文章目录
- 实战遇到的问题
- kotlin data class类型
- lateinit
- field
- Kotlin 具名参数&可变参数
- Kotlin中的object 与companion object的区别
- kotlin 访问修饰符 open final abstract
- Android Kotlin的Class、反射、泛型
- Kotlin 继承
- Kotlin——最详细的抽象类(abstract)、内部类(嵌套类)详解
- Kotlin 笔记 : !!. 与 ?. 的区别
- Kotlin系列之let、with、run、apply、also函数的使用
- Kotlin集合—MutableList可变列表、Set、MuTableSet
- kotlin集成和基础知识整理(二)
- Kotlin简单回调接口(lambda实现)
- 接口、
- kotlin自定义控件
- 第四篇:Kotlin之数组和集合
- 集合间的高级操作
- 高级回调
- Kotlin (一) 复合符号( '?.' '?:' '!!' 'as?' '?' )
var 和 val的区别
var是可写的,在它生命周期中可以被多次赋值,
val是只读的,仅能一次赋值,后面就不能背重新赋值。
使用is运算符进行类型检测
字符串与其模版表达式
- “”"
val follTemplateString="$rawString has ${rawString,length} characters"
when表达式
fun cases(obj:Any) {
when(obj) {
1->print("第一项")
-1, 0 -> print("x == -1 or x == 0")
in 1..10 -> print("x is in the range")
int arrayOf(1,2,3)-> print("x is valid")
!in 1..10 -> print("x is not valide")
"hello" -> print("这个是字符hello")
is Long -> print("这是一个Long类型数据")
!is String -> print("这不是String类型的数据")
else -> print("else类似于Java中的default")
}
}
for 循环
fot(item in collection){
print(item)
}
for ((index, value) in array.withIndex()){
printlin("the element at $index is $value")
}
标签(Label)
fun returnDemo_3() {
val intArray = intArrayOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
intArray.forEach here@{
if (it == 3) return@here;
println(lt)
}
}
this关键字
val thisis = "THIS IS"
fun whatIsThis(): ThisDemo {
println(this.thisis)
this.howIsThis()
return this;
}
fun howIsThis() {
println("HOW IS THIS?")
}
super关键字的使用
open class Father{
open val firstName = "Chen"
open val lastName = "Jason"
fun ff() {
println();
}
}
class Son : Father {
override var firstName = super.firstName;
override var lastName = "Jack"
constructor(lastName:String){
this.lastName= lastName
}
fun love(){
super.ff();
println();
}
}
操作符和操作符的重载
| 表达式 | 翻译为 |
|---|---|
| +a | a.unaryPlus() |
| -a | a.unaryMinus() |
| !a | a.not() |
| 优先级 | 标题 | 符号 |
|---|---|---|
| 最高 | 后缀(Postfix) | ++, --, ., ?., ? |
| 前缀(Prefix) | -, +, ++, --, !, labelDefinition@ | |
| 右手类型运算(Type RHS, right-hand side class type (RHS)) | :, as, as? | |
| 乘除取余(Multiplicative) | *, /, % | |
| 加减(Additive) | +, - | |
| 区间范围(Range) | … | |
| infix函数 | 例如:给Int定义扩展infix fun Int.shl(x:Int):Int{…},这样调用1 shl 2,等同于1.shl(2) | |
| Elvis操作符 | ?: | |
| 命名检查符(Named checks) | in, !in, is, !is | |
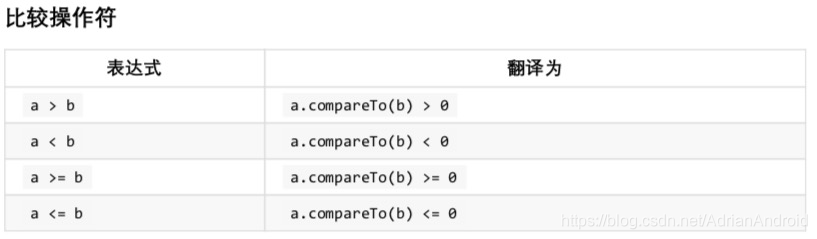
| 比较大小(Comparison) | <, >, <=, >= | |
| 相等性判断(Equality) | ==, != | |
| 与(Conjunction) | && | |
| 或(Disjunction) | || | |
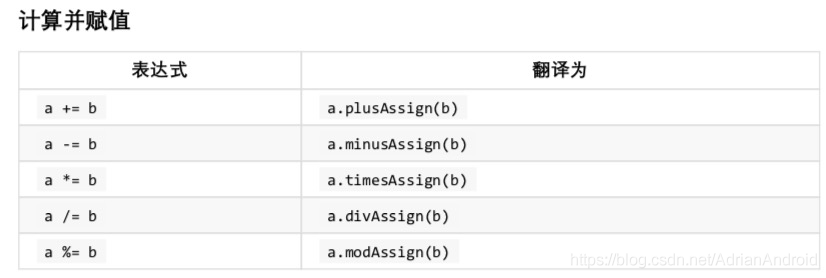
