目录
一、MyBatis-Plus简介
1、简介
**MyBatis-Plus (简称 MP)**是一个 MyBatis的增强工具,在 MyBatis 的基础上只做增强不做改变,为 简化开发、提高效率而生。Mybatis-Plus提供了通用的Mapper和Service,**可以在不编写任何SQL语句的前提下,快速的实现单表的增删改查(CURD),批量,逻辑删除,分页等操作。**只要把MyBatis-Plus的特性到优秀插件,以及多数据源的配置进行详细讲解。

2、特性
无侵入:只做增强不做改变,引入它不会对现有工程产生影响,如丝般顺滑。
损耗小:启动即会自动注入基本 CURD,性能基本无损耗,直接面向对象操作强大的 CRUD 操作:内置通用 Mapper、通用 Service,仅仅通过少量配置即可实现单表大部分 CRUD 操作,更有强大的条件构造器,满足各类使用需求。
支持 Lambda 形式调用:通过 Lambda 表达式,方便的编写各类查询条件,无需再担心字段写错 支持主键自动生成:支持多达 4 种主键策略(内含分布式唯一 ID 生成器 - Sequence),可自由配置,完美解决主键问题。
支持 ActiveRecord 模式:支持 ActiveRecord 形式调用,实体类只需继承 Model 类即可进行强 大的 CRUD 操作。
支持自定义全局通用操作:支持全局通用方法注入(Write once, use anywhere )。
内置代码生成器:采用代码或者 Maven 插件可快速生成 Mapper 、 Model 、 Service 、 Controller 层代码,支持模板引擎,更有超多自定义配置等您来使用内置分页插件:基于 MyBatis 物理分页,开发者无需关心具体操作,配置好插件之后,写分页等 同于普通 List 查询。
分页插件支持多种数据库:支持 MySQL、 MariaDB、Oracle、 DB2、 H2、 HSQL、SQLite、 Postgre、SQLServer 等多种数据库。
内置性能分析插件:可输出 SQL 语句以及其执行时间,建议开发测试时启用该功能,能快速揪出 慢查询。
内置全局拦截插件:提供全表 delete 、 update 操作智能分析阻断,也可自定义拦截规则,预防 误操作。
3、框架结构
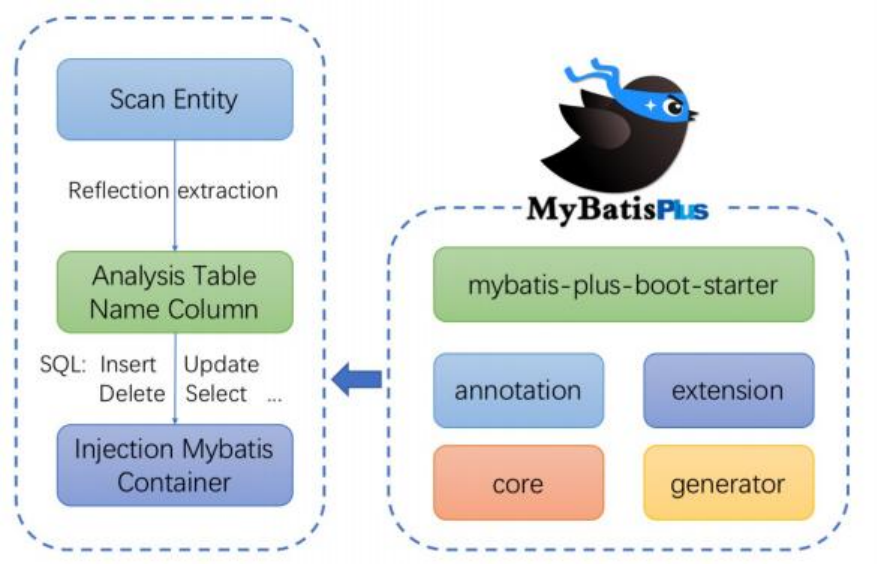
4、代码及文档地址
官方地址: http://mp.baomidou.com
代码发布地址:Github: https://github.com/baomidou/mybatis-plus
Gitee: https://gitee.com/baomidou/mybatis-plus
文档发布地址: https://baomidou.com/pages/24112f
二、入门案例
1、创建数据库及表
创建数据库如下:
CREATE DATABASE `mybatis_plus` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 */; use `mybatis_plus`;
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '主键ID',
`name` varchar(30) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '姓名 ',
`age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '年龄 ',
`email` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '邮箱 ',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
添加下面的数据:
INSERT INTO user (id, name, age, email) VALUES
(1, 'Jone', 18, 'test1@baomidou.com'),
(2, 'Jack', 20, 'test2@baomidou.com'),
(3, 'Tom', 28, 'test3@baomidou.com'),
(4, 'Sandy', 21, 'test4@baomidou.com'),
(5, 'Billie', 24, 'test5@baomidou.com');
2、引入数据库依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.5.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
三、编写代码
1、编写application.yml文件
spring:
datasource:
# 配置数据源类型
type: com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
# 配置连接数据库信息
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis_plus?characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false
username: root
password: root
#mybatis:
# mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml #对应mapper映射xml文件所在路径
# type-aliases-package: #对应实体类路径
# 配置MyBatis日志
mybatis-plus:
