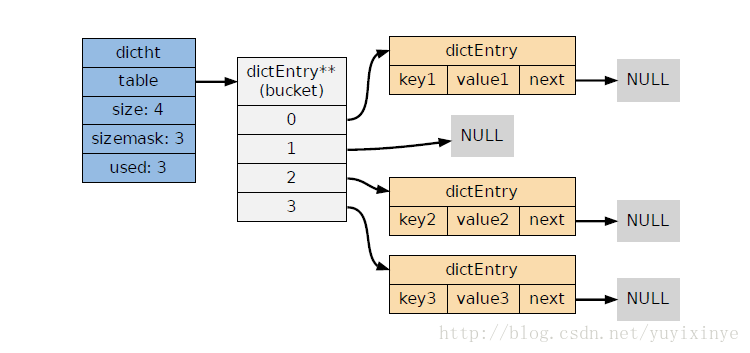
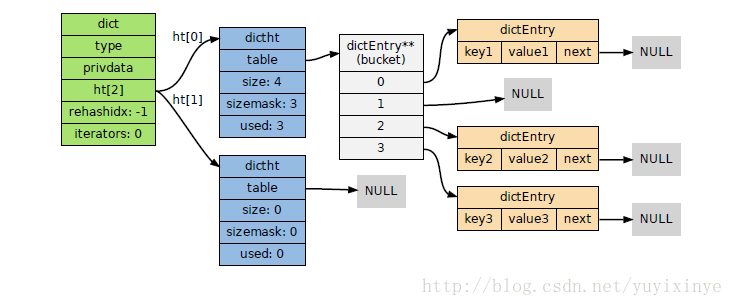
在这哈希结构即字典结构,在文件dict.h/dict.c中实现。 基本的K-V记录节点为dictEntry结构体; 哈希表的基本操作函数指针在dictType结构体中声明; 结构体dictht具体实现了哈希表,其中的成员dictEntry** table为哈希表的节点指针数组(即一个桶节点); 结构体dict 为整个哈希系统结构,包含两个哈希表,其中0号表为主要使用的哈希表,1号表在程序对0号进行rehash时才使用。
哈希结构如下图所示:
图1:由一个dictht和数个哈希节点dictEntry组成哈希表结构
图2:一个包含两个dictht哈希表的dict哈希系统
具体分析见注释。dict.h:
<<span style="font-size:18px;">span style="font-size:18px;color:#000099;">/* Hash Tables Implementation.
*
* This file implements in-memory hash tables with insert/del/replace/find/
* get-random-element operations. Hash tables will auto-resize if needed
* tables of power of two in size are used, collisions are handled by
* chaining. See the source code for more information... :
*/
#include <stdint.h>
#ifndef __DICT_H
#define __DICT_H
#define DICT_OK 0
#define DICT_ERR 1
/* Unused arguments generate annoying warnings... */
#define DICT_NOTUSED(V) ((void) V)
//哈希表节点 存储K-V值对
typedef struct dictEntry {
void *key;
union {
void *val;
uint64_t u64;
int64_t s64;
double d;
} v;
struct dictEntry *next;
} dictEntry;
//字典类型 定义了相关的操作函数指针
typedef struct dictType {
unsigned int (*hashFunction)(const void *key);//hash函数指针
void *(*keyDup)(void *privdata, const void *key);//复制key
void *(*valDup)(void *privdata, const void *obj);//复制value
int (*keyCompare)(void *privdata, const void *key1, const void *key2);//比较key
void (*keyDestructor)(void *privdata, void *key);//析构key
void (*valDestructor)(void *privdata, void *obj);//析构value
} dictType;
/* This is our hash table structure. Every dictionary has two of this as we
* implement incremental rehashing, for the old to the new table. */
#ifdef _WIN32
//hash的具体实现结构体。用数组(桶)+开链的方式保存记录
typedef struct dictht {
dictEntry **table;//哈希表的节点指针数组(table指向一个dictEntry *数组,数组中的每个dictEntry *元素指向一个桶),
size_t size; //每个table数组的大小(即桶的数目),为2的指数
size_t sizemask;//size-1,方便哈希值根据size取模(指针数组的长度掩码,用于计算索引值)
size_t used;//哈希表中现有节点数目
} dictht;
#endif
//整个哈希系统 结构。包含两个哈希表,其中0号表为主要使用的哈希表,1号表在程序对0号进行rehash时才使用
typedef struct dict {
dictType *type; //特定类型的处理函数
void *privdata;//类型处理函数的私有数据
dictht ht[2]; //两个哈希表实例。rehashidx指明下一个需要扩容的哈希表实例的编号,为-1时不扩容。
long rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 */
int iterators; /* number of iterators currently running *///当前安全迭代器数量
} dict;
/* If safe is set to 1 this is a safe iterator, that means, you can call
* dictAdd, dictFind, and other functions against the dictionary even while
* iterating. Otherwise it is a non safe iterator, and only dictNext()
* should be called while iterating. */
//safe设为1表示为安全迭代器,即即使在对哈希表进行迭代器时也能对其进行dictAdd, dictFind和其他操作;
//若为非安全迭代器则只能dictNext()操作
typedef struct dictIterator {
dict *d; //字典实例
long index;//正在迭代的表的桶索引
int table, safe;//table表示当前操作的是哪张哈希表,safe设置是否为安全迭代器
dictEntry *entry, *nextEntry; //当前/next哈希节点
/* unsafe iterator fingerprint for misuse detection. */
//指纹表识,防止非安全迭代器滥用
long long fingerprint;
} dictIterator;
//哈希表的遍历方法
typedef void (dictScanFunction)(void *privdata, const dictEntry *de);
/* This is the initial size of every hash table */
#define DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE 4 //哈希表的初始长度
/* ------------------------------- Macros ------------------------------------*/
//释放哈希节点。 如果定义dictType定义了valDestructor函数指针,则调用之
#define dictFreeVal(d, entry) \
if ((d)->type->valDestructor) \
(d)->type->valDestructor((d)->privdata, (entry)->v.val)
//设置哈希节点的value值。 如果dictType设置了valDup函数指针则使用其复制,否则直接复制
#define dictSetVal(d, entry, _val_) do { \
if ((d)->type->valDup) \
entry->v.val = (d)->type->valDup((d)->privdata, _val_); \
else \
entry->v.val = (_val_); \
} while(0)
//设置节点的整型value值
#define dictSetSignedIntegerVal(entry, _val_) \
