总列表:http://hg.openjdk.java.net/
小版本:http://hg.openjdk.java.net/jdk8u
jdk:http://hg.openjdk.java.net/jdk8u/jdk8u60/file/d8f4022fe0cd
hotspot:http://hg.openjdk.java.net/jdk8u/jdk8u60/hotspot/file/37240c1019fd
调用本地native方法
package sun.nio.ch;
public class IOUtil {
...
public static native void configureBlocking(FileDescriptor var0, boolean var1) throws IOException;对应jdk文件位置:
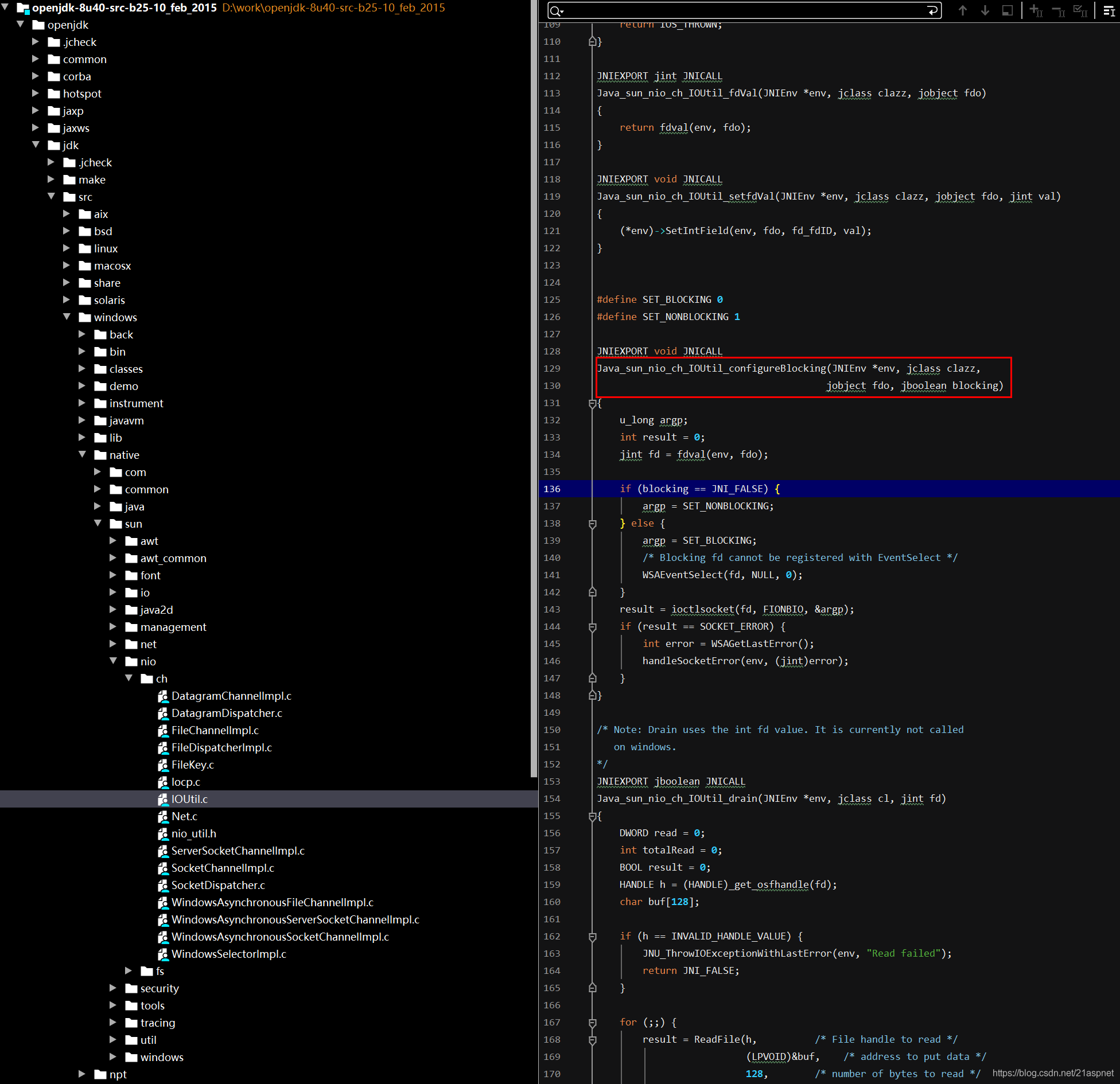
https://blog.csdn.net/wangyangzhizhou/article/details/42613273
https://www.cnblogs.com/binarylei/p/11142083.html
EPoll.c
JNIEXPORT jint JNICALL
Java_sun_nio_ch_EPoll_epollWait(JNIEnv *env, jclass c,
jint epfd, jlong address, jint numfds)
{
struct epoll_event *events = jlong_to_ptr(address);
int res;
RESTARTABLE(epoll_wait(epfd, events, numfds, -1), res);
if (res < 0) {
JNU_ThrowIOExceptionWithLastError(env, "epoll_wait failed");
}
return res;
}
这种情况在同一层可以省略EPoll,否则是找不到的
package sun.nio.ch
class EPollArrayWrapper{
private native int epollCreate();
private native void epollCtl(int epfd, int opcode, int fd, int events);
private native int epollWait(long pollAddress, int numfds, long timeout,
int epfd) throws IOException;
private static native int sizeofEPollEvent();
private static native int offsetofData();
private static native void interrupt(int fd);
private static native void init();
}void initInterrupt(int fd0, int fd1) {
outgoingInterruptFD = fd1;
incomingInterruptFD = fd0;
epollCtl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fd0, EPOLLIN);
}
int poll(long timeout) throws IOException {
updateRegistrations();
updated = epollWait(pollArrayAddress, NUM_EPOLLEVENTS, timeout, epfd);
for (int i=0; i<updated; i++) {
if (getDescriptor(i) == incomingInterruptFD) {
interruptedIndex = i;
interrupted = true;
break;
}
}
return updated;
}
调用方
package sun.nio.ch;
class EPollSelectorImpl{
/**
* Package private constructor called by factory method in
* the abstract superclass Selector.
*/
EPollSelectorImpl(SelectorProvider sp) throws IOException {
super(sp);
long pipeFds = IOUtil.makePipe(false);
fd0 = (int) (pipeFds >>> 32);
fd1 = (int) pipeFds;
pollWrapper = new EPollArrayWrapper();
pollWrapper.initInterrupt(fd0, fd1);
fdToKey = new HashMap<>();
}
protected int doSelect(long timeout) throws IOException {
if (closed)
throw new ClosedSelectorException();
processDeregisterQueue();
try {
begin();
pollWrapper.poll(timeout);
} finally {
end();
}
processDeregisterQueue();
int numKeysUpdated = updateSelectedKeys();
if (pollWrapper.interrupted()) {
// Clear the wakeup pipe
pollWrapper.putEventOps(pollWrapper.interruptedIndex(), 0);
synchronized (interruptLock) {
pollWrapper.clearInterrupted();
IOUtil.drain(fd0);
interruptTriggered = false;
}
}
return numKeysUpdated;
}
}https://www.cnblogs.com/Jack-Blog/p/12394487.html
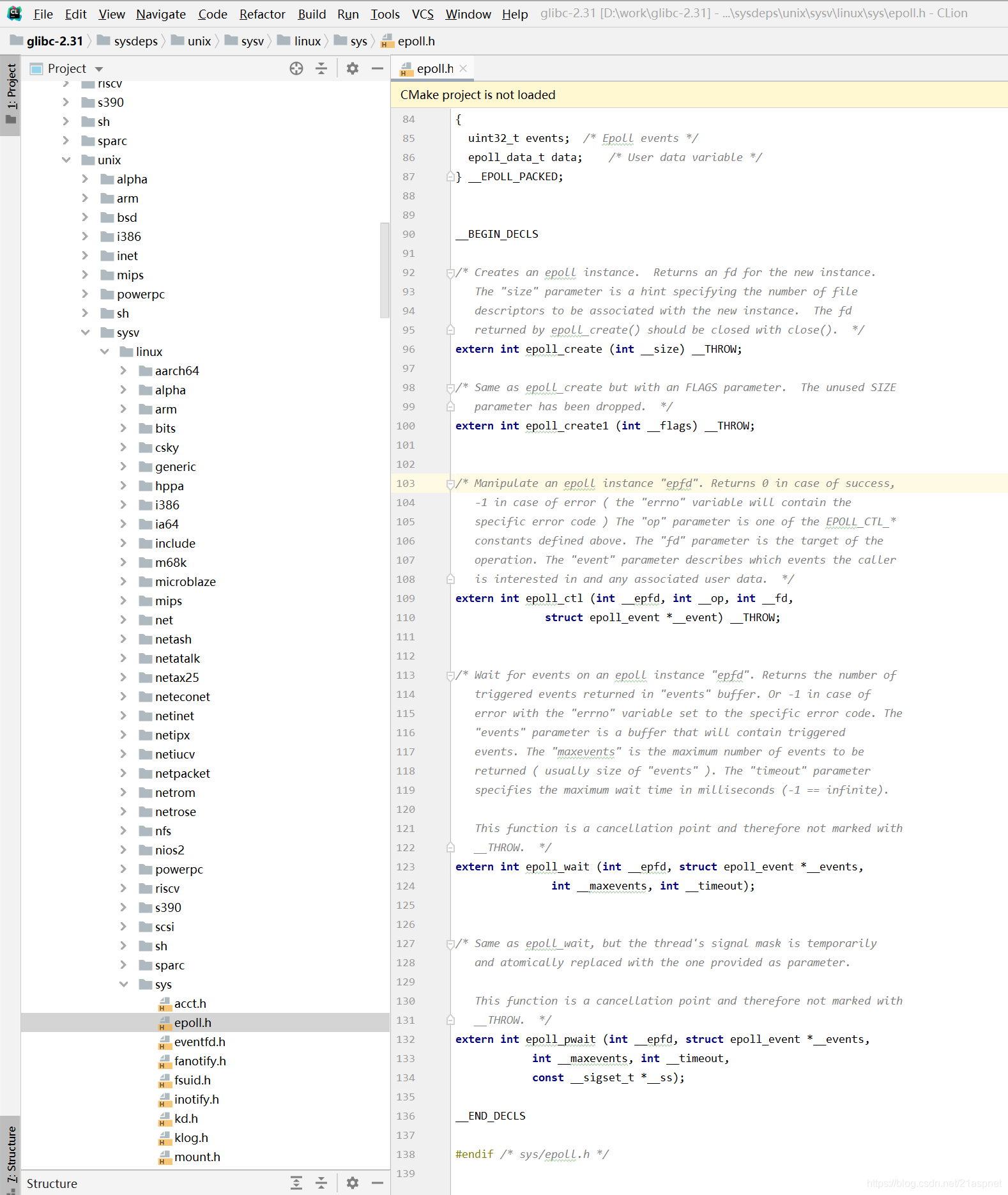
注意:epoll_wait在 \glibc-2.31\sysdeps\unix\sysv\linux\sys\epoll.h
glibc是gnu发布的libc库,也即c运行库。glibc是linux 系统中最底层的api(应用程序开发接口),几乎其它任何的运行库都会倚赖于glibc。
/* Copyright (C) 2002-2020 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This file is part of the GNU C Library.
