本篇主要学习以下几个知识点
- alloc/reatin/release/dealloc 理解
- autorelease 理解
- autorelease GUN 实现
- autorelease 苹果 实现
alloc/reatin/release/dealloc 实现
我们来看看 GUNstep 源代码中 NSObject 类的的 alloc 类方法。
id obj = [NSObject alloc];
上述调用 NSObject 类的 alloc 类方法在 NSObjecr.m 源代码中的实现如下。
+ (id) alloc
{
return [self allocWithZone: NSDefaultMallocZone()];
}
+ (id) allocWithZone:(NSZone *)z
{
return NSAllocateObject(self,0,z);
}通过 allocWithZone: 类方法调用 N\NSAllocateObject 函数分配对象。下面我们查看 NSAllocateObject 函数.
struct obj_layout {
NSUInterger retained;
}
inline id NSAllocateObject (Class aClass, NSUInterger extraBytes, NSZone *zone) {
int size = 计算容纳对象所需内存大小;
id new = NSZoneMalloc(zone, size);
memset(new, 0, size);
new = (id)&((struct obj_layout *) new)[1];
}NSAllocateObject 函数通过调用 NSZoneMalloc 函数来分配存放对象所需的内存空间,之后将改内存空间置0,最后返回作为对象而使用的指针。
以下是去掉 NSZone 后简化了源代码:
struct obj_layout {
NSUInterger retained;
}
+ (id) alloc {
int size = sizeof(struct obj_layout) + 对象大小;
struct obj_layout *p = (struct obj_layout *)calloc(1, size);
return (id)(p+1);
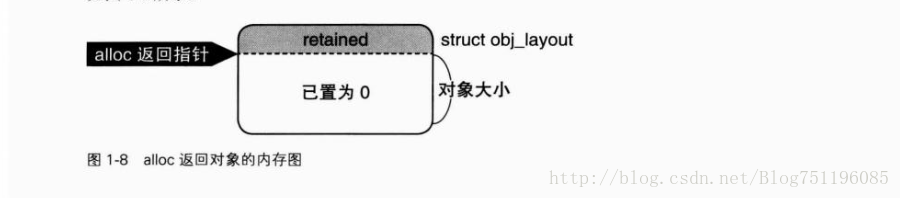
}alloc 类方法用 struct obj_layout 中的 retained 整数来保存引用计数,并将其写入对象内存头部,该对象内存全部置0后返回。
以下用图来展示有关 GUNstep 的实现,alloc类方法返回对象,如图
对象的引用计数可通过 retainCount 实例方法来取得。
id obj = [NSObject alloc];
NSLog(@"retainCount=%d", [obj retainCount]); // => 1
执行alloc后对象的 retainCount 是 “1”。下面通过 GUNstep 的源代码来确认。
- (NSUInteger)retainCount {
return NSExtraRefCount(self) + 1;
}
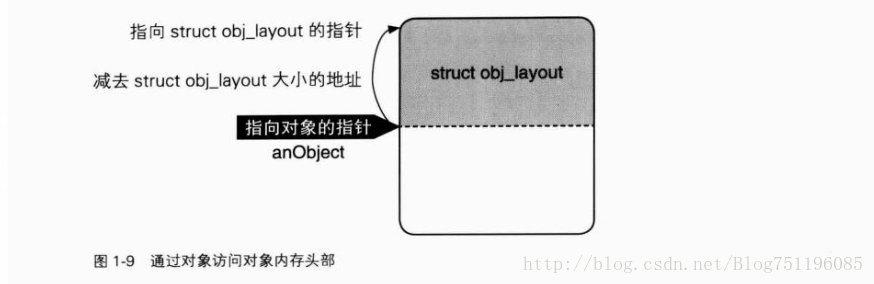
inline NSUInterger NSExtraRefCount(id anObject) {
return ((struct obj_layout *) anObject)[-1].retained;
}由对象寻址找到对象内存头部,从而访问其中的retained变量。如图:
autorelease
autorelease 就是自动释放。这看上去很像ARC,但实际上它更类似于C语言中的自动变量(局部变量)的特性。
{
int a;
}
/*
因为超出变量作用域,自动变量 "int a" 被废弃,不可再访问
*/autorelease 会像 C 语言的自动变量那样来对待对象实例。当超出其作用域(相当于变量作用域)时,对象实例的 release 实例方法被调用。另外,同 C 语言的自动变量不同的是,编程人员可以设定变量的作用域。
autorelease 的具体使用方法如下:
- 生成并持有 NSAutoreleasePool 对象
- 调用已分配对象的 autorelease 实例方法
- 废弃 NSAutoreleasePood 对象
NSAutoreleasePool 对象的声明周期相当于 C 语言变量的作用域。对于所有调用过 autorelease 实例方法的对象,在废弃 NSAutoreleasePool 对象时,都将调用 release 实例方法。如上图。
NSAutoreleasePool *pool = [[NSAutoreleasePool alloc] init];
id obj = [[NSObject alloc] init];
[obj autorelease];
[pool drain];“[pool drain]” 等同于 “[obj release]”。
在 Cocoa 框架中,相当于程序主循环的 NSRunLoop 或者在其他程序可运行的地方,对 NSAutoreleasePool 对象进行生成、持有和废弃处理。因此,应用程序开发者不一定非得使用 NSAutoreleasePool 对象来进行开发工作。
意思就是我们不一定需要去管理 NSAutoreleasePool。
尽管如此,但在大量产生 autorelease 的对象时,只要不废弃 NSAutoreleasePool 对象,那么生成的对象就不能被释放,因此有时会产生内存不足的现象。
典型的例子:读入大量图像的同时改变尺寸。图像文件读入到 NSData 对象,并从中生成 UIImage 对象,改变该对象尺寸后生成新的 UIImage 对象。这种情况下,就会大量生成 autorelease 对象。
for (int i = 0; i < 图像数; ++i){
/*
读入图像
大量产生 autorelease 对象
由于没有废弃 NSAutoreleasePool 对象
最终导致内存不足
*/
}在此情况下,有必要在适当的地方生成,持有或者废弃 NSAutoreleasePool 对象。
for (int i = 0; i < 图像数; ++i){
NSAutoreleasePool *pool = [[NSAutoreleasePool alloc] init];
