cocos2d-x 游戏开发之有限状态机(FSM) (四)
虽然我们了解了FSM,并且可以写自己的FSM,但是有更好的工具帮我们完成这个繁琐的工作。SMC(http://smc.sourceforge.net/)就是这样的工具。下载地址:
http://sourceforge.net/projects/smc/files/latest/download
在bin下面的Smc.jar是用于生成状态类的命令行工具。使用如下命令:
$ java -jar Smc.jar Monkey.sm1 真实世界的FSM
首先定义一个状态机纯文本文件:Monkey.sm,内容如下:
// cheungmine
// 2015-01-22
// entity class
%class Monkey
// entity class header
%header Monkey.h
// inital state
%start MonkeyMap::STOP
// entity state map
%map MonkeyMap
%%
STOP
Entry {
stop();
}
Exit {
exit();
}
{
walk WALK {}
}
WALK
Entry {
walk();
}
Exit {
exit();
}
{
stop STOP {}
turn TURN {}
}
TURN
Entry {
turn();
}
Exit {
exit();
}
{
walk WALK {}
}
%%
其中%class Monkey 说明实体类的名字:Monkey (Monkey.h和Monkey.cpp)
%header 指定头文件:Monkey.h
%map 指明状态图类,这个类包含全部状态。这里是:MonkeyMap
%start 指明其实的状态,这里是STOP,对应的类是:MonkeyMap_STOP
%%...%%之间的部分定义每个状态。格式如下:
STOP // 状态名
Entry {
// 执行这个函数进入该状态
stop();
}
Exit {
// 执行这个函数退出该状态
exit();
}
{
// 状态切换逻辑
walk WALK {}
}当运行下面的命令,会自动生成文件:Monkey_sm.h和Monkey_sm.cpp。连同自带的statemap.h一起加入到项目中。
java -jar Smc.jar Monkey.sm2 实体类
业务逻辑仍然要我们自己实现,那就是写Monkey.h和Monkey.cpp。不过这次写Monkey类需要按一定的规则,下面是源代码:
// Monkey.h
//
#ifndef MONKEY_H_
#define MONKEY_H_
#include "cocos2d.h"
USING_NS_CC;
#include "Monkey_sm.h"
#define MAX_STOP_TIME 3
#define MAX_WALK_TIME 10
#define MAX_WALK_DIST 200
class Monkey : public Node
{
public:
CREATE_FUNC(Monkey);
virtual bool init();
void stop();
void walk();
void turn();
void exit();
private:
MonkeyContext * _fsm;
int _step;
int _curPos;
time_t _curTime;
// Sprite * _sprite;
private:
void onIdleStop(float dt)
{
int d = (int) (time(0) - _curTime);
if (d > MAX_STOP_TIME) {
_fsm->walk();
}
}
void onIdleWalk(float dt)
{
if (_curPos > MAX_WALK_DIST || _curPos < -MAX_WALK_DIST) {
_fsm->turn();
}
int d = (int) (time(0) - _curTime);
if (d > MAX_WALK_TIME) {
_fsm->stop();
}
_curPos += _step;
}
void onIdleTurn(float dt)
{
_fsm->walk();
}
};
#endif // MONKEY_H_
上面的onIdle????是触发状态的回调函数,实体状态改变的业务逻辑在这里实现。
// Monkey.cpp
//
#include "Monkey.h"
#include <time.h>
#include <assert.h>
void Monkey::exit()
{
this->unscheduleAllCallbacks();
cocos2d::log("exit()");
}
bool Monkey::init()
{
_step = 1;
_curPos = 0;
_curTime = time(0);
// _sprite = Sprite::create("monkey.png");
// addChild(_sprite);
_fsm = new MonkeyContext(*this);
assert(_fsm);
_fsm->setDebugFlag(true);
_fsm->enterStartState();
return true;
}
void Monkey::stop()
{
_curTime = time(0);
cocos2d::log("stop(): pos=%d", _curPos);
this->schedule(schedule_selector(Monkey::onIdleStop), 0.1f);
}
void Monkey::walk()
{
_curTime = time(0);
cocos2d::log("walk(): pos=%d", _curPos);
this->schedule(schedule_selector(Monkey::onIdleWalk), 0.1f);
}
void Monkey::turn()
{
_step *= -1;
cocos2d::log("turn(): step=%d", _step);
this->schedule(schedule_selector(Monkey::onIdleTurn), 0.1f);
}
3 状态机类
框架代码Smc已经帮我们生成好了:Monkey_sm.h和Monkey_sm.cpp:
//
// ex: set ro:
// DO NOT EDIT.