The GNU C Library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
The GNU C Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
Lesser General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
License along with the GNU C Library; if not, see
<https://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. */
#ifndef _SYS_EPOLL_H
#define _SYS_EPOLL_H 1
#include <stdint.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <bits/types/sigset_t.h>
/* Get the platform-dependent flags. */
#include <bits/epoll.h>
#ifndef __EPOLL_PACKED
# define __EPOLL_PACKED
#endif
enum EPOLL_EVENTS
{
EPOLLIN = 0x001,
#define EPOLLIN EPOLLIN
EPOLLPRI = 0x002,
#define EPOLLPRI EPOLLPRI
EPOLLOUT = 0x004,
#define EPOLLOUT EPOLLOUT
EPOLLRDNORM = 0x040,
#define EPOLLRDNORM EPOLLRDNORM
EPOLLRDBAND = 0x080,
#define EPOLLRDBAND EPOLLRDBAND
EPOLLWRNORM = 0x100,
#define EPOLLWRNORM EPOLLWRNORM
EPOLLWRBAND = 0x200,
#define EPOLLWRBAND EPOLLWRBAND
EPOLLMSG = 0x400,
#define EPOLLMSG EPOLLMSG
EPOLLERR = 0x008,
#define EPOLLERR EPOLLERR
EPOLLHUP = 0x010,
#define EPOLLHUP EPOLLHUP
EPOLLRDHUP = 0x2000,
#define EPOLLRDHUP EPOLLRDHUP
EPOLLEXCLUSIVE = 1u << 28,
#define EPOLLEXCLUSIVE EPOLLEXCLUSIVE
EPOLLWAKEUP = 1u << 29,
#define EPOLLWAKEUP EPOLLWAKEUP
EPOLLONESHOT = 1u << 30,
#define EPOLLONESHOT EPOLLONESHOT
EPOLLET = 1u << 31
#define EPOLLET EPOLLET
};
/* Valid opcodes ( "op" parameter ) to issue to epoll_ctl(). */
#define EPOLL_CTL_ADD 1 /* Add a file descriptor to the interface. */
#define EPOLL_CTL_DEL 2 /* Remove a file descriptor from the interface. */
#define EPOLL_CTL_MOD 3 /* Change file descriptor epoll_event structure. */
typedef union epoll_data
{
void *ptr;
int fd;
uint32_t u32;
uint64_t u64;
} epoll_data_t;
struct epoll_event
{
uint32_t events; /* Epoll events */
epoll_data_t data; /* User data variable */
} __EPOLL_PACKED;
__BEGIN_DECLS
/* Creates an epoll instance. Returns an fd for the new instance.
The "size" parameter is a hint specifying the number of file
descriptors to be associated with the new instance. The fd
returned by epoll_create() should be closed with close(). */
extern int epoll_create (int __size) __THROW;
/* Same as epoll_create but with an FLAGS parameter. The unused SIZE
parameter has been dropped. */
extern int epoll_create1 (int __flags) __THROW;
/* Manipulate an epoll instance "epfd". Returns 0 in case of success,
-1 in case of error ( the "errno" variable will contain the
specific error code ) The "op" parameter is one of the EPOLL_CTL_*
constants defined above. The "fd" parameter is the target of the
operation. The "event" parameter describes which events the caller
is interested in and any associated user data. */
extern int epoll_ctl (int __epfd, int __op, int __fd,
struct epoll_event *__event) __THROW;
/* Wait for events on an epoll instance "epfd". Returns the number of
triggered events returned in "events" buffer. Or -1 in case of
error with the "errno" variable set to the specific error code. The
"events" parameter is a buffer that will contain triggered
events. The "maxevents" is the maximum number of events to be
returned ( usually size of "events" ). The "timeout" parameter
specifies the maximum wait time in milliseconds (-1 == infinite).
This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with
__THROW. */
extern int epoll_wait (int __epfd, struct epoll_event *__events,
int __maxevents, int __timeout);
/* Same as epoll_wait, but the thread's signal mask is temporarily
and atomically replaced with the one provided as parameter.
This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with
__THROW. */
extern int epoll_pwait (int __epfd, struct epoll_event *__events,
int __maxevents, int __timeout,
const __sigset_t *__ss);
__END_DECLS
#endif /* sys/epoll.h */
Epoll实现机制:
epoll fd有一个私有的struct eventpoll,它记录哪一个fd注册到了epfd上。
eventpoll 同样有一个等待队列,记录所有等待的线程。还有一个预备好的fd列表,这些fd可以进行读或写。
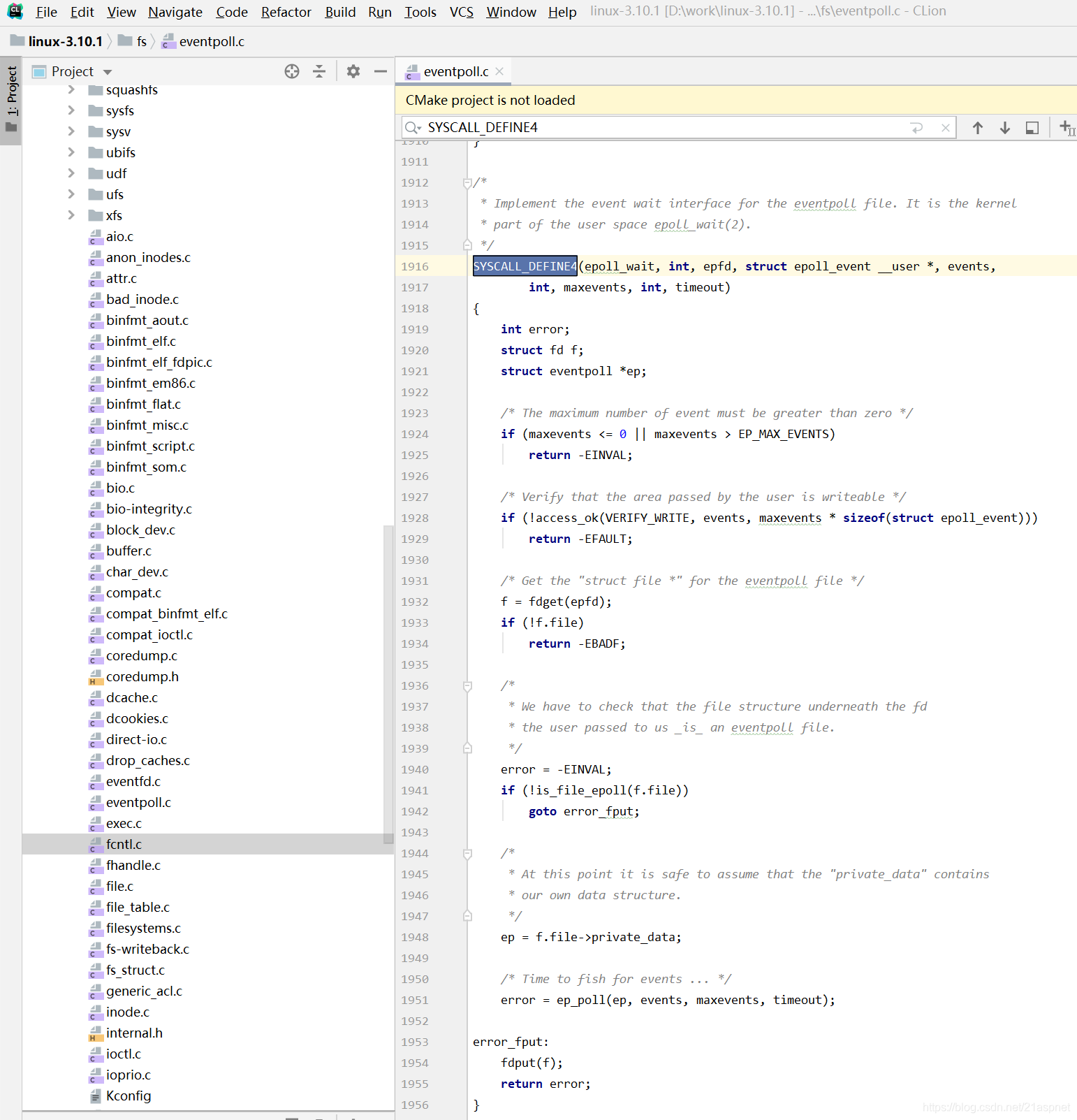
相关内核实现代码在fs/eventpoll.c
https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/master/fs/eventpoll.c
判断是否tcp有激活事件:net/ipv4/tcp.c:tcp_poll函数
/*
* fs/eventpoll.c (Efficient event retrieval implementation)
* Copyright (C) 2001,...,2009 Davide Libenzi
*
* This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
* the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
* (at your option) any later version.
*
* Davide Libenzi <davidel@xmailserver.org>
*
*/
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/file.h>
#include <linux/signal.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/mm.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include <linux/string.h>
#include <linux/list.h>
#include <linux/hash.h>
#include <linux/spinlock.h>
#include <linux/syscalls.h>
#include <linux/rbtree.h>
#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/eventpoll.h>
#include <linux/mount.h>
#include <linux/bitops.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/anon_inodes.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
#include <asm/mman.h>
#include <linux/atomic.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
#include <linux/compat.h>
/*
* LOCKING:
* There are three level of locking required by epoll :
*
* 1) epmutex (mutex)
* 2) ep->mtx (mutex)
* 3) ep->lock (spinlock)
*
* The acquire order is the one listed above, from 1 to 3.