do { entry->v.s64 = _val_; } while(0)
//设置节点的非整型value值
#define dictSetUnsignedIntegerVal(entry, _val_) \
do { entry->v.u64 = _val_; } while(0)
//设置节点的double型value值
#define dictSetDoubleVal(entry, _val_) \
do { entry->v.d = _val_; } while(0)
//析构哈希表中节点的key
#define dictFreeKey(d, entry) \
if ((d)->type->keyDestructor) \
(d)->type->keyDestructor((d)->privdata, (entry)->key)
//设置哈希表中节点的key
#define dictSetKey(d, entry, _key_) do { \
if ((d)->type->keyDup) \
entry->key = (d)->type->keyDup((d)->privdata, _key_); \
else \
entry->key = (_key_); \
} while(0)
//比较哈希表中的两个key
#define dictCompareKeys(d, key1, key2) \
(((d)->type->keyCompare) ? \
(d)->type->keyCompare((d)->privdata, key1, key2) : \
(key1) == (key2))
#define dictHashKey(d, key) (d)->type->hashFunction(key)//查找哈希表中key对应的节点
#define dictGetKey(he) ((he)->key) //获取dictEntry的key
#define dictGetVal(he) ((he)->v.val) //获取dictEntry的共用体中定义的value值
#define dictGetSignedIntegerVal(he) ((he)->v.s64)//获取dictEntry的共用体中定义的有符号值
#define dictGetUnsignedIntegerVal(he) ((he)->v.u64)//获取dictEntry的共用体中定义的无符号值
#define dictGetDoubleVal(he) ((he)->v.d) //获取dictEntry的共用体中定义的double值
#define dictSlots(d) ((d)->ht[0].size+(d)->ht[1].size)//获取哈希结构系统中的两张哈希表的总的大小 ?
#define dictSize(d) ((d)->ht[0].used+(d)->ht[1].used)//获取哈希结构系统中的两张哈希表总的现有节点数
#define dictIsRehashing(d) ((d)->rehashidx != -1) //哈希表是否正在被rehashing
/* API */
//创建一个新字典
dict *dictCreate(dictType *type, void *privDataPtr);
#ifdef _WIN32
//字典扩容
int dictExpand(dict *d, size_t size);
#else
int dictExpand(dict *d, unsigned long size);
#endif
//添加新的K-V对到字典
int dictAdd(dict *d, void *key, void *val);
//添加一个原始的value的k-V到字典,并返回该k-v的指针
dictEntry *dictAddRaw(dict *d, void *key);
//添加或更新给定的key对应的value
int dictReplace(dict *d, void *key, void *val);
//添加或更新key对应的value为原始value值。并返回该k-v的指针
dictEntry *dictReplaceRaw(dict *d, void *key);
//删除字典中的key对应的K-V值对
int dictDelete(dict *d, const void *key);
//删除字典中的key对应的K-V值对,但该k-v值对不被释放掉
int dictDeleteNoFree(dict *d, const void *key);
//清空并释放字典
void dictRelease(dict *d);
//在字典中查找key对应的节点
dictEntry * dictFind(dict *d, const void *key);
//在字典中查找key对应的节点的value
void *dictFetchValue(dict *d, const void *key);
//调整字典大小
int dictResize(dict *d);
//获取字典的迭代器
dictIterator *dictGetIterator(dict *d);
//获取字典的安全迭代器
dictIterator *dictGetSafeIterator(dict *d);
//获取字典的迭代器的next节点
dictEntry *dictNext(dictIterator *iter);
//释放字典的迭代器
void dictReleaseIterator(dictIterator *iter);
//随机返回字典的一个节点
dictEntry *dictGetRandomKey(dict *d);
//打印字典的状态
void dictPrintStats(dict *d);
//输入key和目标长度,计算出对应的hash值
unsigned int dictGenHashFunction(const void *key, int len);
//对字符串计算出对应的hash值
unsigned int dictGenCaseHashFunction(const unsigned char *buf, int len);
//清空并重置(但不释放)字典
void dictEmpty(dict *d, void(callback)(void*));
//启用调整方法
void dictEnableResize(void);
//禁用调整方法
void dictDisableResize(void);
//对字典进行给定步数的rehash
int dictRehash(dict *d, int n);
//在给定毫秒内对字典进行rehash
int dictRehashMilliseconds(dict *d, int ms);
//设置字典hash方法种子
int dictSetHashFunctionSeed(unsigned int initval);
//获取字典hash方法种子
unsigned int dictGetHashFunctionSeed(void);
//遍历字典
unsigned long dictScan(dict *d, unsigned long v, dictScanFunction *fn, void *privdata);
/* Hash table types */
//声明几种dictType
extern dictType dictTypeHeapStringCopyKey;
extern dictType dictTypeHeapStrings;
extern dictType dictTypeHeapStringCopyKeyValue;
#endif /* __DICT_H */</span>
</span>实现代码分析dict.c:
<span style="font-size:18px;">/* Using dictEnableResize() / dictDisableResize() we make possible to
* enable/disable resizing of the hash table as needed. This is very important
* for Redis, as we use copy-on-write and don't want to move too much memory
* around when there is a child performing saving operations.