| 最低 | 赋值(Assignment) | =, +=, -=, *=, /=, %= |
一元操作符
class OperatorDemo{
}
data class Point(val x:Int, val y:Int)
operator fun Point.unaryMinus() = Point(-x, -y);
class OperatiionDemoTest{
fun testPointUnaryMinus() {
val p = Point(1,1)
val np = -p;
}
}
递增和递减
| 表达式 | 翻译为 |
|---|---|
| a++ | a.inc() 返回值是a |
| a– | a.dec() 返回值是a |
| ++a | a.inc() 返回值是a+z |
| --a | a.dec() 返回值是a-1 |
二元操作符
| 表达式 | 翻译为 |
|---|---|
| a + b | a.plus(b) |
| a - b | a.minus(b) |
| a * b | a.times(b) |
| a / b | a.div(b) |
| a % b | a.rem(b) , a.mod(b) |
| a…b | a.rangeTo(b) |
字符串+的运算符重载
data class Counter(var index:Int)
operator fun Counter.plus(increment:Int) : Counter{
return Counter(index + increment)
}
fun testCounterIndexPlus(){
val c = Counter(1);
val plus = c + 10
}
in操作符


调用操作符
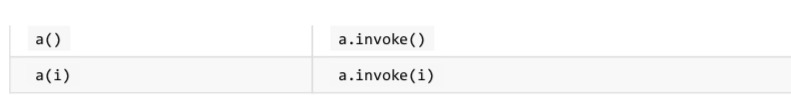

用infix函数自定义中缀操作符
data class Persion(val name: String, val age: Int)
infix fun Persion.grow(years: Int): Persion {
return Persion(name, age + years)
}
函数扩展和属性扩展(Extensions)
val <T> List<T>.lastIndex: Int get() = size - 1;
fun String.notEmpty(): Boolean {
return !this.isEmpty()
}
companion
基本类型(数字、字符、布尔和数组)
数字类型
| 类型 | 宽度(Bit) |
|---|---|
| Double | 64 |
| Float | 32 |
| Long | 64 |
| Int | 32 |
| short | 16 |
| Byte | 8 |
字面常量值
数字常量字面:
- 十进制:123
- Long类型用大写L标记:123L
- 十六进制:0x0F
- 二进制:0b00001011
浮点数
- 默认double:123.5、123.5e10
- Float用f或者F标记:123.5f
运算符+重载
public operator fun plus(other:Byte):Long{}
public operator fun plus(other:Short):Long{}
public operator fun plus(other:Int):Long{}
public operator fun plus(other:Long):Long{}
public operator fun plus(other:Float):Long{}
public operator fun plus(other:Double):Long{}
Boolean 布尔类型
布尔运算有
- !逻辑非not()
- &&短路逻辑与and()
- || 短路逻辑或or()
- xor 异或(相同false,不同true)
字符串模版
>>> val h = 100
>>> var str = "A hundred is $h"
>>> str
A hundred is 100
或者
>>> val s = "abc"
>>>val str = "$s.length is ${s.length}"
>>>str
abc.length is 3
原生字符串和转义字符内部都支持模版
>>> val price=9.9
>>> val str="""Price is $$price"""
>>> str
Price is $9.9
>>> val str = "Price is $$price"
>>>str
Price is $9.9
>>> val quantity=100
>>>val str="Quantity is $quantity"
>>>str
Quantity is 100
>>>val str = """Quantity is $quantity"""
>>>str
Quantity is 100
Array:数组类型
>>> arrayof(1,2,3)
>>> arrayof(1,2,3):class
>>> arrayof(1,2,3):class.java
// 不同类型
>>>val arr = arrayOf(1,"2",true)
>>>arr.forEach{println(it)}
原生数组类型
BooleanArray
ByteArray
CharArray
ShortArray
IntArray
LongArray
FlatArray
DoubleArray
BooleanArray
可空类型 ?
fun getLength2(str:String?) : Int?=str.length
fun getLenght2(str:String?) : Int?{
return str?.length
}
可空类型 ?.
