内存堆管理器GenCollectedHeap在执行Gc回收垃圾对象的时候,无论是它自己还是垃圾回收策略MarkSweepPolicy都没有具体去规定一个垃圾对象应该如何被回收,而只是在整体上决策这次的Gc应该回收那些内存代中的垃圾对象,至于这些内存代管理器是如何做的,GenCollectedHeap并不关心. 从前文分析内存堆管理器GenCollectedHeap执行Gc策略调度内存代管理器去回收该内存代中垃圾对象的过程, 不难发现,主要涉及到内存代管理器的几个核心的方法实现:
bool full_collects_younger_generations(); //当前内存代是否支持回收比其年青的所有内存代的垃圾
bool should_collect(bool full, size_t word_size, bool is_tlab); //当前内存代是否应该进行垃圾回收
void collect(bool full, bool clear_all_soft_refs, size_t word_size, bool is_tlab) = 0; //对当前内存代进行垃圾回收
由于DefNewGeneration只能用作新生代的内存管理器,所以它是不可能支持其它年青代垃圾对象回收的:
//当前内存代是否支持回收比其年青的所有内存代的垃圾
virtual bool full_collects_younger_generations() const { return false; }
/**
* 当前内存代是否应该进行垃圾回收
*/
virtual bool should_collect(bool full,
size_t word_size,
bool is_tlab) {
return (full || should_allocate(word_size, is_tlab));
}
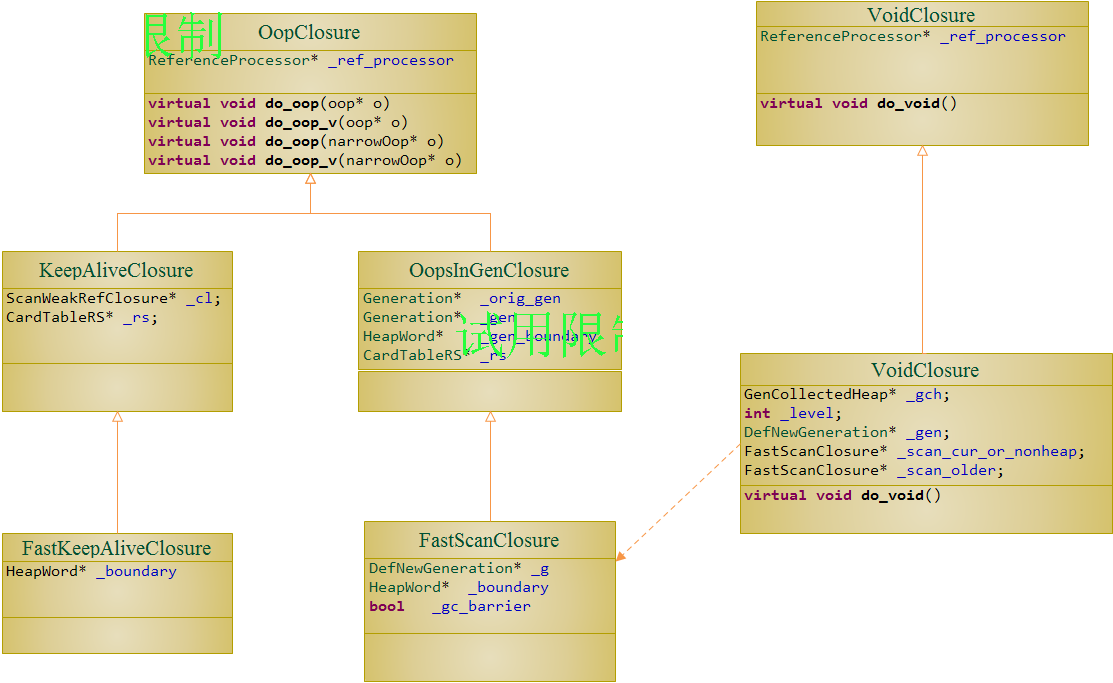
在内存代管理器DefNewGeneration回收垃圾对象的过程中,使用FastScanClosure处理所有的根对象,FastEvacuateFollowersClosure处理所有的引用对象,而所有的软/弱引用对象则使用FastKeepAliveClosure来处理:
/**
* 执行本内存代的垃圾对象回收
*/
void DefNewGeneration::collect(bool full,
bool clear_all_soft_refs,
size_t size,
bool is_tlab) {
assert(full || size > 0, "otherwise we don't want to collect");
GenCollectedHeap* gch = GenCollectedHeap::heap();
//下一个内存代管理器(主要用于active对象升级或转存储)
_next_gen = gch->next_gen(this);
//当前内存代管理器只用于年青代
assert(_next_gen != NULL, "This must be the youngest gen, and not the only gen");
//检查回收当前内存代的垃圾对象是否安全,若不安全则放弃回收该内存代,并通知内存堆管理器关闭当前的增量式垃圾回收方式
if (!collection_attempt_is_safe()) {
if (Verbose && PrintGCDetails) {
gclog_or_tty->print(" :: Collection attempt not safe :: ");
}
//告诉内存堆管理器不要再考虑增量式Gc(Minor Gc),因为一定会失败
gch->set_incremental_collection_failed(); // Slight lie: we did not even attempt one
return;
}
assert(to()->is_empty(), "Else not collection_attempt_is_safe");
init_assuming_no_promotion_failure();
TraceTime t1("GC", PrintGC && !PrintGCDetails, true, gclog_or_tty);
//记录该Gc之前,内存堆的使用量
size_t gch_prev_used = gch->used();
SpecializationStats::clear();
// These can be shared for all code paths