mapper-locations: classpath*:com/qcby/mapper/*.xml
type-aliases-package: com.qcby.entity
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
2、启动类添加扫描注解
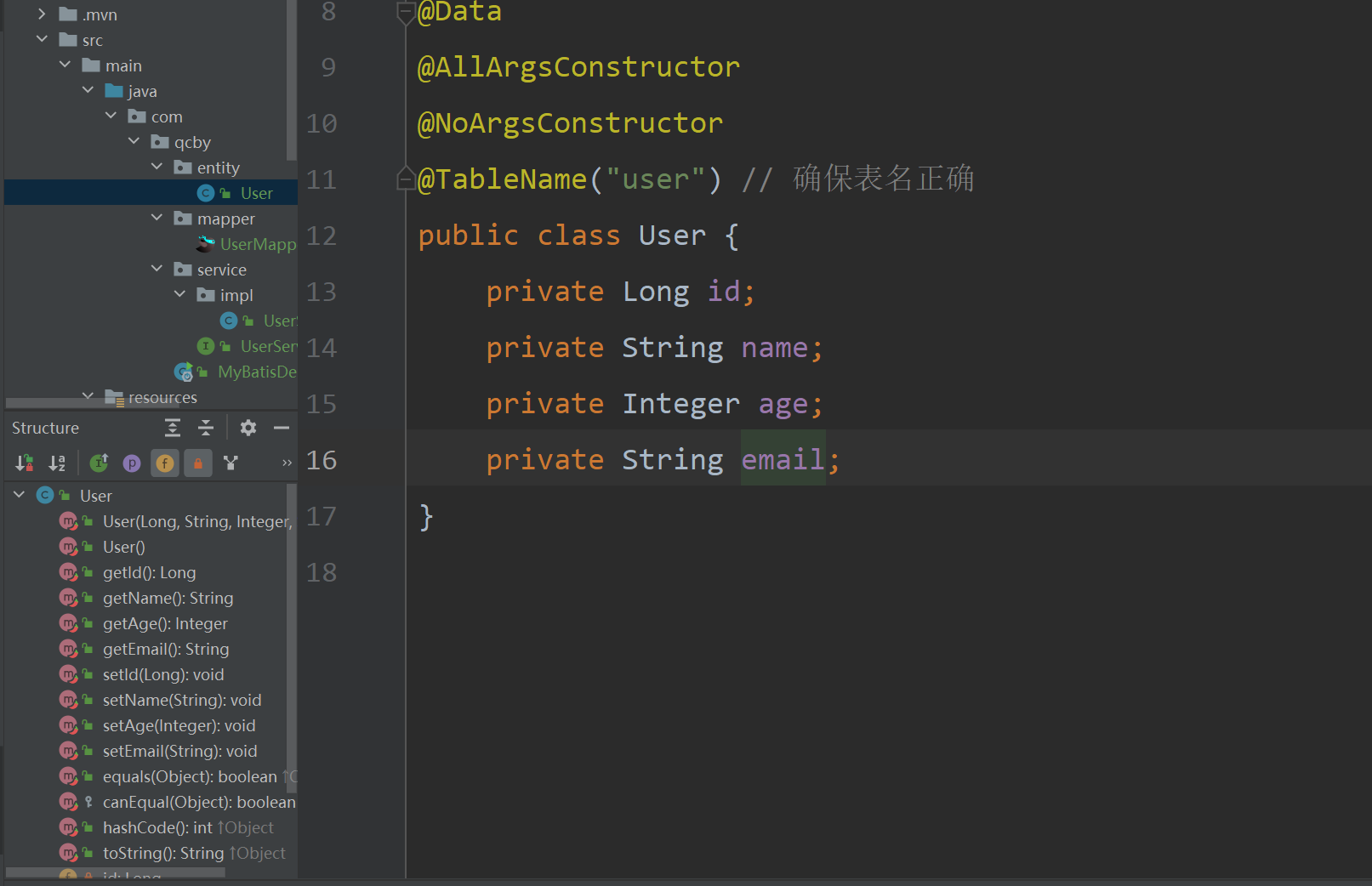
3、添加实体
package com.qcby.entity;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableName;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@TableName("user") // 确保表名正确
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
}
使用ait+7查看该实体类中的get和set方法,并且进行查看:
BaseMapper是MyBatis-Plus提供的模板mapper,其中包含了基本的CRUD方法,泛型为操作的 实体类型
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
}
4、添加日志
在application.yml中配置日志输出
mybatis-plus:
mapper-locations: classpath*:com/qcby/mapper/*.xml
type-aliases-package: com.qcby.entity
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
一、基本CRUD
当我使用MybatisPlus的时候,需要自己定义Mapper的接口用于继承BaseMapper,其中BaseMapper中有以下的方法:
public interface BaseMapper<T> extends Mapper<T> {
int insert(T entity);
int deleteById(Serializable id);
int deleteById(T entity);
int deleteByMap(@Param("cm") Map<String, Object> columnMap);
int delete(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
int deleteBatchIds(@Param("coll") Collection<?> idList);
int updateById(@Param("et") T entity);
int update(@Param("et") T entity, @Param("ew") Wrapper<T> updateWrapper);
T selectById(Serializable id);
List<T> selectBatchIds(@Param("coll") Collection<? extends Serializable> idList);
List<T> selectByMap(@Param("cm") Map<String, Object> columnMap);
default T selectOne(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper) {
List<T> list = this.selectList(queryWrapper);
if (list.size() == 1) {
return list.get(0);
} else if (list.size() > 1) {
throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());
} else {
return null;
}
}
default boolean exists(Wrapper<T> queryWrapper) {
Long count = this.selectCount(queryWrapper);
return null != count && count > 0L;
}
Long selectCount(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
List<T> selectList(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
List<Map<String, Object>> selectMaps(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
List<Object> selectObjs(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
<P extends IPage<T>> P selectPage(P page, @Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
<P extends IPage<Map<String, Object>>> P selectMapsPage(P page, @Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
}
1、增加