可空类型 !!
可空类型层次体系
>>> 1 is Any
true
>>> 1 is Any?
true
>>> null is Any
false
>>> null is Any?
true
>>> Any() is Any?
true
kotlin.Unit类型
>>> fun unitExample() {println("Hello,Unit")}
>>>val helloUnit = unitExample()
Hello.Unit
>>> helloUnit
kotlin.Unit
>>>println(helloUnit)
kotlin.Unit
kotlin.Nothing类型 = (Void = Nothing?)
fun formatCell(value:Double) : String =
if (value.isNaN())
throw IllegalArgumentException("$value is not a number")
else
value.toString()
Nothing?可以只包含一个值:null
>>> var nul:Nothing? = null
>>> nul = 1
error: the integer literal does not conform to the expected type Nothing?
nul = 1
|
>>> nul = true
error:the boolean literal does not conform to the expected type Nothong?
nul = true
|
>>> nul = null
>>> nul
null
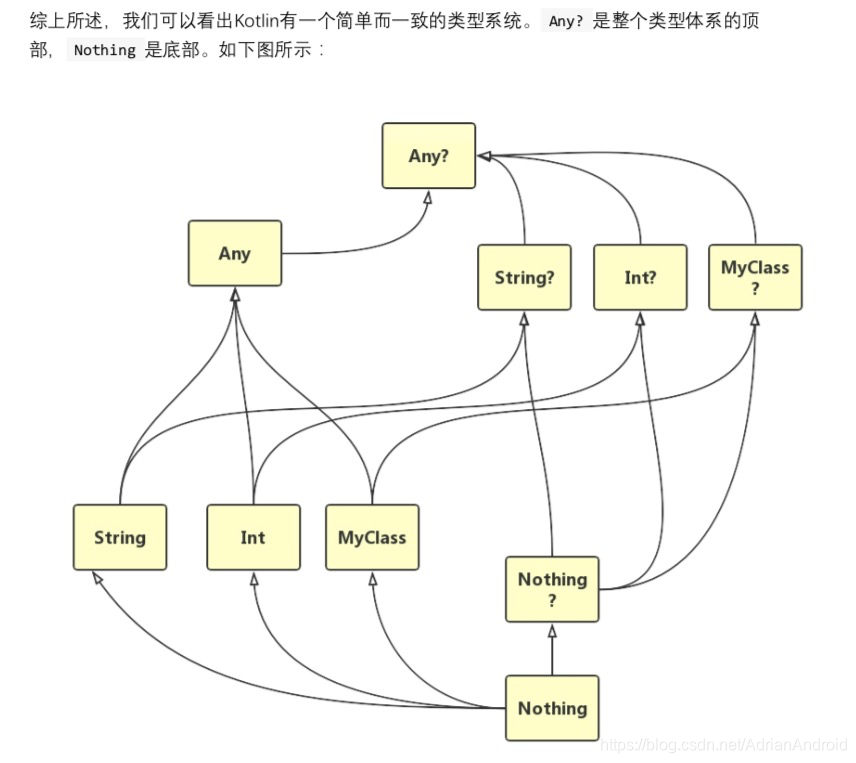
类型检测与类型转换
is,!is运算符
as 运算符
>>> open class Foo
>>>class Goo:Foo()
>>>val foo = Foo()
>>> val goo = Goo()
>>> foo as Goo
java.lang.ClassCastExeption:Line69$Foo canot be cast to Line71&Goo
>>> foo as? Goo
null
>>> goo as Foo
>Line71$Goo@73ce0e5
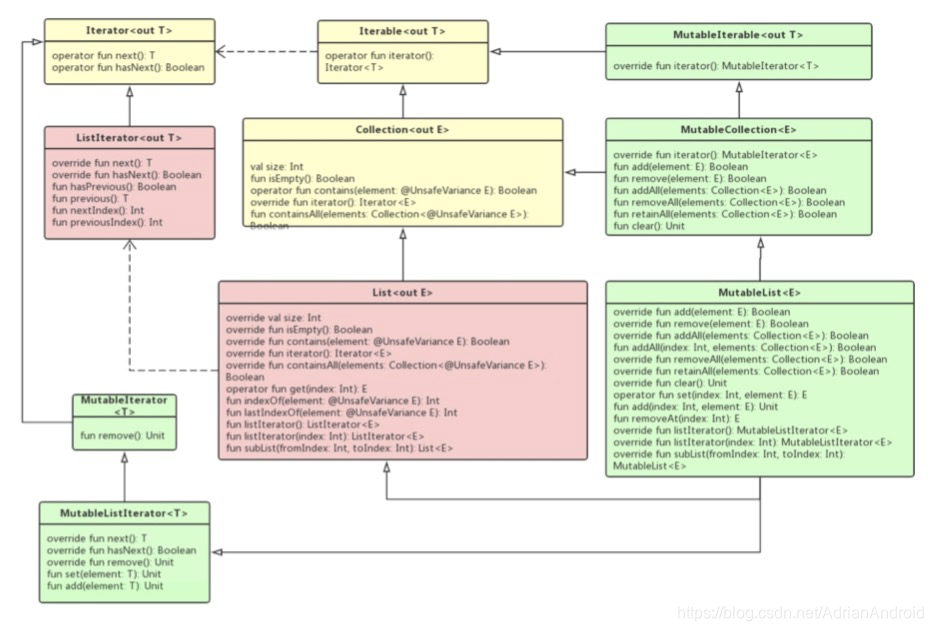
集合类(可变集合类(Mutable)与不可编集合类(Immutable))
集合类型主要有3种:list(列表)、set(集)、map(映射)
List
@kotline.internal.InlineOnly
public inline fun <T> listOf():List<T>=emptyList()
public fun <T> listOf(vararg elements:T):List<T>=if(elements.size>0)elements.as List() else emptyLIst()
@JvmVersion
public fun <T> listOf(element:T):List<T>=java.util.Collections.singletonList(element)
>>> val list:List<Int> = listof()
>>> avl list = listOf(1)
创建可变集合MutableList
>>> val list = mutableListOf(1,2,3)
>>>list
[1,2,3]
>>> list::class
class java.util.ArrayList
>>> val list2 = mutableListOf<Int>()
>>> list2
[]
>>>list2::class
class java.util.ArrayList
>>>val list3 = mutableListof(1)
>>>list3
[1]
>>>list3:class
class java.util.Arraylist
实战遇到的问题
kotlin data class类型
lateinit
从原理分析Kotlin的延迟初始化: lateinit var和by lazy
field
Kotlin 具名参数&可变参数
Kotlin中的object 与companion object的区别
Kotlin中的object 与companion object的区别
companion object {
private val MY_TAG = "DemoManager"
