} else {
test = false;
}
// Shorthand
let test = (x > 10) ? true : false;
//or we can use directly
let test = x > 10;
console.log(test);
如果有嵌套的条件,可以这么做。
let x = 300,
test2 = (x > 100) ? ‘greater 100’ : (x < 50) ? ‘less 50’ : ‘between 50 and 100’;
console.log(test2); // “greater than 100”
3. 声明变量
当我们想要声明两个具有相同的值或相同类型的变量时,可以使用这种简写。
//Longhand
let test1;
let test2 = 1;
//Shorthand
let test1, test2 = 1;
4. null、undefined 和空值检查
当我们创建了新变量,有时候想要检查引用的变量是不是为非 null 或 undefined。JavaScript 确实有一个很好的快捷方式来实现这种检查。
// Longhand
if (test1 !== null || test1 !== undefined || test1 !== ‘’) {
let test2 = test1;
}
// Shorthand
let test2 = test1 || ‘’;
5. null 检查和默认赋值
let test1 = null,
test2 = test1 || ‘’;
console.log(“null check”, test2); // output will be “”
6. undefined 检查和默认赋值
let test1 = undefined,
test2 = test1 || ‘’;
console.log(“undefined check”, test2); // output will be “”
一般值检查
let test1 = ‘test’,
test2 = test1 || ‘’;
console.log(test2); // output: ‘test’
另外,对于上述的 4、5、6 点,都可以使用?? 操作符。
如果左边值为 null 或 undefined,就返回右边的值。默认情况下,它将返回左边的值。
const test= null ?? ‘default’;
console.log(test);
// expected output: “default”
const test1 = 0 ?? 2;
console.log(test1);
// expected output: 0
7. 给多个变量赋值
当我们想给多个不同的变量赋值时,这种技巧非常有用。
//Longhand
let test1, test2, test3;
test1 = 1;
test2 = 2;
test3 = 3;
//Shorthand
let [test1, test2, test3] = [1, 2, 3];
8. 简便的赋值操作符
在编程过程中,我们要处理大量的算术运算符。这是 JavaScript 变量赋值操作符的有用技巧之一。
// Longhand
test1 = test1 + 1;
test2 = test2 - 1;
test3 = test3 * 20;
// Shorthand
test1++;
test2–;
test3 *= 20;
9. if 判断值是否存在
这是我们都在使用的一种常用的简便技巧,在这里仍然值得再提一下。
// Longhand
if (test1 === true) or if (test1 !== “”) or if (test1 !== null)
// Shorthand //it will check empty string,null and undefined too
if (test1)
注意:如果 test1 有值,将执行 if 之后的逻辑,这个操作符主要用于 null 或 undefinded 检查。
10. 用于多个条件判断的 && 操作符
如果只在变量为 true 时才调用函数,可以使用 && 操作符。
//Longhand
if (test1) {
callMethod();
}
//Shorthand
test1 && callMethod();
11. foreach 循环
这是一种常见的循环简化技巧。
// Longhand
for (var i = 0; i < testData.length; i++)
// Shorthand
for (let i in testData) or for (let i of testData)
遍历数组的每一个变量。
function testData(element, index, array) {
console.log(‘test[’ + index + '] = ’ + element);
}
[11, 24, 32].forEach(testData);
// logs: test[0] = 11, test[1] = 24, test[2] = 32
12. 比较后返回
我们也可以在 return 语句中使用比较,它可以将 5 行代码减少到 1 行。
// Longhand
let test;
function checkReturn() {
if (!(test === undefined)) {
return test;
} else {
return callMe(‘test’);
}
}
var data = checkReturn();
console.log(data); //output test
function callMe(val) {
console.log(val);
}
// Shorthand
function checkReturn() {
return test || callMe(‘test’);
}
13. 箭头函数
//Longhand
