法中会去调用computeScroll方法,然后我们在computScroll中判断,Scroller的滚动是否结束,没有的话,把当前的View滚动到现在Scroller的位置,然后继续调用postInvalidate,这样一个循环的过程。
画张图方便大家理解,ps:没找到什么好的画图工具,那rose随便画了,莫计较。
源码点击此处下载
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/lmj623565791/article/details/23692439





















 537
537











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








