个人小结: 网络编程的实质就是两个(或多个)设备(例如计算机)之间的数据传输。数据传输的基础是双方使用统一的协议,网络通讯的协议主要有TCP和UDP两种,本篇主要介绍如何通过TCP协议进行网络通讯,以及URL对象和URLConnection对象的常见用法。
一、TCP传输步骤:
1、Socket和ServerSocket
2、建立客户端和服务器端
3、建立连接后,通过Socket中的IO流进行数据的传输
4、关闭Socket
ps:客户端和服务端也是两个独立的应用程序。
</pre><pre name="code" class="java"><pre name="code" class="java">/*
客户端,通过查阅socket对象,发现在该对象建立时,就可以去链接指定主机。
因为tcp是面向链接的,所以在建立socket服务时,就要有服务端存在,并连接成功,
形成通路后,在该通道进行数据传输。
需求:给服务端发送一个文本数据。
*/
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
class TcpClient
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
String ip = InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostAddress();
//创建客户端的socket服务,指定目的主机和端口
Socket s = new Socket(ip,10003);
//为了发送数据,应该获取socket流中的输出流
OutputStream out = s.getOutputStream();
out.write("tcp ge men lai le".getBytes());
s.close();
}
}
/*
需求:定义端点接收数据并打印在控制台上。
服务端:
1、建立服务端的socket服务,通过ServerSocket();
并监听一个端口。
2、获取连接过来的客户端对象,通过ServerSocket 的 accept方法。
所以这个方法是阻塞式的。没有连接就会等。
3、客户端如果发过来数据,那么服务端要使用对应的客户端对象,并
获取到该客户端的读取流来读取发过来的数据,并打印到控制台。
4、关闭服务端(可选操作)
*/
class TcpServer
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
//1、建立服务端的socket服务,并监听一个端口
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10003);
//通过accept方法获取连接过来的客户端对象。
Socket s = ss.accept();
String ip = s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress();
System.out.println(ip+"......connected");
//获取客户端发过来的数据,那么要用到客户端对象的读取流来读取数据。
InputStream in = s.getInputStream();
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = in.read(buf);
System.out.println(new String(buf,0,len));
s.close();//关闭客户端。
ss.close();
}
}运行结果:
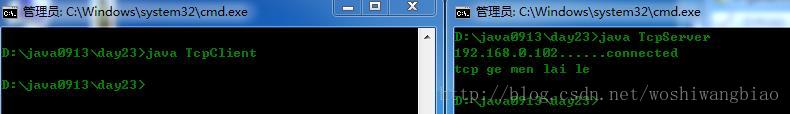
练习:演示tcp的传输的客户端和服务端的互访
/*
演示tcp的传输的客户端和服务端的互访
需求:客户端给服务端发送数据,服务端收到后,给客户端反馈信息。
*/
/*
客户端:
1、建立socket服务,指定要连接主机和端口
2、获取socket流中的输出流,将数据写到该流中,通过网络发送到服务端。
3、获取socket流中的输入流,将服务端反馈的数据获取到,并打印。
4、关闭客户端资源。
*/
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
class TcpClient2
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
String ip = InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostAddress();
Socket s = new Socket("192.168.0.102",50004);
OutputStream out = s.getOutputStream();
out.write("服务端,你好!".getBytes());
InputStream in = s.getInputStream();
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = in.read(buf);//这里的读取之所以不会冲突,是因为read是阻塞式方法,没数据我就等
System.out.println(new String(buf,0,len));
s.close();
}
}
class TcpServer2
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(50004);
Socket s = ss.accept();
String ip = s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress();
System.out.println(ip+"....is connected");
InputStream in = s.getInputStream();
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = in.read(buf);
String data = new String(buf,0,len);
System.out.println(data);
OutputStream out = s.getOutputStream();
//Thread.sleep(6000);
out.write("哥们收到了,你也好".getBytes());
s.close();
ss.close();
}
}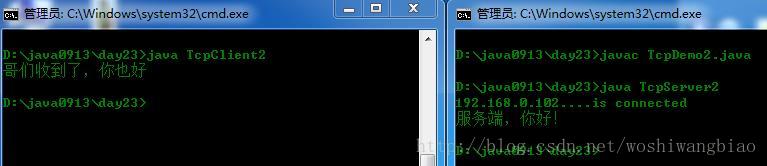
练习:建立一个文本转换服务器
/*
需求:建立一个文本转换服务器
客户端给服务端发送文本,服务端会将文本转换成大写再返回给客户端。而且客户端可以不断进行文本转换,当客户端输入over时,转换结束。
分析:
客户端:
既然是操作设备上的数据,那么就可以使用io技术,并按照io的操作规律来思考
源:键盘录入
目的:网络设备,网络输出流。
而且操作的是文本数据。可以选择字符流。
步骤:
1、建立服务
2、获取键盘录入
3、将数据发给服务端
4.获取服务端返回的大写数据
5、结束,关闭资源
都是文本数据,可以使用字符流进行操作,同时提高效率,加入缓冲。
*/
/*
该例子出现的问题:
现象:客户端和服务端都在莫名的等待,为什么?
