workqueue是另一种将工作推后的形式,它允许重新调度及休眠。
workqueue的实现
本文基于linux 内核4.10,workqueue 实现为CMWQ(Concurrency Managed Workqueue),引入cmwq的原因可以参考CMWQ概述 。
workqueue数据结构
struct workqueue_struct {
struct list_head pwqs; /* WR: all pwqs of this wq */
struct list_head list; /* PR: list of all workqueues */
struct mutex mutex; /* protects this wq */
int work_color; /* WQ: current work color */
int flush_color; /* WQ: current flush color */
atomic_t nr_pwqs_to_flush; /* flush in progress */
struct wq_flusher *first_flusher; /* WQ: first flusher */
struct list_head flusher_queue; /* WQ: flush waiters */
struct list_head flusher_overflow; /* WQ: flush overflow list */
struct list_head maydays; /* MD: pwqs requesting rescue */
struct worker *rescuer; /* I: rescue worker */
int nr_drainers; /* WQ: drain in progress */
int saved_max_active; /* WQ: saved pwq max_active */
struct workqueue_attrs *unbound_attrs; /* PW: only for unbound wqs */
struct pool_workqueue *dfl_pwq; /* PW: only for unbound wqs */
#ifdef CONFIG_SYSFS
struct wq_device *wq_dev; /* I: for sysfs interface */
#ifdef CONFIG_LOCKDEP
struct lockdep_map lockdep_map;
#endif
char name[WQ_NAME_LEN]; /* I: workqueue name */
/*
* Destruction of workqueue_struct is sched-RCU protected to allow
* walking the workqueues list without grabbing wq_pool_mutex.
* This is used to dump all workqueues from sysrq.
*/
struct rcu_head rcu;
/* hot fields used during command issue, aligned to cacheline */
unsigned int flags ____cacheline_aligned; /* WQ: WQ_* flags */
struct pool_workqueue __percpu *cpu_pwqs; /* I: per-cpu pwqs */
struct pool_workqueue __rcu *numa_pwq_tbl[]; /* PWR: unbound pwqs indexed by node */
};
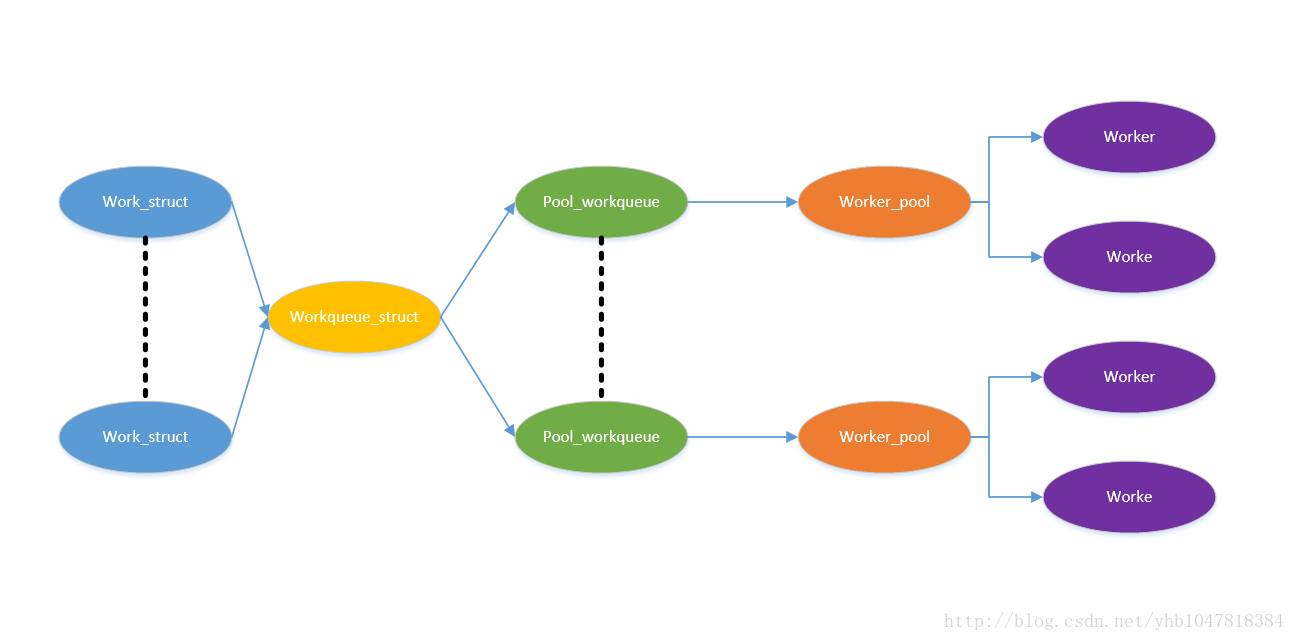
可以这样理解,
work_struct: 工作
workqueue_struct:工作的集合
pool_workqueue: 中间人,负责建立起 workqueue 和 worker_pool 之间的关系。
worker_pool: 工人的集合
worker: 工人
workqueue的使用方法
1.workqueue的创建
#define alloc_ordered_workqueue(fmt, flags, args...) \
alloc_workqueue(fmt, WQ_UNBOUND | __WQ_ORDERED | (flags), 1, ##args)
#define create_workqueue(name) \
alloc_workqueue("%s", __WQ_LEGACY | WQ_MEM_RECLAIM, 1, (name))
#define create_freezable_workqueue(name) \
alloc_workqueue("%s", __WQ_LEGACY | WQ_FREEZABLE | WQ_UNBOUND | \
WQ_MEM_RECLAIM, 1, (name))
#define create_singlethread_workqueue(name) \
alloc_ordered_workqueue("%s", __WQ_LEGACY | WQ_MEM_RECLAIM, name)参数含义:
name: workqueue名字;