IsAliveClosure is_alive(this);
ScanWeakRefClosure scan_weak_ref(this);
age_table()->clear();
to()->clear(SpaceDecorator::Mangle);
gch->rem_set()->prepare_for_younger_refs_iterate(false);
//标记所有内存代当前分配对象存储空间的起始位置
assert(gch->no_allocs_since_save_marks(0), "save marks have not been newly set.");
// Not very pretty.
CollectorPolicy* cp = gch->collector_policy();
FastScanClosure fsc_with_no_gc_barrier(this, false);
FastScanClosure fsc_with_gc_barrier(this, true);
set_promo_failure_scan_stack_closure(&fsc_with_no_gc_barrier);
//用于分析对象的引用关系并进行回收
FastEvacuateFollowersClosure evacuate_followers(gch, _level, this,
&fsc_with_no_gc_barrier,
&fsc_with_gc_barrier);
//标记所有内存代当前分配对象存储空间的起始位置
assert(gch->no_allocs_since_save_marks(0), "save marks have not been newly set.");
//遍历当前内存代上的所有根对象,并复制它们到新的存储空间
gch->gen_process_strong_roots(_level,
true, // Process younger gens, if any, as strong roots.
true, // activate StrongRootsScope
false, // not collecting perm generation.
SharedHeap::SO_AllClasses,
&fsc_with_no_gc_barrier,
true, // walk *all* scavengable nmethods
&fsc_with_gc_barrier);
//迭代递归遍历当前内存代上的所有根对象的引用对象,并进行垃圾回收(复制active对象到新的存储空间)
evacuate_followers.do_void();
//清理软引用对象
FastKeepAliveClosure keep_alive(this, &scan_weak_ref);
ReferenceProcessor* rp = ref_processor();
rp->setup_policy(clear_all_soft_refs);
rp->process_discovered_references(&is_alive, &keep_alive, &evacuate_followers, NULL);
if (!promotion_failed()) { //当前内存代(年青代)在本次Gc过程中没有发生对象升级失败
//Eden/From区清零
eden()->clear(SpaceDecorator::Mangle);
from()->clear(SpaceDecorator::Mangle);
if (ZapUnusedHeapArea) {
// This is now done here because of the piece-meal mangling which
// can check for valid mangling at intermediate points in the
// collection(s). When a minor collection fails to collect
// sufficient space resizing of the young generation can occur
// an redistribute the spaces in the young generation. Mangle
// here so that unzapped regions don't get distributed to
// other spaces.