* We need a spinlock (ep->lock) because we manipulate objects
* from inside the poll callback, that might be triggered from
* a wake_up() that in turn might be called from IRQ context.
* So we can't sleep inside the poll callback and hence we need
* a spinlock. During the event transfer loop (from kernel to
* user space) we could end up sleeping due a copy_to_user(), so
* we need a lock that will allow us to sleep. This lock is a
* mutex (ep->mtx). It is acquired during the event transfer loop,
* during epoll_ctl(EPOLL_CTL_DEL) and during eventpoll_release_file().
* Then we also need a global mutex to serialize eventpoll_release_file()
* and ep_free().
* This mutex is acquired by ep_free() during the epoll file
* cleanup path and it is also acquired by eventpoll_release_file()
* if a file has been pushed inside an epoll set and it is then
* close()d without a previous call to epoll_ctl(EPOLL_CTL_DEL).
* It is also acquired when inserting an epoll fd onto another epoll
* fd. We do this so that we walk the epoll tree and ensure that this
* insertion does not create a cycle of epoll file descriptors, which
* could lead to deadlock. We need a global mutex to prevent two
* simultaneous inserts (A into B and B into A) from racing and
* constructing a cycle without either insert observing that it is
* going to.
* It is necessary to acquire multiple "ep->mtx"es at once in the
* case when one epoll fd is added to another. In this case, we
* always acquire the locks in the order of nesting (i.e. after
* epoll_ctl(e1, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, e2), e1->mtx will always be acquired
* before e2->mtx). Since we disallow cycles of epoll file
* descriptors, this ensures that the mutexes are well-ordered. In
* order to communicate this nesting to lockdep, when walking a tree
* of epoll file descriptors, we use the current recursion depth as
* the lockdep subkey.
* It is possible to drop the "ep->mtx" and to use the global
* mutex "epmutex" (together with "ep->lock") to have it working,
* but having "ep->mtx" will make the interface more scalable.
* Events that require holding "epmutex" are very rare, while for
* normal operations the epoll private "ep->mtx" will guarantee
* a better scalability.
*/
/* Epoll private bits inside the event mask */
#define EP_PRIVATE_BITS (EPOLLWAKEUP | EPOLLONESHOT | EPOLLET)
/* Maximum number of nesting allowed inside epoll sets */
#define EP_MAX_NESTS 4
#define EP_MAX_EVENTS (INT_MAX / sizeof(struct epoll_event))
#define EP_UNACTIVE_PTR ((void *) -1L)
#define EP_ITEM_COST (sizeof(struct epitem) + sizeof(struct eppoll_entry))
struct epoll_filefd {
struct file *file;
int fd;
} __packed;
/*
* Structure used to track possible nested calls, for too deep recursions
* and loop cycles.
*/
struct nested_call_node {
struct list_head llink;
void *cookie;
void *ctx;
};
/*
* This structure is used as collector for nested calls, to check for
* maximum recursion dept and loop cycles.
*/
struct nested_calls {
struct list_head tasks_call_list;
spinlock_t lock;
};
/*
* Each file descriptor added to the eventpoll interface will
* have an entry of this type linked to the "rbr" RB tree.
* Avoid increasing the size of this struct, there can be many thousands
* of these on a server and we do not want this to take another cache line.
*/
struct epitem {
/* RB tree node used to link this structure to the eventpoll RB tree */
struct rb_node rbn;
/* List header used to link this structure to the eventpoll ready list */
struct list_head rdllink;
/*
* Works together "struct eventpoll"->ovflist in keeping the
* single linked chain of items.
*/
struct epitem *next;
/* The file descriptor information this item refers to */
struct epoll_filefd ffd;
/* Number of active wait queue attached to poll operations */
int nwait;
/* List containing poll wait queues */
struct list_head pwqlist;
/* The "container" of this item */
struct eventpoll *ep;
/* List header used to link this item to the "struct file" items list */
struct list_head fllink;
/* wakeup_source used when EPOLLWAKEUP is set */
struct wakeup_source __rcu *ws;
/* The structure that describe the interested events and the source fd */
struct epoll_event event;
};
/*
* This structure is stored inside the "private_data" member of the file
* structure and represents the main data structure for the eventpoll
* interface.
*/
struct eventpoll {
/* Protect the access to this structure */
spinlock_t lock;
/*
* This mutex is used to ensure that files are not removed
* while epoll is using them. This is held during the event
* collection loop, the file cleanup path, the epoll file exit
* code and the ctl operations.
*/
struct mutex mtx;
/* Wait queue used by sys_epoll_wait() */
wait_queue_head_t wq;
/* Wait queue used by file->poll() */
wait_queue_head_t poll_wait;
/* List of ready file descriptors */
struct list_head rdllist;
/* RB tree root used to store monitored fd structs */
struct rb_root rbr;
/*
* This is a single linked list that chains all the "struct epitem" that
* happened while transferring ready events to userspace w/out
* holding ->lock.
*/
struct epitem *ovflist;
/* wakeup_source used when ep_scan_ready_list is running */
struct wakeup_source *ws;
/* The user that created the eventpoll descriptor */
struct user_struct *user;
struct file *file;
/* used to optimize loop detection check */
int visited;
struct list_head visited_list_link;
};
/* Wait structure used by the poll hooks */
struct eppoll_entry {
/* List header used to link this structure to the "struct epitem" */
struct list_head llink;
/* The "base" pointer is set to the container "struct epitem" */
struct epitem *base;
/*
* Wait queue item that will be linked to the target file wait
* queue head.
*/
wait_queue_t wait;
/* The wait queue head that linked the "wait" wait queue item */
wait_queue_head_t *whead;
};
/* Wrapper struct used by poll queueing */
struct ep_pqueue {
poll_table pt;
struct epitem *epi;
};
/* Used by the ep_send_events() function as callback private data */
struct ep_send_events_data {
int maxevents;
struct epoll_event __user *events;
};
/*
* Configuration options available inside /proc/sys/fs/epoll/
*/
/* Maximum number of epoll watched descriptors, per user */
static long max_user_watches __read_mostly;
/*
* This mutex is used to serialize ep_free() and eventpoll_release_file().
*/
static DEFINE_MUTEX(epmutex);
/* Used to check for epoll file descriptor inclusion loops */
static struct nested_calls poll_loop_ncalls;
/* Used for safe wake up implementation */
static struct nested_calls poll_safewake_ncalls;
/* Used to call file's f_op->poll() under the nested calls boundaries */
static struct nested_calls poll_readywalk_ncalls;
/* Slab cache used to allocate "struct epitem" */
static struct kmem_cache *epi_cache __read_mostly;
/* Slab cache used to allocate "struct eppoll_entry" */
static struct kmem_cache *pwq_cache __read_mostly;
/* Visited nodes during ep_loop_check(), so we can unset them when we finish */
static LIST_HEAD(visited_list);
/*
* List of files with newly added links, where we may need to limit the number
* of emanating paths. Protected by the epmutex.
*/
static LIST_HEAD(tfile_check_list);
#ifdef CONFIG_SYSCTL
#include <linux/sysctl.h>
static long zero;
static long long_max = LONG_MAX;
ctl_table epoll_table[] = {
{
.procname = "max_user_watches",
.data = &max_user_watches,
.maxlen = sizeof(max_user_watches),
.mode = 0644,
.proc_handler = proc_doulongvec_minmax,
.extra1 = &zero,
.extra2 = &long_max,
},
{ }
};
#endif /* CONFIG_SYSCTL */
static const struct file_operations eventpoll_fops;
static inline int is_file_epoll(struct file *f)
{
return f->f_op == &eventpoll_fops;
}
/* Setup the structure that is used as key for the RB tree */
static inline void ep_set_ffd(struct epoll_filefd *ffd,
struct file *file, int fd)
{
ffd->file = file;
ffd->fd = fd;
}
/* Compare RB tree keys */
static inline int ep_cmp_ffd(struct epoll_filefd *p1,
struct epoll_filefd *p2)
{
return (p1->file > p2->file ? +1:
(p1->file < p2->file ? -1 : p1->fd - p2->fd));
}
/* Tells us if the item is currently linked */
static inline int ep_is_linked(struct list_head *p)
{
return !list_empty(p);
}
static inline struct eppoll_entry *ep_pwq_from_wait(wait_queue_t *p)
{
return container_of(p, struct eppoll_entry, wait);
}
/* Get the "struct epitem" from a wait queue pointer */
static inline struct epitem *ep_item_from_wait(wait_queue_t *p)
{
return container_of(p, struct eppoll_entry, wait)->base;
}
/* Get the "struct epitem" from an epoll queue wrapper */
static inline struct epitem *ep_item_from_epqueue(poll_table *p)
{
return container_of(p, struct ep_pqueue, pt)->epi;
}
/* Tells if the epoll_ctl(2) operation needs an event copy from userspace */
static inline int ep_op_has_event(int op)
{
return op != EPOLL_CTL_DEL;
}
/* Initialize the poll safe wake up structure */
static void ep_nested_calls_init(struct nested_calls *ncalls)
{
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&ncalls->tasks_call_list);
spin_lock_init(&ncalls->lock);
}
/**
* ep_events_available - Checks if ready events might be available.
*
* @ep: Pointer to the eventpoll context.
*
* Returns: Returns a value different than zero if ready events are available,
* or zero otherwise.
*/
static inline int ep_events_available(struct eventpoll *ep)
{
return !list_empty(&ep->rdllist) || ep->ovflist != EP_UNACTIVE_PTR;
}
/**
* ep_call_nested - Perform a bound (possibly) nested call, by checking
* that the recursion limit is not exceeded, and that
* the same nested call (by the meaning of same cookie) is
* no re-entered.
*
* @ncalls: Pointer to the nested_calls structure to be used for this call.
* @max_nests: Maximum number of allowed nesting calls.
* @nproc: Nested call core function pointer.
* @priv: Opaque data to be passed to the @nproc callback.
