第4章 CUDA C并行编程
4.1 目标
了解CUDA在实现并行是采用的一种重要方式。
4.2 CUDA并行编程
__global__ 修饰符
并行执行设备核函数
4.2.1 矢量求和运算
两数组中对应元素两两相加,保存到第三个数组中,其实是一个矢量求和运算。
1.基于CPU的矢量求和
#ifndef __BOOK_H__
#define __BOOK_H__
#include <stdio.h>
static void HandleError( cudaError_t err,
const char *file,
int line ) {
if (err != cudaSuccess) {
printf( "%s in %s at line %d\n", cudaGetErrorString( err ),
file, line );
exit( EXIT_FAILURE );
}
}
#define HANDLE_ERROR( err ) (HandleError( err, __FILE__, __LINE__ ))
#define HANDLE_NULL( a ) {if (a == NULL) { \
printf( "Host memory failed in %s at line %d\n", \
__FILE__, __LINE__ ); \
exit( EXIT_FAILURE );}}
template< typename T >
void swap( T& a, T& b ) {
T t = a;
a = b;
b = t;
}
void* big_random_block( int size ) {
unsigned char *data = (unsigned char*)malloc( size );
HANDLE_NULL( data );
for (int i=0; i<size; i++)
data[i] = rand();
return data;
}
int* big_random_block_int( int size ) {
int *data = (int*)malloc( size * sizeof(int) );
HANDLE_NULL( data );
for (int i=0; i<size; i++)
data[i] = rand();
return data;
}
// a place for common kernels - starts here
__device__ unsigned char value( float n1, float n2, int hue ) {
if (hue > 360) hue -= 360;
else if (hue < 0) hue += 360;
if (hue < 60)
return (unsigned char)(255 * (n1 + (n2-n1)*hue/60));
if (hue < 180)
return (unsigned char)(255 * n2);
if (hue < 240)
return (unsigned char)(255 * (n1 + (n2-n1)*(240-hue)/60));
return (unsigned char)(255 * n1);
}
__global__ void float_to_color( unsigned char *optr,
const float *outSrc ) {
// map from threadIdx/BlockIdx to pixel position
int x = threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x;
int y = threadIdx.y + blockIdx.y * blockDim.y;
int offset = x + y * blockDim.x * gridDim.x;
float l = outSrc[offset];
float s = 1;
int h = (180 + (int)(360.0f * outSrc[offset])) % 360;
float m1, m2;
if (l <= 0.5f)
m2 = l * (1 + s);
else
m2 = l + s - l * s;
m1 = 2 * l - m2;
optr[offset*4 + 0] = value( m1, m2, h+120 );
optr[offset*4 + 1] = value( m1, m2, h );
optr[offset*4 + 2] = value( m1, m2, h -120 );
optr[offset*4 + 3] = 255;
}
__global__ void float_to_color( uchar4 *optr,
const float *outSrc ) {
// map from threadIdx/BlockIdx to pixel position
int x = threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x;
int y = threadIdx.y + blockIdx.y * blockDim.y;
int offset = x + y * blockDim.x * gridDim.x;
float l = outSrc[offset];
float s = 1;
int h = (180 + (int)(360.0f * outSrc[offset])) % 360;
float m1, m2;
if (l <= 0.5f)
m2 = l * (1 + s);
else
m2 = l + s - l * s;
m1 = 2 * l - m2;
optr[offset].x = value( m1, m2, h+120 );
optr[offset].y = value( m1, m2, h );
optr[offset].z = value( m1, m2, h -120 );
optr[offset].w = 255;
}
#if _WIN32
//Windows threads.
#include <windows.h>
typedef HANDLE CUTThread;
typedef unsigned (WINAPI *CUT_THREADROUTINE)(void *);
#define CUT_THREADPROC unsigned WINAPI
#define CUT_THREADEND return 0
#else
//POSIX threads.
#include <pthread.h>
typedef pthread_t CUTThread;
typedef void *(*CUT_THREADROUTINE)(void *);
#define CUT_THREADPROC void
#define CUT_THREADEND
#endif
//Create thread.