WQ_NON_REENTRANT:默认情况下,工作队列只是确保在同一 CPU 上不可重入,即工作项不能在同一 CPU 上被多个工作者线程并发执行,但容许在多个 CPU 上并发执行。但该标志标明在多个 CPU 上也是不可重入的,工作项将在一个不可重入工作队列中排队,并确保至多在一个系统范围内的工作者线程被执行。
WQ_UNBOUND:没有被限定到特定的 CPU,
WQ_FREEZEABLE:可冻结 wq 参与系统的暂停操作。该工作队列的工作项将被暂停,除非被唤醒,否则没有新的工作项被执行。
WQ_MEM_RECLAIM:所有的工作队列可能在内存回收路径上被使用。使用该标志则保证至少有一个执行上下文而不管在任何内存压力之下。
WQ_HIGHPRI:高优先级的工作项将被排练在队列头上,并且执行时不考虑并发级别;换句话说,只要资源可用,高优先级的工作项将尽可能快的执行。高优先工作项之间依据提交的顺序被执行。
WQ_CPU_INTENSIVE:CPU 密集的工作项对并发级别并无贡献,换句话说,可运行的 CPU 密集型工作项将不阻止其它工作项。这对于限定得工作项非常有用,因为它期望更多的 CPU 时钟周期,所以将它们的执行调度交给系统调度器。
第三个参数’1’: maxactive,决定了一个wq在per-CPU上能执行的最大工作项。比如 max_active 设置为16,表示一个工作队列上最多16个工作项能同时在per-CPU上同时执行。
2.workqueue的初始化
#define INIT_WORK(_work, _func) \
__INIT_WORK((_work), (_func), 0)
#define INIT_WORK_ONSTACK(_work, _func) \
__INIT_WORK((_work), (_func), 1)
#define INIT_DELAYED_WORK(_work, _func) \
__INIT_DELAYED_WORK(_work, _func, 0)
#define INIT_DELAYED_WORK_ONSTACK(_work, _func) \
__INIT_DELAYED_WORK_ONSTACK(_work, _func, 0)
#define INIT_DEFERRABLE_WORK(_work, _func) \
__INIT_DELAYED_WORK(_work, _func, TIMER_DEFERRABLE)
#define INIT_DEFERRABLE_WORK_ONSTACK(_work, _func) \
__INIT_DELAYED_WORK_ONSTACK(_work, _func, TIMER_DEFERRABLE)3.workqueue的调度
extern bool queue_work_on(int cpu, struct workqueue_struct *wq,
struct work_struct *work);
extern bool queue_delayed_work_on(int cpu, struct workqueue_struct *wq,
struct delayed_work *work, unsigned long delay);
extern bool mod_delayed_work_on(int cpu, struct workqueue_struct *wq,
struct delayed_work *dwork, unsigned long delay);4.workqueue的销毁
extern void destroy_workqueue(struct workqueue_struct *wq);使用示例
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/workqueue.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
void myfunc(struct work_struct*ws);
struct workqueue_struct *test_wq;
DECLARE_WORK(mywork,myfunc);
void myfunc(struct work_struct *ws)
{
printk("hello world, current pid is %d\n", current->pid);
}
static int __init test_init(void)
{
//struct work_struct *mywork;
test_wq = create_workqueue("test_wq");
if (!test_wq) {
printk("Error: allocate workqueue fail!\n");
return -ENOMEM;
}
queue_work(test_wq, &mywork);
}
static void __exit test_exit(void)
{
destroy_workqueue(test_wq);
}
module_init(test_init);
module_exit(test_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");





















 677
677











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