*
* Note that even when dict_can_resize is set to 0, not all resizes are
* prevented: a hash table is still allowed to grow if the ratio between
* the number of elements and the buckets > dict_force_resize_ratio. */
/* redis用了dictEnableResize() / dictDisableResize()方法可以重新调整哈希表的长度,
*因为redis采用的是写时复制的算法,不会挪动太多的内存。当把dict_can_resize is set to 0时,
当节点数目与桶的数目的比例大于dict_force_resize_ratio时,还是能 resizes */
static int dict_can_resize = 1;//允许resize
static unsigned int dict_force_resize_ratio = 5;//强制ersize的比例
/* -------------------------- private prototypes ---------------------------- */
//私有方法原型
static int _dictExpandIfNeeded(dict *ht);//字典是否需要扩容
#ifdef _WIN32
static size_t _dictNextPower(size_t size);//
#else
static unsigned long _dictNextPower(unsigned long size);
#endif
static int _dictKeyIndex(dict *ht, const void *key);//获取key在字典中的索引
static int _dictInit(dict *ht, dictType *type, void *privDataPtr);//字典初始化方法
/* -------------------------- hash functions -------------------------------- */
//hash索引计算算法
/* Thomas Wang's 32 bit Mix Function */
//输入key获取索引值
unsigned int dictIntHashFunction(unsigned int key)
{
key += ~(key << 15);
key ^= (key >> 10);
key += (key << 3);
key ^= (key >> 6);
key += ~(key << 11);
key ^= (key >> 16);
return key;
}
//hash方法种子
#define DICT_HASH_FUNCTION_SEED_UNITIALIZED 5381
static uint32_t dict_hash_function_seed = DICT_HASH_FUNCTION_SEED_UNITIALIZED;
//重设hash种子
int dictSetHashFunctionSeed(uint32_t seed) {
if (dict_hash_function_seed == DICT_HASH_FUNCTION_SEED_UNITIALIZED) {
dict_hash_function_seed = seed;
return 0;
} else {
errno = E_FAIL;
return -1;
}
}
//获取hash种子
uint32_t dictGetHashFunctionSeed(void) {
return dict_hash_function_seed;
}
//MurmurHash 是一种非加密型哈希函数,适用于一般的哈希检索操作。 由Austin Appleby在2008年发明, 并出现了多个变种,
//与其它流行的哈希函数相比,对于规律性较强的key,MurmurHash的随机分布特征表现更良好。
/* MurmurHash2, by Austin Appleby
* Note - This code makes a few assumptions about how your machine behaves -
* 1. We can read a 4-byte value from any address without crashing
* 2. sizeof(int) == 4
*
* And it has a few limitations -
*
* 1. It will not work incrementally.
* 2. It will not produce the same results on little-endian and big-endian
* machines.
*/
/* 输入的key值,目标长度,此方法帮你计算出索引值,此方法特别表明,
* 不会因为机器之间高低位存储的不同而产生相同的结果 */
unsigned int dictGenHashFunction(const void *key, int len) {
/* 'm' and 'r' are mixing constants generated offline.
They're not really 'magic', they just happen to work well. */
//seed m r都会参与到h的计算中
uint32_t seed = dict_hash_function_seed;
const uint32_t m = 0x5bd1e995;
const int r = 24;
/* Initialize the hash to a 'random' value */
uint32_t h = seed ^ len;
/* Mix 4 bytes at a time into the hash */
const unsigned char *data = (const unsigned char *)key;
while(len >= 4) {
uint32_t k = *(uint32_t*)data;
k *= m;
k ^= k >> r;
k *= m;
h *= m;
h ^= k;
data += 4;
len -= 4;
}
/* Handle the last few bytes of the input array */
switch(len) {
case 3: h ^= data[2] << 16;
case 2: h ^= data[1] << 8;
case 1: h ^= data[0]; h *= m;
};
/* Do a few final mixes of the hash to ensure the last few
* bytes are well-incorporated. */
h ^= h >> 13;
h *= m;
h ^= h >> 15;
return (unsigned int)h;
}
/* And a case insensitive hash function (based on djb hash) */
//hash 算法 djb2 将一个字符串hash为一个的整数
unsigned int dictGenCaseHashFunction(const unsigned char *buf, int len) {
unsigned int hash = (unsigned int)dict_hash_function_seed;
while (len--)
hash = ((hash << 5) + hash) + (tolower(*buf++)); /* hash * 33 + c */ //tolower大写转换为小写
return hash;
}
/* ----------------------------- API implementation ------------------------- */
/* Reset a hash table already initialized with ht_init().
