参考
一、概念
对于在Springboot中,利用自定义注解+切面来实现接口权限的控制这个大家应该都很熟悉,也有大量的博客来介绍整个的实现过程,整体来说思路如下:
- 自定义一个权限校验的注解,包含参数value
- 配置在对应的接口上
- 定义一个切面类,指定切点
- 在切入的方法体里写上权限判断的逻辑
SpEL表达式
本文前面提到SpEL,那么到底SpEL是啥呢? SpEL的全称为Spring Expression Language,即Spring表达式语言。是Spring3.0提供的。他最强大的功能是可以通过运行期间执行的表达式将值装配到我们的属性或构造函数之中。如果有小伙伴之前没有接触过,不太理解这句话的含义,那么不要紧,继续往下看,通过后续的实践你就能明白他的作用了。
二、开发
引入包
<!--spring aop + aspectj-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>5.0.8.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjrt</artifactId>
<version>1.8.9</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.8.9</version>
</dependency>
<!--spring aop + aspectj-->
定义注解
我们仅需要定义一个value属性用于接收表达式即可。
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface PreAuth {
/**
*
*
* permissionAll()-----只要配置了角色就可以访问
* hasPermission("MENU.QUERY")-----有MENU.QUERY操作权限的角色可以访问
* hasAnyPermission("MENU.QUERY","MENU.ADD")-----有MENU.QUERY操作权限的角色可以访问
* permitAll()-----放行所有请求
* denyAll()-----只有超级管理员角色才可访问
* hasAuth()-----只有登录后才可访问
* hasTimeAuth(1,,10)-----只有在1-10点间访问
* hasRole(‘管理员’)-----具有管理员角色的人才能访问
* hasAnyRole(‘管理员’,'总工程师')-----同时具有管理员
* hasAllRole(‘管理员’,'总工程师')-----同时具有管理员、总工程师角色的人才能访问、总工程师角色的人才能访问
*
* Spring el
* 文档地址:<a href="https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/5.1.6.RELEASE/spring-framework-reference/core.html#expressions">...</a>
*/
String value();
}
定义切面
我们就需要定义切面了。这里要考虑一个点。我们希望的是如果方法上有注解,则对方法进行限制,若方法上无注解,单是类上有注解,那么类上的权限注解对该类下所有的接口生效。因此,我们切点的话要用@within注解
// 方式一
@Pointcut(value = "execution(* com.edevp.spring.spel.auth..*.*(..))")
// 方式二 直接切入注解
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.edevp.spring.spel.auth.annotation.PreAuth) || @within(com.edevp.spring.spel.auth.annotation.PreAuth)")
/**
* 必须的注解
* @create 2023/5/24
*/
@Component
@Aspect
@Slf4j
public class AuthAspect {
@Resource
private AuthContext authContext;
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
log.info("鉴权切面初始化");
}
/**
* Spel解析器 关键点来了。这里我们要引入SpEL。
*/
private static final ExpressionParser EXPRESSION_PARSER = new SpelExpressionParser();
// @Pointcut(value = "execution(* com.edevp.spring.spel.auth..*.*(..))")