因为客户端和服务端都有阻塞式的方法,这些方法没有读到结束标记就会一直等,从而导致两端都在等待。
*/
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
class TransClient
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
String ip = InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostAddress();
Socket s = new Socket(ip,10005);
//源,定义读取键盘数据的流对象
BufferedReader bufr =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
//定义目的,将数据写入到socket输出流,发给服务端。
//BufferedWriter bufOut =
// new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(s.getOutputStream()));
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(s.getOutputStream(),true);
//定义一个socket读取流,读取服务端返回的大写数据。
BufferedReader bufIn =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));
String line = null;
while ((line = bufr.readLine())!=null)
{
if("over".equals(line))
break;
out.println(line);
//bufOut.write(line);
//bufOut.newLine();
//bufOut.flush();
String str = bufIn.readLine();
System.out.println("server:"+str);
}
bufr.close();
s.close();
}
}
/*
服务端:
源:socket读取流
目的:socket输出流
都是文本,装饰一下。
*/
class TransServer
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10005);
Socket s = ss.accept();
String ip = s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress();
System.out.println(ip+"....is connected");
//定义源:读取socket读取流中的数据
BufferedReader bufIn =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));
//目的:socket输出流,将大写数据写入到socket输出流,并发送给客户端。
//BufferedWriter bufOut =
//new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(s.getOutputStream()));
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(s.getOutputStream(),true);
String line = null;
while ((line = bufIn.readLine())!=null)//readLine是阻塞式的,他读到回车符的时候才会返回数据。
{
System.out.println(line);
out.println(line.toUpperCase());
//bufOut.write(line.toUpperCase());
//bufOut.newLine();
//bufOut.flush();
}
s.close();
ss.close();
}
}运行结果:
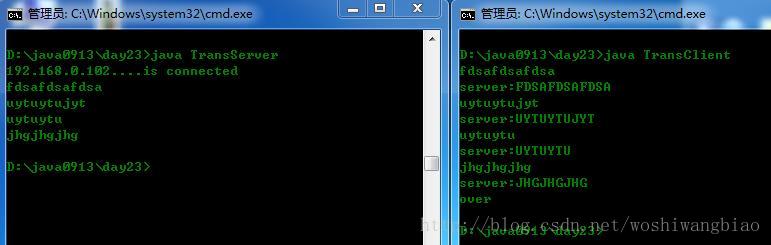
练习:向服务器上传一个文件
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
class TextClient
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
String ip = InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostAddress();
Socket s = new Socket(ip,10006);
//源:硬盘上的文本文件
BufferedReader bufr =
new BufferedReader(new FileReader("TcpTest.java"));
//目的:socket输出流
BufferedWriter bufOut =
new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(s.getOutputStream()));
String line = null;
while ((line=bufr.readLine())!=null)
{
bufOut.write(line);
bufOut.newLine();
bufOut.flush();
}
bufr.close();
s.shutdownOutput();//关闭客户端的输出流,相当于给流中加入一个结束标记-1。
BufferedReader bufIn =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));
String str = bufIn.readLine();
System.out.println(str);
s.close();
}
}
class TextServer
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10006);
Socket s = ss.accept();
String ip = s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress();
System.out.println(ip+"....is connected");
//源:socket读取流
BufferedReader bufIn =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));
//目的:硬盘上的文本文件
BufferedWriter bufw =
new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("copy.txt"));
String line = null;
while ((line=bufIn.readLine())!=null)
{
bufw.write(line);
bufw.newLine();
bufw.flush();
}
bufw.close();
System.out.println("上传完毕!");
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(s.getOutputStream(),true);
out.println("sever:上传完毕!");
s.close();
ss.close();
}
}练习:并发上传图片
/*
需求:上传图片
客户端:
1、建立服务端点
2、读取客户端已有的图片数据
3、通过socket输出流将数据发给服务端
4、读取服务端反馈的信息
5、关闭
*/
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
class PicClient
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
if (args.length!=1)
{
System.out.println("请选择一个jpg格式的图片");
return;
}
File file = new File(args[0]);
if ( !( file.exists() && file.isFile() ) )
{
System.out.println("该文件有问题,要么不存在,要么不是文件");
return;
}
if (!file.getName().endsWith(".jpg"))
{
System.out.println("图片格式错误,请重新选择");
return;
}
if (file.length()>1024*1024*5)//file 有length()方法吗?