* NOTE: This function should only be called by ht_destroy(). */
//对一个已经初始化的哈希表reset,注意:该方法只能被哈希表的析构函数调用
static void _dictReset(dictht *ht)
{
ht->table = NULL;
ht->size = 0;
ht->sizemask = 0;
ht->used = 0;
}
/* Create a new hash table */
//创建一个新的字典结构
dict *dictCreate(dictType *type,
void *privDataPtr)
{
dict *d = zmalloc(sizeof(*d));//分配空间
_dictInit(d,type,privDataPtr);
return d;
}
/* Initialize the hash table */
//初始化字典
int _dictInit(dict *d, dictType *type,
void *privDataPtr)
{
_dictReset(&d->ht[0]);//重置字典中的哈希表0
_dictReset(&d->ht[1]);//重置字典中的哈希表1
d->type = type;
d->privdata = privDataPtr;
d->rehashidx = -1;
d->iterators = 0;
return DICT_OK;
}
/* Resize the table to the minimal size that contains all the elements,
* but with the invariant of a USED/BUCKETS ratio near to <= 1 */
//重置字典中的哈希表0为最小size。最下长度为能容纳所有的节点,且满足不等式USED/BUCKETS ratio near to <= 1
int dictResize(dict *d)
{
int minimal;
if (!dict_can_resize || dictIsRehashing(d)) return DICT_ERR;
minimal = (int)d->ht[0].used;
if (minimal < DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE)
minimal = DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE;
return dictExpand(d, minimal);
}
#ifdef _WIN32
/* Expand or create the hash table */
int dictExpand(dict *d, size_t size)
{
dictht n; /* the new hash table */
size_t realsize = _dictNextPower(size);
/* the size is invalid if it is smaller than the number of
* elements already inside the hash table */
if (dictIsRehashing(d) || d->ht[0].used > size)
return DICT_ERR;
/* Allocate the new hash table and initialize all pointers to NULL */
n.size = realsize;
n.sizemask = realsize-1;
n.table = zcalloc(realsize*sizeof(dictEntry*));
n.used = (size_t) 0;
/* Is this the first initialization? If so it's not really a rehashing
* we just set the first hash table so that it can accept keys. */
if (d->ht[0].table == NULL) {
d->ht[0] = n;
return DICT_OK;
}
/* Prepare a second hash table for incremental rehashing */
d->ht[1] = n;
d->rehashidx = 0;
/* Expand or create the hash table */
return DICT_OK;
}
#else
/* Expand or create the hash table */
//扩容或者创建一个表
int dictExpand(dict *d, unsigned long size)
{
dictht n; /* the new hash table */
unsigned long realsize = _dictNextPower(size);
/* the size is invalid if it is smaller than the number of
* elements already inside the hash table */
if (dictIsRehashing(d) || d->ht[0].used > size)//如果表正在扩容或者size小于已有节点数,则无效
return DICT_ERR;
/* Allocate the new hash table and initialize all pointers to NULL */
n.size = realsize;//节点数目
n.sizemask = realsize-1;//掩码
n.table = zcalloc(realsize*sizeof(dictEntry*));//为桶数组指针table分配空间
n.used = 0;
/* Is this the first initialization? If so it's not really a rehashing
* we just set the first hash table so that it can accept keys. */
//如果表0为初次初始化,则设置表0为前面创建的表,使其可以接受key
if (d->ht[0].table == NULL) {
d->ht[0] = n;
return DICT_OK;
}
/* Prepare a second hash table for incremental rehashing */
//准备好表1,以备rehahsh使用
d->ht[1] = n;
d->rehashidx = 0;
return DICT_OK;
}
#endif
/* Performs N steps of incremental rehashing. Returns 1 if there are still
* keys to move from the old to the new hash table, otherwise 0 is returned.
* Note that a rehashing step consists in moving a bucket (that may have more
* than one key as we use chaining) from the old to the new hash table. */
//操作N步,rehashing表0到表1.如果正在rehashing则返回1(即还没有完成全部通的迁移),否则已完成返回0.
int dictRehash(dict *d, int n) {
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return 0;//没有正在rehash则返回0
while(n--) {//n步不能确保能把所有的桶迁移到新表
dictEntry *de, *nextde;
/* Check if we already rehashed the whole table... */
if (d->ht[0].used == 0) {//检测是否已完成rehash
zfree(d->ht[0].table);//释放旧表0
d->ht[0] = d->ht[1];//把新表1复制到表0
_dictReset(&d->ht[1]);//迁移完成后,表0被置为null
d->rehashidx = -1;
return 0;
}
/* Note that rehashidx can't overflow as we are sure there are more
* elements because ht[0].used != 0 */
assert(d->ht[0].size > (unsigned long)d->rehashidx);//还没有完成全部迁移,因此已经迁移的桶数目rehashidx应该小于旧表总的桶数目
while(d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] == NULL) d->rehashidx++;//已经迁移的桶数目,最终rehashidx为下一个即将迁移的桶索引
de = d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx];//de指向即将迁移的旧桶
/* Move all the keys in this bucket from the old to the new hash HT */
while(de) {
unsigned int h;
nextde = de->next;
/* Get the index in the new hash table */
h = dictHashKey(d, de->key) & d->ht[1].sizemask;//获取新表中的索引
de->next = d->ht[1].table[h];//新迁移来的节点放在新表的对应桶的顶部(每个桶为一个单链表,next指针指向桶底)
d->ht[1].table[h] = de;
d->ht[0].used--;//旧表节点计数递减
d->ht[1].used++;//新表节点计数递增
de = nextde;
}
d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] = NULL;//旧表中的该桶已为空
d->rehashidx++;//桶索引递增
}
return 1;//表明还有桶没有迁移
}
//获取当前毫秒时间
long long timeInMilliseconds(void) {
#ifdef _WIN32
return GetTickCount();
#else
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv,NULL);
return (((long long)tv.tv_sec)*1000)+(tv.tv_usec/1000);
#endif
}
/* Rehash for an amount of time between ms milliseconds and ms+1 milliseconds */
//在给定时间内rehash,返回rehash的步数
int dictRehashMilliseconds(dict *d, int ms) {
long long start = timeInMilliseconds();
int rehashes = 0;
while(dictRehash(d,100)) {
rehashes += 100;
if (timeInMilliseconds()-start > ms) break;
}
return rehashes;
}
/* This function performs just a step of rehashing, and only if there are
* no safe iterators bound to our hash table. When we have iterators in the
* middle of a rehashing we can't mess with the two hash tables otherwise
* some element can be missed or duplicated.
*
* This function is called by common lookup or update operations in the
* dictionary so that the hash table automatically migrates from H1 to H2
* while it is actively used. */
//当没有安全迭代器时的一步rehash算法
static void _dictRehashStep(dict *d) {
if (d->iterators == 0) dictRehash(d,1);
}
/* Add an element to the target hash table */
//添加节点到目标表。
int dictAdd(dict *d, void *key, void *val)
{
dictEntry *entry = dictAddRaw(d,key);
if (!entry) return DICT_ERR;
dictSetVal(d, entry, val);
return DICT_OK;
}
/* Low level add. This function adds the entry but instead of setting
* a value returns the dictEntry structure to the user, that will make
* sure to fill the value field as he wishes.