CUTThread start_thread( CUT_THREADROUTINE, void *data );
//Wait for thread to finish.
void end_thread( CUTThread thread );
//Destroy thread.
void destroy_thread( CUTThread thread );
//Wait for multiple threads.
void wait_for_threads( const CUTThread *threads, int num );
#if _WIN32
//Create thread
CUTThread start_thread(CUT_THREADROUTINE func, void *data){
return CreateThread(NULL, 0, (LPTHREAD_START_ROUTINE)func, data, 0, NULL);
}
//Wait for thread to finish
void end_thread(CUTThread thread){
WaitForSingleObject(thread, INFINITE);
CloseHandle(thread);
}
//Destroy thread
void destroy_thread( CUTThread thread ){
TerminateThread(thread, 0);
CloseHandle(thread);
}
//Wait for multiple threads
void wait_for_threads(const CUTThread * threads, int num){
WaitForMultipleObjects(num, threads, true, INFINITE);
for(int i = 0; i < num; i++)
CloseHandle(threads[i]);
}
#else
//Create thread
CUTThread start_thread(CUT_THREADROUTINE func, void * data){
pthread_t thread;
pthread_create(&thread, NULL, func, data);
return thread;
}
//Wait for thread to finish
void end_thread(CUTThread thread){
pthread_join(thread, NULL);
}
//Destroy thread
void destroy_thread( CUTThread thread ){
pthread_cancel(thread);
}
//Wait for multiple threads
void wait_for_threads(const CUTThread * threads, int num){
for(int i = 0; i < num; i++)
end_thread( threads[i] );
}
#endif
#endif // __BOOK_H__
#include "../common/book.h"
#define N 10
void add( int *a, int *b, int *c ) {
int tid = 0; // this is CPU zero, so we start at zero
while (tid < N) {
c[tid] = a[tid] + b[tid];
tid += 1; // we have one CPU, so we increment by one
}
}
int main( void ) {
int a[N], b[N], c[N];
// fill the arrays 'a' and 'b' on the CPU
for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
a[i] = -i;
b[i] = i * i;
}
add( a, b, c );
// display the results
for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
printf( "%d + %d = %d\n", a[i], b[i], c[i] );
}
return 0;
}分析:
add
void add(int *a, int *b,int *c)
{
for(int i = 0;i<N;++i)
{
c[i] = a[i]+b[i];
}
}而上面采取while虽有些复杂,但这是为了是其能再多个cpu或者gpu核的系统上并行运行。
2.基于GPU的矢量求和
#include "../common/book.h"
#define N 10
<span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 51);">__global__ </span>void add( int *a, int *b, int *c ) {
int tid = blockIdx.x; // this thread handles the data at its thread id
if (tid < N)
c[tid] = a[tid] + b[tid];
}
int main( void ) {
int a[N], b[N], c[N];
int *dev_a, *dev_b, *dev_c;
// allocate the memory on the GPU
HANDLE_ERROR( cudaMalloc( (void**)&dev_a, N * sizeof(int) ) );
HANDLE_ERROR( cudaMalloc( (void**)&dev_b, N * sizeof(int) ) );
HANDLE_ERROR( cudaMalloc( (void**)&dev_c, N * sizeof(int) ) );
// fill the arrays 'a' and 'b' on the CPU
for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
a[i] = -i;
b[i] = i * i;
}
// copy the arrays 'a' and 'b' to the GPU
HANDLE_ERROR( cudaMemcpy( dev_a, a, N * sizeof(int),
cudaMemcpyHostToDevice ) );
HANDLE_ERROR( cudaMemcpy( dev_b, b, N * sizeof(int),
cudaMemcpyHostToDevice ) );
add<<<N,1>>>( dev_a, dev_b, dev_c );
// copy the array 'c' back from the GPU to the CPU
HANDLE_ERROR( cudaMemcpy( c, dev_c, N * sizeof(int),
cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost ) );
// display the results
for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
printf( "%d + %d = %d\n", a[i], b[i], c[i] );
}
// free the memory allocated on the GPU