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
//Shorthand
const add = (a, b) => a + b;
更多例子:
function callMe(name) {
console.log(‘Hello’, name);
}
callMe = name => console.log(‘Hello’, name);
14. 简短的函数调用
我们可以使用三元操作符来实现多个函数调用。
// Longhand
function test1() {
console.log(‘test1’);
};
function test2() {
console.log(‘test2’);
};
var test3 = 1;
if (test3 == 1) {
test1();
} else {
test2();
}
// Shorthand
(test3 === 1? test1:test2)();
15. switch 简化
我们可以将条件保存在键值对象中,并根据条件来调用它们。
// Longhand
switch (data) {
case 1:
test1();
break;
case 2:
test2();
break;
case 3:
test();
break;
// And so on…
}
// Shorthand
var data = {
1: test1,
2: test2,
3: test
};
data[something] && datasomething;
16. 隐式返回
通过使用箭头函数,我们可以直接返回值,不需要 return 语句。
//longhand
function calculate(diameter) {
return Math.PI * diameter
}
//shorthand
calculate = diameter => (
Math.PI * diameter;
)
17. 指数表示法
// Longhand
for (var i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { … }
// Shorthand
for (var i = 0; i < 1e4; i++) {
18. 默认参数值
//Longhand
function add(test1, test2) {
if (test1 === undefined)
test1 = 1;
if (test2 === undefined)
test2 = 2;
return test1 + test2;
}
//shorthand
add = (test1 = 1, test2 = 2) => (test1 + test2);
add() //output: 3
19. 延展操作符简化
//longhand
// joining arrays using concat
const data = [1, 2, 3];
const test = [4 ,5 , 6].concat(data);
//shorthand
// joining arrays
const data = [1, 2, 3];
const test = [4 ,5 , 6, …data];
console.log(test); // [ 4, 5, 6, 1, 2, 3]
我们也可以使用延展操作符进行克隆。
//longhand
// cloning arrays
const test1 = [1, 2, 3];
const test2 = test1.slice()
//shorthand
// cloning arrays
const test1 = [1, 2, 3];
const test2 = […test1];
20. 模板字面量
如果你厌倦了使用 + 将多个变量连接成一个字符串,那么这个简化技巧将让你不再头痛。
//longhand
const welcome = 'Hi ’ + test1 + ’ ’ + test2 + ‘.’
//shorthand
const welcome = Hi ${test1} ${test2};
21. 跨行字符串
当我们在代码中处理跨行字符串时,可以这样做。
//longhand
const data = ‘abc abc abc abc abc abc\n\t’
- ‘test test,test test test test\n\t’
//shorthand
const data = `abc abc abc abc abc abc
test test,test test test test`
22. 对象属性赋值
let test1 = ‘a’;
let test2 = ‘b’;
//Longhand
let obj = {test1: test1, test2: test2};
//Shorthand
let obj = {test1, test2};
23. 将字符串转成数字
//Longhand
let test1 = parseInt(‘123’);
let test2 = parseFloat(‘12.3’);
//Shorthand
let test1 = +‘123’;
let test2 = +‘12.3’;
24. 解构赋值
//longhand
const test1 = this.data.test1;
const test2 = this.data.test2;
紧跟潮流
大前端和全栈是以后前端的一个趋势,懂后端的前端,懂各端的前端更加具有竞争力,以后可以往这个方向靠拢。
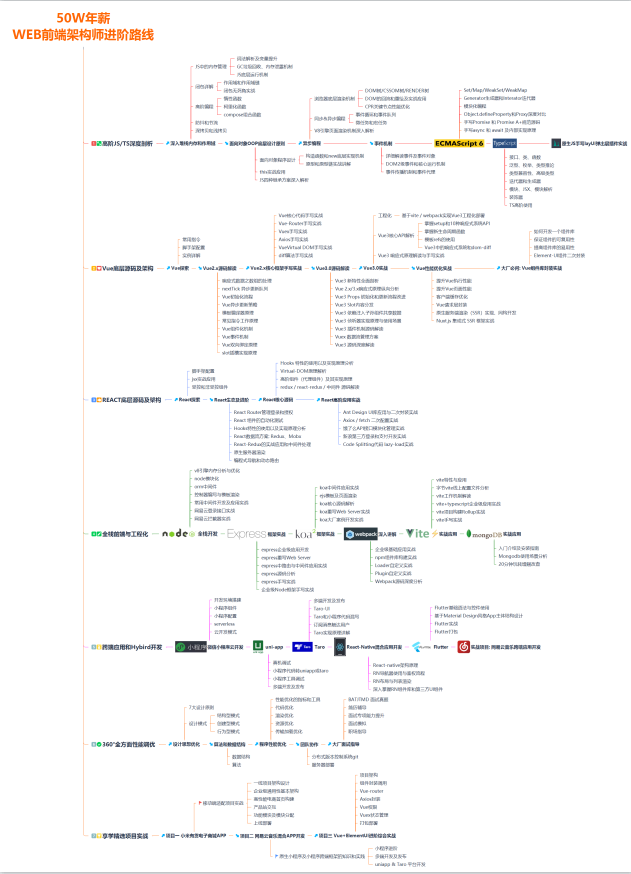
这边整理了一个对标“阿里 50W”年薪企业高级前端工程师成长路线,由于图片太大仅展示一小部分





















 1798
1798

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