{
System.out.println("文件过大,没安好心");
return;
}
String ip = InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostAddress();
Socket s = new Socket(ip,10007);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
OutputStream out = s.getOutputStream();
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while ((len= fis.read(buf))!=-1)
{
out.write(buf,0,len);
}
s.shutdownOutput();
InputStream in = s.getInputStream();
byte[] bufIn = new byte[1024];
int lenIn = in.read(bufIn);
System.out.println(new String(bufIn,0,lenIn));
fis.close();
s.close();
}
}
/*
服务端
这个服务端有个局限性:当A客户端连接上后,被服务端获取到,服务端执行具体流程,
这时B客户端连接,只有等待,因为服务端还没有处理完A客户端的请求,还没有循环
回来执行下次accept方法,所以暂时获取不到B客户端对象。
那么为了可以让多个客户端同时并发访问服务端,
服务端最好就是将每个客户端封装到一个单独的线程中,这样就可以同时处理
多个客户端请求。
如何定义线程?
只要明确了服务端操作每一个客户端时所执行的代码即可,将该代码存入run方法中。
*/
class PicThread implements Runnable
{
private Socket s;
PicThread(Socket s)
{
this.s = s;
}
public void run()
{
int count =1;
String ip = s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress();
try
{
System.out.println(ip+"....is connected");
InputStream in = s.getInputStream();
File file = new File(ip+"("+count+").jpg");
while (file.exists())
{
file = new File(ip+"("+(count++)+").jpg");
}
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while ((len = in.read(buf))!=-1)
{
fos.write(buf,0,len);
}
OutputStream Out = s.getOutputStream();
Out.write("图片上传成功!".getBytes());
fos.close();
s.close();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
throw new RuntimeException(ip+":图片上传失败!");
}
}
}
class PicServer
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10007);
while (true)
{
Socket s = ss.accept();
new Thread(new PicThread(s)).start();
}
//ss.close();
}
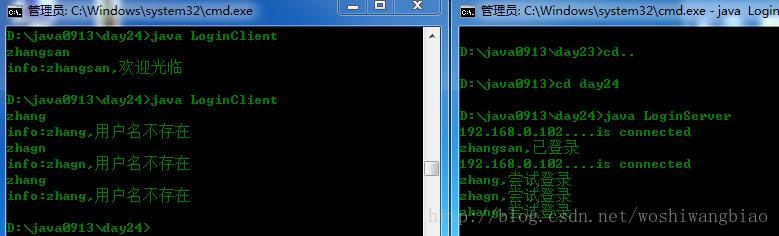
}练习:客户端并发登录
/*
客户端通过键盘录入用户名。
服务端对这个用户名进行校验。
如果该用户存在,在服务端显示xxx,已登录
并在客户端显示 xxx,欢迎光临
如果该用户不存在,在服务端显示xxx,尝试登录
并在客户端显示 xxx,该用户不存在。
最多就登录三次。
*/
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
class LoginClient
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
String ip = InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostAddress();
Socket s = new Socket(ip,10008);
BufferedReader bufr =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(s.getOutputStream(),true);
BufferedReader bufIn =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));
for (int x =0 ; x<3 ; x++)
{
//读取键盘录入
String line = bufr.readLine();
//如果没录入就按ctrl+c 结束,那么line就等于null,此时不用再往下进行了。不能把null发到服务端。
if(line==null)
break;
//把登录名发给服务端
pw.println(line);
//读取服务端反馈回来的结果,并打印出来
String info = bufIn.readLine();
System.out.println("info:"+info);
//如果结果中包含“欢迎”字样,说明校验成功,不用再继续循环校验。
if(info.contains("欢迎"))
break;
}
bufr.close();
s.close();
}
}
class UserThread implements Runnable
{
private Socket s;
UserThread(Socket s)
{
this.s = s;
}
public void run()
{
String ip = s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress();
System.out.println(ip+"....is connected");
try
{
for (int x = 0; x<3 ; x++ )
{
BufferedReader bufIn =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));
String name = bufIn.readLine();
if(name==null)//当客户端强制结束登录,服务端读到-1,名字返回null,这时就要停止访问。(健壮性考虑)
break;
BufferedReader bufr =
new BufferedReader(new FileReader("user.txt"));
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(s.getOutputStream(),true);
String line = null;
//定义一个标记,标记服务器核对所有用户名后,客户端发来的名称是否存在
boolean flag = false;
while ((line= bufr.readLine())!=null)
{
if (line.equals(name))
{
flag = true;
break;//如果存在,立即跳出查找循环,返回查找结果为true
}
}
if (flag)//如果存在,显示下列信息
{
System.out.println(name+",已登录");
pw.println(name+",欢迎光临");
break;//如果存在,也没必要再循环登录了。
}
else//如果不存在,显示下列信息
{
System.out.println(name+",尝试登录");
pw.println(name+",用户名不存在");
}
}
//如果三次都不存在,就直接关闭此客户端连接。
s.close();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
