层次结构和类图
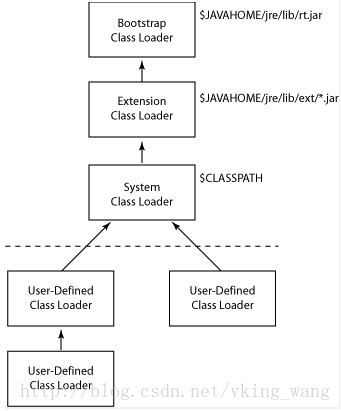
ClassLoader层次结构:
UML类图:
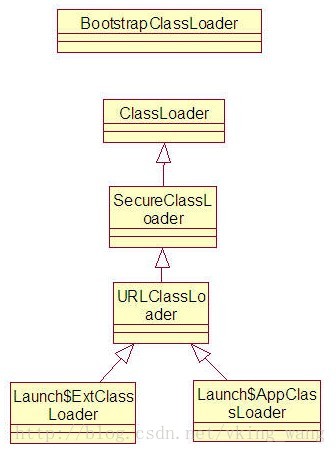
- sun.misc.Launcher.ExtClassLoader
- sun.misc.Launcher.AppClassLoader
显式加载类
在代码中显式加载某个类,有三种方法:
- this.getClass().getClassLoader().loadClass()
- Class.forName()
- MyClassLoader.findClass()
ClassLoader.loadClass()
ClassLoader.loadClass()的加载步骤为:
- 调用
findLoadedClass(String)来检查是否已经加载类。 - 在父类加载器上调用
loadClass方法。如果父类加载器为 null,则使用虚拟机的内置类加载器。 - 调用
findClass(String)方法查找类。
public Class<?> loadClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
return loadClass(name, false);
}
/**
* Loads the class with the specified <a href="#name">binary name</a>. The
* default implementation of this method searches for classes in the
* following order:
*
* <p><ol>
*
* <li><p> Invoke {@link #findLoadedClass(String)} to check if the class
* has already been loaded. </p></li>
*
* <li><p> Invoke the {@link #loadClass(String) <tt>loadClass</tt>} method
* on the parent class loader. If the parent is <tt>null</tt> the class
* loader built-in to the virtual machine is used, instead. </p></li>
*
* <li><p> Invoke the {@link #findClass(String)} method to find the
* class. </p></li>
*
* </ol>
*
* <p>
*/
protected synchronized Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)
throws ClassNotFoundException
{
// First, check if the class has already been loaded
Class c = findLoadedClass(name);








 本文详细探讨了Java ClassLoader的工作原理,包括层次结构、显式加载类的方式、loadClass()和findClass()的区别,以及自定义加载器的实现。特别强调了在自定义ClassLoader时,如何覆盖findClass()和loadClass()方法以改变加载路径和机制。同时,文章还提到了类的热部署策略和一些不可覆盖的final方法。
本文详细探讨了Java ClassLoader的工作原理,包括层次结构、显式加载类的方式、loadClass()和findClass()的区别,以及自定义加载器的实现。特别强调了在自定义ClassLoader时,如何覆盖findClass()和loadClass()方法以改变加载路径和机制。同时,文章还提到了类的热部署策略和一些不可覆盖的final方法。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 5万+
5万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








