一.简介
项目中经常会比较两个值或两个对象是否相等,那么是使用了equals还是==呢。你是否清楚二者的区别呢。
<1> equals()是方法,而==是运算符。
<2> ==运算符
(1) 基本数据类型(int,long...)只有==来比较两个数值是否相等。即对于基本类型来说==就是比较的两个值是否相等。
(2) 引用数据类型(String,数组,Java Bean...)==比较的是两个值在堆内存的地址是否相等。
<3> equals方法
只有引用数据类型存在此方法,比较值是否相等。
<4> 结论
基本类型比较用==运算符,引用类型比较用equals方法。
对于String类比较特殊,String str="abc" 此时的str相当于基本类型(==比较的是数值),而String str=new String() 此时str就是引用类型。==比较的是堆内存中的地址 equals比较的是数值。
下面结合代码一一讲解
代码
package com.example.myapplication;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
initMethod1();
initMethod2();
initMethod3();
}
private void initMethod1() {
int a = 10;
int b = 10;
long c = 10;
float d = 10;
double e = 10.00;
boolean b1 = (a == b);//true
boolean b2 = (a == c);//true
boolean b3 = (a == d);//true
boolean b4 = (a == e);//true
Log.d("TAG", "b1----:" + b1);
Log.d("TAG", "b2----:" + b2);
Log.d("TAG", "b3----:" + b3);
Log.d("TAG", "b4----:" + b4);
Log.d("TAG", "-----------------------------");
}
private void initMethod2() {
int a = 100;
Integer b = 100;
Integer c = new Integer(100);
boolean b1 = (a == b);//true
boolean b2 = (a == c);//true
boolean b3 = (b == c);//false
boolean b4 = (b.equals(a));//true
boolean b5 = (b.equals(c));//true
Log.d("TAG", "b1----:" + b1);
Log.d("TAG", "b2----:" + b2);
Log.d("TAG", "b3----:" + b3);
Log.d("TAG", "b4----:" + b4);
Log.d("TAG", "b5----:" + b5);
Log.d("TAG", "-----------------------------");
}
private void initMethod3() {
String s1 = "abc";
String s2 = new String("abc");
String s3 = "abc";
String s4 = new String("abc");
boolean b1 = (s1 == s2);//false
boolean b2 = (s1 == s3);//true
boolean b3 = (s2 == s4);//false
boolean b4 = (s1.equals(s2));//true
boolean b5 = (s1.equals(s3));//true
boolean b6 = (s2.equals(s4));//true
Log.d("TAG", "b1----:" + b1);
Log.d("TAG", "b2----:" + b2);
Log.d("TAG", "b3----:" + b3);
Log.d("TAG", "b4----:" + b4);
Log.d("TAG", "b5----:" + b5);
Log.d("TAG", "b6----:" + b6);
}
}
结果
D/TAG: b1----:true
D/TAG: b2----:true
D/TAG: b3----:true
D/TAG: b4----:true
D/TAG: -----------------------------
D/TAG: b1----:true
D/TAG: b2----:true
D/TAG: b3----:false
D/TAG: b4----:true
D/TAG: b5----:true
D/TAG: -----------------------------
D/TAG: b1----:false
D/TAG: b2----:true
D/TAG: b3----:false
D/TAG: b4----:true
D/TAG: b5----:true
D/TAG: b6----:true
注意
<1> int 类型的包装类Integer类取值
Integer类取值和 int 类型取值一致,取值范围是从-2147483648 至 2147483647(-231至 231-1) ,包括-2147483648 和 2147483647。
但是对于Integer类java为了提高效率,初始化了-128--127之间的整数对象,因此Integer类取值-128--127的时候效率最高。
代码
package com.example.myapplication;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
initMethod();
}
private void initMethod() {
Integer a = 100;
Integer b = 100;
Integer c = -10;
Integer d = -10;
boolean b1 = (a == b);//true
boolean b2 = (c == d);//true
Log.d("TAG", "b1----:" + b1);
Log.d("TAG", "b2----:" + b2);
Integer e = 128;
Integer f = 128;
Integer g = -129;
Integer h = -129;
boolean b3 = (e == f);//false
boolean b4 = (g == h);//false
Log.d("TAG", "b3----:" + b3);
Log.d("TAG", "b4----:" + b4);
}
}
结果
D/TAG: b1----:true
D/TAG: b2----:true
D/TAG: b3----:false
D/TAG: b4----:false
原因
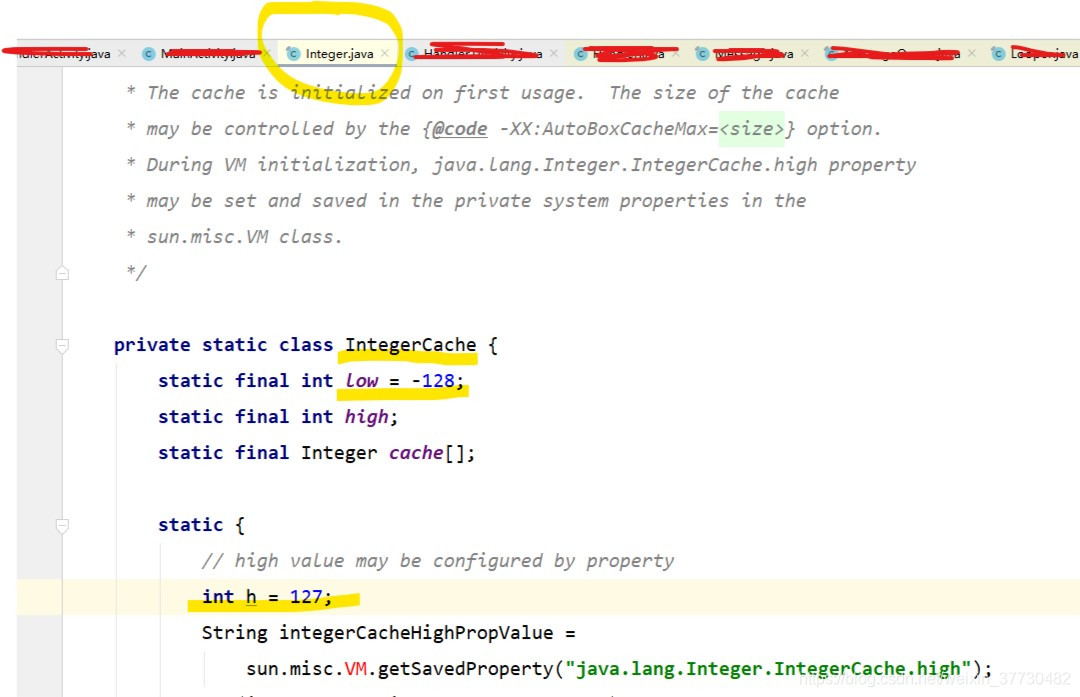
所以使用Int的包装类Integer类时比较大小需要注意。
附:
String类equals方法源码:
public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
if (this == anObject) {
return true;
}
if (anObject instanceof String) {
String anotherString = (String) anObject;
int n = count;
if (n == anotherString.count) {
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int i = offset;
int j = anotherString.offset;
while (n-- != 0) {
if (v1[i++] != v2[j++])
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}





















 398
398











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