* @cookie: Cookie to be used to identify this nested call.
* @ctx: This instance context.
*
* Returns: Returns the code returned by the @nproc callback, or -1 if
* the maximum recursion limit has been exceeded.
*/
static int ep_call_nested(struct nested_calls *ncalls, int max_nests,
int (*nproc)(void *, void *, int), void *priv,
void *cookie, void *ctx)
{
int error, call_nests = 0;
unsigned long flags;
struct list_head *lsthead = &ncalls->tasks_call_list;
struct nested_call_node *tncur;
struct nested_call_node tnode;
spin_lock_irqsave(&ncalls->lock, flags);
/*
* Try to see if the current task is already inside this wakeup call.
* We use a list here, since the population inside this set is always
* very much limited.
*/
list_for_each_entry(tncur, lsthead, llink) {
if (tncur->ctx == ctx &&
(tncur->cookie == cookie || ++call_nests > max_nests)) {
/*
* Ops ... loop detected or maximum nest level reached.
* We abort this wake by breaking the cycle itself.
*/
error = -1;
goto out_unlock;
}
}
/* Add the current task and cookie to the list */
tnode.ctx = ctx;
tnode.cookie = cookie;
list_add(&tnode.llink, lsthead);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ncalls->lock, flags);
/* Call the nested function */
error = (*nproc)(priv, cookie, call_nests);
/* Remove the current task from the list */
spin_lock_irqsave(&ncalls->lock, flags);
list_del(&tnode.llink);
out_unlock:
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ncalls->lock, flags);
return error;
}
/*
* As described in commit 0ccf831cb lockdep: annotate epoll
* the use of wait queues used by epoll is done in a very controlled
* manner. Wake ups can nest inside each other, but are never done
* with the same locking. For example:
*
* dfd = socket(...);
* efd1 = epoll_create();
* efd2 = epoll_create();
* epoll_ctl(efd1, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, dfd, ...);
* epoll_ctl(efd2, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, efd1, ...);
*
* When a packet arrives to the device underneath "dfd", the net code will
* issue a wake_up() on its poll wake list. Epoll (efd1) has installed a
* callback wakeup entry on that queue, and the wake_up() performed by the
* "dfd" net code will end up in ep_poll_callback(). At this point epoll
* (efd1) notices that it may have some event ready, so it needs to wake up
* the waiters on its poll wait list (efd2). So it calls ep_poll_safewake()
* that ends up in another wake_up(), after having checked about the
* recursion constraints. That are, no more than EP_MAX_POLLWAKE_NESTS, to
* avoid stack blasting.
*
* When CONFIG_DEBUG_LOCK_ALLOC is enabled, make sure lockdep can handle
* this special case of epoll.
*/
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_LOCK_ALLOC
static inline void ep_wake_up_nested(wait_queue_head_t *wqueue,
unsigned long events, int subclass)
{
unsigned long flags;
spin_lock_irqsave_nested(&wqueue->lock, flags, subclass);
wake_up_locked_poll(wqueue, events);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&wqueue->lock, flags);
}
#else
static inline void ep_wake_up_nested(wait_queue_head_t *wqueue,
unsigned long events, int subclass)
{
wake_up_poll(wqueue, events);
}
#endif
static int ep_poll_wakeup_proc(void *priv, void *cookie, int call_nests)
{
ep_wake_up_nested((wait_queue_head_t *) cookie, POLLIN,
1 + call_nests);
return 0;
}
/*
* Perform a safe wake up of the poll wait list. The problem is that
* with the new callback'd wake up system, it is possible that the
* poll callback is reentered from inside the call to wake_up() done
* on the poll wait queue head. The rule is that we cannot reenter the
* wake up code from the same task more than EP_MAX_NESTS times,
* and we cannot reenter the same wait queue head at all. This will
* enable to have a hierarchy of epoll file descriptor of no more than
* EP_MAX_NESTS deep.
*/
static void ep_poll_safewake(wait_queue_head_t *wq)
{
int this_cpu = get_cpu();
ep_call_nested(&poll_safewake_ncalls, EP_MAX_NESTS,
ep_poll_wakeup_proc, NULL, wq, (void *) (long) this_cpu);
put_cpu();
}
static void ep_remove_wait_queue(struct eppoll_entry *pwq)
{
wait_queue_head_t *whead;
rcu_read_lock();
/* If it is cleared by POLLFREE, it should be rcu-safe */
whead = rcu_dereference(pwq->whead);
if (whead)
remove_wait_queue(whead, &pwq->wait);
rcu_read_unlock();
}
/*
* This function unregisters poll callbacks from the associated file
* descriptor. Must be called with "mtx" held (or "epmutex" if called from
* ep_free).
*/
static void ep_unregister_pollwait(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epitem *epi)
{
struct list_head *lsthead = &epi->pwqlist;
struct eppoll_entry *pwq;
while (!list_empty(lsthead)) {
pwq = list_first_entry(lsthead, struct eppoll_entry, llink);
list_del(&pwq->llink);
ep_remove_wait_queue(pwq);
kmem_cache_free(pwq_cache, pwq);
}
}
/* call only when ep->mtx is held */
static inline struct wakeup_source *ep_wakeup_source(struct epitem *epi)
{
return rcu_dereference_check(epi->ws, lockdep_is_held(&epi->ep->mtx));
}
/* call only when ep->mtx is held */
static inline void ep_pm_stay_awake(struct epitem *epi)
{
struct wakeup_source *ws = ep_wakeup_source(epi);
if (ws)
__pm_stay_awake(ws);
}
static inline bool ep_has_wakeup_source(struct epitem *epi)
{
return rcu_access_pointer(epi->ws) ? true : false;
}
/* call when ep->mtx cannot be held (ep_poll_callback) */
static inline void ep_pm_stay_awake_rcu(struct epitem *epi)
{
struct wakeup_source *ws;
rcu_read_lock();
ws = rcu_dereference(epi->ws);
if (ws)
__pm_stay_awake(ws);
rcu_read_unlock();
}
/**
* ep_scan_ready_list - Scans the ready list in a way that makes possible for
* the scan code, to call f_op->poll(). Also allows for
* O(NumReady) performance.
*
* @ep: Pointer to the epoll private data structure.
* @sproc: Pointer to the scan callback.
* @priv: Private opaque data passed to the @sproc callback.
* @depth: The current depth of recursive f_op->poll calls.
*
* Returns: The same integer error code returned by the @sproc callback.
*/
static int ep_scan_ready_list(struct eventpoll *ep,
int (*sproc)(struct eventpoll *,
struct list_head *, void *),
void *priv,
int depth)
{
int error, pwake = 0;
unsigned long flags;
struct epitem *epi, *nepi;
LIST_HEAD(txlist);
/*
* We need to lock this because we could be hit by
* eventpoll_release_file() and epoll_ctl().
*/
mutex_lock_nested(&ep->mtx, depth);
/*
* Steal the ready list, and re-init the original one to the
* empty list. Also, set ep->ovflist to NULL so that events
* happening while looping w/out locks, are not lost. We cannot
* have the poll callback to queue directly on ep->rdllist,
* because we want the "sproc" callback to be able to do it
* in a lockless way.
*/
spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);
list_splice_init(&ep->rdllist, &txlist);
ep->ovflist = NULL;
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);
/*
* Now call the callback function.
*/
error = (*sproc)(ep, &txlist, priv);
spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);
/*
* During the time we spent inside the "sproc" callback, some
* other events might have been queued by the poll callback.
* We re-insert them inside the main ready-list here.
*/
for (nepi = ep->ovflist; (epi = nepi) != NULL;
nepi = epi->next, epi->next = EP_UNACTIVE_PTR) {
/*
* We need to check if the item is already in the list.
* During the "sproc" callback execution time, items are
* queued into ->ovflist but the "txlist" might already
* contain them, and the list_splice() below takes care of them.
*/
if (!ep_is_linked(&epi->rdllink)) {
list_add_tail(&epi->rdllink, &ep->rdllist);
ep_pm_stay_awake(epi);
}
}
/*
* We need to set back ep->ovflist to EP_UNACTIVE_PTR, so that after
* releasing the lock, events will be queued in the normal way inside
* ep->rdllist.
*/
ep->ovflist = EP_UNACTIVE_PTR;
/*
* Quickly re-inject items left on "txlist".
*/
list_splice(&txlist, &ep->rdllist);
__pm_relax(ep->ws);
if (!list_empty(&ep->rdllist)) {
/*
* Wake up (if active) both the eventpoll wait list and
* the ->poll() wait list (delayed after we release the lock).
*/
if (waitqueue_active(&ep->wq))
wake_up_locked(&ep->wq);
if (waitqueue_active(&ep->poll_wait))
pwake++;
}
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);
mutex_unlock(&ep->mtx);
/* We have to call this outside the lock */
if (pwake)
ep_poll_safewake(&ep->poll_wait);
return error;
}
/*
* Removes a "struct epitem" from the eventpoll RB tree and deallocates
* all the associated resources. Must be called with "mtx" held.
*/
static int ep_remove(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epitem *epi)
{
unsigned long flags;
struct file *file = epi->ffd.file;
/*
* Removes poll wait queue hooks. We _have_ to do this without holding
* the "ep->lock" otherwise a deadlock might occur. This because of the
* sequence of the lock acquisition. Here we do "ep->lock" then the wait
* queue head lock when unregistering the wait queue. The wakeup callback
* will run by holding the wait queue head lock and will call our callback
* that will try to get "ep->lock".
*/
ep_unregister_pollwait(ep, epi);
/* Remove the current item from the list of epoll hooks */
spin_lock(&file->f_lock);
if (ep_is_linked(&epi->fllink))
list_del_init(&epi->fllink);
spin_unlock(&file->f_lock);
rb_erase(&epi->rbn, &ep->rbr);
spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);
if (ep_is_linked(&epi->rdllink))
list_del_init(&epi->rdllink);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);
wakeup_source_unregister(ep_wakeup_source(epi));
/* At this point it is safe to free the eventpoll item */
kmem_cache_free(epi_cache, epi);
atomic_long_dec(&ep->user->epoll_watches);
return 0;
}
static void ep_free(struct eventpoll *ep)
{
struct rb_node *rbp;
struct epitem *epi;
/* We need to release all tasks waiting for these file */
if (waitqueue_active(&ep->poll_wait))
ep_poll_safewake(&ep->poll_wait);
/*
* We need to lock this because we could be hit by
* eventpoll_release_file() while we're freeing the "struct eventpoll".
