windows下Qt实现串口编程的例子,仅作参考(Qt 5.1.1环境下编译运行通过):
工程所需文件如图
所有文件源代码
/************mainwindow.h*************/
#ifndef MAINWINDOW_H
#define MAINWINDOW_H
#include <QMainWindow>
#include <QTextBrowser>
#include <QLabel>
#include "win_qextserialport.h"
class MainWindow : public QMainWindow
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
MainWindow(QWidget *parent = 0);
~MainWindow();
Win_QextSerialPort *myCom;
QTextBrowser *text;
public slots:
void readMyCom();
};
#endif // MAINWINDOW_H
/*************qextserialbase.h*************/
#ifndef _QEXTSERIALBASE_H_
#define _QEXTSERIALBASE_H_
#include <QIODevice>
#include <QFile>
#include <QThread>
#include <QMutex>
/*if all warning messages are turned off, flag portability warnings to be turned off as well*/
#ifdef _TTY_NOWARN_
#define _TTY_NOWARN_PORT_
#endif
/*macros for thread support*/
#define LOCK_MUTEX() mutex->lock()
#define UNLOCK_MUTEX() mutex->unlock()
/*macros for warning and debug messages*/
#ifdef _TTY_NOWARN_PORT_
#define TTY_PORTABILITY_WARNING(s)
#else
#define TTY_PORTABILITY_WARNING(s) qWarning(s)
#endif /*_TTY_NOWARN_PORT_*/
#ifdef _TTY_NOWARN_
#define TTY_WARNING(s)
#else
#define TTY_WARNING(s) qWarning(s)
#endif /*_TTY_NOWARN_*/
/*line status constants*/
#define LS_CTS 0x01
#define LS_DSR 0x02
#define LS_DCD 0x04
#define LS_RI 0x08
#define LS_RTS 0x10
#define LS_DTR 0x20
#define LS_ST 0x40
#define LS_SR 0x80
/*error constants*/
#define E_NO_ERROR 0
#define E_INVALID_FD 1
#define E_NO_MEMORY 2
#define E_CAUGHT_NON_BLOCKED_SIGNAL 3
#define E_PORT_TIMEOUT 4
#define E_INVALID_DEVICE 5
#define E_BREAK_CONDITION 6
#define E_FRAMING_ERROR 7
#define E_IO_ERROR 8
#define E_BUFFER_OVERRUN 9
#define E_RECEIVE_OVERFLOW 10
#define E_RECEIVE_PARITY_ERROR 11
#define E_TRANSMIT_OVERFLOW 12
#define E_READ_FAILED 13
#define E_WRITE_FAILED 14
/*!
* Enums for port settings.
*/
enum NamingConvention
{
WIN_NAMES,
IRIX_NAMES,
HPUX_NAMES,
SUN_NAMES,
DIGITAL_NAMES,
FREEBSD_NAMES,
LINUX_NAMES
};
enum BaudRateType
{
BAUD50, //POSIX ONLY
BAUD75, //POSIX ONLY
BAUD110,
BAUD134, //POSIX ONLY
BAUD150, //POSIX ONLY
BAUD200, //POSIX ONLY
BAUD300,
BAUD600,
BAUD1200,
BAUD1800, //POSIX ONLY
BAUD2400,
BAUD4800,
BAUD9600,
BAUD14400, //WINDOWS ONLY
BAUD19200,
BAUD38400,
BAUD56000, //WINDOWS ONLY
BAUD57600,
BAUD76800, //POSIX ONLY
BAUD115200,
BAUD128000, //WINDOWS ONLY
BAUD256000 //WINDOWS ONLY
};
enum DataBitsType
{
DATA_5,
DATA_6,
DATA_7,
DATA_8
};
enum ParityType
{
PAR_NONE,
PAR_ODD,
PAR_EVEN,
PAR_MARK, //WINDOWS ONLY
PAR_SPACE
};
enum StopBitsType
{
STOP_1,
STOP_1_5, //WINDOWS ONLY
STOP_2
};
enum FlowType
{
FLOW_OFF,
FLOW_HARDWARE,
FLOW_XONXOFF
};
/**
* structure to contain port settings
*/
struct PortSettings
{
BaudRateType BaudRate;
DataBitsType DataBits;
ParityType Parity;
StopBitsType StopBits;
FlowType FlowControl;
long Timeout_Millisec;
};
/*!
* \author Stefan Sander
* \author Michal Policht
*
* A common base class for Win_QextSerialBase, Posix_QextSerialBase and QextSerialPort.
*/
class QextSerialBase : public QIODevice
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
enum QueryMode {
Polling,
EventDriven
};
protected:
QMutex* mutex;
QString port;
PortSettings Settings;
ulong lastErr;
QextSerialBase::QueryMode _queryMode;
virtual qint64 readData(char * data, qint64 maxSize)=0;
virtual qint64 writeData(const char * data, qint64 maxSize)=0;
public:
QextSerialBase();
QextSerialBase(const QString & name);
virtual ~QextSerialBase();
virtual void construct();
virtual void setPortName(const QString & name);
virtual QString portName() const;
/**!
* Get query mode.
* \return query mode.
*/
inline QextSerialBase::QueryMode queryMode() const { return _queryMode; };
/*!
* Set desired serial communication handling style. You may choose from polling
* or event driven approach. This function does nothing when port is open; to
* apply changes port must be reopened.
*
* In event driven approach read() and write() functions are acting
* asynchronously. They return immediately and the operation is performed in
* the background, so they doesn't freeze the calling thread.
* To determine when operation is finished, QextSerialPort runs separate thread
* and monitors serial port events. Whenever the event occurs, adequate signal
* is emitted.
*
* When polling is set, read() and write() are acting synchronously. Signals are
* not working in this mode and some functions may not be available. The advantage
* of polling is that it generates less overhead due to lack of signals emissions
* and it doesn't start separate thread to monitor events.
*
* Generally event driven approach is more capable and friendly, although some
* applications may need as low overhead as possible and then polling comes.
*
* \param mode query mode.
*/
virtual void setQueryMode(QueryMode mode);
// virtual void setBlockingRead(bool block) = 0; ///< @todo implement.
virtual void setBaudRate(BaudRateType)=0;
virtual BaudRateType baudRate() const;
virtual void setDataBits(DataBitsType)=0;
virtual DataBitsType dataBits() const;
virtual void setParity(ParityType)=0;
virtual ParityType parity() const;
virtual void setStopBits(StopBitsType)=0;
virtual StopBitsType stopBits() const;
virtual void setFlowControl(FlowType)=0;
virtual FlowType flowControl() const;
virtual void setTimeout(long)=0;
virtual bool open(OpenMode mode)=0;
virtual bool isSequential() const;
virtual void close()=0;
virtual void flush()=0;
virtual qint64 size() const=0;
virtual qint64 bytesAvailable()=0;
virtual bool atEnd() const;
virtual void ungetChar(char c)=0;
virtual qint64 readLine(char * data, qint64 maxSize);
virtual ulong lastError() const;
virtual void translateError(ulong error)=0;
virtual void setDtr(bool set=true)=0;
virtual void setRts(bool set=true)=0;
virtual ulong lineStatus()=0;
signals:
/**
* This signal is emitted whenever port settings are updated.
* \param valid \p true if settings are valid, \p false otherwise.
*
* @todo implement.
*/
// void validSettings(bool valid);
/*!
* This signal is emitted whenever dsr line has changed its state. You may
* use this signal to check if device is connected.
* \param status \p true when DSR signal is on, \p false otherwise.
*
* \see lineStatus().