/*
读入图像
大量产生 autorelease 对象
*/
[pool drain];
}另外,Cocoa 框架中也有很多类方法用于返回 autorelease 的对象。比如 NSMutableArray 类的 arrayWithCapacity 类方法。
id array = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:1];此源代码等同于以下源代码
id array = [[[NSMutableArray alloc] initWithCapacity:1] autorelease];autorelease 实现 - GUNstep是如何实现的
[obj autorelease];此源代码调用 NSObject 类的 autorelease 实例方法。
GUNstep实现:
- (id) autorelease {
[NSAutoreleasePool addObject:self];
}
autorelease 实例方法的本质就是调用 NSAutoreleasePool 对象的 addObject 类方法。
+ (void) addObject:(id)anObj {
NSAutoreleasePool *pool = 取得正在使用的 NSAutoreleasePool 对象;
if (pool != nil) {
[pool addObject: anObjc];
}else{
NSLog(@"NSAutoreleasePool 对象非存在状态下调用 autorelease")
}
}addObject 类方法调用正在使用的 NSAutoreleasePool 对象的 addObject 实例方法。
如果嵌套或者持有 NSAutoreleasePool 对象,理所当然会使用最内侧的对象。
- (void) drain {
[self dealloc];
}
- (void) dellloc {
[self emptyPool];
[array release];
}
- (void) emptyPool {
for (id obj in array){
[obj release];
}
}虽然调用了好几个方法,但是可以确定对于数组中的所以对象都调用了 release 实例方法。
苹果 autorelease 的实现
objc4 库的 runtime/objc-arr.mm 来确认苹果中 autorelease 的实现
Class AutoreleasePoolPage
{
static inline void *push (){
相当于生成或者持有 NSAutoreleasePool 对象
}
static inline void *pop (void *token){
releaseAll();
}
static inline id autorelease (id obj){
相当于 NSAutoreleasePool 类的 addObject 类方法
NSAutoreleasePoolPage *autoreleasePoolPage = 取得正在使用的实例;
autoreleasePoolPage ->add(obj);
}
id *add (id obj) {
将对象追加到内部数组中
}
void releaseAll(){
调用内部数组中对象的release实例方法
}
}
void *objc_autoreleasePoolPush(void){
return AutoreleasePoolPage::push();
}
void *objc_autoreleasePoolPop(void *ctxt){
return AutoreleasePoolPage::pop(ctxt);
}
id *obj_autorelease(id obj) {
return AutoreleasePoolPage:autorelease(obj);
}C++类中虽然有动态数组的实现,但其行为和GUNstep的实现完全相同。
我们使用调试器来观察一下NSAutoreleasePool类方法和 autorelease 方法的运行过程。如下所示,这些方法调用了关联于 objc4 库的 autorelease 实现的函数。
NSAutoreleasePool *pool = [[NSAutoreleasePool alloc] init];
/*= objc_autoreleasePoolPush()*/
id obj = [[NSObject alloc] init];
[obj autorelease];
/*= obj_autorelease(obj)*/
[pool drain];
/*= objc_autoreleasePoolPop(pool)*/另外,可通过 NSAutoreleasePool 类中的调试用非公开类方法 showPools 来确认已被 autorelease 的对象情况。
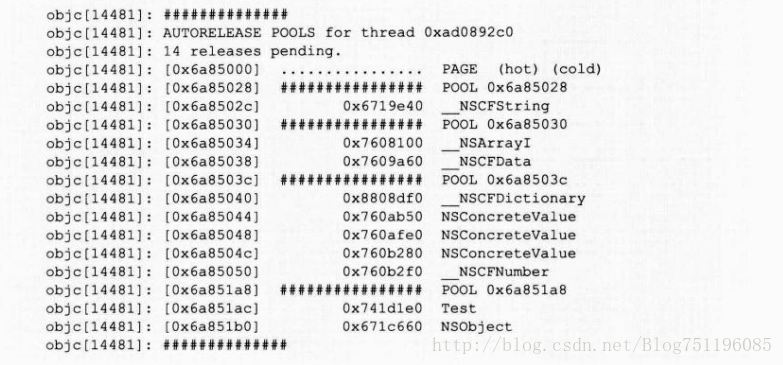
[NSAutoreleasePool showPools];NSAutoreleasePool 类的 showPools 类方法只能在 iOS 中使用,作为替代,在现在的运行时系统中我们使用调试用非公开函数 _objc_autoreleasePoolPrint()。
/* 函数声明 */
extend void _objc_autoreleasePoolPrint();
/* autorelesepool 调试用输出开始*/
_objc_autoreleasePoolPrint();如果运行此函数,就能像下面这样在控制台中来确认 AutoreleasePoolPage 类的情况。
NSAutoreleasePool 调用 autorelease 会如何?发生异常
通常在使用 Obejctive-C,也就是 Foundation 框架时,无论调用哪一个对象的 autorelease 实例方法,实际上调用都是 NSObject 类的 autorelease 实例方法。但是对于 NSAutoreleasePool 类,autorelease 实例方法已被该类重载,因此运行时就会报错。


























 7367
7367











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