MyBatisPlus中的方法中只有下面这一个增加好的方法:
int insert(T entity);
测试方法:
@Test
public void testInsert(){
User user = new User();
user.setName("张三");
user.setAge(23);
// user.setEmail("asdasdas@163.com");
int rows = userMapper.insert(user);
// SQL: INSERT INTO user ( name, age, email ) VALUES ( ?, ?, ? )
}
上面方法使用的雪花算法,添加的id值不是随之之前的自动递增的,而是雪花算法计算出来的。
雪花算法(Snowflake) 是 Twitter 开源的分布式ID生成算法,生成的ID是64位的Long类型数字,结构如下:
0 - 0000000000 0000000000 0000000000 0000000000 0 - 00000 - 00000 - 000000000000
1位:符号位(始终为0)
41位:时间戳(毫秒级,可用69年)
10位:机器ID(5位数据中心 + 5位机器ID)
12位:序列号(每毫秒可生成4096个ID)
可以在application.yaml文件中进行配置,配置如下:
mybatis-plus:
global-config:
db-config:
id-type: assign_id # 使用雪花算法生成ID
# 其他可选值:
# auto: 数据库自增
# none: 未设置主键类型
# input: 用户输入ID
# assign_id: 雪花算法
# assign_uuid: UUID
第二种方式如下:
@Data
@TableName("user")
public class User {
@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO) // 只需要这个注解即可
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
}
插入后ID会自动回填到实体对象中
2、删除
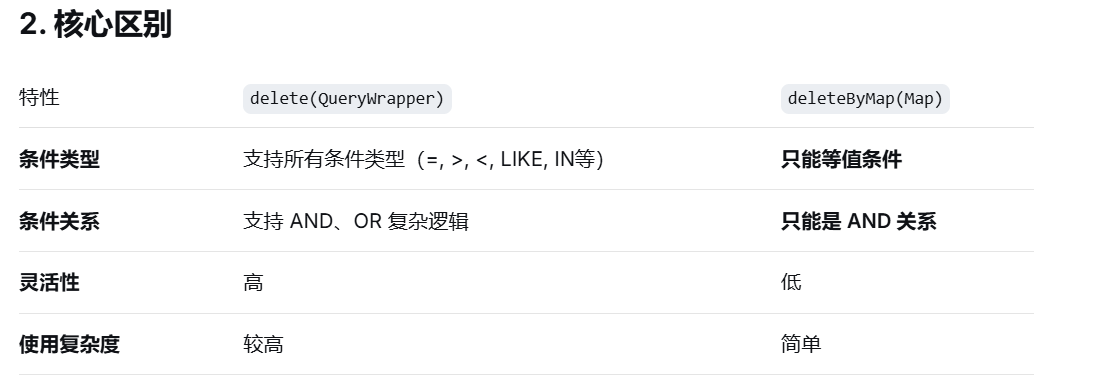
MybatisPlus中的删除的方法一共有以下的几种方法:
int deleteById(Serializable id);
int deleteById(T entity);
int deleteByMap(@Param("cm") Map<String, Object> columnMap);
int delete(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
int deleteBatchIds(@Param("coll") Collection<?> idList);
其中的第一个是根据id进行删除:
等同于下面的情况:
int rows = userMapper.deleteById(4L);
// SQL: DELETE FROM user WHERE id = 4
其中的第二个是根据id进行删除:
等同于下面的情况:
User user = new User();
user.setName("张三");
int rows3 = userMapper.deleteById(user);
// SQL: DELETE FROM user WHERE name = '张三'
其余的使用方式:
int rows1 = userMapper.delete(new QueryWrapper<User>().eq("name", "张三"));
// SQL: DELETE FROM user WHERE name = '张三'
int rows2 = userMapper.deleteBatchIds(Arrays.asList(5L, 6L));
// SQL: DELETE FROM user WHERE id in (5,6)
int rouw3 = userMapper.deleteByMap(new HashMap<String, Object>(){
{
put("name", "张三");
put("age", 23);
}
});
// SQL: DELETE FROM user WHERE name = '张三' and age = 23
3、修改
修改有下面的方法:
int updateById(@Param("et") T entity);
int update(@Param("et") T entity, @Param("ew") Wrapper<T> updateWrapper);
测试方法如下:
public void testUpdate(){
userMapper.updateById(new User(4L, "admin", 22, "asadasdas@163.com"));
UpdateWrapper<User> wrapper = new UpdateWrapper<>();
wrapper.set("age", 30) // 设置字段
.set("email", "new@email.com") // 设置字段
.eq("name", "张三"); // 设置条件
int rows = userMapper.update(null, wrapper);
// SQL: UPDATE user SET age=30, email='new@email.com' WHERE name = '张三'
}
4、查询
T selectById(Serializable id);
