本文主要总结一下 Struts2的工作原理,相关源码分析,以及与Struts1的区别。
1. Struts2的工作原理
Struts2的工作原理可以用下面这张图进行描述:
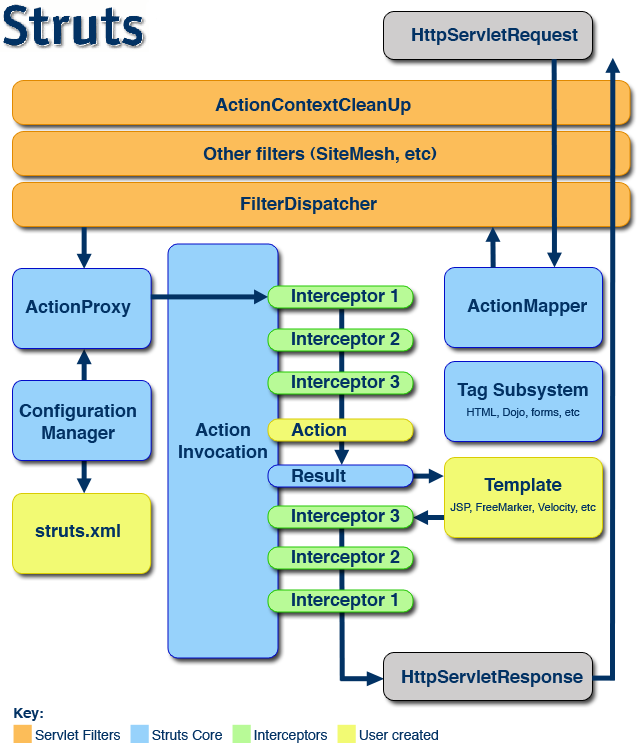
(1)客户端初始化一个指向Servlet容器(例如Tomcat)的请求(HttpServletRequest)
(2)这个请求经过一系列的 Filter(首先是ActionContextCleanUp,然后是其他过滤器Other filters,最后是FilterDispatcher)
(3) FilterDispatcher是控制器的核心,它首先询问ActionMapper这个请求是否需要调用某个Action,如果 ActionMapper决定调用某个Action,FilterDispatcher把请求转交给 ActionProxy
(4) ActionProxy通过 ConfigurationManager读取分析框架的配置文件struts.xml,找到对应的Action类,创建一个 ActionInvocation的实例(ActionInvocation里面有Action,以及它配置的一堆拦截器Intercepters)
(5) ActionInvocation在调用Action的前后会根据配置文件,调用配置的 Intercepter拦截器,一旦Action执行完毕,ActionInvocation根据配置文件找到对应的返回结果 Result
(6)产生一个HttpServletResponse响应
从Struts 2.1.3开始,FilterDispatcher已经不推荐使用,推荐使用升级版的StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter,Struts2就是通过配置在web.xml的StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter过滤器启动的。
StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter的核心方法是doFilter()
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
try {
prepare.setEncodingAndLocale(request, response);
prepare.createActionContext(request, response);
prepare.assignDispatcherToThread();
if ( excludedPatterns != null && prepare.isUrlExcluded(request, excludedPatterns)) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
} else {
// 重新包装request
request = prepare.wrapRequest(request);
// 询问ActionMapping 这个request请求是否需要调用某个Action
ActionMapping mapping = prepare.findActionMapping(request, response, true);
if (mapping == null) {
// 如果没有相应的Action 查看是否访问的是静态资源
boolean handled = execute.executeStaticResourceRequest(request, response);
if (!handled) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
} else {
// 如果找到相应的Action,执行Action,会调用 dispatcher的serviceAction()方法
execute.executeAction(request, response, mapping);
}
}
} finally {
prepare.cleanupRequest(request);
}
}// Dispatcher的serviceAction()方法
public void serviceAction(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, ServletContext context,
ActionMapping mapping) throws ServletException {
...
try {
UtilTimerStack.push(timerKey);
String namespace = mapping.getNamespace();
String name = mapping.getName();
String method = mapping.getMethod();
// 拿到ConfigurationManager实例
Configuration config = configurationManager.getConfiguration();
// 生产ActionProxy的实例proxy
ActionProxy proxy = config.getContainer().getInstance(ActionProxyFactory.class).createActionProxy(
namespace, name, method, extraContext, true, false);
request.setAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY, proxy.getInvocation().getStack());
// if the ActionMapping says to go straight to a result, do it!
if (mapping.getResult() != null) {
Result result = mapping.getResult();
result.execute(proxy.getInvocation());
} else {
// 执行ActionProxy的execute()方法
// 会调用ActionInvocation的invoke()方法
proxy.execute();
}
}
...