*/
void dsrChanged(bool status);
};
#endif
/*************qextserialport.h**************/
#ifndef _QEXTSERIALPORT_H_
#define _QEXTSERIALPORT_H_
/*POSIX CODE*/
#ifdef _TTY_POSIX_
#include "posix_qextserialport.h"
#define QextBaseType Posix_QextSerialPort
/*MS WINDOWS CODE*/
#else
#include "win_qextserialport.h"
#define QextBaseType Win_QextSerialPort
#endif
class QextSerialPort: public QextBaseType
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
typedef QextSerialBase::QueryMode QueryMode;
QextSerialPort();
QextSerialPort(const QString & name, QueryMode mode = QextSerialPort::Polling);
QextSerialPort(PortSettings const& s, QueryMode mode = QextSerialPort::Polling);
QextSerialPort(const QString & name, PortSettings const& s, QueryMode mode = QextSerialPort::Polling);
QextSerialPort(const QextSerialPort& s);
QextSerialPort& operator=(const QextSerialPort&);
virtual ~QextSerialPort();
};
#endif
/************win_qextserialport.h************/
#ifndef _WIN_QEXTSERIALPORT_H_
#define _WIN_QEXTSERIALPORT_H_
#include "qextserialbase.h"
#include <windows.h>
#include <QThread>
/*if all warning messages are turned off, flag portability warnings to be turned off as well*/
#ifdef _TTY_NOWARN_
#define _TTY_NOWARN_PORT_
#endif
class QReadWriteLock;
class Win_QextSerialThread;
/*!
\author Stefan Sander
\author Michal Policht
A cross-platform serial port class.
This class encapsulates the Windows portion of QextSerialPort. The user will be notified of
errors and possible portability conflicts at run-time by default - this behavior can be turned
off by defining _TTY_NOWARN_ (to turn off all warnings) or _TTY_NOWARN_PORT_ (to turn off
portability warnings) in the project. Note that defining _TTY_NOWARN_ also defines
_TTY_NOWARN_PORT_.
\note
On Windows NT/2000/XP this class uses Win32 serial port functions by default. The user may
select POSIX behavior under NT, 2000, or XP ONLY by defining _TTY_POSIX_ in the project. I can
make no guarantees as to the quality of POSIX support under NT/2000 however.
\todo remove copy constructor and assign operator.
*/
class Win_QextSerialPort: public QextSerialBase
{
Q_OBJECT
friend class Win_QextSerialThread;
private:
/*!
* This method is a part of constructor.
*/
void init();
protected:
HANDLE Win_Handle;
HANDLE threadStartEvent;
HANDLE threadTerminateEvent;
OVERLAPPED overlap;
OVERLAPPED overlapWrite;
COMMCONFIG Win_CommConfig;
COMMTIMEOUTS Win_CommTimeouts;
QReadWriteLock * bytesToWriteLock; ///< @todo maybe move to QextSerialBase.
qint64 _bytesToWrite; ///< @todo maybe move to QextSerialBase (and implement in POSIX).
Win_QextSerialThread * overlapThread; ///< @todo maybe move to QextSerialBase (and implement in POSIX).
void monitorCommEvent();
void terminateCommWait();
virtual qint64 readData(char *data, qint64 maxSize);
virtual qint64 writeData(const char *data, qint64 maxSize);
public:
Win_QextSerialPort();
Win_QextSerialPort(Win_QextSerialPort const& s);
Win_QextSerialPort(const QString & name, QextSerialBase::QueryMode mode = QextSerialBase::Polling);
Win_QextSerialPort(const PortSettings& settings, QextSerialBase::QueryMode mode = QextSerialBase::Polling);
Win_QextSerialPort(const QString & name, const PortSettings& settings, QextSerialBase::QueryMode mode = QextSerialBase::Polling);
Win_QextSerialPort& operator=(const Win_QextSerialPort& s);
virtual ~Win_QextSerialPort();
virtual bool open(OpenMode mode);
virtual void close();
virtual void flush();
virtual qint64 size() const;
virtual void ungetChar(char c);
virtual void setFlowControl(FlowType);
virtual void setParity(ParityType);
virtual void setDataBits(DataBitsType);
virtual void setStopBits(StopBitsType);
virtual void setBaudRate(BaudRateType);
virtual void setDtr(bool set=true);
virtual void setRts(bool set=true);
virtual ulong lineStatus(void);
virtual qint64 bytesAvailable();
virtual void translateError(ulong);
virtual void setTimeout(long);
/*!
* Return number of bytes waiting in the buffer. Currently this shows number
* of bytes queued within write() and before the TX_EMPTY event occured. TX_EMPTY
* event is created whenever last character in the system buffer was sent.
*
* \return number of bytes queued within write(), before the first TX_EMPTY
* event occur.
*
* \warning this function may not give you expected results since TX_EMPTY may occur
* while writing data to the buffer. Eventually some TX_EMPTY events may not be
* catched.
*
* \note this function always returns 0 in polling mode.
*
* \see flush().
*/
virtual qint64 bytesToWrite() const;
virtual bool waitForReadyRead(int msecs); ///< @todo implement.
};
/*!
* This thread monitors communication events.
*/
class Win_QextSerialThread: public QThread
{
Win_QextSerialPort * qesp;
bool terminate;
public:
/*!
* Constructor.
*
* \param qesp valid serial port object.
*/
Win_QextSerialThread(Win_QextSerialPort * qesp);
/*!
* Stop the thread.
*/
void stop();
protected:
//overriden
virtual void run();
};
#endif
/***********main.cpp*************/
#include "mainwindow.h"
#include <QApplication>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QApplication a(argc, argv);
MainWindow w;
w.show();
return a.exec();
}
/*************mainwindow.cpp************/
#include "mainwindow.h"
#include <iostream>
MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent)
: QMainWindow(parent)
{
this->setGeometry(200,200,300,300);
QLabel *ql=new QLabel("Qt串口编程测试:",this);
ql->setGeometry(20,20,250,50);
text=new QTextBrowser(this);
text->setGeometry(20,80,250,160);
struct PortSettings myComSetting = {BAUD2400,DATA_8,PAR_NONE,STOP_1,FLOW_OFF,0};
myCom=new Win_QextSerialPort("com5",myComSetting,QextSerialBase::EventDriven);
myCom->open(QIODevice::ReadWrite);
myCom->setBaudRate(BAUD2400); //一定要在这儿添上这句,否则可能发生无法解释的异常。
connect(myCom,SIGNAL(readyRead()),this,SLOT(readMyCom()));
}
MainWindow::~MainWindow()
{
}
void MainWindow::readMyCom(){
QByteArray temp=myCom->readAll();
if(temp.size()>=1){
text->insertPlainText("收到:");
text->insertPlainText(temp);
}
}
/************qextserialbase.cpp***************/
#include "qextserialbase.h"
/*!
\fn QextSerialBase::QextSerialBase()
Default constructor.
*/
QextSerialBase::QextSerialBase()
: QIODevice()
{
#ifdef _TTY_WIN_
setPortName("COM1");
#elif defined(_TTY_IRIX_)
setPortName("/dev/ttyf1");
#elif defined(_TTY_HPUX_)
setPortName("/dev/tty1p0");
#elif defined(_TTY_SUN_)
setPortName("/dev/ttya");
#elif defined(_TTY_DIGITAL_)
setPortName("/dev/tty01");
#elif defined(_TTY_FREEBSD_)
setPortName("/dev/ttyd1");
#else
setPortName("/dev/ttyS0");
#endif
construct();
}
/*!