fun b() {
Log.e(MY_TAG,"此时 companion objec t表示 伴生对象")
}
}
kotlin 访问修饰符 open final abstract
kotlin 访问修饰符 open final abstract
- final kotlin中默认类和方法是final。
2.如果你允许创建一个类的子类,需要使用open 修饰符来标示这个类,另外需要给每一个可以被重写的属性或者方法添加open 修饰符
3.abstract Kotlin中可以将一个类声明为abstract ,这种类不能被实例化。抽象类中抽象成员始终是open的,所以不需要显示的使用open修饰符,非抽象函数并不是默认open,但是可以标注为open的
Android Kotlin的Class、反射、泛型
Kotlin 继承
Kotlin——最详细的抽象类(abstract)、内部类(嵌套类)详解
Kotlin——最详细的抽象类(abstract)、内部类(嵌套类)详解
Kotlin 笔记 : !!. 与 ?. 的区别
//kotlin:
a?.run()
//与java相同:
if(a!=null){
a.run();
}
//kotlin:
a!!.run()
//与java相同:
if(a!=null){
a.run();
}else{
throw new KotlinNullPointException();
}
Kotlin系列之let、with、run、apply、also函数的使用
Kotlin系列之let、with、run、apply、also函数的使用
- 内联扩展函数之let
let扩展函数的实际上是一个作用域函数,当你需要去定义一个变量在一个特定的作用域范围内,let函数的是一个不错的选择;let函数另一个作用就是可以避免写一些判断null的操作。
Kotlin集合—MutableList可变列表、Set、MuTableSet
Kotlin集合—MutableList可变列表、Set、MuTableSet
kotlin集成和基础知识整理(二)
Kotlin简单回调接口(lambda实现)
Kotlin简单回调接口(lambda实现)
kotlin 定义接口并实现回调
View.OnClickListener在Kotlin中的进化
- 定义接口
interface CallBack{
fun callBack(info:String)
}
- 实现接口:为继承/实现
class CallBacks:CallBack{
override fun callBack(info:String)
}
private var mCallBack = object:CallBack{
override fun callBack(info:String){
Log.d("MainApp", "current ifno $info")
}
}
- 定义带回掉方法的函数
private fun initData(callBack:CallBack):Boolean{
callBack?.callBack("我来自回掉")
return true
}
- 实现回调,调用方式与实现接口对应
initData(CallBacks())
initData(mCallBack)
方法无参无返回值回掉
- 声明回调接口,以及初始化接口
private var onUpdateListener:(()->Unit)?=null
fun setOnUpdateListener(()->Unit){
this.onUpdateListener = onUpdateListener
}
- 接口返回方法的调用
(mView.findViewById(R.id.tv_update) as TextView).setOnClickListener{
onUpdateListener?.invoke()
}
- 外部调用接口
versionInfoDialog?.setOnUpdateListener{
versionInfoDialog?.dismiss()
if(!verstionDialog?.isShowing()!!) {
versionDialog?.show()
}
mActivity.startService<VersionService>( ...params:"url" to result.url)
}
- 方法有参无返回值回掉
(1)声明回掉接口,以及初始化
private var sureListener:((flat:Int)->Unit) ?= null