to()->mangle_unused_area();
}
//交换From/To区
swap_spaces();
assert(to()->is_empty(), "to space should be empty now");
//重新计算对象可进入下一个内存代的存活时间阈值
_tenuring_threshold = age_table()->compute_tenuring_threshold(to()->capacity()/HeapWordSize);
// A successful scavenge should restart the GC time limit count which is
// for full GC's.
AdaptiveSizePolicy* size_policy = gch->gen_policy()->size_policy();
size_policy->reset_gc_overhead_limit_count();
if (PrintGC && !PrintGCDetails) {
gch->print_heap_change(gch_prev_used);
}
assert(!gch->incremental_collection_failed(), "Should be clear");
} else { //当前内存代(年青代)在本次Gc过程中发生了对象升级失败(年老代没有足够的空闲空间来容纳从年青代转存储过来的active对象)
assert(_promo_failure_scan_stack.is_empty(), "post condition");
_promo_failure_scan_stack.clear(true); // Clear cached segments.
remove_forwarding_pointers();
if (PrintGCDetails) {
gclog_or_tty->print(" (promotion failed) ");
}
// Add to-space to the list of space to compact
// when a promotion failure has occurred. In that
// case there can be live objects in to-space
// as a result of a partial evacuation of eden
// and from-space.
swap_spaces(); // For uniformity wrt ParNewGeneration.
//设置From区下一个可压缩内存区为To区,以便在下一次的Full Gc中压缩调整
from()->set_next_compaction_space(to());
gch->set_incremental_collection_failed();
//通知旧生代发生了对象升级失败(你的空闲空间不够)
_next_gen->promotion_failure_occurred();
// Reset the PromotionFailureALot counters.
NOT_PRODUCT(Universe::heap()->reset_promotion_should_fail();)
}
// set new iteration safe limit for the survivor spaces
from()->set_concurrent_iteration_safe_limit(from()->top());
to()->set_concurrent_iteration_safe_limit(to()->top());
SpecializationStats::print();
// We need to use a monotonically non-deccreasing time in ms
// or we will see time-warp warnings and os::javaTimeMillis()
// does not guarantee monotonicity.
jlong now = os::javaTimeNanos() / NANOSECS_PER_MILLISEC;
update_time_of_last_gc(now);
}在DefNewGeneration正式进行Gc前会先检测一下本次Minor Gc是否安全,如果不安全则直接放弃本次Gc,检查策略是:
1.To区空闲
2.下一个内存代的可用空间能够容纳当前内存代的所有对象(用于对象升级)/**
* 检查本内存代当前进行垃圾回收是否安全
*/
bool DefNewGeneration::collection_attempt_is_safe() {
if (!to()->is_empty()) {
if (Verbose && PrintGCDetails) {
gclog_or_tty->print(" :: to is not empty :: ");
}
return false;
}
if (_next_gen == NULL) {
GenCollectedHeap* gch = GenCollectedHeap::heap();
_next_gen = gch->next_gen(this);
assert(_next_gen != NULL,
"This must be the youngest gen, and not the only gen");