*
* This function is also directly exposed to user API to be called
* mainly in order to store non-pointers inside the hash value, example:
*
* entry = dictAddRaw(dict,mykey);
* if (entry != NULL) dictSetSignedIntegerVal(entry,1000);
*
* Return values:
*
* If key already exists NULL is returned.
* If key was added, the hash entry is returned to be manipulated by the caller.
*/
//添加节点到表中。 如果key已经存在则返回null,否则返回添加的节点的指针(value设为原始值)
dictEntry *dictAddRaw(dict *d, void *key)
{
int index;
dictEntry *entry;
dictht *ht;
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
/* Get the index of the new element, or -1 if
* the element already exists. */
if ((index = _dictKeyIndex(d, key)) == -1)
return NULL;
/* Allocate the memory and store the new entry */
ht = dictIsRehashing(d) ? &d->ht[1] : &d->ht[0];
entry = zmalloc(sizeof(*entry));
entry->next = ht->table[index];//插入到对应的桶顶
ht->table[index] = entry;
ht->used++;
/* Set the hash entry fields. */
dictSetKey(d, entry, key);
return entry;
}
/* Add an element, discarding the old if the key already exists.
* Return 1 if the key was added from scratch, 0 if there was already an
* element with such key and dictReplace() just performed a value update
* operation. */
//添加新k-v,如果已经存在则替换其value,并返回0,。如果没有对应的key则添加新节点,返回1.
int dictReplace(dict *d, void *key, void *val)
{
dictEntry *entry, auxentry;
/* Try to add the element. If the key
* does not exists dictAdd will suceed. */
if (dictAdd(d, key, val) == DICT_OK)
return 1;
/* It already exists, get the entry */
entry = dictFind(d, key);
/* Set the new value and free the old one. Note that it is important
* to do that in this order, as the value may just be exactly the same
* as the previous one. In this context, think to reference counting,
* you want to increment (set), and then decrement (free), and not the
* reverse. */
auxentry = *entry;
dictSetVal(d, entry, val);
dictFreeVal(d, &auxentry);//释放旧value
return 0;
}
/* dictReplaceRaw() is simply a version of dictAddRaw() that always
* returns the hash entry of the specified key, even if the key already
* exists and can't be added (in that case the entry of the already
* existing key is returned.)
*
* See dictAddRaw() for more information. */
//添加一个key节点,返回节点指针,如果已经存在则返回原key对应节点指针
dictEntry *dictReplaceRaw(dict *d, void *key) {
dictEntry *entry = dictFind(d,key);
return entry ? entry : dictAddRaw(d,key);
}
/* Search and remove an element */
//查找两张表中所有key节点并删除该节点,nofee=0,则释放该节点
static int dictGenericDelete(dict *d, const void *key, int nofree)
{
unsigned int h, idx;
dictEntry *he, *prevHe;
int table;
if (d->ht[0].size == 0) return DICT_ERR; /* d->ht[0].table is NULL */
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
h = dictHashKey(d, key);
for (table = 0; table <= 1; table++) {
idx = h & d->ht[table].sizemask;
he = d->ht[table].table[idx];
prevHe = NULL;
while(he) {
if (dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key)) {//桶链中删除该节点
/* Unlink the element from the list */
if (prevHe)
prevHe->next = he->next;
else
d->ht[table].table[idx] = he->next;
if (!nofree) {
dictFreeKey(d, he);
dictFreeVal(d, he);
}
zfree(he);
d->ht[table].used--;
return DICT_OK;
}
prevHe = he;
he = he->next;
}
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) break;
}
return DICT_ERR; /* not found */
}
//删除并释放所有key对应节点
int dictDelete(dict *ht, const void *key) {
return dictGenericDelete(ht,key,0);
}
//删除但不释放 所有key节点
int dictDeleteNoFree(dict *ht, const void *key) {
return dictGenericDelete(ht,key,1);
}
/* Destroy an entire dictionary */
//析构字典中的整个表ht
int _dictClear(dict *d, dictht *ht, void(callback)(void *)) {
#ifdef _WIN32
size_t i;
#else
unsigned long i;
#endif
/* Free all the elements */
for (i = 0; i < ht->size && ht->used > 0; i++) {//释放所有桶
dictEntry *he, *nextHe;
if (callback && (i & 65535) == 0) callback(d->privdata);
if ((he = ht->table[i]) == NULL) continue;
while(he) {//释放一个桶中的所有节点
nextHe = he->next;
dictFreeKey(d, he);
dictFreeVal(d, he);
zfree(he);
ht->used--;
he = nextHe;
}
}
/* Free the table and the allocated cache structure */
zfree(ht->table);
/* Re-initialize the table */
_dictReset(ht);
return DICT_OK; /* never fails */
}
/* Clear & Release the hash table */
//清空并释放字典的所有表
void dictRelease(dict *d)
{
_dictClear(d,&d->ht[0],NULL);
_dictClear(d,&d->ht[1],NULL);
zfree(d);
}
//在字典中查找key对应节点。从表0开始查找,找到即返回节点指针
dictEntry *dictFind(dict *d, const void *key)
{
dictEntry *he;
unsigned int h, idx, table;
if (d->ht[0].size == 0) return NULL; /* We don't have a table at all */
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
h = dictHashKey(d, key);//桶索引
for (table = 0; table <= 1; table++) {
idx = h & d->ht[table].sizemask;
he = d->ht[table].table[idx];
while(he) {//在桶中逐个查找
if (dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key))
return he;
he = he->next;
}
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return NULL;
}
return NULL;
}
//在字典中查找key对应的节点的value
void *dictFetchValue(dict *d, const void *key) {
dictEntry *he;
he = dictFind(d,key);
return he ? dictGetVal(he) : NULL;
}
/* A fingerprint is a 64 bit number that represents the state of the dictionary
* at a given time, it's just a few dict properties xored together.
* When an unsafe iterator is initialized, we get the dict fingerprint, and check
* the fingerprint again when the iterator is released.