fun setSureListener(sureListener:((flat:Int)->Unit){
this.sureListener = sureListener
}
(2)接口方法的调用
text_account_open?.setOnClickListener{
sureListener?.invoke(flag)
mThis.dismiss()
}
(3)外部调用接口
mAccountOrBankDialog?.setSureListener{
when(it){
2802 -> {
val bundle = Bundle()
bundle.putBoolean("fromUnBank", true)
bundle.putInt("accountType", 1)
bundle.putSerializable("unBankInfo", unBankInfo)
toOtherActivity(BankBindActivity::class.java, bundle, true)
}
else -> toast("获取信息失败")
}
}
mAccountOrBankDialog?.setSureListener{ flag ->
}
- 方法有参有返回值回调
(1)接口声明,以及初始化
private var sureListener:((flag:Int)->Int)?=null
fun setSureListener(sureListener:((flag:Int)->Int){
this.sureLirtener = sureListener
}
(2)接口方法调用
text_account_open?.setOnClickListener{
val flag = sureLisstener?.invoke(flag)
Logger.e(flag.toString())
mThis.dismiss()
}
(3)外部调用接口
mAccountOrBankDialog?.setSureListener{flag->
.toast(flag)
0 //返回值放在后面
}
接口、
kotlin自定义控件
class CommonItemLayout : FrameLayout {
private lateinit var mIcon: ImageView
private lateinit var mTitle: TextView
private lateinit var mLable: TextView
private lateinit var mArrowIcon: ImageView
private lateinit var mLine: View
constructor(context: Context) : this(context, null)
constructor(context: Context, attributeSet: AttributeSet?) : this(context, attributeSet, 0)
constructor(context: Context, attributeSet: AttributeSet?, defStyleAttr: Int) : super(context, attributeSet, defStyleAttr) {
init(context, attributeSet)
}
}
第四篇:Kotlin之数组和集合
https://www.jianshu.com/p/6d95db6e9f87
val intArray: IntArray = intArrayOf(1, 3, 5, 7)
val charArray: CharArray = charArrayOf('H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', ' ', 'K', 'o', 't', 'l', 'i', 'n')
val strArray: Array<String> = arrayOf("你", "好", ",Kotlin!")
集合间的高级操作
Kotlin入门第二课:集合操作
kotlin集合(List)使用方法整理
Kotlin集合—MutableList可变列表、Set、MuTableSet
Kotlin——高级篇(四):集合(Array、List、Set、Map)基础
kotlin list集合操作






















 1430
1430











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