HANDLE_ERROR( cudaFree( dev_a ) );
HANDLE_ERROR( cudaFree( dev_b ) );
HANDLE_ERROR( cudaFree( dev_c ) );
return 0;
}- cudaMalloc() 在设备上为三个数组分配内存: 在其中两个数组(dev_a和dev_b)中包含了输入值,而在数组dev_c中包含了计算结果。
- cudaMemcpy() 数据复制: cudaMemcpyHostToDevice 是数据复制到设备上;cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost是设备复制到主机。
- cudaFree() 是否设备内存
- 尖括号: 在主机main() 函数中执行add()设备代码。
数组: 每一维最大数量都不能超过65535,硬件限制。
4.2.2 一个有趣的示例
Julia集:是满足某个复数计算函数的所有点构成的边界。这是数学中漂亮的形状之一。Julia集是一个在复平面上形成分形的点的集合,它最早由法国数学家Gaston Julia发现。
Julia集合可以由下式进行反复迭代得到:f(z) = z2 + c, 其中z是复平面某一点,c是一个复常数。把这个公式反复迭代,最终会得到一个复数C,然后根据C的模的大小,把这个点映射成不同的颜色,漂亮的Julia集分形就出来了。可以参阅 这篇文章,其中有详细的介绍。
Julia集合可以由下式进行反复迭代得到:f(z) = z2 + c, 其中z是复平面某一点,c是一个复常数。把这个公式反复迭代,最终会得到一个复数C,然后根据C的模的大小,把这个点映射成不同的颜色,漂亮的Julia集分形就出来了。可以参阅 这篇文章,其中有详细的介绍。
生成Julia集算法:通过一个简单的迭代等式对复平面中的点求值。如果在计算某个点时,迭代等式的计算结果是发散的,那么这个点就不属于Julia集合。也就是说,如果在迭代等式中计算得到的一系列值朝着无穷大的方向增长,那么这个点就被认为不属于Julia集合。相反,如果在迭代等式中计算得到的一系列值都位于某个边界范围之内,那么这个点就属于Julia集合。
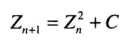 等式4.1
等式4.1
1.基于CPU的Julia集
#ifndef __GL_HELPER_H__
#define __GL_HELPER_H__
/*
On 64-bit Windows, we need to prevent GLUT from automatically linking against
glut32. We do this by defining GLUT_NO_LIB_PRAGMA. This means that we need to
manually add opengl32.lib and glut64.lib back to the link using pragmas.
Alternatively, this could be done on the compilation/link command-line, but
we chose this so that compilation is identical between 32- and 64-bit Windows.
*/
#ifdef _WIN64
#define GLUT_NO_LIB_PRAGMA
#pragma comment (lib, "opengl32.lib") /* link with Microsoft OpenGL lib */
#pragma comment (lib, "glut64.lib") /* link with Win64 GLUT lib */
#endif //_WIN64
#ifdef _WIN32
/* On Windows, include the local copy of glut.h and glext.h */
#include "GL/glut.h"
#include "GL/glext.h"
#define GET_PROC_ADDRESS( str ) wglGetProcAddress( str )
#else
/* On Linux, include the system's copy of glut.h, glext.h, and glx.h */
#include <GL/glut.h>
#include <GL/glext.h>
#include <GL/glx.h>
#define GET_PROC_ADDRESS( str ) glXGetProcAddress( (const GLubyte *)str )
#endif //_WIN32
#endif //__GL_HELPER_H__'#ifndef __CPU_BITMAP_H__
#define __CPU_BITMAP_H__
#include "gl_helper.h"
struct CPUBitmap {
unsigned char *pixels;
int x, y;
void *dataBlock;
void (*bitmapExit)(void*);
CPUBitmap( int width, int height, void *d = NULL ) {
pixels = new unsigned char[width * height * 4];
x = width;
y = height;
dataBlock = d;
}
~CPUBitmap() {
delete [] pixels;
}
unsigned char* get_ptr( void ) const { return pixels; }
long image_size( void ) const { return x * y * 4; }
void display_and_exit( void(*e)(void*) = NULL ) {
CPUBitmap** bitmap = get_bitmap_ptr();
*bitmap = this;
bitmapExit = e;
// a bug in the Windows GLUT implementation prevents us from
// passing zero arguments to glutInit()
int c=1;
char* dummy = "";
glutInit( &c, &dummy );
glutInitDisplayMode( GLUT_SINGLE | GLUT_RGBA );
glutInitWindowSize( x, y );
glutCreateWindow( "bitmap" );
glutKeyboardFunc(Key);
glutDisplayFunc(Draw);
glutMainLoop();
}
// static method used for glut callbacks
static CPUBitmap** get_bitmap_ptr( void ) {
static CPUBitmap *gBitmap;
return &gBitmap;
}
// static method used for glut callbacks
static void Key(unsigned char key, int x, int y) {
switch (key) {
case 27:
CPUBitmap* bitmap = *(get_bitmap_ptr());
if (bitmap->dataBlock != NULL && bitmap->bitmapExit != NULL)
bitmap->bitmapExit( bitmap->dataBlock );