}// ActionInvocation的invoke()方法
public String invoke() throws Exception {
...
// 如果interceptors还有拦截器
if (interceptors.hasNext()) {
final InterceptorMapping interceptor = interceptors.next();
String interceptorMsg = "interceptor: " + interceptor.getName();
UtilTimerStack.push(interceptorMsg);
try {
// 那么 从interceptors拿到拦截器并调用它的intercept()方法,并把当前的ActionInvocation传过去
resultCode = interceptor.getInterceptor().intercept(DefaultActionInvocation.this);
}
finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(interceptorMsg);
}
} else {
// 所有拦截器执行完毕之后,才调用Action
resultCode = invokeActionOnly();
}
...
}// interceptor的intercept()方法
public String intercept(ActionInvocation invocation) throws Exception {
String result;
try {
// 这里的invocation 是我们传递过来的,继续调用invoke()方法
// 这样又返回ActionInvocation中继续从interceptors中那下一个interceptor调用,直到interceptor全部调用完毕
result = invocation.invoke();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (isLogEnabled()) {
handleLogging(e);
}
List<ExceptionMappingConfig> exceptionMappings = invocation.getProxy().getConfig().getExceptionMappings();
String mappedResult = this.findResultFromExceptions(exceptionMappings, e);
if (mappedResult != null) {
result = mappedResult;
publishException(invocation, new ExceptionHolder(e));
} else {
throw e;
}
}
return result;
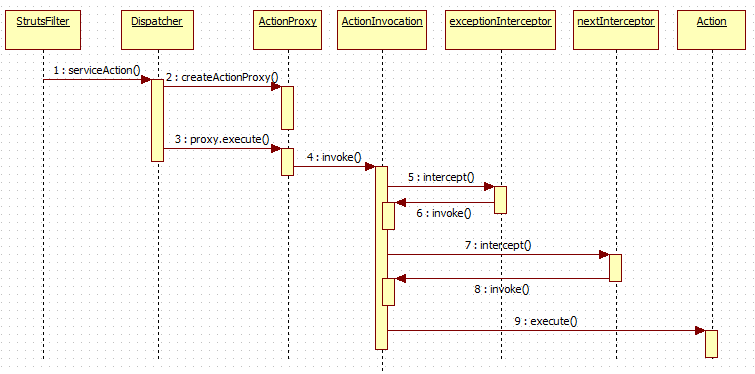
}相关顺序图:
Struts2与Struts1的区别:
( 1)Action类的实现方式:
Struts1的Action在实现的时候必须扩展Action类或者Action的子类,Struts2的Action类实现的时候可以不用实现任何类和接口,虽然Struts2中提供一个ActionSupport类,但是,不是必须的。
(2)Struts1的Action类是单例模式,必须设计成线程安全的,Struts2则为每一个请求产生一个实例
(3)Struts1的Action类依赖与Servlet API,从其execute的方法签名可看出,execute方法有两个Servlet的参数HttpServletRequest和HttpServletResponse,Struts2则不依赖于Servlet API
(4)以为Struts1依赖于Servlet API这些Web元素,因此对Struts1的Action进行测试的时候是很困难的,需要借助与其他的测试工具,Struts2的Action可以象测试其他的一些Model层的Service类一样进行测试
( 5)Struts1的Action与View通过ActionForm或者其子类进行数据传递,虽然也有LazyValidationForm这样的ActionForm的出现,但是,还是不能象其他层面那样通过一个简单的POJO进行数据传递,而Struts2将这样的奢望变成了现实
(6)Struts1绑定了JSTL,为页面的编写带来方便,Struts2整合了ONGL,也可以使用JSTL,因此,Struts2下的表达式语言更加强大






















 3930
3930

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