* We do not need to hold "ep->mtx" here because the epoll file
* is on the way to be removed and no one has references to it
* anymore. The only hit might come from eventpoll_release_file() but
* holding "epmutex" is sufficient here.
*/
mutex_lock(&epmutex);
/*
* Walks through the whole tree by unregistering poll callbacks.
*/
for (rbp = rb_first(&ep->rbr); rbp; rbp = rb_next(rbp)) {
epi = rb_entry(rbp, struct epitem, rbn);
ep_unregister_pollwait(ep, epi);
}
/*
* Walks through the whole tree by freeing each "struct epitem". At this
* point we are sure no poll callbacks will be lingering around, and also by
* holding "epmutex" we can be sure that no file cleanup code will hit
* us during this operation. So we can avoid the lock on "ep->lock".
* We do not need to lock ep->mtx, either, we only do it to prevent
* a lockdep warning.
*/
mutex_lock(&ep->mtx);
while ((rbp = rb_first(&ep->rbr)) != NULL) {
epi = rb_entry(rbp, struct epitem, rbn);
ep_remove(ep, epi);
}
mutex_unlock(&ep->mtx);
mutex_unlock(&epmutex);
mutex_destroy(&ep->mtx);
free_uid(ep->user);
wakeup_source_unregister(ep->ws);
kfree(ep);
}
static int ep_eventpoll_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
struct eventpoll *ep = file->private_data;
if (ep)
ep_free(ep);
return 0;
}
static inline unsigned int ep_item_poll(struct epitem *epi, poll_table *pt)
{
pt->_key = epi->event.events;
return epi->ffd.file->f_op->poll(epi->ffd.file, pt) & epi->event.events;
}
static int ep_read_events_proc(struct eventpoll *ep, struct list_head *head,
void *priv)
{
struct epitem *epi, *tmp;
poll_table pt;
init_poll_funcptr(&pt, NULL);
list_for_each_entry_safe(epi, tmp, head, rdllink) {
if (ep_item_poll(epi, &pt))
return POLLIN | POLLRDNORM;
else {
/*
* Item has been dropped into the ready list by the poll
* callback, but it's not actually ready, as far as
* caller requested events goes. We can remove it here.
*/
__pm_relax(ep_wakeup_source(epi));
list_del_init(&epi->rdllink);
}
}
return 0;
}
static int ep_poll_readyevents_proc(void *priv, void *cookie, int call_nests)
{
return ep_scan_ready_list(priv, ep_read_events_proc, NULL, call_nests + 1);
}
static unsigned int ep_eventpoll_poll(struct file *file, poll_table *wait)
{
int pollflags;
struct eventpoll *ep = file->private_data;
/* Insert inside our poll wait queue */
poll_wait(file, &ep->poll_wait, wait);
/*
* Proceed to find out if wanted events are really available inside
* the ready list. This need to be done under ep_call_nested()
* supervision, since the call to f_op->poll() done on listed files
* could re-enter here.
*/
pollflags = ep_call_nested(&poll_readywalk_ncalls, EP_MAX_NESTS,
ep_poll_readyevents_proc, ep, ep, current);
return pollflags != -1 ? pollflags : 0;
}
#ifdef CONFIG_PROC_FS
static int ep_show_fdinfo(struct seq_file *m, struct file *f)
{
struct eventpoll *ep = f->private_data;
struct rb_node *rbp;
int ret = 0;
mutex_lock(&ep->mtx);
for (rbp = rb_first(&ep->rbr); rbp; rbp = rb_next(rbp)) {
struct epitem *epi = rb_entry(rbp, struct epitem, rbn);
ret = seq_printf(m, "tfd: %8d events: %8x data: %16llx\n",
epi->ffd.fd, epi->event.events,
(long long)epi->event.data);
if (ret)
break;
}
mutex_unlock(&ep->mtx);
return ret;
}
#endif
/* File callbacks that implement the eventpoll file behaviour */
static const struct file_operations eventpoll_fops = {
#ifdef CONFIG_PROC_FS
.show_fdinfo = ep_show_fdinfo,
#endif
.release = ep_eventpoll_release,
.poll = ep_eventpoll_poll,
.llseek = noop_llseek,
};
/*
* This is called from eventpoll_release() to unlink files from the eventpoll
* interface. We need to have this facility to cleanup correctly files that are
* closed without being removed from the eventpoll interface.
*/
void eventpoll_release_file(struct file *file)
{
struct list_head *lsthead = &file->f_ep_links;
struct eventpoll *ep;
struct epitem *epi;
/*
* We don't want to get "file->f_lock" because it is not
* necessary. It is not necessary because we're in the "struct file"
* cleanup path, and this means that no one is using this file anymore.
* So, for example, epoll_ctl() cannot hit here since if we reach this
* point, the file counter already went to zero and fget() would fail.
* The only hit might come from ep_free() but by holding the mutex
* will correctly serialize the operation. We do need to acquire
* "ep->mtx" after "epmutex" because ep_remove() requires it when called
* from anywhere but ep_free().
*
* Besides, ep_remove() acquires the lock, so we can't hold it here.
*/
mutex_lock(&epmutex);
while (!list_empty(lsthead)) {
epi = list_first_entry(lsthead, struct epitem, fllink);
ep = epi->ep;
list_del_init(&epi->fllink);
mutex_lock_nested(&ep->mtx, 0);
ep_remove(ep, epi);
mutex_unlock(&ep->mtx);
}
mutex_unlock(&epmutex);
}
static int ep_alloc(struct eventpoll **pep)
{
int error;
struct user_struct *user;
struct eventpoll *ep;
user = get_current_user();
error = -ENOMEM;
ep = kzalloc(sizeof(*ep), GFP_KERNEL);
if (unlikely(!ep))
goto free_uid;
spin_lock_init(&ep->lock);
mutex_init(&ep->mtx);
init_waitqueue_head(&ep->wq);
init_waitqueue_head(&ep->poll_wait);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&ep->rdllist);
ep->rbr = RB_ROOT;
ep->ovflist = EP_UNACTIVE_PTR;
ep->user = user;
*pep = ep;
return 0;
free_uid:
free_uid(user);
return error;
}
/*
* Search the file inside the eventpoll tree. The RB tree operations
* are protected by the "mtx" mutex, and ep_find() must be called with
* "mtx" held.
*/
static struct epitem *ep_find(struct eventpoll *ep, struct file *file, int fd)
{
int kcmp;
struct rb_node *rbp;
struct epitem *epi, *epir = NULL;
struct epoll_filefd ffd;
ep_set_ffd(&ffd, file, fd);
for (rbp = ep->rbr.rb_node; rbp; ) {
epi = rb_entry(rbp, struct epitem, rbn);
kcmp = ep_cmp_ffd(&ffd, &epi->ffd);
if (kcmp > 0)
rbp = rbp->rb_right;
else if (kcmp < 0)
rbp = rbp->rb_left;
else {
epir = epi;
break;
}
}
return epir;
}
/*
* This is the callback that is passed to the wait queue wakeup
* mechanism. It is called by the stored file descriptors when they
* have events to report.
*/
static int ep_poll_callback(wait_queue_t *wait, unsigned mode, int sync, void *key)
{
int pwake = 0;
unsigned long flags;
struct epitem *epi = ep_item_from_wait(wait);
struct eventpoll *ep = epi->ep;
if ((unsigned long)key & POLLFREE) {
ep_pwq_from_wait(wait)->whead = NULL;
/*
* whead = NULL above can race with ep_remove_wait_queue()
* which can do another remove_wait_queue() after us, so we
* can't use __remove_wait_queue(). whead->lock is held by
* the caller.
*/
list_del_init(&wait->task_list);
}
spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);
/*
* If the event mask does not contain any poll(2) event, we consider the
* descriptor to be disabled. This condition is likely the effect of the
* EPOLLONESHOT bit that disables the descriptor when an event is received,
* until the next EPOLL_CTL_MOD will be issued.
*/
if (!(epi->event.events & ~EP_PRIVATE_BITS))
goto out_unlock;
/*
* Check the events coming with the callback. At this stage, not
* every device reports the events in the "key" parameter of the
* callback. We need to be able to handle both cases here, hence the
* test for "key" != NULL before the event match test.
*/
if (key && !((unsigned long) key & epi->event.events))
goto out_unlock;
/*
* If we are transferring events to userspace, we can hold no locks
* (because we're accessing user memory, and because of linux f_op->poll()
* semantics). All the events that happen during that period of time are
* chained in ep->ovflist and requeued later on.
*/
if (unlikely(ep->ovflist != EP_UNACTIVE_PTR)) {
if (epi->next == EP_UNACTIVE_PTR) {
epi->next = ep->ovflist;
ep->ovflist = epi;
if (epi->ws) {
/*
* Activate ep->ws since epi->ws may get
* deactivated at any time.
*/
__pm_stay_awake(ep->ws);
}
}
goto out_unlock;
}
/* If this file is already in the ready list we exit soon */
if (!ep_is_linked(&epi->rdllink)) {
list_add_tail(&epi->rdllink, &ep->rdllist);
ep_pm_stay_awake_rcu(epi);
}
/*
* Wake up ( if active ) both the eventpoll wait list and the ->poll()
* wait list.
*/
if (waitqueue_active(&ep->wq))
wake_up_locked(&ep->wq);
if (waitqueue_active(&ep->poll_wait))
pwake++;
out_unlock:
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);
/* We have to call this outside the lock */
if (pwake)
ep_poll_safewake(&ep->poll_wait);
return 1;
}
/*
* This is the callback that is used to add our wait queue to the
* target file wakeup lists.