\fn QextSerialBase::QextSerialBase(const QString & name)
Construct a port and assign it to the device specified by the name parameter.
*/
QextSerialBase::QextSerialBase(const QString & name)
: QIODevice()
{
setPortName(name);
construct();
}
/*!
\fn QextSerialBase::~QextSerialBase()
Standard destructor.
*/
QextSerialBase::~QextSerialBase()
{
delete mutex;
}
/*!
\fn void QextSerialBase::construct()
Common constructor function for setting up default port settings.
(115200 Baud, 8N1, Hardware flow control where supported, otherwise no flow control, and 0 ms timeout).
*/
void QextSerialBase::construct()
{
Settings.BaudRate=BAUD115200;
Settings.DataBits=DATA_8;
Settings.Parity=PAR_NONE;
Settings.StopBits=STOP_1;
Settings.FlowControl=FLOW_HARDWARE;
Settings.Timeout_Millisec=500;
mutex = new QMutex( QMutex::Recursive );
setOpenMode(QIODevice::NotOpen);
}
void QextSerialBase::setQueryMode(QueryMode mechanism)
{
_queryMode = mechanism;
}
/*!
\fn void QextSerialBase::setPortName(const QString & name)
Sets the name of the device associated with the object, e.g. "COM1", or "/dev/ttyS0".
*/
void QextSerialBase::setPortName(const QString & name)
{
port = name;
}
/*!
\fn QString QextSerialBase::portName() const
Returns the name set by setPortName().
*/
QString QextSerialBase::portName() const
{
return port;
}
/*!
\fn BaudRateType QextSerialBase::baudRate(void) const
Returns the baud rate of the serial port. For a list of possible return values see
the definition of the enum BaudRateType.
*/
BaudRateType QextSerialBase::baudRate(void) const
{
return Settings.BaudRate;
}
/*!
\fn DataBitsType QextSerialBase::dataBits() const
Returns the number of data bits used by the port. For a list of possible values returned by
this function, see the definition of the enum DataBitsType.
*/
DataBitsType QextSerialBase::dataBits() const
{
return Settings.DataBits;
}
/*!
\fn ParityType QextSerialBase::parity() const
Returns the type of parity used by the port. For a list of possible values returned by
this function, see the definition of the enum ParityType.
*/
ParityType QextSerialBase::parity() const
{
return Settings.Parity;
}
/*!
\fn StopBitsType QextSerialBase::stopBits() const
Returns the number of stop bits used by the port. For a list of possible return values, see
the definition of the enum StopBitsType.
*/
StopBitsType QextSerialBase::stopBits() const
{
return Settings.StopBits;
}
/*!
\fn FlowType QextSerialBase::flowControl() const
Returns the type of flow control used by the port. For a list of possible values returned
by this function, see the definition of the enum FlowType.
*/
FlowType QextSerialBase::flowControl() const
{
return Settings.FlowControl;
}
/*!
\fn bool QextSerialBase::isSequential() const
Returns true if device is sequential, otherwise returns false. Serial port is sequential device
so this function always returns true. Check QIODevice::isSequential() documentation for more
information.
*/
bool QextSerialBase::isSequential() const
{
return true;
}
/*!
\fn bool QextSerialBase::atEnd() const
This function will return true if the input buffer is empty (or on error), and false otherwise.
Call QextSerialBase::lastError() for error information.
*/
bool QextSerialBase::atEnd() const
{
if (size()) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
/*!
\fn qint64 QextSerialBase::readLine(char * data, qint64 maxSize)
This function will read a line of buffered input from the port, stopping when either maxSize bytes
have been read, the port has no more data available, or a newline is encountered.
The value returned is the length of the string that was read.
*/
qint64 QextSerialBase::readLine(char * data, qint64 maxSize)
{
qint64 numBytes = bytesAvailable();
char* pData = data;
if (maxSize < 2) //maxSize must be larger than 1
return -1;
/*read a byte at a time for MIN(bytesAvail, maxSize - 1) iterations, or until a newline*/
while (pData<(data+numBytes) && --maxSize) {
readData(pData, 1);
if (*pData++ == '\n') {
break;
}
}
*pData='\0';
/*return size of data read*/
return (pData-data);
}
/*!
\fn ulong QextSerialBase::lastError() const
Returns the code for the last error encountered by the port, or E_NO_ERROR if the last port
operation was successful. Possible error codes are:
\verbatim
Error Explanation
--------------------------- -------------------------------------------------------------
E_NO_ERROR No Error has occured
E_INVALID_FD Invalid file descriptor (port was not opened correctly)
E_NO_MEMORY Unable to allocate memory tables (POSIX)
E_CAUGHT_NON_BLOCKED_SIGNAL Caught a non-blocked signal (POSIX)
E_PORT_TIMEOUT Operation timed out (POSIX)
E_INVALID_DEVICE The file opened by the port is not a character device (POSIX)
E_BREAK_CONDITION The port detected a break condition
E_FRAMING_ERROR The port detected a framing error
(usually caused by incorrect baud rate settings)
E_IO_ERROR There was an I/O error while communicating with the port
E_BUFFER_OVERRUN Character buffer overrun
E_RECEIVE_OVERFLOW Receive buffer overflow
E_RECEIVE_PARITY_ERROR The port detected a parity error in the received data
E_TRANSMIT_OVERFLOW Transmit buffer overflow
E_READ_FAILED General read operation failure
E_WRITE_FAILED General write operation failure
\endverbatim
*/
ulong QextSerialBase::lastError() const
{
return lastErr;
}
/*****************qextserialport.cpp***************/
/*!
\class QextSerialPort
\author Stefan Sander
\author Michal Policht
A cross-platform serial port class.
This class encapsulates a serial port on both POSIX and Windows systems. The user will be
notified of errors and possible portability conflicts at run-time by default - this behavior can
be turned off by defining _TTY_NOWARN_ (to turn off all warnings) or _TTY_NOWARN_PORT_ (to turn
off portability warnings) in the project.
You may choose from polling or event driven API. For details check setQueryMode() documentation.
\note
On Windows NT/2000/XP this class uses Win32 serial port functions by default. The user may
select POSIX behavior under NT, 2000, or XP ONLY by defining _TTY_POSIX_ in the project. I can
make no guarantees as to the quality of POSIX support under NT/2000 however.
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include "qextserialport.h"
/*!
Default constructor. Note that the naming convention used by a QextSerialPort constructed with
this constructor will be determined by #defined constants, or lack thereof - the default behavior
is the same as _TTY_LINUX_. Possible naming conventions and their associated constants are:
\verbatim
Constant Used By Naming Convention
---------- ------------- ------------------------
_TTY_WIN_ Windows COM1, COM2
_TTY_IRIX_ SGI/IRIX /dev/ttyf1, /dev/ttyf2
_TTY_HPUX_ HP-UX /dev/tty1p0, /dev/tty2p0
_TTY_SUN_ SunOS/Solaris /dev/ttya, /dev/ttyb
_TTY_DIGITAL_ Digital UNIX /dev/tty01, /dev/tty02
_TTY_FREEBSD_ FreeBSD /dev/ttyd0, /dev/ttyd1
_TTY_LINUX_ Linux /dev/ttyS0, /dev/ttyS1
<none> Linux /dev/ttyS0, /dev/ttyS1
\endverbatim
The object will be associated with the first port in the system, e.g. COM1 on Windows systems.
See the other constructors if you need to use a port other than the first.
*/
QextSerialPort::QextSerialPort()
: QextBaseType()
{}
/*!