throw new RuntimeException(ip+":校验失败");
}
}
}
class LoginServer
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10008);
//不停接收连接进来的客户端
while (true)
{
Socket s = ss.accept();
//每个客户端一进来就另开一个线程,使互不干涉。
new Thread(new UserThread(s)).start();
}
}
}
二、URL和URLConnection:
URL的常用方法:
String getFile() 获取此 URL 的文件名。
String getHost() 获取此 URL 的主机名(如果适用)。
String getPath() 获取此 URL 的路径部分。
int getPort() 获取此 URL 的端口号。
String getProtocol() 获取此 URL 的协议名称。
String getQuery() 获取此 URL 的查询部分。
URLConnection:
String getHost() 获取此 URL 的主机名(如果适用)。
String getPath() 获取此 URL 的路径部分。
int getPort() 获取此 URL 的端口号。
String getProtocol() 获取此 URL 的协议名称。
String getQuery() 获取此 URL 的查询部分。
URLConnection:
InputStream getInputStream() 获取输入流
OutputStream getOutputStream() 获取输出流
OutputStream getOutputStream() 获取输出流
import java.net.*;
class URLDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws MalformedURLException
{
URL url = new URL("http://192.168.0.102/myweb/demo.html?name=hah&age=30");
System.out.println("getProtocol():"+url.getProtocol());
System.out.println("getHost():"+url.getHost());
System.out.println("getPort():"+url.getPort());
System.out.println("getPath():"+url.getPath());
System.out.println("getFile():"+url.getFile());
System.out.println("getQuery():"+url.getQuery());
/*如果port是-1,我就写80进去,如果不是-1,我就写你指定的端口进去。
int port = url.getPort();
if(port==-1)
port = 80;
*/
}
}
/*
显示结果:
getProtocol():http
getHost():192.168.0.102
getPort():8080
getPath():/myweb/demo.html
getFile():/myweb/demo.html?name=hah&age=30
getQuery():name=hah&age=30
*/练习:用GUI自定义一个浏览器客户端,并访问服务器
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
class MyIEByGUI2
{
private Frame f;
private TextField tf;
private Button but;
private TextArea ta;
private Dialog d;
private Label lab;
private Button okBut;
MyIEByGUI2()
{
init();
}
public void init()
{
f = new Frame("my window");
f.setBounds(300,100,800,500);
f.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
tf = new TextField(50);
but = new Button("转到");
ta = new TextArea(25,60);
f.add(tf);
f.add(but);
f.add(ta);
d = new Dialog(f,"提示信息——self",true);//如果是false,不关闭对话框,还能操作相应窗体
d.setBounds(200,50,300,150);
d.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
lab = new Label();
okBut = new Button("确定");
d.add(lab);
d.add(okBut);
myEvent();
f.setVisible(true);
}
private void myEvent()
{
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter()
{
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e)
{
System.exit(0);
}
});
but.addActionListener(new ActionListener()
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
try
{
showDir();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
}
}
});
d.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter()
{
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e)
{
d.setVisible(false);
}
});
okBut.addActionListener(new ActionListener()
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
d.setVisible(false);
}
});
tf.addKeyListener(new KeyAdapter()
{
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e)
{
try
{
if(e.getKeyCode()==KeyEvent.VK_ENTER)
showDir();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
}
}
});
}
private void showDir() throws Exception
{
ta.setText("");
String urlPath = tf.getText();//http://192.168.0.102:8080/myweb/demo.html
URL url = new URL(urlPath);
//URLConnection conn = url.openConnection();
//InputStream in = conn.getInputStream();
InputStream in = url.openStream();
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = in.read(buf);
ta.setText(new String(buf,0,len));
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
new MyIEByGUI2();
}
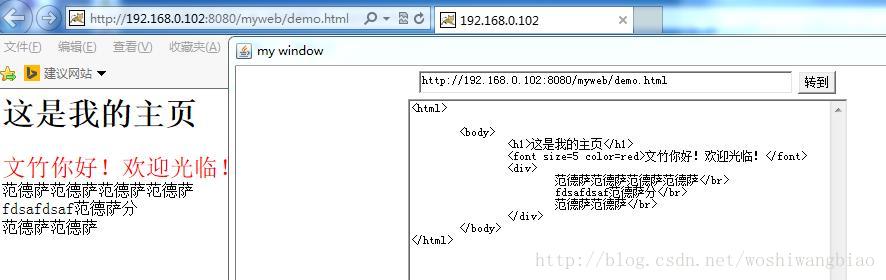
}运行结果:





















 3947
3947











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