*/
static void ep_ptable_queue_proc(struct file *file, wait_queue_head_t *whead,
poll_table *pt)
{
struct epitem *epi = ep_item_from_epqueue(pt);
struct eppoll_entry *pwq;
if (epi->nwait >= 0 && (pwq = kmem_cache_alloc(pwq_cache, GFP_KERNEL))) {
init_waitqueue_func_entry(&pwq->wait, ep_poll_callback);
pwq->whead = whead;
pwq->base = epi;
add_wait_queue(whead, &pwq->wait);
list_add_tail(&pwq->llink, &epi->pwqlist);
epi->nwait++;
} else {
/* We have to signal that an error occurred */
epi->nwait = -1;
}
}
static void ep_rbtree_insert(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epitem *epi)
{
int kcmp;
struct rb_node **p = &ep->rbr.rb_node, *parent = NULL;
struct epitem *epic;
while (*p) {
parent = *p;
epic = rb_entry(parent, struct epitem, rbn);
kcmp = ep_cmp_ffd(&epi->ffd, &epic->ffd);
if (kcmp > 0)
p = &parent->rb_right;
else
p = &parent->rb_left;
}
rb_link_node(&epi->rbn, parent, p);
rb_insert_color(&epi->rbn, &ep->rbr);
}
#define PATH_ARR_SIZE 5
/*
* These are the number paths of length 1 to 5, that we are allowing to emanate
* from a single file of interest. For example, we allow 1000 paths of length
* 1, to emanate from each file of interest. This essentially represents the
* potential wakeup paths, which need to be limited in order to avoid massive
* uncontrolled wakeup storms. The common use case should be a single ep which
* is connected to n file sources. In this case each file source has 1 path
* of length 1. Thus, the numbers below should be more than sufficient. These
* path limits are enforced during an EPOLL_CTL_ADD operation, since a modify
* and delete can't add additional paths. Protected by the epmutex.
*/
static const int path_limits[PATH_ARR_SIZE] = { 1000, 500, 100, 50, 10 };
static int path_count[PATH_ARR_SIZE];
static int path_count_inc(int nests)
{
/* Allow an arbitrary number of depth 1 paths */
if (nests == 0)
return 0;
if (++path_count[nests] > path_limits[nests])
return -1;
return 0;
}
static void path_count_init(void)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < PATH_ARR_SIZE; i++)
path_count[i] = 0;
}
static int reverse_path_check_proc(void *priv, void *cookie, int call_nests)
{
int error = 0;
struct file *file = priv;
struct file *child_file;
struct epitem *epi;
list_for_each_entry(epi, &file->f_ep_links, fllink) {
child_file = epi->ep->file;
if (is_file_epoll(child_file)) {
if (list_empty(&child_file->f_ep_links)) {
if (path_count_inc(call_nests)) {
error = -1;
break;
}
} else {
error = ep_call_nested(&poll_loop_ncalls,
EP_MAX_NESTS,
reverse_path_check_proc,
child_file, child_file,
current);
}
if (error != 0)
break;
} else {
printk(KERN_ERR "reverse_path_check_proc: "
"file is not an ep!\n");
}
}
return error;
}
/**
* reverse_path_check - The tfile_check_list is list of file *, which have
* links that are proposed to be newly added. We need to
* make sure that those added links don't add too many
* paths such that we will spend all our time waking up
* eventpoll objects.
*
* Returns: Returns zero if the proposed links don't create too many paths,
* -1 otherwise.
*/
static int reverse_path_check(void)
{
int error = 0;
struct file *current_file;
/* let's call this for all tfiles */
list_for_each_entry(current_file, &tfile_check_list, f_tfile_llink) {
path_count_init();
error = ep_call_nested(&poll_loop_ncalls, EP_MAX_NESTS,
reverse_path_check_proc, current_file,
current_file, current);
if (error)
break;
}
return error;
}
static int ep_create_wakeup_source(struct epitem *epi)
{
const char *name;
struct wakeup_source *ws;
if (!epi->ep->ws) {
epi->ep->ws = wakeup_source_register("eventpoll");
if (!epi->ep->ws)
return -ENOMEM;
}
name = epi->ffd.file->f_path.dentry->d_name.name;
ws = wakeup_source_register(name);
if (!ws)
return -ENOMEM;
rcu_assign_pointer(epi->ws, ws);
return 0;
}
/* rare code path, only used when EPOLL_CTL_MOD removes a wakeup source */
static noinline void ep_destroy_wakeup_source(struct epitem *epi)
{
struct wakeup_source *ws = ep_wakeup_source(epi);
RCU_INIT_POINTER(epi->ws, NULL);
/*
* wait for ep_pm_stay_awake_rcu to finish, synchronize_rcu is
* used internally by wakeup_source_remove, too (called by
* wakeup_source_unregister), so we cannot use call_rcu
*/
synchronize_rcu();
wakeup_source_unregister(ws);
}
/*
* Must be called with "mtx" held.
*/
static int ep_insert(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epoll_event *event,
struct file *tfile, int fd)
{
int error, revents, pwake = 0;
unsigned long flags;
long user_watches;
struct epitem *epi;
struct ep_pqueue epq;
user_watches = atomic_long_read(&ep->user->epoll_watches);
if (unlikely(user_watches >= max_user_watches))
return -ENOSPC;
if (!(epi = kmem_cache_alloc(epi_cache, GFP_KERNEL)))
return -ENOMEM;
/* Item initialization follow here ... */
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&epi->rdllink);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&epi->fllink);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&epi->pwqlist);
epi->ep = ep;
ep_set_ffd(&epi->ffd, tfile, fd);
epi->event = *event;
epi->nwait = 0;
epi->next = EP_UNACTIVE_PTR;
if (epi->event.events & EPOLLWAKEUP) {
error = ep_create_wakeup_source(epi);
if (error)
goto error_create_wakeup_source;
} else {
RCU_INIT_POINTER(epi->ws, NULL);
}
/* Initialize the poll table using the queue callback */
epq.epi = epi;
init_poll_funcptr(&epq.pt, ep_ptable_queue_proc);
/*
* Attach the item to the poll hooks and get current event bits.
* We can safely use the file* here because its usage count has
* been increased by the caller of this function. Note that after
* this operation completes, the poll callback can start hitting
* the new item.
*/
revents = ep_item_poll(epi, &epq.pt);
/*
* We have to check if something went wrong during the poll wait queue
* install process. Namely an allocation for a wait queue failed due
* high memory pressure.
*/
error = -ENOMEM;
if (epi->nwait < 0)
goto error_unregister;
/* Add the current item to the list of active epoll hook for this file */
spin_lock(&tfile->f_lock);
list_add_tail(&epi->fllink, &tfile->f_ep_links);
spin_unlock(&tfile->f_lock);
/*
* Add the current item to the RB tree. All RB tree operations are
* protected by "mtx", and ep_insert() is called with "mtx" held.
*/
ep_rbtree_insert(ep, epi);
/* now check if we've created too many backpaths */
error = -EINVAL;
if (reverse_path_check())
goto error_remove_epi;
/* We have to drop the new item inside our item list to keep track of it */
spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);
/* If the file is already "ready" we drop it inside the ready list */
if ((revents & event->events) && !ep_is_linked(&epi->rdllink)) {
list_add_tail(&epi->rdllink, &ep->rdllist);
ep_pm_stay_awake(epi);
/* Notify waiting tasks that events are available */
if (waitqueue_active(&ep->wq))
wake_up_locked(&ep->wq);
if (waitqueue_active(&ep->poll_wait))
pwake++;
}
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);
atomic_long_inc(&ep->user->epoll_watches);
/* We have to call this outside the lock */
if (pwake)
ep_poll_safewake(&ep->poll_wait);
return 0;
error_remove_epi:
spin_lock(&tfile->f_lock);
if (ep_is_linked(&epi->fllink))
list_del_init(&epi->fllink);
spin_unlock(&tfile->f_lock);
rb_erase(&epi->rbn, &ep->rbr);
error_unregister:
ep_unregister_pollwait(ep, epi);
/*
* We need to do this because an event could have been arrived on some
* allocated wait queue. Note that we don't care about the ep->ovflist
* list, since that is used/cleaned only inside a section bound by "mtx".
* And ep_insert() is called with "mtx" held.
*/
spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);
if (ep_is_linked(&epi->rdllink))
list_del_init(&epi->rdllink);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);
wakeup_source_unregister(ep_wakeup_source(epi));
error_create_wakeup_source:
kmem_cache_free(epi_cache, epi);
return error;
}
/*
* Modify the interest event mask by dropping an event if the new mask
* has a match in the current file status. Must be called with "mtx" held.
*/
static int ep_modify(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epitem *epi, struct epoll_event *event)
{
int pwake = 0;
unsigned int revents;
poll_table pt;
init_poll_funcptr(&pt, NULL);
/*
* Set the new event interest mask before calling f_op->poll();
* otherwise we might miss an event that happens between the
* f_op->poll() call and the new event set registering.
*/
epi->event.events = event->events; /* need barrier below */
epi->event.data = event->data; /* protected by mtx */
if (epi->event.events & EPOLLWAKEUP) {
if (!ep_has_wakeup_source(epi))
ep_create_wakeup_source(epi);
} else if (ep_has_wakeup_source(epi)) {
ep_destroy_wakeup_source(epi);
}
/*
* The following barrier has two effects:
*
* 1) Flush epi changes above to other CPUs. This ensures
* we do not miss events from ep_poll_callback if an
* event occurs immediately after we call f_op->poll().
* We need this because we did not take ep->lock while
* changing epi above (but ep_poll_callback does take
* ep->lock).
*
* 2) We also need to ensure we do not miss _past_ events
* when calling f_op->poll(). This barrier also
* pairs with the barrier in wq_has_sleeper (see
* comments for wq_has_sleeper).
*
* This barrier will now guarantee ep_poll_callback or f_op->poll
* (or both) will notice the readiness of an item.
*/
smp_mb();
/*
* Get current event bits. We can safely use the file* here because
* its usage count has been increased by the caller of this function.
*/
revents = ep_item_poll(epi, &pt);
/*
* If the item is "hot" and it is not registered inside the ready
* list, push it inside.