Constructs a serial port attached to the port specified by name.
name is the name of the device, which is windowsystem-specific,
e.g."COM1" or "/dev/ttyS0".
\see setQueryMode().
*/
QextSerialPort::QextSerialPort(const QString & name, QueryMode mode)
: QextBaseType(name, mode)
{
}
/*!
Constructs a port with default name and settings specified by the settings parameter.
\see setQueryMode().
*/
QextSerialPort::QextSerialPort(PortSettings const& settings, QueryMode mode)
: QextBaseType(settings, mode)
{}
/*!
Constructs a port with the name and settings specified.
\see setQueryMode().
*/
QextSerialPort::QextSerialPort(const QString & name, PortSettings const& settings, QueryMode mode)
: QextBaseType(name, settings, mode)
{}
/*!
Copy constructor.
\deprecated
*/
QextSerialPort::QextSerialPort(const QextSerialPort& s)
: QextBaseType(s)
{}
/*!
\fn QextSerialPort& QextSerialPort::operator=(const QextSerialPort& s)
Overrides the = operator.
\deprecated
*/
QextSerialPort& QextSerialPort::operator=(const QextSerialPort& s)
{
return (QextSerialPort&)QextBaseType::operator=(s);
}
/*!
\fn QextSerialPort::~QextSerialPort()
Standard destructor.
*/
QextSerialPort::~QextSerialPort()
{}
/***************win_qextserialport.cpp***************/
#include <QReadWriteLock>
#include "win_qextserialport.h"
/*!
\fn Win_QextSerialPort::Win_QextSerialPort()
Default constructor. Note that the name of the device used by a Win_QextSerialPort constructed
with this constructor will be determined by #defined constants, or lack thereof - the default
behavior is the same as _TTY_LINUX_. Possible naming conventions and their associated constants
are:
\verbatim
Constant Used By Naming Convention
---------- ------------- ------------------------
_TTY_WIN_ Windows COM1, COM2
_TTY_IRIX_ SGI/IRIX /dev/ttyf1, /dev/ttyf2
_TTY_HPUX_ HP-UX /dev/tty1p0, /dev/tty2p0
_TTY_SUN_ SunOS/Solaris /dev/ttya, /dev/ttyb
_TTY_DIGITAL_ Digital UNIX /dev/tty01, /dev/tty02
_TTY_FREEBSD_ FreeBSD /dev/ttyd0, /dev/ttyd1
_TTY_LINUX_ Linux /dev/ttyS0, /dev/ttyS1
<none> Linux /dev/ttyS0, /dev/ttyS1
\endverbatim
This constructor associates the object with the first port on the system, e.g. COM1 for Windows
platforms. See the other constructor if you need a port other than the first.
*/
Win_QextSerialPort::Win_QextSerialPort():
QextSerialBase()
{
Win_Handle=INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE;
init();
}
/*!
\fn Win_QextSerialPort::Win_QextSerialPort(const Win_QextSerialPort&)
Copy constructor.
*/
Win_QextSerialPort::Win_QextSerialPort(const Win_QextSerialPort& s):
QextSerialBase(s.port)
{
Win_Handle=INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE;
_queryMode = s._queryMode;
_bytesToWrite = s._bytesToWrite;
bytesToWriteLock = new QReadWriteLock;
overlapThread = new Win_QextSerialThread(this);
memcpy(& overlap, & s.overlap, sizeof(OVERLAPPED));
memcpy(& overlapWrite, & s.overlapWrite, sizeof(OVERLAPPED));
setOpenMode(s.openMode());
lastErr=s.lastErr;
port = s.port;
Settings.FlowControl=s.Settings.FlowControl;
Settings.Parity=s.Settings.Parity;
Settings.DataBits=s.Settings.DataBits;
Settings.StopBits=s.Settings.StopBits;
Settings.BaudRate=s.Settings.BaudRate;
Win_Handle=s.Win_Handle;
memcpy(&Win_CommConfig, &s.Win_CommConfig, sizeof(COMMCONFIG));
memcpy(&Win_CommTimeouts, &s.Win_CommTimeouts, sizeof(COMMTIMEOUTS));
if (s.overlapThread->isRunning())
overlapThread->start();
}
/*!
\fn Win_QextSerialPort::Win_QextSerialPort(const QString & name)
Constructs a serial port attached to the port specified by devName.
devName is the name of the device, which is windowsystem-specific,
e.g."COM2" or "/dev/ttyS0".
*/
Win_QextSerialPort::Win_QextSerialPort(const QString & name, QextSerialBase::QueryMode mode):
QextSerialBase(name)
{
Win_Handle=INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE;
setQueryMode(mode);
init();
}
/*!
\fn Win_QextSerialPort::Win_QextSerialPort(const PortSettings& settings)
Constructs a port with default name and specified settings.
*/
Win_QextSerialPort::Win_QextSerialPort(const PortSettings& settings, QextSerialBase::QueryMode mode) {
Win_Handle=INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE;
setBaudRate(settings.BaudRate);
setDataBits(settings.DataBits);
setStopBits(settings.StopBits);
setParity(settings.Parity);
setFlowControl(settings.FlowControl);
setTimeout(settings.Timeout_Millisec);
setQueryMode(mode);
init();
}
/*!
\fn Win_QextSerialPort::Win_QextSerialPort(const QString & name, const PortSettings& settings)
Constructs a port with specified name and settings.
*/
Win_QextSerialPort::Win_QextSerialPort(const QString & name, const PortSettings& settings, QextSerialBase::QueryMode mode) {
Win_Handle=INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE;
setPortName(name);
setBaudRate(settings.BaudRate);
setDataBits(settings.DataBits);
setStopBits(settings.StopBits);
setParity(settings.Parity);
setFlowControl(settings.FlowControl);
setTimeout(settings.Timeout_Millisec);
setQueryMode(mode);
init();
}
void Win_QextSerialPort::init()
{
_bytesToWrite = 0;
overlap.Internal = 0;
overlap.InternalHigh = 0;
overlap.Offset = 0;
overlap.OffsetHigh = 0;
overlap.hEvent = CreateEvent(NULL, true, false, NULL);
overlapThread = new Win_QextSerialThread(this);
bytesToWriteLock = new QReadWriteLock;
}
/*!
\fn Win_QextSerialPort::~Win_QextSerialPort()
Standard destructor.
*/
Win_QextSerialPort::~Win_QextSerialPort() {
if (isOpen()) {
close();
}
CloseHandle(overlap.hEvent);
delete overlapThread;
delete bytesToWriteLock;
}
/*!
\fn Win_QextSerialPort& Win_QextSerialPort::operator=(const Win_QextSerialPort& s)
overrides the = operator
*/
Win_QextSerialPort& Win_QextSerialPort::operator=(const Win_QextSerialPort& s) {
setOpenMode(s.openMode());
_queryMode = s._queryMode;
_bytesToWrite = s._bytesToWrite;
bytesToWriteLock = new QReadWriteLock;
overlapThread = new Win_QextSerialThread(this);
memcpy(& overlap, & s.overlap, sizeof(OVERLAPPED));
memcpy(& overlapWrite, & s.overlapWrite, sizeof(OVERLAPPED));
lastErr=s.lastErr;
port = s.port;
Settings.FlowControl=s.Settings.FlowControl;
Settings.Parity=s.Settings.Parity;
Settings.DataBits=s.Settings.DataBits;
Settings.StopBits=s.Settings.StopBits;
Settings.BaudRate=s.Settings.BaudRate;
Win_Handle=s.Win_Handle;
memcpy(&Win_CommConfig, &s.Win_CommConfig, sizeof(COMMCONFIG));
memcpy(&Win_CommTimeouts, &s.Win_CommTimeouts, sizeof(COMMTIMEOUTS));
if (s.overlapThread->isRunning())
overlapThread->start();
return *this;
}
/*!