}
return _next_gen->promotion_attempt_is_safe(used());
}1.根对象的扫描处理(FastScanClosure)
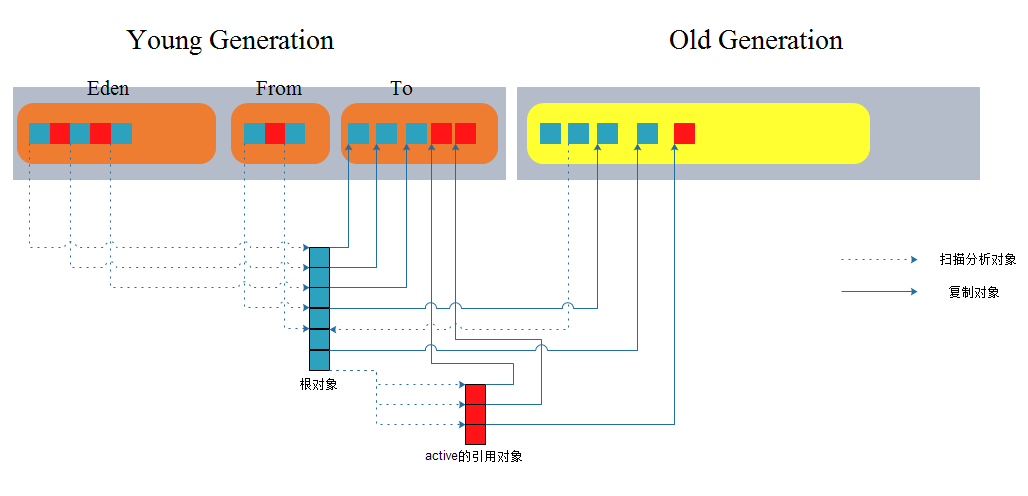
内存代管理器DefNewGeneration对根对象的处理很简单,就是优先考察该根对象是否可以进入旧生代,如果可以则升级到旧生代,否则将它们复制到年青代的To区,如果T此时o区没有足够的空闲空间则将它们转存储到旧生代;如果旧生代没有足够的空间则此次Minor Gc就可以终止了.
template <class T> inline void FastScanClosure::do_oop_work(T* p) {
T heap_oop = oopDesc::load_heap_oop(p);
// Should we copy the obj?
if (!oopDesc::is_null(heap_oop)) { //非空对象
oop obj = oopDesc::decode_heap_oop_not_null(heap_oop);
if ((HeapWord*)obj < _boundary) { //对象的存储空间在当前被回收的内存代中
//确保对象不在年青代的To区
assert(!_g->to()->is_in_reserved(obj), "Scanning field twice?");
//复制对象到新的存储空间
oop new_obj = obj->is_forwarded() ? obj->forwardee() : _g->copy_to_survivor_space(obj);
//更新对象的存储空间地址映射
oopDesc::encode_store_heap_oop_not_null(p, new_obj);
if (_gc_barrier) {
// Now call parent closure
do_barrier(p);
}
}
}
}
inline void FastScanClosure::do_oop_nv(oop* p) { FastScanClosure::do_oop_work(p); }
inline void FastScanClosure::do_oop_nv(narrowOop* p) { FastScanClosure::do_oop_work(p); }
/**
* 将Eden/From区中的某个对象复制到To区或年老代中(当前内存代正在GC)
*/
oop DefNewGeneration::copy_to_survivor_space(oop old) {
assert(is_in_reserved(old) && !old->is_forwarded(), "shouldn't be scavenging this oop");
//复制对象大小
size_t s = old->size();
oop obj = NULL;
//如果复制对象的存活时间还未超过设置的阈值,则优先将其拷贝到To区
if (old->age() < tenuring_threshold()) {
obj = (oop) to()->allocate(s);
}
if (obj == NULL) { //To区内存不够存储该对象或该对象可以升级到下一个内存代(旧生代)
obj = _next_gen->promote(old, s);
if (obj == NULL) {
handle_promotion_failure(old);
return old;
}
} else { //将复制对象拷贝到To区
// Prefetch beyond obj
const intx interval = PrefetchCopyIntervalInBytes;
Prefetch::write(obj, interval);
//复制旧对象的值到新对象中
Copy::aligned_disjoint_words((HeapWord*)old, (HeapWord*)obj, s);
//增加对象的存活时间
obj->incr_age();
age_table()->add(obj, s);
}
// Done, insert forward pointer to obj in this header
old->forward_to(obj);
return obj;
}1).常规的根对象
2).比待回收的内存代Older的内存代上分配的所有对象
3).比待回收的内存代Younger的内存代上分配的所有对象2.引用对象的扫描处理(FastEvacuateFollowersClosure)
由于对象之间的引用关系一般是一个有向图结构,而处理图结构最常用的方式就是迭代式的广度优先搜索或升读优先搜索.无论哪种方式, 可能都需要使用临时的存储空间来保存下一次迭代的任务(也就是本次迭代的输出),这种临时存储空间一般是栈或者队列的数据结构.对于内存代管理器DefNewGeneration而言,它采用广度优先的方式来处理所有的引用对象.所使用的临时的存储空间则看起来极为巧妙:在处理根对象之前,先标记保存年青代Eden区和旧生代分配内存空间的起始位置,然后处理所有的根对象;根对象处理完之后,年青代Eden区和旧生代分配内存空间的起始位置可能已经都变化了,而变化的这一部分就是需要处理的引用对象,之后的情况一次类推.不难看出,这种处理方式本质上就是队列的思想.
