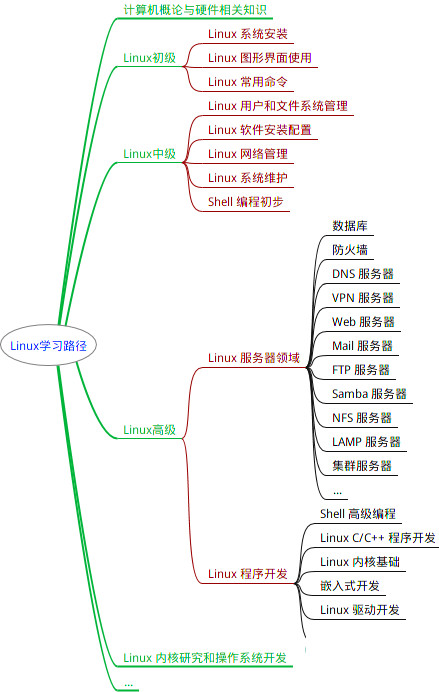
最全的Linux教程,Linux从入门到精通
======================
-
linux从入门到精通(第2版)
-
Linux系统移植
-
Linux驱动开发入门与实战
-
LINUX 系统移植 第2版
-
Linux开源网络全栈详解 从DPDK到OpenFlow

第一份《Linux从入门到精通》466页
====================
内容简介
====
本书是获得了很多读者好评的Linux经典畅销书**《Linux从入门到精通》的第2版**。本书第1版出版后曾经多次印刷,并被51CTO读书频道评为“最受读者喜爱的原创IT技术图书奖”。本书第﹖版以最新的Ubuntu 12.04为版本,循序渐进地向读者介绍了Linux 的基础应用、系统管理、网络应用、娱乐和办公、程序开发、服务器配置、系统安全等。本书附带1张光盘,内容为本书配套多媒体教学视频。另外,本书还为读者提供了大量的Linux学习资料和Ubuntu安装镜像文件,供读者免费下载。