* If the two fingerprints are different it means that the user of the iterator
* performed forbidden operations against the dictionary while iterating. */
//指纹是表示字典当前时刻状态的一个64位数值,多个状态属性可通过位异或来表示。
//当一个非安全迭代器初始化时检测一次指纹,该迭代器释放以后再检测一次指纹,
//如果两次指纹不一致,则说明通过该非安全迭代器执行了禁止的操作
//该指纹值是通过当前字典中两张表的相关参数经过hash计算得到的。不同的状态值计算得到不同的指纹值
long long dictFingerprint(dict *d) {
long long integers[6], hash = 0;
int j;
integers[0] = (long) d->ht[0].table;
integers[1] = d->ht[0].size;
integers[2] = d->ht[0].used;
integers[3] = (long) d->ht[1].table;
integers[4] = d->ht[1].size;
integers[5] = d->ht[1].used;
/* We hash N integers by summing every successive integer with the integer
* hashing of the previous sum. Basically:
*
* Result = hash(hash(hash(int1)+int2)+int3) ...
*
* This way the same set of integers in a different order will (likely) hash
* to a different number. */
for (j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
hash += integers[j];
/* For the hashing step we use Tomas Wang's 64 bit integer hash. */
hash = (~hash) + (hash << 21); // hash = (hash << 21) - hash - 1;
hash = hash ^ (hash >> 24);
hash = (hash + (hash << 3)) + (hash << 8); // hash * 265
hash = hash ^ (hash >> 14);
hash = (hash + (hash << 2)) + (hash << 4); // hash * 21
hash = hash ^ (hash >> 28);
hash = hash + (hash << 31);
}
return hash;
}
//获取迭代器,默认不安全的
dictIterator *dictGetIterator(dict *d)
{
dictIterator *iter = zmalloc(sizeof(*iter));
iter->d = d;
iter->table = 0;//操作0号表
iter->index = -1;
iter->safe = 0;
iter->entry = NULL;
iter->nextEntry = NULL;
return iter;
}
//获取安全迭代器
dictIterator *dictGetSafeIterator(dict *d) {
dictIterator *i = dictGetIterator(d);
i->safe = 1;
return i;
}
//返回原next节点,迭代器移到next节点,
dictEntry *dictNext(dictIterator *iter)
{
while (1) {
if (iter->entry == NULL) {
dictht *ht = &iter->d->ht[iter->table];
if (iter->index == -1 && iter->table == 0) {
if (iter->safe)
iter->d->iterators++;//为安全迭代器,则迭代器计数递增
else
iter->fingerprint = dictFingerprint(iter->d);//非安全迭代器,则计算初始时刻的指纹
}
iter->index++;
if (iter->index >= (long) ht->size) {
if (dictIsRehashing(iter->d) && iter->table == 0) {
iter->table++;
iter->index = 0;
ht = &iter->d->ht[1];
} else {
break;
}
}
iter->entry = ht->table[iter->index];
} else {
iter->entry = iter->nextEntry;
}
if (iter->entry) {
/* We need to save the 'next' here, the iterator user
* may delete the entry we are returning. */
iter->nextEntry = iter->entry->next;
return iter->entry;
}
}
return NULL;
}
//释放迭代器
void dictReleaseIterator(dictIterator *iter)
{
if (!(iter->index == -1 && iter->table == 0)) {
if (iter->safe)
iter->d->iterators--;//安全迭代器,计数递减
else
assert(iter->fingerprint == dictFingerprint(iter->d));//非安全迭代器,则判断前后指纹释放一致
}
zfree(iter);//释放迭代器
}
/* Return a random entry from the hash table. Useful to
* implement randomized algorithms */
//返回一个随机key节点
dictEntry *dictGetRandomKey(dict *d)
{
dictEntry *he, *orighe;
unsigned int h;
int listlen, listele;
if (dictSize(d) == 0) return NULL;
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
//根据是否sehash过随机在表0/表1中找到一个非空的桶
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) {
do {
h = random() % (d->ht[0].size+d->ht[1].size);
he = (h >= d->ht[0].size) ? d->ht[1].table[h - d->ht[0].size] :
d->ht[0].table[h];
} while(he == NULL);
} else {
do {
h = random() & d->ht[0].sizemask;
he = d->ht[0].table[h];
} while(he == NULL);
}
/* Now we found a non empty bucket, but it is a linked
* list and we need to get a random element from the list.
* The only sane way to do so is counting the elements and
* select a random index. */
//在前面得到的桶中随机取得一个节点
listlen = 0;
orighe = he;
while(he) {//计算桶长度
he = he->next;
listlen++;
}
listele = random() % listlen;//获得一个随机索引
he = orighe;
while(listele--) he = he->next;//返回桶中该索引的节点指针
return he;
}
/* Function to reverse bits. Algorithm from:
* http://graphics.stanford.edu/~seander/bithacks.html#ReverseParallel */
//位翻转算法
static unsigned long rev(unsigned long v) {
unsigned long s = 8 * sizeof(v); // bit size; must be power of 2
unsigned long mask = ~0;
while ((s >>= 1) > 0) {
mask ^= (mask << s);
v = ((v >> s) & mask) | ((v << s) & ~mask);
}
return v;
}
/* dictScan() is used to iterate over the elements of a dictionary.
*
* Iterating works in the following way:
*
* 1) Initially you call the function using a cursor (v) value of 0.
* 2) The function performs one step of the iteration, and returns the
* new cursor value that you must use in the next call.
* 3) When the returned cursor is 0, the iteration is complete.
*
* The function guarantees that all the elements that are present in the
* dictionary from the start to the end of the iteration are returned.
* However it is possible that some element is returned multiple time.
*
* For every element returned, the callback 'fn' passed as argument is
* called, with 'privdata' as first argument and the dictionar entry
* 'de' as second argument.
*
* HOW IT WORKS.
*
* The algorithm used in the iteration was designed by Pieter Noordhuis.