\fn bool Win_QextSerialPort::open(OpenMode mode)
Opens a serial port. Note that this function does not specify which device to open. If you need
to open a device by name, see Win_QextSerialPort::open(const char*). This function has no effect
if the port associated with the class is already open. The port is also configured to the current
settings, as stored in the Settings structure.
*/
bool Win_QextSerialPort::open(OpenMode mode) {
unsigned long confSize = sizeof(COMMCONFIG);
Win_CommConfig.dwSize = confSize;
DWORD dwFlagsAndAttributes = 0;
if (queryMode() == QextSerialBase::EventDriven)
dwFlagsAndAttributes += FILE_FLAG_OVERLAPPED;
LOCK_MUTEX();
if (mode == QIODevice::NotOpen)
return isOpen();
if (!isOpen()) {
/*open the port*/
Win_Handle=CreateFileA(port.toLatin1(), GENERIC_READ|GENERIC_WRITE,
FILE_SHARE_READ|FILE_SHARE_WRITE, NULL, OPEN_EXISTING, dwFlagsAndAttributes, NULL);
if (Win_Handle!=INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE) {
/*configure port settings*/
GetCommConfig(Win_Handle, &Win_CommConfig, &confSize);
GetCommState(Win_Handle, &(Win_CommConfig.dcb));
/*set up parameters*/
Win_CommConfig.dcb.fBinary=TRUE;
Win_CommConfig.dcb.fInX=FALSE;
Win_CommConfig.dcb.fOutX=FALSE;
Win_CommConfig.dcb.fAbortOnError=FALSE;
Win_CommConfig.dcb.fNull=FALSE;
setBaudRate(Settings.BaudRate);
setDataBits(Settings.DataBits);
setStopBits(Settings.StopBits);
setParity(Settings.Parity);
setFlowControl(Settings.FlowControl);
setTimeout(Settings.Timeout_Millisec);
SetCommConfig(Win_Handle, &Win_CommConfig, sizeof(COMMCONFIG));
//init event driven approach
if (queryMode() == QextSerialBase::EventDriven) {
Win_CommTimeouts.ReadIntervalTimeout = MAXDWORD;
Win_CommTimeouts.ReadTotalTimeoutMultiplier = 0;
Win_CommTimeouts.ReadTotalTimeoutConstant = 0;
Win_CommTimeouts.WriteTotalTimeoutMultiplier = 0;
Win_CommTimeouts.WriteTotalTimeoutConstant = 0;
SetCommTimeouts(Win_Handle, &Win_CommTimeouts);
if (!SetCommMask( Win_Handle, EV_TXEMPTY | EV_RXCHAR | EV_DSR)) {
qWarning("Failed to set Comm Mask. Error code: %ld", GetLastError());
UNLOCK_MUTEX();
return false;
}
overlapThread->start();
}
QIODevice::open(mode);
}
} else {
UNLOCK_MUTEX();
return false;
}
UNLOCK_MUTEX();
return isOpen();
}
/*!
\fn void Win_QextSerialPort::close()
Closes a serial port. This function has no effect if the serial port associated with the class
is not currently open.
*/
void Win_QextSerialPort::close()
{
LOCK_MUTEX();
if (isOpen()) {
flush();
if (overlapThread->isRunning()) {
overlapThread->stop();
if (QThread::currentThread() != overlapThread)
overlapThread->wait();
}
if (CloseHandle(Win_Handle))
Win_Handle = INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE;
_bytesToWrite = 0;
QIODevice::close();
}
UNLOCK_MUTEX();
}
/*!
\fn void Win_QextSerialPort::flush()
Flushes all pending I/O to the serial port. This function has no effect if the serial port
associated with the class is not currently open.
*/
void Win_QextSerialPort::flush() {
LOCK_MUTEX();
if (isOpen()) {
FlushFileBuffers(Win_Handle);
}
UNLOCK_MUTEX();
}
/*!
\fn qint64 Win_QextSerialPort::size() const
This function will return the number of bytes waiting in the receive queue of the serial port.
It is included primarily to provide a complete QIODevice interface, and will not record errors
in the lastErr member (because it is const). This function is also not thread-safe - in
multithreading situations, use Win_QextSerialPort::bytesAvailable() instead.
*/
qint64 Win_QextSerialPort::size() const {
int availBytes;
COMSTAT Win_ComStat;
DWORD Win_ErrorMask=0;
ClearCommError(Win_Handle, &Win_ErrorMask, &Win_ComStat);
availBytes = Win_ComStat.cbInQue;
return (qint64)availBytes;
}
/*!
\fn qint64 Win_QextSerialPort::bytesAvailable()
Returns the number of bytes waiting in the port's receive queue. This function will return 0 if
the port is not currently open, or -1 on error. Error information can be retrieved by calling
Win_QextSerialPort::getLastError().
*/
qint64 Win_QextSerialPort::bytesAvailable() {
LOCK_MUTEX();
if (isOpen()) {
DWORD Errors;
COMSTAT Status;
bool success=ClearCommError(Win_Handle, &Errors, &Status);
translateError(Errors);
if (success) {
lastErr=E_NO_ERROR;
UNLOCK_MUTEX();
return Status.cbInQue + QIODevice::bytesAvailable();
}
UNLOCK_MUTEX();
return (unsigned int)-1;
}
UNLOCK_MUTEX();
return 0;
}
/*!
\fn void Win_QextSerialPort::translateError(ulong error)
Translates a system-specific error code to a QextSerialPort error code. Used internally.
*/
void Win_QextSerialPort::translateError(ulong error) {
if (error&CE_BREAK) {
lastErr=E_BREAK_CONDITION;
}
else if (error&CE_FRAME) {
lastErr=E_FRAMING_ERROR;
}
else if (error&CE_IOE) {
lastErr=E_IO_ERROR;
}
else if (error&CE_MODE) {
lastErr=E_INVALID_FD;
}
else if (error&CE_OVERRUN) {
lastErr=E_BUFFER_OVERRUN;
}
else if (error&CE_RXPARITY) {
lastErr=E_RECEIVE_PARITY_ERROR;
}
else if (error&CE_RXOVER) {
lastErr=E_RECEIVE_OVERFLOW;
}
else if (error&CE_TXFULL) {
lastErr=E_TRANSMIT_OVERFLOW;
}
}
/*!
\fn qint64 Win_QextSerialPort::readData(char *data, qint64 maxSize)
Reads a block of data from the serial port. This function will read at most maxlen bytes from
the serial port and place them in the buffer pointed to by data. Return value is the number of
bytes actually read, or -1 on error.
\warning before calling this function ensure that serial port associated with this class
is currently open (use isOpen() function to check if port is open).
*/
qint64 Win_QextSerialPort::readData(char *data, qint64 maxSize)
{
DWORD retVal;
LOCK_MUTEX();
retVal = 0;
if (queryMode() == QextSerialBase::EventDriven) {
OVERLAPPED overlapRead;
overlapRead.Internal = 0;
overlapRead.InternalHigh = 0;
overlapRead.Offset = 0;
overlapRead.OffsetHigh = 0;
overlapRead.hEvent = CreateEvent(NULL, true, false, NULL);
if (!ReadFile(Win_Handle, (void*)data, (DWORD)maxSize, & retVal, & overlapRead)) {
if (GetLastError() == ERROR_IO_PENDING)
GetOverlappedResult(Win_Handle, & overlapRead, & retVal, true);
else {
lastErr = E_READ_FAILED;
retVal = (DWORD)-1;
}
}
CloseHandle(overlapRead.hEvent);
} else if (!ReadFile(Win_Handle, (void*)data, (DWORD)maxSize, & retVal, NULL)) {
lastErr = E_READ_FAILED;
retVal = (DWORD)-1;
}
UNLOCK_MUTEX();
return (qint64)retVal;
}
/*!