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.edevp.spring.spel.auth.annotation.PreAuth) || @within(com.edevp.spring.spel.auth.annotation.PreAuth)")
private void beforePointcut(){
//切面,方法里的内容不会执行
}
/**
* 前置通知
* @param joinPoint 切点
*/
@Before(value = "beforePointcut()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){
//@Before是在方法执行前无法终止原方法执行
log.info("前置通知。。。"+joinPoint);
if (handleAuth(joinPoint)) {
return;
}
throw new NoAuthException("没权限");
}
/**
* 环绕通知
* @param joinPoint 切点
* @return Object
*/
@Around("beforePointcut()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
//@Before是在方法执行前无法终止原方法执行
log.info("环绕通知。。。"+joinPoint);
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
/**
* 判断是否有权限
* @param point 切点
* @return boolean
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private boolean handleAuth(JoinPoint point) {
MethodSignature ms = point.getSignature() instanceof MethodSignature? (MethodSignature) point.getSignature():null;
assert ms != null;
Method method = ms.getMethod();
// 读取权限注解,优先方法上,没有则读取类
PreAuth preAuth = method.getAnnotation(PreAuth.class);
if(preAuth == null){
preAuth = (PreAuth) ms.getDeclaringType().getDeclaredAnnotation(PreAuth.class);
}
// 判断表达式
String condition = preAuth.value();
if (StringUtil.isNotBlank(condition)) {
Expression expression = EXPRESSION_PARSER.parseExpression(condition);
StandardEvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext(authContext);
// 获取解析计算的结果
return Boolean.TRUE.equals(expression.getValue(context, Boolean.class));
}
return false;
}
}
定义用户上下文
有的同学会问,你权限校验的逻辑呢?别急,关键点在这:StandardEvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext(authContext );在上文代码中找到了吧。
这个AuthFun就是我们进行权限校验的对象。所以呢,我们还得在定义一下这个对象。进行具体的权限校验逻辑处理,这里定的每一个方法都可以作为表达式在权限注解中使用。代码如下:
方法对应PreAuth中的方法字符串
@Component
public class AuthContext {
private static final ThreadLocal<UserContext> USER_CONTEXT_THREAD_LOCAL = new NamedThreadLocal<>("user context");
public static void setUserContext(UserContext user){
USER_CONTEXT_THREAD_LOCAL.set(user);
}
public static UserContext getUserContext(){
return USER_CONTEXT_THREAD_LOCAL.get();
}
public static void removeUserContext(){
USER_CONTEXT_THREAD_LOCAL.remove();
}
/**
* 判断角色是否具有接口权限
*
* @param permission 权限编号,对应菜单的MENU_CODE
* @return {boolean}
*/
public boolean hasPermission(String permission) {
//TODO
return hasAnyPermission(permission);
}
/**
* 判断角色是否具有接口权限
*
* @param permission 权限编号,对应菜单的MENU_CODE
* @return {boolean}
*/
public boolean hasAllPermission(String... permission) {
//TODO
for (String r : permission) {
if (!hasPermission(r)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* 放行所有请求
*
* @return {boolean}
*/
public boolean permitAll() {
return true;
}
/**
* 只有超管角色才可访问
*
* @return {boolean}
*/
public boolean denyAll() {
return hasRole("admin");
}
/**
* 是否有时间授权
*
* @param start 开始时间
* @param end 结束时间
* @return {boolean}
*/
public boolean hasTimeAuth(Integer start, Integer end) {
/*Integer hour = DateUtil.hour();
return hour >= start && hour <= end;*/
return true;
}
/**
* 判断是否有该角色权限
*
* @param role 单角色
* @return {boolean}
*/
public boolean hasRole(String role) {
return hasAnyRole(role);
}
/**
* 判断是否具有所有角色权限
*
* @param role 角色集合
* @return {boolean}
*/
public boolean hasAllRole(String... role) {
for (String r : role) {
if (!hasRole(r)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* 判断是否有该角色权限
*
* @param roles 角色集合