DefNewGeneration::EvacuateFollowersClosure::
EvacuateFollowersClosure(GenCollectedHeap* gch, int level,
ScanClosure* cur, ScanClosure* older) :
_gch(gch), _level(level),
_scan_cur_or_nonheap(cur), _scan_older(older)
{}
void DefNewGeneration::EvacuateFollowersClosure::do_void() {
do {
_gch->oop_since_save_marks_iterate(_level, _scan_cur_or_nonheap,
_scan_older);
} while (!_gch->no_allocs_since_save_marks(_level));
}
void GenCollectedHeap::oop_since_save_marks_iterate(int level, \
OopClosureType* cur, \
OopClosureType* older) { \
_gens[level]->oop_since_save_marks_iterate##nv_suffix(cur); \
for (int i = level+1; i < n_gens(); i++) { \
_gens[i]->oop_since_save_marks_iterate##nv_suffix(older); \
} \
perm_gen()->oop_since_save_marks_iterate##nv_suffix(older); \
}
/**
* 内存堆中的个内存堆是否都没有发生新的对象内存分配事件,同时标记个内存代及其各内存区当前分配对象存储空间的起始位置
*/
bool GenCollectedHeap::no_allocs_since_save_marks(int level) {
for (int i = level; i < _n_gens; i++) {
if (!_gens[i]->no_allocs_since_save_marks()) return false;
}
return perm_gen()->no_allocs_since_save_marks();
}void DefNewGeneration:: \
oop_since_save_marks_iterate##nv_suffix(OopClosureType* cl) { \
cl->set_generation(this); \
eden()->oop_since_save_marks_iterate##nv_suffix(cl); \
to()->oop_since_save_marks_iterate##nv_suffix(cl); \
from()->oop_since_save_marks_iterate##nv_suffix(cl); \
cl->reset_generation(); \
save_marks(); \
}
void ContiguousSpace:: \
oop_since_save_marks_iterate##nv_suffix(OopClosureType* blk) { \
HeapWord* t; \
HeapWord* p = saved_mark_word(); //上一次标记的分配位置 \
assert(p != NULL, "expected saved mark"); \
\
const intx interval = PrefetchScanIntervalInBytes; \
do { \
t = top(); //当前的分配位置 \
while (p < t) { \
Prefetch::write(p, interval); \
debug_only(HeapWord* prev = p); \
oop m = oop(p); \
p += m->oop_iterate(blk); \
} \
} while (t < top()); \
\
set_saved_mark_word(p); \
}3.软/弱引用对象的扫描处理(FastKeepAliveClosure)
内存代管理器DefNewGeneration对软/弱引用对象的处理主要还是依赖于JVM配置的软/弱引用对象处理策略,目前的实现的引用对象处理策略主要有三种:
1.AlwaysClearPolicy
2.LRUMaxHeapPolicy
3.LRUCurrentHeapPolicy内存代管理器在Gc完成之后一般会调整本内存代中各内存区大小,要么扩展内存代内存容量,要么缩小内存代内存容量.DefNewGeneration会根据年老代当前容量/NewRatio/当前非守护线程数量/NewSizeThreadIncrease来确定年青代的容量,大体原则是:
扩展年青代的物理空间: From/To区完全空闲
缩小年青代的物理空间: Eden/From/To区完全空闲void DefNewGeneration::compute_new_size() {
// This is called after a gc that includes the following generation
// (which is required to exist.) So from-space will normally be empty.