\fn qint64 Win_QextSerialPort::writeData(const char *data, qint64 maxSize)
Writes a block of data to the serial port. This function will write len bytes
from the buffer pointed to by data to the serial port. Return value is the number
of bytes actually written, or -1 on error.
\warning before calling this function ensure that serial port associated with this class
is currently open (use isOpen() function to check if port is open).
*/
qint64 Win_QextSerialPort::writeData(const char *data, qint64 maxSize)
{
DWORD retVal;
LOCK_MUTEX();
retVal = 0;
if (queryMode() == QextSerialBase::EventDriven) {
bytesToWriteLock->lockForWrite();
_bytesToWrite += maxSize;
bytesToWriteLock->unlock();
overlapWrite.Internal = 0;
overlapWrite.InternalHigh = 0;
overlapWrite.Offset = 0;
overlapWrite.OffsetHigh = 0;
overlapWrite.hEvent = CreateEvent(NULL, true, false, NULL);
if (!WriteFile(Win_Handle, (void*)data, (DWORD)maxSize, & retVal, & overlapWrite)) {
lastErr = E_WRITE_FAILED;
retVal = (DWORD)-1;
} else
retVal = maxSize;
} else if (!WriteFile(Win_Handle, (void*)data, (DWORD)maxSize, & retVal, NULL)) {
lastErr = E_WRITE_FAILED;
retVal = (DWORD)-1;
}
UNLOCK_MUTEX();
return (qint64)retVal;
}
/*!
\fn void Win_QextSerialPort::ungetChar(char c)
This function is included to implement the full QIODevice interface, and currently has no
purpose within this class. This function is meaningless on an unbuffered device and currently
only prints a warning message to that effect.
*/
void Win_QextSerialPort::ungetChar(char c) {
/*meaningless on unbuffered sequential device - return error and print a warning*/
TTY_WARNING("Win_QextSerialPort: ungetChar() called on an unbuffered sequential device - operation is meaningless");
}
/*!
\fn void Win_QextSerialPort::setFlowControl(FlowType flow)
Sets the flow control used by the port. Possible values of flow are:
\verbatim
FLOW_OFF No flow control
FLOW_HARDWARE Hardware (RTS/CTS) flow control
FLOW_XONXOFF Software (XON/XOFF) flow control
\endverbatim
*/
void Win_QextSerialPort::setFlowControl(FlowType flow) {
LOCK_MUTEX();
if (Settings.FlowControl!=flow) {
Settings.FlowControl=flow;
}
if (isOpen()) {
switch(flow) {
/*no flow control*/
case FLOW_OFF:
Win_CommConfig.dcb.fOutxCtsFlow=FALSE;
Win_CommConfig.dcb.fRtsControl=RTS_CONTROL_DISABLE;
Win_CommConfig.dcb.fInX=FALSE;
Win_CommConfig.dcb.fOutX=FALSE;
SetCommConfig(Win_Handle, &Win_CommConfig, sizeof(COMMCONFIG));
break;
/*software (XON/XOFF) flow control*/
case FLOW_XONXOFF:
Win_CommConfig.dcb.fOutxCtsFlow=FALSE;
Win_CommConfig.dcb.fRtsControl=RTS_CONTROL_DISABLE;
Win_CommConfig.dcb.fInX=TRUE;
Win_CommConfig.dcb.fOutX=TRUE;
SetCommConfig(Win_Handle, &Win_CommConfig, sizeof(COMMCONFIG));
break;
case FLOW_HARDWARE:
Win_CommConfig.dcb.fOutxCtsFlow=TRUE;
Win_CommConfig.dcb.fRtsControl=RTS_CONTROL_HANDSHAKE;
Win_CommConfig.dcb.fInX=FALSE;
Win_CommConfig.dcb.fOutX=FALSE;
SetCommConfig(Win_Handle, &Win_CommConfig, sizeof(COMMCONFIG));
break;
}
}
UNLOCK_MUTEX();
}
/*!
\fn void Win_QextSerialPort::setParity(ParityType parity)
Sets the parity associated with the serial port. The possible values of parity are:
\verbatim
PAR_SPACE Space Parity
PAR_MARK Mark Parity
PAR_NONE No Parity
PAR_EVEN Even Parity
PAR_ODD Odd Parity
\endverbatim
*/
void Win_QextSerialPort::setParity(ParityType parity) {
LOCK_MUTEX();
if (Settings.Parity!=parity) {
Settings.Parity=parity;
}
if (isOpen()) {
Win_CommConfig.dcb.Parity=(unsigned char)parity;
switch (parity) {
/*space parity*/
case PAR_SPACE:
if (Settings.DataBits==DATA_8) {
TTY_PORTABILITY_WARNING("Win_QextSerialPort Portability Warning: Space parity with 8 data bits is not supported by POSIX systems.");
}
Win_CommConfig.dcb.fParity=TRUE;
break;
/*mark parity - WINDOWS ONLY*/
case PAR_MARK:
TTY_PORTABILITY_WARNING("Win_QextSerialPort Portability Warning: Mark parity is not supported by POSIX systems");
Win_CommConfig.dcb.fParity=TRUE;
break;
/*no parity*/
case PAR_NONE:
Win_CommConfig.dcb.fParity=FALSE;
break;
/*even parity*/
case PAR_EVEN:
Win_CommConfig.dcb.fParity=TRUE;
break;
/*odd parity*/
case PAR_ODD:
Win_CommConfig.dcb.fParity=TRUE;
break;
}
SetCommConfig(Win_Handle, &Win_CommConfig, sizeof(COMMCONFIG));
}
UNLOCK_MUTEX();
}
/*!
\fn void Win_QextSerialPort::setDataBits(DataBitsType dataBits)
Sets the number of data bits used by the serial port. Possible values of dataBits are:
\verbatim
DATA_5 5 data bits
DATA_6 6 data bits
DATA_7 7 data bits
DATA_8 8 data bits
\endverbatim
\note
This function is subject to the following restrictions:
\par
5 data bits cannot be used with 2 stop bits.
\par
1.5 stop bits can only be used with 5 data bits.
\par
8 data bits cannot be used with space parity on POSIX systems.