* @return {boolean}
*/
public boolean hasAnyRole(String... roles) {
UserContext user = getUser();
if(user!= null){
return hasAnyStr(user.getRoles(),roles);
}
return false;
}
/**
* 判断是否有该角色权限
*
* @param authorities 角色集合
* @return {boolean}
*/
public boolean hasAnyPermission(String... authorities) {
UserContext user = getUser();
if(user!= null){
return hasAnyStr(user.getAuthorities(),authorities);
}
return false;
}
public boolean hasAnyStr(String hasStrings,String... strings) {
if(StringUtil.isNotEmpty(hasStrings)){
String[] roleArr = hasStrings.split(SymbolConstant.COMMA);
return Arrays.stream(strings).anyMatch(r-> Arrays.asList(roleArr).contains(r));
}
return false;
}
public UserContext getUser(){
UserContext o = AuthContext.getUserContext();
if(o != null){
return o;
}
return null;
}
}
三、测试
在使用的时候,我们只需要在类上或者接口上,加上@PreAuth的直接,value值写的时候要注意一下,value应该是我们在AuthContext 类中定义的方法和参数,如我们定义了解析方法hasAllRole(String… role),那么在注解中,我们就可以这样写@PreAuth(“hasAllRole(‘角色1’,‘角色2’)”),需要注意的是,参数要用单引号包括。
根据上面的实际使用,可以看到。SpEL表达式解析将我们注解中的"hasAllRole(‘角色1’,‘角色2’)"这样的字符串,给动态解析为了hasAllRole(参数1,参数1),并调用我们注册类中同名的方法。
新建Service在方法上注解
@Slf4j
@Component
public class AuthTestMethodService {
@PreAuth("hasRole('admin')")
public void testHasRole(){
log.info("测试 hasRole('admin')");
}
@PreAuth("hasAnyRole('admin','test')")
public void testHasAnyRole(){
log.info("测试 testHasAnyRole('admin')");
}
@PreAuth("hasAllRole('admin','test')")
public void testHasAllRole(){
log.info("测试 testHasAllRole('admin')");
}
@PreAuth("hasPermission('sys:user:add')")
public void testHasPermission(){
log.info("测试 hasPermission('admin')");
}
}
新建Service在类上注解
@Slf4j
@Component
@PreAuth("hasRole('admin')")
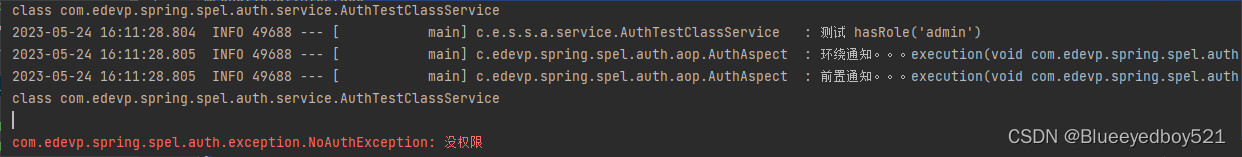
public class AuthTestClassService {
public void testHasRole(){
log.info("测试 hasRole('admin')");
}
}
运行
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Executer {
/**
* 执行
*/
void run();
}
...
...
@SpringBootTest
public class AuthTest {
@Resource
private AuthTestMethodService authTestService;
@Resource
private AuthTestClassService authTestClassService;
@Test
void testInit(){
AuthTestMethodService authTestService2 = new AuthTestMethodService();
authTestService2.testHasRole();
System.out.println("================");
UserContext user = new UserContext();
user.setRoles("admin,test");
/* testAuth(user,()->{
authTestService.testHasRole();
});*/
testAuth(user,()->{
authTestService.testHasRole();
authTestService.testHasAllRole();
});
user.setRoles("test");
testAuth(user,()->{
authTestService.testHasAnyRole();
authTestService.testHasAllRole();
});
}
@Test
void testClass(){
System.out.println("================");
UserContext user = new UserContext();
user.setRoles("admin,test");
testAuth(user,()->{
authTestClassService.testHasRole();
});
user.setRoles("test");
testAuth(user,()->{
authTestClassService.testHasRole();
});
}
private void testAuth(UserContext user, Executer executer) {
AuthContext.setUserContext(user);
// 执行
try{
executer.run();
}catch (Exception e){
throw e;
}finally {
AuthContext.removeUserContext();
}
}
}





 本文介绍在Spring Boot中利用自定义注解+切面实现接口权限控制,引入SpEL表达式。阐述了SpEL概念,其可在运行期将值装配到属性或构造函数。还说明了开发步骤,包括引入包、定义注解、切面和用户上下文,最后介绍了测试方法。
本文介绍在Spring Boot中利用自定义注解+切面实现接口权限控制,引入SpEL表达式。阐述了SpEL概念,其可在运行期将值装配到属性或构造函数。还说明了开发步骤,包括引入包、定义注解、切面和用户上下文,最后介绍了测试方法。

















 301
301

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