// generated by smc (http://smc.sourceforge.net/)
// from file : Monkey.sm
//
#ifndef MONKEY_SM_H
#define MONKEY_SM_H
#define SMC_USES_IOSTREAMS
#include "statemap.h"
// Forward declarations.
class MonkeyMap;
class MonkeyMap_STOP;
class MonkeyMap_WALK;
class MonkeyMap_TURN;
class MonkeyMap_Default;
class MonkeyState;
class MonkeyContext;
class Monkey;
class MonkeyState :
public statemap::State
{
public:
MonkeyState(const char * const name, const int stateId)
: statemap::State(name, stateId)
{};
virtual void Entry(MonkeyContext&) {};
virtual void Exit(MonkeyContext&) {};
virtual void stop(MonkeyContext& context);
virtual void turn(MonkeyContext& context);
virtual void walk(MonkeyContext& context);
protected:
virtual void Default(MonkeyContext& context);
};
class MonkeyMap
{
public:
static MonkeyMap_STOP STOP;
static MonkeyMap_WALK WALK;
static MonkeyMap_TURN TURN;
};
class MonkeyMap_Default :
public MonkeyState
{
public:
MonkeyMap_Default(const char * const name, const int stateId)
: MonkeyState(name, stateId)
{};
};
class MonkeyMap_STOP :
public MonkeyMap_Default
{
public:
MonkeyMap_STOP(const char * const name, const int stateId)
: MonkeyMap_Default(name, stateId)
{};
virtual void Entry(MonkeyContext&);
virtual void Exit(MonkeyContext&);
virtual void walk(MonkeyContext& context);
};
class MonkeyMap_WALK :
public MonkeyMap_Default
{
public:
MonkeyMap_WALK(const char * const name, const int stateId)
: MonkeyMap_Default(name, stateId)
{};
virtual void Entry(MonkeyContext&);
virtual void Exit(MonkeyContext&);
virtual void stop(MonkeyContext& context);
virtual void turn(MonkeyContext& context);
};
class MonkeyMap_TURN :
public MonkeyMap_Default
{
public:
MonkeyMap_TURN(const char * const name, const int stateId)
: MonkeyMap_Default(name, stateId)
{};
virtual void Entry(MonkeyContext&);
virtual void Exit(MonkeyContext&);
virtual void walk(MonkeyContext& context);
};
class MonkeyContext :
public statemap::FSMContext
{
public:
explicit MonkeyContext(Monkey& owner)
: FSMContext(MonkeyMap::STOP),
_owner(&owner)
{};
MonkeyContext(Monkey& owner, const statemap::State& state)
: FSMContext(state),
_owner(&owner)
{};
virtual void enterStartState()
{
getState().Entry(*this);
}
inline Monkey& getOwner()
{
return *_owner;
};
inline MonkeyState& getState()
{
if (_state == NULL)
{
throw statemap::StateUndefinedException();
}
return dynamic_cast<MonkeyState&>(*_state);
};
inline void stop()
{
getState().stop(*this);
};
inline void turn()
{
getState().turn(*this);
};
inline void walk()
{
getState().walk(*this);
};
private:
Monkey* _owner;
};
#endif // MONKEY_SM_H
//
// Local variables:
// buffer-read-only: t
// End:
//
//
// ex: set ro:
// DO NOT EDIT.
// generated by smc (http://smc.sourceforge.net/)
// from file : Monkey.sm
//
#include "Monkey.h"
#include "Monkey_sm.h"
using namespace statemap;
// Static class declarations.