exit(0);
}
}
// static method used for glut callbacks
static void Draw( void ) {
CPUBitmap* bitmap = *(get_bitmap_ptr());
glClearColor( 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0 );
glClear( GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT );
glDrawPixels( bitmap->x, bitmap->y, GL_RGBA, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, bitmap->pixels );
glFlush();
}
};
#endif // __CPU_BITMAP_H__#include "../common/book.h"
#include "../common/cpu_bitmap.h"
#define DIM 1000
struct cuComplex {
float r;
float i;
cuComplex( float a, float b ) : r(a), i(b) {}
float magnitude2( void ) { return r * r + i * i; }
cuComplex operator*(const cuComplex& a) {
return cuComplex(r*a.r - i*a.i, i*a.r + r*a.i);
}
cuComplex operator+(const cuComplex& a) {
return cuComplex(r+a.r, i+a.i);
}
};
int julia( int x, int y ) {
const float scale = 1.5;
float jx = scale * (float)(DIM/2 - x)/(DIM/2);
float jy = scale * (float)(DIM/2 - y)/(DIM/2);
cuComplex c(-0.8, 0.156);
cuComplex a(jx, jy);
int i = 0;
for (i=0; i<200; i++) {
a = a * a + c;
if (a.magnitude2() > 1000)
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
void kernel( unsigned char *ptr ){
for (int y=0; y<DIM; y++) {
for (int x=0; x<DIM; x++) {
int offset = x + y * DIM;
int juliaValue = julia( x, y );
ptr[offset*4 + 0] = 255 * juliaValue;
ptr[offset*4 + 1] = 0;
ptr[offset*4 + 2] = 0;
ptr[offset*4 + 3] = 255;
}
}
}
int main( void ) {
CPUBitmap bitmap( DIM, DIM );
unsigned char *ptr = bitmap.get_ptr();
kernel( ptr );
bitmap.display_and_exit();
}
2.基于GPU的Julia集
#include "../common/book.h"
#include "../common/cpu_bitmap.h"
#define DIM 1000
struct cuComplex {
float r;
float i;
cuComplex( float a, float b ) : r(a), i(b) {}
__device__ float magnitude2( void ) {
return r * r + i * i;
}
__device__ cuComplex operator*(const cuComplex& a) {
return cuComplex(r*a.r - i*a.i, i*a.r + r*a.i);
}
__device__ cuComplex operator+(const cuComplex& a) {
return cuComplex(r+a.r, i+a.i);
}
};
__device__ int julia( int x, int y ) {
const float scale = 1.5;
float jx = scale * (float)(DIM/2 - x)/(DIM/2);
float jy = scale * (float)(DIM/2 - y)/(DIM/2);
cuComplex c(-0.8, 0.156);
cuComplex a(jx, jy);
int i = 0;
for (i=0; i<200; i++) {
a = a * a + c;
if (a.magnitude2() > 1000)
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
__global__ void kernel( unsigned char *ptr ) {
// map from blockIdx to pixel position
int x = blockIdx.x;
int y = blockIdx.y;
int offset = x + y * gridDim.x;
// now calculate the value at that position
int juliaValue = julia( x, y );
ptr[offset*4 + 0] = 255 * juliaValue;
ptr[offset*4 + 1] = 0;
ptr[offset*4 + 2] = 0;
ptr[offset*4 + 3] = 255;
}
// globals needed by the update routine
struct DataBlock {
unsigned char *dev_bitmap;
};
int main( void ) {
DataBlock data;
CPUBitmap bitmap( DIM, DIM, &data );
unsigned char *dev_bitmap;
HANDLE_ERROR( cudaMalloc( (void**)&dev_bitmap, bitmap.image_size() ) );
data.dev_bitmap = dev_bitmap;
dim3 grid(DIM,DIM);
kernel<<<grid,1>>>( dev_bitmap );
HANDLE_ERROR( cudaMemcpy( bitmap.get_ptr(), dev_bitmap,
bitmap.image_size(),
cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost ) );
HANDLE_ERROR( cudaFree( dev_bitmap ) );
bitmap.display_and_exit();
}blockIdx: 判断哪个线程块
gridDim: 获取线程格子的大小






















 901
901











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