本书适合广大Linux初中级用户、开源软件爱好者和大专院校的学生阅读,同时也非常适合准备从事Linux平台开发的各类人员。
需要《Linux入门到精通》、《linux系统移植》、《Linux驱动开发入门实战》、《Linux开源网络全栈》电子书籍及教程的工程师朋友们劳烦您转发+评论
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!
更多参数设置说明:
choosing viral groups (--include-groups)
The available options are dsDNAphage, NCLDV, RNA, ssDNA virus, and lavidaviridae. The default is dsDNAphage and ssDNA (changed from all groups since version 2.2), suitable for those only interested in phage. If you are only interested in RNA virus, you can run:
rm -rf test.out
virsorter run -w test.out -i test.fa --include-groups RNA -j 4 all
re-run with different score cutoff (--min-score and --classify)
VirSorter2 takes one positional argument, all or classify. The default is all, which means running the whole pipeline, including 1) preprocessing, 2) annotation (feature extraction), and 3) classification. The main computational bottleneck is the annotation step, taking about 95% of CPU time. In case you just want to re-run with different score cutoff (–min-score), classify argument can skip the annotation steps, and only re-run only the classify step.
virsorter run -w test.out -i test.fa --include-groups "dsDNAphage,ssDNA" -j 4 --min-score 0.8 classify
The above overwrites the previous final output files. If you want to keep previous results, you can use --label to add a prefix to the new final output files.
virsorter run -w test.out -i test.fa --include-groups "dsDNAphage,ssDNA" -j 4 --min-score 0.9 --label rerun classify
speed up a run (--provirus-off)
In case you need to have some results quickly, there are two options: 1) turn off provirus step with --provirus-off; this reduces sensitivity on sequences that are only partially viral; 2) subsample ORFs from each sequence with --max-orf-per-seq; This option subsamples ORFs if a sequence has more ORFs than the number provided. Note that this option is only availale when --provirus-off is used.
rm -rf test.out
virsorter run -w test.out -i test.fa --provirus-off --max-orf-per-seq 20 all
其他选项
You can run virsorter run -h to see all options. VirSorter2 is a wrapper around snakemake, a great pipeline management tool designed for reproducibility, and running on computer clusters. All snakemake options still work with VirSorter2, and users can simply append those snakemake option to virsorter options (after all or classify). For example, the --forceall snakemake option can be used to re-run the pipeline.
virsorter run -w test.out -i test.fa --provirus-off --max-orf-per-seq 20 all --forceall
When you re-run any VirSorter2 command, it will pick up at the step (rule in snakemake term) where it stopped last time. It will do nothing if it succeeded last time. The --forceall option can be used to enforce the re-run.
DRAMv compatibility
DRAMv is a tool for annotating viral contigs identified by VirSorter. It needs two input files from VirSorter: 1) viral contigs, 2) affi-contigs.tab that have info on viral/nonviral and hallmark genes along contigs. In VirSorter2, these files can be generated by --prep-for-dramv flag.
rm -rf test.out
virsorter run --prep-for-dramv -w test.out -i test.fa -j 4 all
ls test.out/for-dramv
Detailed description on output files
- final-viral-combined.fa
identified viral sequences, including two types:
- full sequences identified as viral (identified with suffix
||full);- partial sequences identified as viral (identified with suffix
||{i}_partial); here{i}can be numbers starting from 0 to max number of viral fragments found in that contig;- short (less than two genes) sequences with hallmark genes identified as viral (identified with suffix
||lt2gene);
- final-viral-score.tsv
This table can be used for further screening of results. It includes the following columns:
- sequence name
- score of each viral sequences across groups (multiple columns)
- max score across groups
- max score group
- contig length
- hallmark gene count
- viral gene %
- nonviral gene %
NOTE
Note that classifiers of different viral groups are not exclusive from each other, and may have overlap in their target viral sequence space, which means this information should not be used or considered as reliable taxonomic classification. We limit the purpose of VirSorter2 to viral idenfication only.
- final-viral-boundary.tsv
only some of the columns in this file might be useful:
- seqname: original sequence name
- trim_orf_index_start, trim_orf_index_end: start and end ORF index on orignal sequence of identified viral sequence
- trim_bp_start, trim_bp_end: start and end position on orignal sequence of identified viral sequence
- trim_pr: score of final trimmed viral sequence
- partial: full sequence as viral or partial sequence as viral; this is defined when a full sequence has score > score cutoff, it is full (0), or else any viral sequence extracted within it is partial (1)
- pr_full: score of the original sequence
- hallmark_cnt: hallmark gene count
- group: the classifier of viral group that gives high score; this should NOT be used as reliable classification
NOTE
VirSorter2 tends to sometimes overestimate the size of viral sequence during provirus extraction procedure in order to achieve better sensitity. We recommend cleaning these provirus predictions to remove potential host genes on the edge of the predicted viral region, e.g. using a tool like CheckV (Bitbucket).
Training customized classifiers
VirSorter2 currently has classifiers of five viral groups (dsDNAphage, NCLDV, RNA, ssNA virus, and lavidaviridae). It’s designed for easy addition of more classifiers. The information of classifiers are store in the database (-d) specified during setup step. For each viral group, it needs four files below:
- model
random forest classifier model for identifying viral sequences
- customized.hmm (optional)
a collection of viral HMMs for gene annotation; if not specified, the one in
db/hmm/viral/combined.hmmis used.
- hallmark-gene.list (optional)
names of hallmark gene hmm in the above viral hmm database file; These hallmark gene hmms can be collected by literature search or identified by comparing hallmark gene sequences (protein) against HMMs database above with
hmmsearch; if not specified, no hallmark genes are counted in feature table
- rbs-prodigal-train.db (optional)
prodigal RBS (ribosomal binding site) motif training model; this can be produced with
-toption in prodigal; This is useful feature for NCLDV due to large genome size for training; For other viral groups, it’s OK to skip this file.
In this tutorial, I will show how to make model for the autolykiviridae family.
First, prepare the dataset needed: 1) high quality viral genomes 2) protein sequence of hallmark gene; and install two more dependecies.
# download genome sequences
wget https://github.com/jiarong/small-dataset/raw/master/autolyki/vibrio_autolyki.fna.gz -O autolyki.fna.gz
# download hallmark gene seqs
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jiarong/small-dataset/master/autolyki/DJR.fa -O DJR.fa
# download source code
git clone https://github.com/jiarong/VirSorter2.git
# install two more dependencies
conda install -c bioconda -y screed hmmer
Then identify hallmark gene HMMs by protein sequences of hallmark genes
Note that we will need the VirSorter2 database here. If you skip the tutorial above, you can download the database by virsorter setup -d db -j 4. This will take 10+ mins.
# compare all HMMs and protein sequences of hallmark gene
# this will take 10+ mins due to large hmm database file
hmmsearch -T 50 --tblout DJR.hmmtbl --cpu 4 -o /dev/null db/hmm/viral/combined.hmm DJR.fa
# get HMMs names that are signicant hits with protein sequences of hallmark gene
python VirSorter2/virsorter/scripts/prepdb-train-get-seq-from-hmm-domtbl.py 50 DJR.hmmtbl > hallmark-gene.list
With hallmark-gene.list and the high quality genomes autolyki.fna.gz, you can train the features that are used for the classifier model.
# train feature file
virsorter train-feature --seqfile autolyki.fna.gz --hallmark hallmark-gene.list --hmm db/hmm/viral/combined.hmm --frags-per-genome 5 --jobs 4 -w autolyki-feature.out
# check output
ls autolyki-feature.out
In the output directory (autolyki-feature.out), all.pdg.ftr is the feature file needed for next step.
To make the classifier model, we also need a feature file from cellular organisms. This can be done by collecting genomes from cellular organisms and repeat the above step. Note number of cellular genomes are very large (>200K). Here I will re-use the feature file I have prepared before.
# fetch feature file for cellular organisms
wget https://zenodo.org/record/3823805/files/nonviral-common-random-fragments.ftr.gz?download=1 -O nonviral.ftr.gz
gzip -d nonviral.ftr.gz
# train the classifier model
virsorter train-model --viral-ftrfile autolyki-feature.out/all.pdg.ftr --nonviral-ftrfile nonviral.ftr --balanced --jobs 4 -w autolyki-model.out
In autolyki-model.out, feature-importances.tsv shows the importance of each feature used. model is the classifier model we need. Then put the model and hallmark-gene.list in database directory as the existing viral groups. Note that only letters are allowed for group directory under db/group/.
### attention: only letters (both upper and lower case) are allowed in group names
mkdir db/group/autolykiviridae
cp autolyki-model.out/model db/group/autolykiviridae
cp hallmark-gene.list db/group/autolykiviridae/
Now you can try this new classifier on the testing dataset, and compare with dsDNAphage classifier:
# download the testing dataset
wget -O test.fa https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jiarong/VirSorter2/master/test/8seq.fa
# identify viral sequences in testing dataset; it takes 10+ mins;
virsorter run -w autolyki-model-test.out -i test.fa --include-groups "dsDNAphage,autolykiviridae" -j 4 --min-score 0.8 all
# check the scores in two classifiers
cat autolyki-model-test.out/final-viral-score.tsv
FAQ
Q: How should I pick a score cutoff?
A: Generally, those with score >0.9 are high confidence. Those with score between 0.5 and 0.9 could be a mixture of viral and non-viral. It’s hard to find a optimal score separating viral and non-viral since it depends on % of host sequence and unknown sequences. So we recommend using the default cutoff (0.5) for maximal sensitivity and then applying a quality checking step using checkV to for removing false positives (other than predicting completeness). Here is the viral identification SOP in the Sullivan Lab https://www.protocols.io/view/viral-sequence-identification-sop-with-virsorter2-btv8nn9w.这里还是给大家推荐一下官方的SOP分析流程,前面已经写了,大家参考使用即可
https://www.protocols.io/view/viral-sequence-identification-sop-with-virsorter2-btv8nn9w.这里还是给大家推荐一下官方的SOP分析流程,前面已经写了,大家参考使用即可
为了做好运维面试路上的助攻手,特整理了上百道 【运维技术栈面试题集锦】 ,让你面试不慌心不跳,高薪offer怀里抱!
这次整理的面试题,小到shell、MySQL,大到K8s等云原生技术栈,不仅适合运维新人入行面试需要,还适用于想提升进阶跳槽加薪的运维朋友。

