引言
课程主页链接:Probabilistic Systems Analysis and Applied Probability
德克萨斯大学达拉斯分校总结出了几个 重要的概率分布,每个分布给出了例子,期望,和方差,参考一下。
Probability Models and Axioms
样本空间(Sample Space),记作 Ω ,是所有可能出现结果的集合。集合必须满足以下2点要求:
- Mutually exclusive. 即实验结束过后只有一种结果出现。
- Collectively exhaustive.
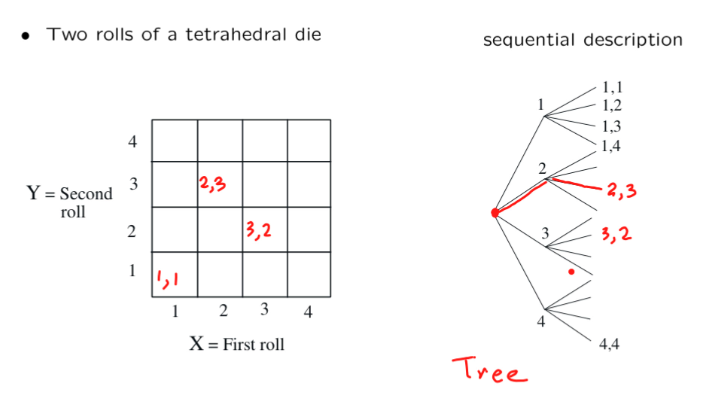
下图是一个离散有穷的样本空间例子,连续扔两个四面形的骰子:
接下来我给出事件(event)的定义:
Event is a subset of the sample space, probability is assigned to events.
下面是3个简单的但是最重要的公理,通过它们3个可以推导出很多其它的定理。
- Nonnegativity: P(A)≥0
- Normalization: P(Ω)=1
- Additivity:如果 A∩B=∅ ,那么 P(A∪B)=P(A)+P(B)
通过上面的3个公理,我们可以得到一些很重要的推论,如下:
- P(A)≤1 .
- P(∅)=0 .
- P(A)+P(AC)=1
- A∪Ac=Ω
- A∩Ac=∅
- If A⊂B , then P(A)≤P(B)
- P(A∪B)=P(A)+P(B)−P(A∩B)
- P(A∪B)≤P(A)+P(B)
- P(A∪B∪C)=P(A)+P(AC∩B)+P(AC∩BC∩C)
关于上面定理的推导很简单,没什么好说的。有兴趣的同学可以参考:课件的8,9,10,和11页。教授在课堂上总结了计算概率的几大步骤:
- Specify the sample space
- Specify a probability law
- Identify an event of interest
- calculate
A probability law in principle specifies the probability of every event, and there’s nothing else to do. But quite often the probability law will be given in some implicit manner, for example, by specifying the probabilities of only some of the events. In that case, you may have to do some additional work to find the probability of the particular event that you care about.
Conditioning and Bayes’ Rule
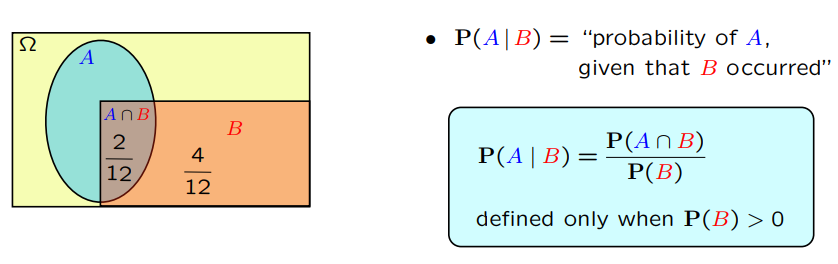
在这个 lecture 中,教授介绍了三个重要的工具,在理解它们之前,我们必须要知道条件概率是什么,下图是关于它的定义,图片的左面给我们一直直观的感受,为什么条件概率是这样定义的。
条件概率也遵循文章前面介绍的公理。比如第3条公理可以写成:如果 A∩B=∅ ,那么 P(A∪C|B)=P(A|B)+P(C|B) ,下图给了你一个直观的感受为什么是这样的!
有了条件概率的定义之后,接下来我总结一下教授课堂上介绍的3个重要的概率工具,它们分别是:Multiplication rule,Total probability theorem,and Bayes’ rule.