List<T> selectBatchIds(@Param("coll") Collection<? extends Serializable> idList);
List<T> selectByMap(@Param("cm") Map<String, Object> columnMap);
default T selectOne(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper) {
List<T> list = this.selectList(queryWrapper);
if (list.size() == 1) {
return list.get(0);
} else if (list.size() > 1) {
throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());
} else {
return null;
}
}
default boolean exists(Wrapper<T> queryWrapper) {
Long count = this.selectCount(queryWrapper);
return null != count && count > 0L;
}
Long selectCount(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
List<T> selectList(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
List<Map<String, Object>> selectMaps(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
List<Object> selectObjs(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
<P extends IPage<T>> P selectPage(P page, @Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
<P extends IPage<Map<String, Object>>> P selectMapsPage(P page, @Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
根据id查询
T selectById(Serializable id);
根据id数组查询
List<T> selectBatchIds(@Param("coll") Collection<? extends Serializable> idList);
根据传入的实体类对象查询,只能等值查询:
List<T> selectByMap(@Param("cm") Map<String, Object> columnMap);
根据查询条件如果有的话且数量为1个则返回,没有返回
default T selectOne(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper) {
List<T> list = this.selectList(queryWrapper);
if (list.size() == 1) {
return list.get(0);
} else if (list.size() > 1) {
throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());
} else {
return null;
}
}
根据自定义的查询条件分别输出数量和数据:
Long selectCount(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
List<T> selectList(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
查询特定字段的数据,并且返回:
List<Map<String, Object>> selectMaps(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
查询并且返回唯一的字段:
List<Object> selectObjs(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
根据输入分页的,页码和每一页的大小以及相对应的条件返回数据;
<P extends IPage<T>> P selectPage(P page, @Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
<P extends IPage<Map<String, Object>>> P selectMapsPage(P page, @Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
测试方法如下:
//selectList()根据MP内置的条件构造器查询一个list集合,null表示没有条件,即查询所有
// 1、查询全部
List<User> userlist = userMapper.selectList(null);
System.out.println(userlist);
// 2、根据id查询
User user = userMapper.selectById(1);