*/
if (revents & event->events) {
spin_lock_irq(&ep->lock);
if (!ep_is_linked(&epi->rdllink)) {
list_add_tail(&epi->rdllink, &ep->rdllist);
ep_pm_stay_awake(epi);
/* Notify waiting tasks that events are available */
if (waitqueue_active(&ep->wq))
wake_up_locked(&ep->wq);
if (waitqueue_active(&ep->poll_wait))
pwake++;
}
spin_unlock_irq(&ep->lock);
}
/* We have to call this outside the lock */
if (pwake)
ep_poll_safewake(&ep->poll_wait);
return 0;
}
static int ep_send_events_proc(struct eventpoll *ep, struct list_head *head,
void *priv)
{
struct ep_send_events_data *esed = priv;
int eventcnt;
unsigned int revents;
struct epitem *epi;
struct epoll_event __user *uevent;
struct wakeup_source *ws;
poll_table pt;
init_poll_funcptr(&pt, NULL);
/*
* We can loop without lock because we are passed a task private list.
* Items cannot vanish during the loop because ep_scan_ready_list() is
* holding "mtx" during this call.
*/
for (eventcnt = 0, uevent = esed->events;
!list_empty(head) && eventcnt < esed->maxevents;) {
epi = list_first_entry(head, struct epitem, rdllink);
/*
* Activate ep->ws before deactivating epi->ws to prevent
* triggering auto-suspend here (in case we reactive epi->ws
* below).
*
* This could be rearranged to delay the deactivation of epi->ws
* instead, but then epi->ws would temporarily be out of sync
* with ep_is_linked().
*/
ws = ep_wakeup_source(epi);
if (ws) {
if (ws->active)
__pm_stay_awake(ep->ws);
__pm_relax(ws);
}
list_del_init(&epi->rdllink);
revents = ep_item_poll(epi, &pt);
/*
* If the event mask intersect the caller-requested one,
* deliver the event to userspace. Again, ep_scan_ready_list()
* is holding "mtx", so no operations coming from userspace
* can change the item.
*/
if (revents) {
if (__put_user(revents, &uevent->events) ||
__put_user(epi->event.data, &uevent->data)) {
list_add(&epi->rdllink, head);
ep_pm_stay_awake(epi);
return eventcnt ? eventcnt : -EFAULT;
}
eventcnt++;
uevent++;
if (epi->event.events & EPOLLONESHOT)
epi->event.events &= EP_PRIVATE_BITS;
else if (!(epi->event.events & EPOLLET)) {
/*
* If this file has been added with Level
* Trigger mode, we need to insert back inside
* the ready list, so that the next call to
* epoll_wait() will check again the events
* availability. At this point, no one can insert
* into ep->rdllist besides us. The epoll_ctl()
* callers are locked out by
* ep_scan_ready_list() holding "mtx" and the
* poll callback will queue them in ep->ovflist.
*/
list_add_tail(&epi->rdllink, &ep->rdllist);
ep_pm_stay_awake(epi);
}
}
}
return eventcnt;
}
static int ep_send_events(struct eventpoll *ep,
struct epoll_event __user *events, int maxevents)
{
struct ep_send_events_data esed;
esed.maxevents = maxevents;
esed.events = events;
return ep_scan_ready_list(ep, ep_send_events_proc, &esed, 0);
}
static inline struct timespec ep_set_mstimeout(long ms)
{
struct timespec now, ts = {
.tv_sec = ms / MSEC_PER_SEC,
.tv_nsec = NSEC_PER_MSEC * (ms % MSEC_PER_SEC),
};
ktime_get_ts(&now);
return timespec_add_safe(now, ts);
}
/**
* ep_poll - Retrieves ready events, and delivers them to the caller supplied
* event buffer.
*
* @ep: Pointer to the eventpoll context.
* @events: Pointer to the userspace buffer where the ready events should be
* stored.
* @maxevents: Size (in terms of number of events) of the caller event buffer.
* @timeout: Maximum timeout for the ready events fetch operation, in
* milliseconds. If the @timeout is zero, the function will not block,
* while if the @timeout is less than zero, the function will block
* until at least one event has been retrieved (or an error
* occurred).
*
* Returns: Returns the number of ready events which have been fetched, or an
* error code, in case of error.
*/
static int ep_poll(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epoll_event __user *events,
int maxevents, long timeout)
{
int res = 0, eavail, timed_out = 0;
unsigned long flags;
long slack = 0;
wait_queue_t wait;
ktime_t expires, *to = NULL;
if (timeout > 0) {
struct timespec end_time = ep_set_mstimeout(timeout);
slack = select_estimate_accuracy(&end_time);
to = &expires;
*to = timespec_to_ktime(end_time);
} else if (timeout == 0) {
/*
* Avoid the unnecessary trip to the wait queue loop, if the
* caller specified a non blocking operation.
*/
timed_out = 1;
spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);
goto check_events;
}
fetch_events:
spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);
if (!ep_events_available(ep)) {
/*
* We don't have any available event to return to the caller.
* We need to sleep here, and we will be wake up by
* ep_poll_callback() when events will become available.
*/
init_waitqueue_entry(&wait, current);
__add_wait_queue_exclusive(&ep->wq, &wait);
for (;;) {
/*
* We don't want to sleep if the ep_poll_callback() sends us
* a wakeup in between. That's why we set the task state
* to TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE before doing the checks.
*/
set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
if (ep_events_available(ep) || timed_out)
break;
if (signal_pending(current)) {
res = -EINTR;
break;
}
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);
if (!schedule_hrtimeout_range(to, slack, HRTIMER_MODE_ABS))
timed_out = 1;
spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);
}
__remove_wait_queue(&ep->wq, &wait);
set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);
}
check_events:
/* Is it worth to try to dig for events ? */
eavail = ep_events_available(ep);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);
/*
* Try to transfer events to user space. In case we get 0 events and
* there's still timeout left over, we go trying again in search of
* more luck.
*/
if (!res && eavail &&
!(res = ep_send_events(ep, events, maxevents)) && !timed_out)
goto fetch_events;
return res;
}
/**
* ep_loop_check_proc - Callback function to be passed to the @ep_call_nested()
* API, to verify that adding an epoll file inside another
* epoll structure, does not violate the constraints, in
* terms of closed loops, or too deep chains (which can
* result in excessive stack usage).
*
* @priv: Pointer to the epoll file to be currently checked.
* @cookie: Original cookie for this call. This is the top-of-the-chain epoll
* data structure pointer.
* @call_nests: Current dept of the @ep_call_nested() call stack.
*
* Returns: Returns zero if adding the epoll @file inside current epoll
* structure @ep does not violate the constraints, or -1 otherwise.
*/
static int ep_loop_check_proc(void *priv, void *cookie, int call_nests)
{
int error = 0;
struct file *file = priv;
struct eventpoll *ep = file->private_data;
struct eventpoll *ep_tovisit;
struct rb_node *rbp;
struct epitem *epi;
mutex_lock_nested(&ep->mtx, call_nests + 1);
ep->visited = 1;
list_add(&ep->visited_list_link, &visited_list);
for (rbp = rb_first(&ep->rbr); rbp; rbp = rb_next(rbp)) {
epi = rb_entry(rbp, struct epitem, rbn);
if (unlikely(is_file_epoll(epi->ffd.file))) {
ep_tovisit = epi->ffd.file->private_data;
if (ep_tovisit->visited)
continue;
error = ep_call_nested(&poll_loop_ncalls, EP_MAX_NESTS,
ep_loop_check_proc, epi->ffd.file,
ep_tovisit, current);
if (error != 0)
break;
} else {
/*
* If we've reached a file that is not associated with
* an ep, then we need to check if the newly added
* links are going to add too many wakeup paths. We do
* this by adding it to the tfile_check_list, if it's
* not already there, and calling reverse_path_check()
* during ep_insert().
*/
if (list_empty(&epi->ffd.file->f_tfile_llink))
list_add(&epi->ffd.file->f_tfile_llink,
&tfile_check_list);
}
}
mutex_unlock(&ep->mtx);
return error;
}
/**
* ep_loop_check - Performs a check to verify that adding an epoll file (@file)
* another epoll file (represented by @ep) does not create
* closed loops or too deep chains.
*
* @ep: Pointer to the epoll private data structure.
* @file: Pointer to the epoll file to be checked.
*
* Returns: Returns zero if adding the epoll @file inside current epoll
* structure @ep does not violate the constraints, or -1 otherwise.
*/
static int ep_loop_check(struct eventpoll *ep, struct file *file)
{
int ret;
struct eventpoll *ep_cur, *ep_next;
ret = ep_call_nested(&poll_loop_ncalls, EP_MAX_NESTS,
ep_loop_check_proc, file, ep, current);
/* clear visited list */
list_for_each_entry_safe(ep_cur, ep_next, &visited_list,
visited_list_link) {
ep_cur->visited = 0;
list_del(&ep_cur->visited_list_link);
}
return ret;
}
static void clear_tfile_check_list(void)
{
struct file *file;
/* first clear the tfile_check_list */
while (!list_empty(&tfile_check_list)) {
file = list_first_entry(&tfile_check_list, struct file,
f_tfile_llink);
list_del_init(&file->f_tfile_llink);
}
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&tfile_check_list);
}
/*
* Open an eventpoll file descriptor.
*/
SYSCALL_DEFINE1(epoll_create1, int, flags)
{
int error, fd;
struct eventpoll *ep = NULL;
struct file *file;
/* Check the EPOLL_* constant for consistency. */
BUILD_BUG_ON(EPOLL_CLOEXEC != O_CLOEXEC);
if (flags & ~EPOLL_CLOEXEC)
return -EINVAL;
/*
* Create the internal data structure ("struct eventpoll").
*/
error = ep_alloc(&ep);
if (error < 0)
return error;
/*
* Creates all the items needed to setup an eventpoll file. That is,
* a file structure and a free file descriptor.
*/
fd = get_unused_fd_flags(O_RDWR | (flags & O_CLOEXEC));
if (fd < 0) {
error = fd;
goto out_free_ep;
}
file = anon_inode_getfile("[eventpoll]", &eventpoll_fops, ep,
O_RDWR | (flags & O_CLOEXEC));
if (IS_ERR(file)) {
error = PTR_ERR(file);
goto out_free_fd;
}
ep->file = file;
fd_install(fd, file);
return fd;
out_free_fd:
put_unused_fd(fd);
out_free_ep:
ep_free(ep);
return error;
}
SYSCALL_DEFINE1(epoll_create, int, size)
{
if (size <= 0)
return -EINVAL;
return sys_epoll_create1(0);
}
/*
* The following function implements the controller interface for
* the eventpoll file that enables the insertion/removal/change of
* file descriptors inside the interest set.