*/
void Win_QextSerialPort::setDataBits(DataBitsType dataBits) {
LOCK_MUTEX();
if (Settings.DataBits!=dataBits) {
if ((Settings.StopBits==STOP_2 && dataBits==DATA_5) ||
(Settings.StopBits==STOP_1_5 && dataBits!=DATA_5)) {
}
else {
Settings.DataBits=dataBits;
}
}
if (isOpen()) {
switch(dataBits) {
/*5 data bits*/
case DATA_5:
if (Settings.StopBits==STOP_2) {
TTY_WARNING("Win_QextSerialPort: 5 Data bits cannot be used with 2 stop bits.");
}
else {
Win_CommConfig.dcb.ByteSize=5;
SetCommConfig(Win_Handle, &Win_CommConfig, sizeof(COMMCONFIG));
}
break;
/*6 data bits*/
case DATA_6:
if (Settings.StopBits==STOP_1_5) {
TTY_WARNING("Win_QextSerialPort: 6 Data bits cannot be used with 1.5 stop bits.");
}
else {
Win_CommConfig.dcb.ByteSize=6;
SetCommConfig(Win_Handle, &Win_CommConfig, sizeof(COMMCONFIG));
}
break;
/*7 data bits*/
case DATA_7:
if (Settings.StopBits==STOP_1_5) {
TTY_WARNING("Win_QextSerialPort: 7 Data bits cannot be used with 1.5 stop bits.");
}
else {
Win_CommConfig.dcb.ByteSize=7;
SetCommConfig(Win_Handle, &Win_CommConfig, sizeof(COMMCONFIG));
}
break;
/*8 data bits*/
case DATA_8:
if (Settings.StopBits==STOP_1_5) {
TTY_WARNING("Win_QextSerialPort: 8 Data bits cannot be used with 1.5 stop bits.");
}
else {
Win_CommConfig.dcb.ByteSize=8;
SetCommConfig(Win_Handle, &Win_CommConfig, sizeof(COMMCONFIG));
}
break;
}
}
UNLOCK_MUTEX();
}
/*!
\fn void Win_QextSerialPort::setStopBits(StopBitsType stopBits)
Sets the number of stop bits used by the serial port. Possible values of stopBits are:
\verbatim
STOP_1 1 stop bit
STOP_1_5 1.5 stop bits
STOP_2 2 stop bits
\endverbatim
\note
This function is subject to the following restrictions:
\par
2 stop bits cannot be used with 5 data bits.
\par
1.5 stop bits cannot be used with 6 or more data bits.
\par
POSIX does not support 1.5 stop bits.
*/
void Win_QextSerialPort::setStopBits(StopBitsType stopBits) {
LOCK_MUTEX();
if (Settings.StopBits!=stopBits) {
if ((Settings.DataBits==DATA_5 && stopBits==STOP_2) ||
(stopBits==STOP_1_5 && Settings.DataBits!=DATA_5)) {
}
else {
Settings.StopBits=stopBits;
}
}
if (isOpen()) {
switch (stopBits) {
/*one stop bit*/
case STOP_1:
Win_CommConfig.dcb.StopBits=ONESTOPBIT;
SetCommConfig(Win_Handle, &Win_CommConfig, sizeof(COMMCONFIG));
break;
/*1.5 stop bits*/
case STOP_1_5:
TTY_PORTABILITY_WARNING("Win_QextSerialPort Portability Warning: 1.5 stop bit operation is not supported by POSIX.");
if (Settings.DataBits!=DATA_5) {
TTY_WARNING("Win_QextSerialPort: 1.5 stop bits can only be used with 5 data bits");
}
else {
Win_CommConfig.dcb.StopBits=ONE5STOPBITS;
SetCommConfig(Win_Handle, &Win_CommConfig, sizeof(COMMCONFIG));
}
break;
/*two stop bits*/
case STOP_2:
if (Settings.DataBits==DATA_5) {
TTY_WARNING("Win_QextSerialPort: 2 stop bits cannot be used with 5 data bits");
}
else {
Win_CommConfig.dcb.StopBits=TWOSTOPBITS;
SetCommConfig(Win_Handle, &Win_CommConfig, sizeof(COMMCONFIG));
}
break;
}
}
UNLOCK_MUTEX();
}
/*!
\fn void Win_QextSerialPort::setBaudRate(BaudRateType baudRate)
Sets the baud rate of the serial port. Note that not all rates are applicable on
all platforms. The following table shows translations of the various baud rate
constants on Windows(including NT/2000) and POSIX platforms. Speeds marked with an *
are speeds that are usable on both Windows and POSIX.
\verbatim
RATE Windows Speed POSIX Speed
----------- ------------- -----------
BAUD50 110 50
BAUD75 110 75
*BAUD110 110 110
BAUD134 110 134.5
BAUD150 110 150
BAUD200 110 200
*BAUD300 300 300
*BAUD600 600 600
*BAUD1200 1200 1200
BAUD1800 1200 1800
*BAUD2400 2400 2400
*BAUD4800 4800 4800
*BAUD9600 9600 9600
BAUD14400 14400 9600
*BAUD19200 19200 19200
*BAUD38400 38400 38400
BAUD56000 56000 38400
*BAUD57600 57600 57600
BAUD76800 57600 76800
*BAUD115200 115200 115200
BAUD128000 128000 115200
BAUD256000 256000 115200
\endverbatim
*/
void Win_QextSerialPort::setBaudRate(BaudRateType baudRate) {
LOCK_MUTEX();
if (Settings.BaudRate!=baudRate) {
switch (baudRate) {
case BAUD50:
case BAUD75:
case BAUD134:
case BAUD150:
case BAUD200:
Settings.BaudRate=BAUD110;
break;
case BAUD1800:
Settings.BaudRate=BAUD1200;
break;
case BAUD76800:
Settings.BaudRate=BAUD57600;
break;
default:
Settings.BaudRate=baudRate;
break;
}
}
if (isOpen()) {
switch (baudRate) {
/*50 baud*/
case BAUD50:
TTY_WARNING("Win_QextSerialPort: Windows does not support 50 baud operation. Switching to 110 baud.");
Win_CommConfig.dcb.BaudRate=CBR_110;
break;
/*75 baud*/
case BAUD75:
TTY_WARNING("Win_QextSerialPort: Windows does not support 75 baud operation. Switching to 110 baud.");
Win_CommConfig.dcb.BaudRate=CBR_110;
break;
/*110 baud*/
case BAUD110:
Win_CommConfig.dcb.BaudRate=CBR_110;
break;
/*134.5 baud*/
case BAUD134:
TTY_WARNING("Win_QextSerialPort: Windows does not support 134.5 baud operation. Switching to 110 baud.");
Win_CommConfig.dcb.BaudRate=CBR_110;
break;
/*150 baud*/
case BAUD150:
TTY_WARNING("Win_QextSerialPort: Windows does not support 150 baud operation. Switching to 110 baud.");
Win_CommConfig.dcb.BaudRate=CBR_110;
break;
/*200 baud*/
case BAUD200:
TTY_WARNING("Win_QextSerialPort: Windows does not support 200 baud operation. Switching to 110 baud.");
Win_CommConfig.dcb.BaudRate=CBR_110;
break;
/*300 baud*/
case BAUD300:
Win_CommConfig.dcb.BaudRate=CBR_300;
break;
/*600 baud*/
case BAUD600:
Win_CommConfig.dcb.BaudRate=CBR_600;
break;
/*1200 baud*/
case BAUD1200:
Win_CommConfig.dcb.BaudRate=CBR_1200;
break;
/*1800 baud*/
case BAUD1800:
TTY_WARNING("Win_QextSerialPort: Windows does not support 1800 baud operation. Switching to 1200 baud.");
Win_CommConfig.dcb.BaudRate=CBR_1200;
break;
/*2400 baud*/
case BAUD2400:
Win_CommConfig.dcb.BaudRate=CBR_2400;
break;
/*4800 baud*/
case BAUD4800:
Win_CommConfig.dcb.BaudRate=CBR_4800;
break;
/*9600 baud*/
case BAUD9600:
Win_CommConfig.dcb.BaudRate=CBR_9600;
break;
/*14400 baud*/
case BAUD14400:
TTY_PORTABILITY_WARNING("Win_QextSerialPort Portability Warning: POSIX does not support 14400 baud operation.");
Win_CommConfig.dcb.BaudRate=CBR_14400;
break;
/*19200 baud*/
case BAUD19200:
Win_CommConfig.dcb.BaudRate=CBR_19200;
break;
/*38400 baud*/
case BAUD38400:
Win_CommConfig.dcb.BaudRate=CBR_38400;
break;
/*56000 baud*/
case BAUD56000:
TTY_PORTABILITY_WARNING("Win_QextSerialPort Portability Warning: POSIX does not support 56000 baud operation.");
Win_CommConfig.dcb.BaudRate=CBR_56000;
break;
/*57600 baud*/
case BAUD57600:
Win_CommConfig.dcb.BaudRate=CBR_57600;
break;
/*76800 baud*/
case BAUD76800:
TTY_WARNING("Win_QextSerialPort: Windows does not support 76800 baud operation. Switching to 57600 baud.");
Win_CommConfig.dcb.BaudRate=CBR_57600;
break;
/*115200 baud*/
case BAUD115200:
Win_CommConfig.dcb.BaudRate=CBR_115200;
break;
/*128000 baud*/
case BAUD128000:
TTY_PORTABILITY_WARNING("Win_QextSerialPort Portability Warning: POSIX does not support 128000 baud operation.");
Win_CommConfig.dcb.BaudRate=CBR_128000;
break;
/*256000 baud*/
case BAUD256000:
TTY_PORTABILITY_WARNING("Win_QextSerialPort Portability Warning: POSIX does not support 256000 baud operation.");
Win_CommConfig.dcb.BaudRate=CBR_256000;
break;
}
SetCommConfig(Win_Handle, &Win_CommConfig, sizeof(COMMCONFIG));
}
UNLOCK_MUTEX();
}
/*!