MonkeyMap_STOP MonkeyMap::STOP("MonkeyMap::STOP", 0);
MonkeyMap_WALK MonkeyMap::WALK("MonkeyMap::WALK", 1);
MonkeyMap_TURN MonkeyMap::TURN("MonkeyMap::TURN", 2);
void MonkeyState::stop(MonkeyContext& context)
{
Default(context);
}
void MonkeyState::turn(MonkeyContext& context)
{
Default(context);
}
void MonkeyState::walk(MonkeyContext& context)
{
Default(context);
}
void MonkeyState::Default(MonkeyContext& context)
{
throw (
TransitionUndefinedException(
context.getState().getName(),
context.getTransition()));
}
void MonkeyMap_STOP::Entry(MonkeyContext& context)
{
Monkey& ctxt = context.getOwner();
ctxt.stop();
}
void MonkeyMap_STOP::Exit(MonkeyContext& context)
{
Monkey& ctxt = context.getOwner();
ctxt.exit();
}
void MonkeyMap_STOP::walk(MonkeyContext& context)
{
context.getState().Exit(context);
context.setState(MonkeyMap::WALK);
context.getState().Entry(context);
}
void MonkeyMap_WALK::Entry(MonkeyContext& context)
{
Monkey& ctxt = context.getOwner();
ctxt.walk();
}
void MonkeyMap_WALK::Exit(MonkeyContext& context)
{
Monkey& ctxt = context.getOwner();
ctxt.exit();
}
void MonkeyMap_WALK::stop(MonkeyContext& context)
{
context.getState().Exit(context);
context.setState(MonkeyMap::STOP);
context.getState().Entry(context);
}
void MonkeyMap_WALK::turn(MonkeyContext& context)
{
context.getState().Exit(context);
context.setState(MonkeyMap::TURN);
context.getState().Entry(context);
}
void MonkeyMap_TURN::Entry(MonkeyContext& context)
{
Monkey& ctxt = context.getOwner();
ctxt.turn();
}
void MonkeyMap_TURN::Exit(MonkeyContext& context)
{
Monkey& ctxt = context.getOwner();
ctxt.exit();
}
void MonkeyMap_TURN::walk(MonkeyContext& context)
{
context.getState().Exit(context);
context.setState(MonkeyMap::WALK);
context.getState().Entry(context);
}
//
// Local variables:
// buffer-read-only: t
// End:
//
4 总结
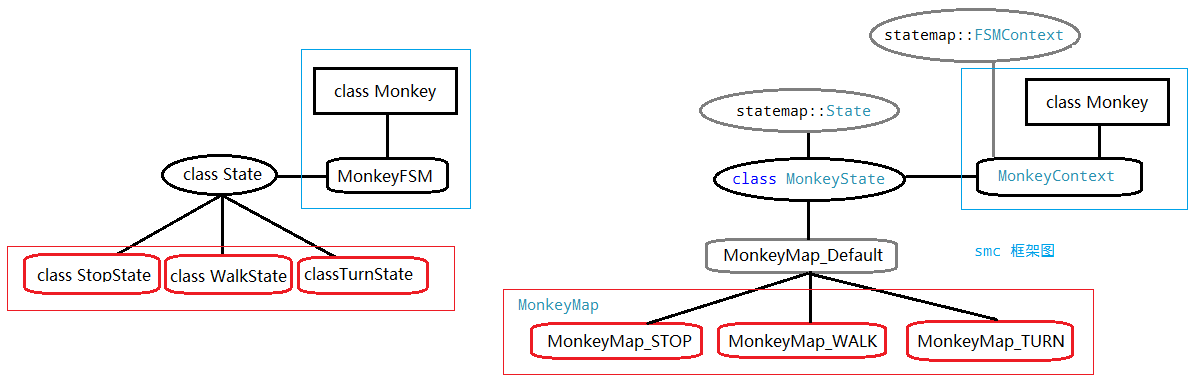
FSM是一种固定的范式,因此采用工具帮我们实现可以减少犯错误的机会。输入的文件就是:实体.sm。我们把重点放在业务逻辑上,所以与状态有关的代码smc都帮我们生成好了。对比一下我们手工创建和smc框架工具自动生成的类:
在cocos2d-x中使用很简单:
bool HelloWorld::init()
{
//////////////////////////////
// 1. super init first
if ( !Layer::init() )
{
return false;
}
auto rootNode = CSLoader::createNode("MainScene.csb");
addChild(rootNode);
auto closeItem = static_cast<ui::Button*>(rootNode->getChildByName("Button_1"));
closeItem->addTouchEventListener(CC_CALLBACK_1(HelloWorld::menuCloseCallback, this));
/////////////////// test ///////////////////////
Monkey * mk = Monkey::create();
addChild(mk);
return true;
}就这样了!不明白的地方请仔细阅读:
Cocos2d-x游戏开发之旅(钟迪龙)







 本文介绍如何使用SMC工具自动生成有限状态机(FSM)代码,以简化cocos2d-x游戏开发中的状态管理。通过定义状态机配置文件Monkey.sm,SMC能生成相应的状态类,减轻开发者负担,使业务逻辑更加清晰。
本文介绍如何使用SMC工具自动生成有限状态机(FSM)代码,以简化cocos2d-x游戏开发中的状态管理。通过定义状态机配置文件Monkey.sm,SMC能生成相应的状态类,减轻开发者负担,使业务逻辑更加清晰。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