System.out.println(user);
// 3、根据ids查询
List<Long> list = Arrays.asList(1L, 2L, 3L);
List<User> users = userMapper.selectBatchIds(list);
// 4、根据条件查询全部字段
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name","张三");
List<User> userCondation = userMapper.selectByMap(map);
// 查询特定字段,返回 Map
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.select("name", "age") // 只查询 name 和 age 字段
.eq("age", 25);
List<Map<String, Object>> mapList = userMapper.selectMaps(wrapper);
// 返回: List<Map>,每个Map的key是字段名,value是字段值
// 使用: mapList.get(0).get("name"), mapList.get(0).get("age")
// 生成的SQL: SELECT name, age FROM user WHERE age = 25
System.out.println(mapList);
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper1 = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.select("name") // 查询 name 字段
.eq("age", 25);
List<Object> names = userMapper.selectObjs(wrapper);
// 返回: ["张三", "李四", "王五"] - 只有 name 字段的值
// 使用: String name = (String) names.get(0);
// 生成的SQL: SELECT name FROM user WHERE age = 25
//
@Test
public void testSelectPage() {
System.out.println("=== selectPage 分页查询实体 ===");
// 1. 创建分页对象
Page<User> page = new Page<>(1, 10); // 第1页,每页10条
// 2. 创建查询条件
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
// 3. 执行分页查询
Page<User> result = userMapper.selectPage(page, wrapper);
// 4. 处理结果
System.out.println("总记录数: " + result.getTotal());
System.out.println("总页数: " + result.getPages());
System.out.println("当前页: " + result.getCurrent());
System.out.println("每页大小: " + result.getSize());
System.out.println("当前页数据: " + result.getRecords().size());
// 遍历当前页数据
result.getRecords().forEach(user -> {
System.out.println("用户: " + user.getName() + ", 年龄: " + user.getAge());
});
}
@Test
public void testSelectPage() {
System.out.println("=== selectPage 分页查询实体 ===");
// 1. 创建分页对象
Page<User> page = new Page<>(1, 10); // 第1页,每页10条
// 2. 创建查询条件
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
// 3. 执行分页查询
Page<User> result = userMapper.selectPage(page, wrapper);
// 4. 处理结果
System.out.println("总记录数: " + result.getTotal());
System.out.println("总页数: " + result.getPages());
System.out.println("当前页: " + result.getCurrent());
System.out.println("每页大小: " + result.getSize());
System.out.println("当前页数据: " + result.getRecords().size());
// 遍历当前页数据
result.getRecords().forEach(user -> {
System.out.println("用户: " + user.getName() + ", 年龄: " + user.getAge());
});
}




















 774
774

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