\fn void Win_QextSerialPort::setDtr(bool set)
Sets DTR line to the requested state (high by default). This function will have no effect if
the port associated with the class is not currently open.
*/
void Win_QextSerialPort::setDtr(bool set) {
LOCK_MUTEX();
if (isOpen()) {
if (set) {
EscapeCommFunction(Win_Handle, SETDTR);
}
else {
EscapeCommFunction(Win_Handle, CLRDTR);
}
}
UNLOCK_MUTEX();
}
/*!
\fn void Win_QextSerialPort::setRts(bool set)
Sets RTS line to the requested state (high by default). This function will have no effect if
the port associated with the class is not currently open.
*/
void Win_QextSerialPort::setRts(bool set) {
LOCK_MUTEX();
if (isOpen()) {
if (set) {
EscapeCommFunction(Win_Handle, SETRTS);
}
else {
EscapeCommFunction(Win_Handle, CLRRTS);
}
}
UNLOCK_MUTEX();
}
/*!
\fn ulong Win_QextSerialPort::lineStatus(void)
returns the line status as stored by the port function. This function will retrieve the states
of the following lines: DCD, CTS, DSR, and RI. On POSIX systems, the following additional lines
can be monitored: DTR, RTS, Secondary TXD, and Secondary RXD. The value returned is an unsigned
long with specific bits indicating which lines are high. The following constants should be used
to examine the states of individual lines:
\verbatim
Mask Line
------ ----
LS_CTS CTS
LS_DSR DSR
LS_DCD DCD
LS_RI RI
\endverbatim
This function will return 0 if the port associated with the class is not currently open.
*/
ulong Win_QextSerialPort::lineStatus(void) {
unsigned long Status=0, Temp=0;
LOCK_MUTEX();
if (isOpen()) {
GetCommModemStatus(Win_Handle, &Temp);
if (Temp&MS_CTS_ON) {
Status|=LS_CTS;
}
if (Temp&MS_DSR_ON) {
Status|=LS_DSR;
}
if (Temp&MS_RING_ON) {
Status|=LS_RI;
}
if (Temp&MS_RLSD_ON) {
Status|=LS_DCD;
}
}
UNLOCK_MUTEX();
return Status;
}
bool Win_QextSerialPort::waitForReadyRead(int msecs)
{
//@todo implement
return false;
}
qint64 Win_QextSerialPort::bytesToWrite() const
{
return _bytesToWrite;
}
void Win_QextSerialPort::monitorCommEvent()
{
DWORD eventMask = 0;
ResetEvent(overlap.hEvent);
if (!WaitCommEvent(Win_Handle, & eventMask, & overlap))
if (GetLastError() != ERROR_IO_PENDING)
qCritical("WaitCommEvent error %ld\n", GetLastError());
if (WaitForSingleObject(overlap.hEvent, INFINITE) == WAIT_OBJECT_0) {
//overlap event occured
DWORD undefined;
if (!GetOverlappedResult(Win_Handle, & overlap, & undefined, false)) {
qWarning("Comm event overlapped error %ld", GetLastError());
return;
}
if (eventMask & EV_RXCHAR) {
if (sender() != this)
emit readyRead();
}
if (eventMask & EV_TXEMPTY) {
DWORD numBytes;
GetOverlappedResult(Win_Handle, & overlapWrite, & numBytes, true);
bytesToWriteLock->lockForWrite();
if (sender() != this)
emit bytesWritten(bytesToWrite());
_bytesToWrite = 0;
bytesToWriteLock->unlock();
}
if (eventMask & EV_DSR)
if (lineStatus() & LS_DSR)
emit dsrChanged(true);
else
emit dsrChanged(false);
}
}
void Win_QextSerialPort::terminateCommWait()
{
SetCommMask(Win_Handle, 0);
}
/*!
\fn void Win_QextSerialPort::setTimeout(ulong millisec);
Sets the read and write timeouts for the port to millisec milliseconds.
Setting 0 for both sec and millisec indicates that timeouts are not used for read nor
write operations. Setting -1 indicates that read and write should return immediately.
\note this function does nothing in event driven mode.
*/
void Win_QextSerialPort::setTimeout(long millisec) {
LOCK_MUTEX();
Settings.Timeout_Millisec = millisec;
if (millisec == -1) {
Win_CommTimeouts.ReadIntervalTimeout = MAXDWORD;
Win_CommTimeouts.ReadTotalTimeoutConstant = 0;
} else {
Win_CommTimeouts.ReadIntervalTimeout = millisec;
Win_CommTimeouts.ReadTotalTimeoutConstant = millisec;
}
Win_CommTimeouts.ReadTotalTimeoutMultiplier = 0;
Win_CommTimeouts.WriteTotalTimeoutMultiplier = millisec;
Win_CommTimeouts.WriteTotalTimeoutConstant = 0;
if (queryMode() != QextSerialBase::EventDriven)
SetCommTimeouts(Win_Handle, &Win_CommTimeouts);
UNLOCK_MUTEX();
}
Win_QextSerialThread::Win_QextSerialThread(Win_QextSerialPort * qesp):
QThread()
{
this->qesp = qesp;
terminate = false;
}
void Win_QextSerialThread::stop()
{
terminate = true;
qesp->terminateCommWait();
}
void Win_QextSerialThread::run()
{
while (!terminate)
qesp->monitorCommEvent();
terminate = false;
}
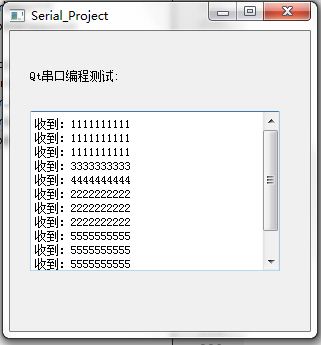
实际运行效果截图:
(-----------完----------)
























 2657
2657











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