本份面试集锦涵盖了
- 174 道运维工程师面试题
- 128道k8s面试题
- 108道shell脚本面试题
- 200道Linux面试题
- 51道docker面试题
- 35道Jenkis面试题
- 78道MongoDB面试题
- 17道ansible面试题
- 60道dubbo面试题
- 53道kafka面试
- 18道mysql面试题
- 40道nginx面试题
- 77道redis面试题
- 28道zookeeper
总计 1000+ 道面试题, 内容 又全含金量又高
- 174道运维工程师面试题
1、什么是运维?
2、在工作中,运维人员经常需要跟运营人员打交道,请问运营人员是做什么工作的?
3、现在给你三百台服务器,你怎么对他们进行管理?
4、简述raid0 raid1raid5二种工作模式的工作原理及特点
5、LVS、Nginx、HAproxy有什么区别?工作中你怎么选择?
6、Squid、Varinsh和Nginx有什么区别,工作中你怎么选择?
7、Tomcat和Resin有什么区别,工作中你怎么选择?
8、什么是中间件?什么是jdk?
9、讲述一下Tomcat8005、8009、8080三个端口的含义?
10、什么叫CDN?
11、什么叫网站灰度发布?
12、简述DNS进行域名解析的过程?
13、RabbitMQ是什么东西?
14、讲一下Keepalived的工作原理?
15、讲述一下LVS三种模式的工作过程?
16、mysql的innodb如何定位锁问题,mysql如何减少主从复制延迟?
17、如何重置mysql root密码?
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!
行域名解析的过程?
13、RabbitMQ是什么东西?
14、讲一下Keepalived的工作原理?
15、讲述一下LVS三种模式的工作过程?
16、mysql的innodb如何定位锁问题,mysql如何减少主从复制延迟?
17、如何重置mysql root密码?
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!








 https://blog.csdn.net/zrc_xiaoguo/article/details/134578766?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
https://blog.csdn.net/zrc_xiaoguo/article/details/134578766?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502













 1428
1428

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








