common.h
#ifndef _COMMON_H_
#define _COMMON_H_
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define INFEASIBLE -1
#define OVERFLOW -2
typedef int Status;
//Status Equal(int a, int b);
#endif
#ifndef _KEY_TYPEDEF_H_
#define _KEY_TYPEDEF_H_
//典型的关键字类型说明
//typedef float KeyType;
typedef int KeyType;
//typedef char *KeyType; //字符串型
//数据元素类型的其他域
typedef char Name[20];
typedef int Score;
//数据元素类型定义
typedef struct
{
KeyType key; //关键字域
//... //其他域
Name name;
Score score;
}SElemType;
//对两个关键字的比较约定为如下的宏定义
//>>>对数值型关键字
#define EQ(a,b) ((a) == (b))
#define LT(a,b) ((a) < (b))
#define LQ(a,b) ((a) <= (b))
//...
//>>>对字符串型关键字
//#define EQ(a,b) (!strcmp((a),(b)))
//#define LT(a,b) (strcmp((a),(b))<0)
//#define LQ(a,b) (strcmp((a),(b))<=0)
//...
#endifSeqSearch.h
#ifndef _SEQSEARCH_H_
#define _SEQSEARCH_H_
#include "common.h"
#include "Key_Typedef.h"
typedef SElemType ElemType;
#define LIST_INIT_SIZE 10 //存储空间的初始分配量
#define LISTINCREMENT 10 //存储空间的分配增量
typedef struct
{
ElemType *elem;
int length; //总长度,也即当前分配的存储容量(注意:注意这个和第二章的顺序线性表不同)
//int listsize; //当前分配的存储容量
}SSTable;
Status PrintElement(ElemType e);
Status Create(SSTable *ST, int n);
Status SearchScanf_Seq(SSTable *ST);
Status Traverse(SSTable ST, Status (* Visit)(ElemType e));
int Search_Seq(SSTable ST, KeyType key);
Status Destroy(SSTable *ST);
#endif
SeqSearch.h
#include "common.h"
#include "SeqSearch.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "string.h"
Status PrintElement(ElemType e)
{
printf("%-3d ",e.key);
printf("%-16s ",e.name); //16个字符长度是我随便定义的,当然可以改变之。
printf("%-3d\n",e.score);
return OK;
}
Status Create(SSTable *ST, int n)
{
ST->elem = (ElemType *)malloc(n*sizeof(ElemType));
if(!ST->elem)
exit(OVERFLOW);
ST->length = n;
return OK;
}
/*
函数功能:向指定的查找表输入数据,约定按下述规则输入数据,当输入的编号是0时结束,且不将0存入查找表。
(编号 姓名 分数)
1空格zhangsan空格85回车
2空格lisi空格91回车
........
0回车
(当然输入的编号可以不必按照从小到大的顺序排列)
说明:让查找表的第0号单元留空
*/
Status SearchScanf_Seq(SSTable *ST)
{
SSTable *p = ST;
int i = 1; //让i从1开始的原因是要让查找表的0号单元留空,0号单元可用于设置哨兵元素,但它还有别的啥用处吗?
KeyType num;
Score sco;
Name name;
if(p == NULL)
{
return ERROR;
}
scanf("%d",&num);
if(num<0 || num>32767) //32767是int型数的最大值,当然实际应用应根据实际情况采取适当限定措施。
return ERROR;
while(num)
{
scanf("%s",name);
scanf("%d",&sco);
p->elem[i].key = num;
strcpy(p->elem[i].name, name);
p->elem[i].score = sco;
scanf("%d", &num);
if(i++ >= p->length)
{
printf("Search Table is full.");
return(OVERFLOW);
}
}
return OK;
}
Status Traverse(SSTable ST, Status (* Visit)(ElemType e))
{
int i = 1; //查找表的0号单元被留空
printf("\n>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>output start>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>\n");
while(ST.elem[i].key>0 && ST.elem[i].key<32767 && i<ST.length)
{
Visit(ST.elem[i]);
i++;
}
printf("\n>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>output end>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>\n\n");
return OK;
}
int Search_Seq(SSTable ST, KeyType key) //search到key在ST表中的位置后,便可以操作key位置处的记录了,具体的操作就实际应用时再说吧。
{
int i;
ST.elem[0].key = key;
for(i=ST.length; !EQ(ST.elem[i].key, key); --i);
return i;
}
Status Destroy(SSTable *ST)
{
free(ST->elem);
return OK;
}
main.c
#include "SeqSearch.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
//参考书目:《数据结构(C语言版)》严蔚敏,第9章,静态查找表的顺序存储结构。
void main(void)
{
SSTable st;
KeyType key = 3;
Create(&st, 10);
SearchScanf_Seq(&st);
//printf("%d %s %d",st.elem->key, st.elem->name, st.elem->score);
Traverse(st,PrintElement);
printf("Keyword %d's position in the Search Table is %d.\n",key, Search_Seq(st, key));
Destroy(&st);
Traverse(st,PrintElement);
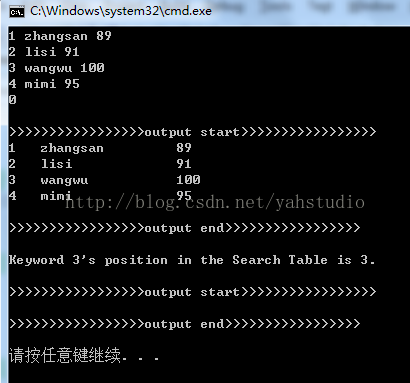
}输出结果如下:





















 1947
1947











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