*/
SYSCALL_DEFINE4(epoll_ctl, int, epfd, int, op, int, fd,
struct epoll_event __user *, event)
{
int error;
int did_lock_epmutex = 0;
struct file *file, *tfile;
struct eventpoll *ep;
struct epitem *epi;
struct epoll_event epds;
error = -EFAULT;
if (ep_op_has_event(op) &&
copy_from_user(&epds, event, sizeof(struct epoll_event)))
goto error_return;
/* Get the "struct file *" for the eventpoll file */
error = -EBADF;
file = fget(epfd);
if (!file)
goto error_return;
/* Get the "struct file *" for the target file */
tfile = fget(fd);
if (!tfile)
goto error_fput;
/* The target file descriptor must support poll */
error = -EPERM;
if (!tfile->f_op || !tfile->f_op->poll)
goto error_tgt_fput;
/* Check if EPOLLWAKEUP is allowed */
if ((epds.events & EPOLLWAKEUP) && !capable(CAP_BLOCK_SUSPEND))
epds.events &= ~EPOLLWAKEUP;
/*
* We have to check that the file structure underneath the file descriptor
* the user passed to us _is_ an eventpoll file. And also we do not permit
* adding an epoll file descriptor inside itself.
*/
error = -EINVAL;
if (file == tfile || !is_file_epoll(file))
goto error_tgt_fput;
/*
* At this point it is safe to assume that the "private_data" contains
* our own data structure.
*/
ep = file->private_data;
/*
* When we insert an epoll file descriptor, inside another epoll file
* descriptor, there is the change of creating closed loops, which are
* better be handled here, than in more critical paths. While we are
* checking for loops we also determine the list of files reachable
* and hang them on the tfile_check_list, so we can check that we
* haven't created too many possible wakeup paths.
*
* We need to hold the epmutex across both ep_insert and ep_remove
* b/c we want to make sure we are looking at a coherent view of
* epoll network.
*/
if (op == EPOLL_CTL_ADD || op == EPOLL_CTL_DEL) {
mutex_lock(&epmutex);
did_lock_epmutex = 1;
}
if (op == EPOLL_CTL_ADD) {
if (is_file_epoll(tfile)) {
error = -ELOOP;
if (ep_loop_check(ep, tfile) != 0) {
clear_tfile_check_list();
goto error_tgt_fput;
}
} else
list_add(&tfile->f_tfile_llink, &tfile_check_list);
}
mutex_lock_nested(&ep->mtx, 0);
/*
* Try to lookup the file inside our RB tree, Since we grabbed "mtx"
* above, we can be sure to be able to use the item looked up by
* ep_find() till we release the mutex.
*/
epi = ep_find(ep, tfile, fd);
error = -EINVAL;
switch (op) {
case EPOLL_CTL_ADD:
if (!epi) {
epds.events |= POLLERR | POLLHUP;
error = ep_insert(ep, &epds, tfile, fd);
} else
error = -EEXIST;
clear_tfile_check_list();
break;
case EPOLL_CTL_DEL:
if (epi)
error = ep_remove(ep, epi);
else
error = -ENOENT;
break;
case EPOLL_CTL_MOD:
if (epi) {
epds.events |= POLLERR | POLLHUP;
error = ep_modify(ep, epi, &epds);
} else
error = -ENOENT;
break;
}
mutex_unlock(&ep->mtx);
error_tgt_fput:
if (did_lock_epmutex)
mutex_unlock(&epmutex);
fput(tfile);
error_fput:
fput(file);
error_return:
return error;
}
/*
* Implement the event wait interface for the eventpoll file. It is the kernel
* part of the user space epoll_wait(2).
*/
SYSCALL_DEFINE4(epoll_wait, int, epfd, struct epoll_event __user *, events,
int, maxevents, int, timeout)
{
int error;
struct fd f;
struct eventpoll *ep;
/* The maximum number of event must be greater than zero */
if (maxevents <= 0 || maxevents > EP_MAX_EVENTS)
return -EINVAL;
/* Verify that the area passed by the user is writeable */
if (!access_ok(VERIFY_WRITE, events, maxevents * sizeof(struct epoll_event)))
return -EFAULT;
/* Get the "struct file *" for the eventpoll file */
f = fdget(epfd);
if (!f.file)
return -EBADF;
/*
* We have to check that the file structure underneath the fd
* the user passed to us _is_ an eventpoll file.
*/
error = -EINVAL;
if (!is_file_epoll(f.file))
goto error_fput;
/*
* At this point it is safe to assume that the "private_data" contains
* our own data structure.
*/
ep = f.file->private_data;
/* Time to fish for events ... */
error = ep_poll(ep, events, maxevents, timeout);
error_fput:
fdput(f);
return error;
}
/*
* Implement the event wait interface for the eventpoll file. It is the kernel
* part of the user space epoll_pwait(2).
*/
SYSCALL_DEFINE6(epoll_pwait, int, epfd, struct epoll_event __user *, events,
int, maxevents, int, timeout, const sigset_t __user *, sigmask,
size_t, sigsetsize)
{
int error;
sigset_t ksigmask, sigsaved;
/*
* If the caller wants a certain signal mask to be set during the wait,
* we apply it here.
*/
if (sigmask) {
if (sigsetsize != sizeof(sigset_t))
return -EINVAL;
if (copy_from_user(&ksigmask, sigmask, sizeof(ksigmask)))
return -EFAULT;
sigdelsetmask(&ksigmask, sigmask(SIGKILL) | sigmask(SIGSTOP));
sigprocmask(SIG_SETMASK, &ksigmask, &sigsaved);
}
error = sys_epoll_wait(epfd, events, maxevents, timeout);
/*
* If we changed the signal mask, we need to restore the original one.
* In case we've got a signal while waiting, we do not restore the
* signal mask yet, and we allow do_signal() to deliver the signal on
* the way back to userspace, before the signal mask is restored.
*/
if (sigmask) {
if (error == -EINTR) {
memcpy(¤t->saved_sigmask, &sigsaved,
sizeof(sigsaved));
set_restore_sigmask();
} else
sigprocmask(SIG_SETMASK, &sigsaved, NULL);
}
return error;
}
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
COMPAT_SYSCALL_DEFINE6(epoll_pwait, int, epfd,
struct epoll_event __user *, events,
int, maxevents, int, timeout,
const compat_sigset_t __user *, sigmask,
compat_size_t, sigsetsize)
{
long err;
compat_sigset_t csigmask;
sigset_t ksigmask, sigsaved;
/*
* If the caller wants a certain signal mask to be set during the wait,
* we apply it here.
*/
if (sigmask) {
if (sigsetsize != sizeof(compat_sigset_t))
return -EINVAL;
if (copy_from_user(&csigmask, sigmask, sizeof(csigmask)))
return -EFAULT;
sigset_from_compat(&ksigmask, &csigmask);
sigdelsetmask(&ksigmask, sigmask(SIGKILL) | sigmask(SIGSTOP));
sigprocmask(SIG_SETMASK, &ksigmask, &sigsaved);
}
err = sys_epoll_wait(epfd, events, maxevents, timeout);
/*
* If we changed the signal mask, we need to restore the original one.
* In case we've got a signal while waiting, we do not restore the
* signal mask yet, and we allow do_signal() to deliver the signal on
* the way back to userspace, before the signal mask is restored.
*/
if (sigmask) {
if (err == -EINTR) {
memcpy(¤t->saved_sigmask, &sigsaved,
sizeof(sigsaved));
set_restore_sigmask();
} else
sigprocmask(SIG_SETMASK, &sigsaved, NULL);
}
return err;
}
#endif
static int __init eventpoll_init(void)
{
struct sysinfo si;
si_meminfo(&si);
/*
* Allows top 4% of lomem to be allocated for epoll watches (per user).
*/
max_user_watches = (((si.totalram - si.totalhigh) / 25) << PAGE_SHIFT) /
EP_ITEM_COST;
BUG_ON(max_user_watches < 0);
/*
* Initialize the structure used to perform epoll file descriptor
* inclusion loops checks.
*/
ep_nested_calls_init(&poll_loop_ncalls);
/* Initialize the structure used to perform safe poll wait head wake ups */
ep_nested_calls_init(&poll_safewake_ncalls);
/* Initialize the structure used to perform file's f_op->poll() calls */
ep_nested_calls_init(&poll_readywalk_ncalls);
/*
* We can have many thousands of epitems, so prevent this from
* using an extra cache line on 64-bit (and smaller) CPUs
*/
BUILD_BUG_ON(sizeof(void *) <= 8 && sizeof(struct epitem) > 128);
/* Allocates slab cache used to allocate "struct epitem" items */
epi_cache = kmem_cache_create("eventpoll_epi", sizeof(struct epitem),
0, SLAB_HWCACHE_ALIGN | SLAB_PANIC, NULL);
/* Allocates slab cache used to allocate "struct eppoll_entry" */
pwq_cache = kmem_cache_create("eventpoll_pwq",
sizeof(struct eppoll_entry), 0, SLAB_PANIC, NULL);
return 0;
}
fs_initcall(eventpoll_init);
https://linux.die.net/man/2/epoll_wait
http://www.man7.org/linux/man-pages/man2/epoll_wait.2.html
epoll内核源码详解+自己总结的流程 这个是比较完整的注释。
内核是导致瓶颈的原因所在,要解决问题需要绕过内核。所以主流解决方案都是旁路网卡IO,绕过内核直接在用户态收发包来解决内核的瓶颈。

图片引自Jingjing Wu的文档《Flow Bifurcation on Intel® Ethernet Controller X710/XL710》
左边是原来的方式数据从 网卡 -> 驱动 -> 协议栈 -> Socket接口 -> 业务
右边是DPDK的方式,基于UIO(Userspace I/O)旁路数据。数据从 网卡 -> DPDK轮询模式-> DPDK基础库 -> 业务
用户态的好处是易用开发和维护,灵活性好。并且Crash也不影响内核运行,鲁棒性强。
























 6万+
6万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