// Note that we check both spaces, since if scavenge failed they revert roles.
// If not we bail out (otherwise we would have to relocate the objects)
if (!from()->is_empty() || !to()->is_empty()) {
return;
}
int next_level = level() + 1;
GenCollectedHeap* gch = GenCollectedHeap::heap();
assert(next_level < gch->_n_gens,
"DefNewGeneration cannot be an oldest gen");
//老年代的内存容量
Generation* next_gen = gch->_gens[next_level];
size_t old_size = next_gen->capacity();
//年青代的当前容量/最小容量/最大容量
size_t new_size_before = _virtual_space.committed_size();
size_t min_new_size = spec()->init_size();
size_t max_new_size = reserved().byte_size();
assert(min_new_size <= new_size_before && new_size_before <= max_new_size, "just checking");
// All space sizes must be multiples of Generation::GenGrain.
size_t alignment = Generation::GenGrain;
//根据参数NewRatio、NewSizeThreadIncrease来确定年青代的新容量
size_t desired_new_size = old_size/NewRatio;
int threads_count = Threads::number_of_non_daemon_threads();
size_t thread_increase_size = threads_count * NewSizeThreadIncrease;
desired_new_size = align_size_up(desired_new_size + thread_increase_size, alignment);
// Adjust new generation size
desired_new_size = MAX2(MIN2(desired_new_size, max_new_size), min_new_size);
assert(desired_new_size <= max_new_size, "just checking");
bool changed = false;
//扩张年青代的物理空间
if (desired_new_size > new_size_before) {
size_t change = desired_new_size - new_size_before;
assert(change % alignment == 0, "just checking");
if (expand(change)) {
changed = true;
}
// If the heap failed to expand to the desired size,
// "changed" will be false. If the expansion failed
// (and at this point it was expected to succeed),
// ignore the failure (leaving "changed" as false).
}
//如果当前Eden区完全空闲,则缩小年青代的物理空间
if (desired_new_size < new_size_before && eden()->is_empty()) {
// bail out of shrinking if objects in eden
size_t change = new_size_before - desired_new_size;
assert(change % alignment == 0, "just checking");
_virtual_space.shrink_by(change);
changed = true;
}
if (changed) {
// The spaces have already been mangled at this point but
// may not have been cleared (set top = bottom) and should be.
// Mangling was done when the heap was being expanded.
compute_space_boundaries(eden()->used(),
SpaceDecorator::Clear,
SpaceDecorator::DontMangle);
MemRegion cmr((HeapWord*)_virtual_space.low(),
(HeapWord*)_virtual_space.high());
Universe::heap()->barrier_set()->resize_covered_region(cmr);
if (Verbose && PrintGC) {
size_t new_size_after = _virtual_space.committed_size();
size_t eden_size_after = eden()->capacity();
size_t survivor_size_after = from()->capacity();
gclog_or_tty->print("New generation size " SIZE_FORMAT "K->"
SIZE_FORMAT "K [eden="
SIZE_FORMAT "K,survivor=" SIZE_FORMAT "K]",
new_size_before/K, new_size_after/K,
eden_size_after/K, survivor_size_after/K);
if (WizardMode) {
gclog_or_tty->print("[allowed " SIZE_FORMAT "K extra for %d threads]",
thread_increase_size/K, threads_count);
}
gclog_or_tty->cr();
}
}
}
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