* The main idea is to increment a cursor starting from the higher order
* bits, that is, instead of incrementing the cursor normally, the bits
* of the cursor are reversed, then the cursor is incremented, and finally
* the bits are reversed again.
*
* This strategy is needed because the hash table may be resized from one
* call to the other call of the same iteration.
*
* dict.c hash tables are always power of two in size, and they
* use chaining, so the position of an element in a given table is given
* always by computing the bitwise AND between Hash(key) and SIZE-1
* (where SIZE-1 is always the mask that is equivalent to taking the rest
* of the division between the Hash of the key and SIZE).
*
* For example if the current hash table size is 16, the mask is
* (in binary) 1111. The position of a key in the hash table will be always
* the last four bits of the hash output, and so forth.
*
* WHAT HAPPENS IF THE TABLE CHANGES IN SIZE?
*
* If the hash table grows, elements can go anyway in one multiple of
* the old bucket: for example let's say that we already iterated with
* a 4 bit cursor 1100, since the mask is 1111 (hash table size = 16).
*
* If the hash table will be resized to 64 elements, and the new mask will
* be 111111, the new buckets that you obtain substituting in ??1100
* either 0 or 1, can be targeted only by keys that we already visited
* when scanning the bucket 1100 in the smaller hash table.
*
* By iterating the higher bits first, because of the inverted counter, the
* cursor does not need to restart if the table size gets bigger, and will
* just continue iterating with cursors that don't have '1100' at the end,
* nor any other combination of final 4 bits already explored.
*
* Similarly when the table size shrinks over time, for example going from
* 16 to 8, If a combination of the lower three bits (the mask for size 8
* is 111) was already completely explored, it will not be visited again
* as we are sure that, we tried for example, both 0111 and 1111 (all the
* variations of the higher bit) so we don't need to test it again.
*
* WAIT... YOU HAVE *TWO* TABLES DURING REHASHING!
*
* Yes, this is true, but we always iterate the smaller one of the tables,
* testing also all the expansions of the current cursor into the larger
* table. So for example if the current cursor is 101 and we also have a
* larger table of size 16, we also test (0)101 and (1)101 inside the larger
* table. This reduces the problem back to having only one table, where
* the larger one, if exists, is just an expansion of the smaller one.
*
* LIMITATIONS
*
* This iterator is completely stateless, and this is a huge advantage,
* including no additional memory used.
*
* The disadvantages resulting from this design are:
*
* 1) It is possible that we return duplicated elements. However this is usually
* easy to deal with in the application level.
* 2) The iterator must return multiple elements per call, as it needs to always
* return all the keys chained in a given bucket, and all the expansions, so
* we are sure we don't miss keys moving.
* 3) The reverse cursor is somewhat hard to understand at first, but this
* comment is supposed to help.
*/
//遍历字典
unsigned long dictScan(dict *d,
unsigned long v,
dictScanFunction *fn,
void *privdata)
{
dictht *t0, *t1;
const dictEntry *de;
unsigned long m0, m1;
if (dictSize(d) == 0) return 0;
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) {
t0 = &(d->ht[0]);
m0 = (unsigned long)t0->sizemask;
/* Emit entries at cursor */
de = t0->table[v & m0];
while (de) {
fn(privdata, de);
de = de->next;
}
} else {
t0 = &d->ht[0];
t1 = &d->ht[1];
/* Make sure t0 is the smaller and t1 is the bigger table */
if (t0->size > t1->size) {
t0 = &d->ht[1];
t1 = &d->ht[0];
}
m0 = (unsigned long)t0->sizemask;
m1 = (unsigned long)t1->sizemask;
/* Emit entries at cursor */
de = t0->table[v & m0];
while (de) {
fn(privdata, de);
de = de->next;
}
/* Iterate over indices in larger table that are the expansion
* of the index pointed to by the cursor in the smaller table */
do {
/* Emit entries at cursor */
de = t1->table[v & m1];
while (de) {
fn(privdata, de);
de = de->next;
}
/* Increment bits not covered by the smaller mask */
v = (((v | m0) + 1) & ~m0) | (v & m0);
/* Continue while bits covered by mask difference is non-zero */
} while (v & (m0 ^ m1));
}
/* Set unmasked bits so incrementing the reversed cursor
* operates on the masked bits of the smaller table */
v |= ~m0;
/* Increment the reverse cursor */
v = rev(v);
v++;
v = rev(v);
return v;
}
/* ------------------------- private functions ------------------------------ */
/* Expand the hash table if needed */
//判断是否需要扩容
static int _dictExpandIfNeeded(dict *d)
{
/* Incremental rehashing already in progress. Return. */
//正在扩容,则返回
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) return DICT_OK;
/* If the hash table is empty expand it to the initial size. */
//原来size为0,则扩容为初始size
if (d->ht[0].size == 0) return dictExpand(d, DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE);
/* If we reached the 1:1 ratio, and we are allowed to resize the hash
* table (global setting) or we should avoid it but the ratio between
* elements/buckets is over the "safe" threshold, we resize doubling
* the number of buckets. */
if (d->ht[0].used >= d->ht[0].size &&
(dict_can_resize ||
d->ht[0].used/d->ht[0].size > dict_force_resize_ratio))
{
return dictExpand(d, d->ht[0].used*2);//扩容为原来的2倍
}
return DICT_OK;
}
#ifdef _WIN32
/* Our hash table capability is a power of two */
//哈希表的容量始终为2的指数
static size_t _dictNextPower(size_t size)
{
size_t i = DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE;
if (size >= LONG_MAX) return LONG_MAX;
while(1) {
if (i >= size)
return i;
i *= 2;
}
}
#else
/* Our hash table capability is a power of two */
static unsigned long _dictNextPower(unsigned long size)
{
unsigned long i = DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE;
if (size >= LONG_MAX) return LONG_MAX;
while(1) {
if (i >= size)
return i;
i *= 2;
}
}
#endif
/* Returns the index of a free slot that can be populated with
* a hash entry for the given 'key'.