Multiplication rule
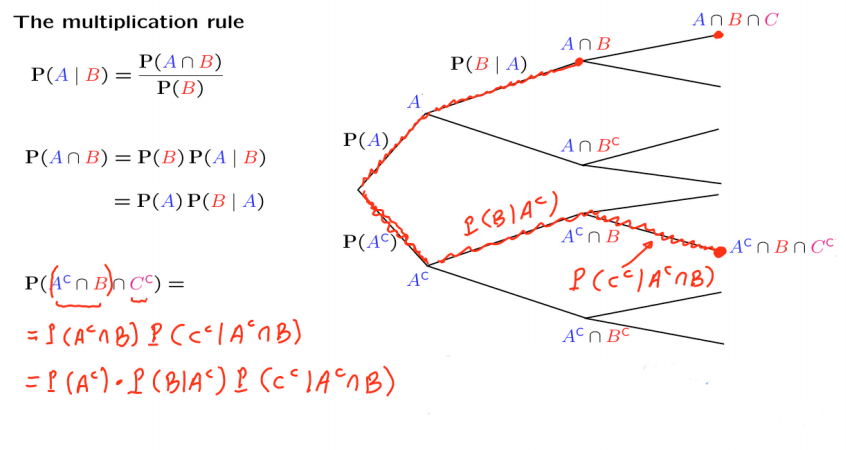
multiplication rule 中的第6页有个例子,看完它以后可以更好地帮你理解乘法公式(multiplication rule)。实际上,乘法公式就是条件概率的变形,下图中的右半部分是 sequential description,有了它可以让我们更加直观的理解乘法公式。
上图中只描述了3个事件,但是我们可以推广到更多的事件,得到下面的通式:
Total probability
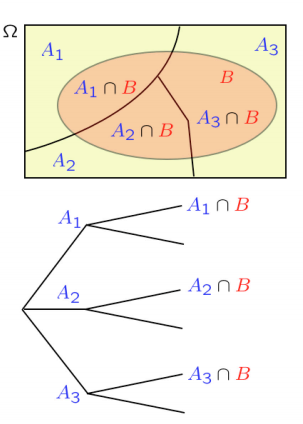
全概率公式用了 divide and conquer 的策略。比如下图中的例子:把样本空间拆分成3个子空间: A1,A2,A3 ,我们知道每个子空间的概率: P(A1),P(A2),P(A3) ,同时我们也知道在每个子空间下,事件B发生的概率,即条件概率: P(B|A1),P(B|A2),P(B|A3) ,通过全概率公式我们可以得到事件B发生的概率: P(B)=P(A1)P(B|A1)+P(A2)P(B|A2)+P(A3)P(B|A3)
Note that the sum of the probabilities of the different scenarios is of course equal to 1. 对于上面的例子来说就是: P(A1)+P(A2)+P(A3)=1 . As a matter of fact, the probability above is a weighted average of the conditional probabilities of event B. In words, the probability that an event occurs is a weighted average of the probability that it has under each possible scenario, where the weights are the probabilities of the different scenarios.
上面的例子只是把样本空间拆分成3个子空间,然而,我们可以划分出更多的子空间,得到下面的通式, ∑iP(Ai)=1
Bayes’ rule
在全概率的公式中,我们已知 each possible scenario 下的概率,然后又知道每个 scenario 下事件B发生的概率,从而得到事件B发生的概率。然而,贝叶斯公式正是与它“相反”。我们已知事件B发生的概率,又知道某个 scenario 与B一同发生的概率,然后想要求出在事件B发生的情况下,在这个 scenario 的概率有多大。把我这段描述可以写成如下的公式:
通过条件概率的定义替换分子,通过全概率公式替换分母,我们可以得到下面的公式,即贝叶斯公式:
Independence
Two events are independent if the occurrence of one event does not change our beliefs about the other. It does not affect the probability that the other event also occurs. 因此,一个比较直观的定义就是: P(B|A)=P(B) . 这个定义有2个缺点:1)不对称,即它没有说明 P(A|B)=P(A) . 2)条件概率需要分母的概率不能为0. 下面是独立性正式的定义:
如果 A 与 B 相互独立的,那么 A 与 BC 也是相互独立的。似的,只要A和B是相互独立的,那么A和 BC 、 BC 和 AC 也都是相互独立的。接下来,我来介绍一下 conditional independence, 定义如下:
Conditional independence, given C, is defined as independence under the probability law P(⋅|C) . 举个例子: P(A∩B|C)=P(A|C)⋅P(B|C)
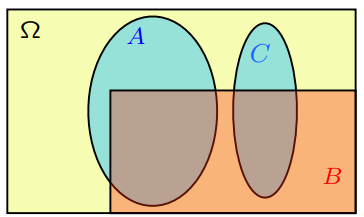
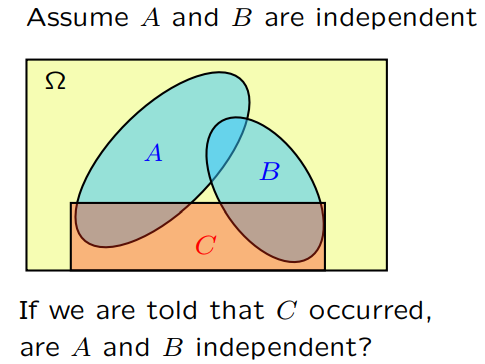
加上条件以后有可能会影响到独立性。比如下图中的事件 A 与 B 是相互独立的,但是在事件 C 作为条件的情况下,影响了它们的独立性。即,在事件 C 发生的前提下,如果有人告诉你事件 A 发生了,那么你一定就会知道事件 B 没有发生,这改变了事件A与事件B之间的独立性。从这个例子我们也可以看出,being independent is something completely different from being disjoint.
接下来我给出一系列事件之间相互独立的定义:








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章














 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