* If the key already exists, -1 is returned.
*
* Note that if we are in the process of rehashing the hash table, the
* index is always returned in the context of the second (new) hash table. */
//返回可用给定key填充的自由位置,如果该key已经存在,则返回-1.
//如果正在rehash则返回在新表中的位置索引
static int _dictKeyIndex(dict *d, const void *key)
{
unsigned int h, idx, table;
dictEntry *he;
/* Expand the hash table if needed */
if (_dictExpandIfNeeded(d) == DICT_ERR)
return -1;
/* Compute the key hash value */
h = dictHashKey(d, key);
for (table = 0; table <= 1; table++) {
idx = h & d->ht[table].sizemask;//桶索引
/* Search if this slot does not already contain the given key */
he = d->ht[table].table[idx];
while(he) {
if (dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key))
return -1;
he = he->next;
}
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) break;//如果没有rehash过,则只需要在表0中查找
}
return idx;
}
//清空字典
void dictEmpty(dict *d, void(callback)(void*)) {
_dictClear(d,&d->ht[0],callback);
_dictClear(d,&d->ht[1],callback);
d->rehashidx = -1;
d->iterators = 0;
}
//启用resize
void dictEnableResize(void) {
dict_can_resize = 1;
}
//禁用resize
void dictDisableResize(void) {
dict_can_resize = 0;
}
#if 0
/* The following is code that we don't use for Redis currently, but that is part
of the library. */
/* ----------------------- Debugging ------------------------*/
#define DICT_STATS_VECTLEN 50
static void _dictPrintStatsHt(dictht *ht) {
unsigned long i, slots = 0, chainlen, maxchainlen = 0;
unsigned long totchainlen = 0;
unsigned long clvector[DICT_STATS_VECTLEN];
if (ht->used == 0) {
printf("No stats available for empty dictionaries\n");
return;
}
for (i = 0; i < DICT_STATS_VECTLEN; i++) clvector[i] = 0;
for (i = 0; i < ht->size; i++) {
dictEntry *he;
if (ht->table[i] == NULL) {
clvector[0]++;
continue;
}
slots++;
/* For each hash entry on this slot... */
chainlen = 0;
he = ht->table[i];
while(he) {
chainlen++;
he = he->next;
}
clvector[(chainlen < DICT_STATS_VECTLEN) ? chainlen : (DICT_STATS_VECTLEN-1)]++;
if (chainlen > maxchainlen) maxchainlen = chainlen;
totchainlen += chainlen;
}
printf("Hash table stats:\n");
printf(" table size: %ld\n", ht->size);
printf(" number of elements: %ld\n", ht->used);
printf(" different slots: %ld\n", slots);
printf(" max chain length: %ld\n", maxchainlen);
printf(" avg chain length (counted): %.02f\n", (float)totchainlen/slots);
printf(" avg chain length (computed): %.02f\n", (float)ht->used/slots);
printf(" Chain length distribution:\n");
for (i = 0; i < DICT_STATS_VECTLEN-1; i++) {
if (clvector[i] == 0) continue;
printf(" %s%ld: %ld (%.02f%%)\n",(i == DICT_STATS_VECTLEN-1)?">= ":"", i, clvector[i], ((float)clvector[i]/ht->size)*100);
}
}
void dictPrintStats(dict *d) {
_dictPrintStatsHt(&d->ht[0]);
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) {
printf("-- Rehashing into ht[1]:\n");
_dictPrintStatsHt(&d->ht[1]);
}
}
/* ----------------------- StringCopy Hash Table Type ------------------------*/
static unsigned int _dictStringCopyHTHashFunction(const void *key)
{
return dictGenHashFunction(key, strlen(key));
}
static void *_dictStringDup(void *privdata, const void *key)
{
int len = strlen(key);
char *copy = zmalloc(len+1);
DICT_NOTUSED(privdata);
memcpy(copy, key, len);
copy[len] = '\0';
return copy;
}
static int _dictStringCopyHTKeyCompare(void *privdata, const void *key1,
const void *key2)
{
DICT_NOTUSED(privdata);
return strcmp(key1, key2) == 0;
}
static void _dictStringDestructor(void *privdata, void *key)
{
DICT_NOTUSED(privdata);
zfree(key);
}
dictType dictTypeHeapStringCopyKey = {
_dictStringCopyHTHashFunction, /* hash function */
_dictStringDup, /* key dup */
NULL, /* val dup */
_dictStringCopyHTKeyCompare, /* key compare */
_dictStringDestructor, /* key destructor */
NULL /* val destructor */
};
/* This is like StringCopy but does not auto-duplicate the key.
* It's used for intepreter's shared strings. */
dictType dictTypeHeapStrings = {
_dictStringCopyHTHashFunction, /* hash function */
NULL, /* key dup */
NULL, /* val dup */
_dictStringCopyHTKeyCompare, /* key compare */
_dictStringDestructor, /* key destructor */
NULL /* val destructor */
};
/* This is like StringCopy but also automatically handle dynamic
* allocated C strings as values. */
dictType dictTypeHeapStringCopyKeyValue = {
_dictStringCopyHTHashFunction, /* hash function */
_dictStringDup, /* key dup */
_dictStringDup, /* val dup */
_dictStringCopyHTKeyCompare, /* key compare */
_dictStringDestructor, /* key destructor */
_dictStringDestructor, /* val destructor */
};
#endif
</span>小结:
# Redis中的数据库和哈希键都基于字典来实现
# Redis字典的底层实现为哈希表,每个字典使用两张哈希表,一般只是用表0,只有在进行rehash时,才会同时使用表0和表1.其中表1用作迁移过渡表。
# 哈希表使用链地址法(桶节点)来解决键索引冲突的问题。
# 对哈希表的rehash是分多次,渐进式的进行的。





















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








