在项目开发中,经常需要在项目启动的时候去读取配置文件、或者把数据库的数据加载到缓存中。Spring Boot提供了ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner来帮助我们实现这些需求,他们都是在Spring容器初始化完毕之后执行起run方法。
SpringApplication-run方法
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// 1、创建并启动计时监控类
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
// 2、初始化应用上下文和异常报告集合
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
// 3、设置系统属性 `java.awt.headless` 的值,默认值为:true
configureHeadlessProperty();
// 4、创建所有 Spring 运行监听器并发布应用启动事件
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
try {
// 5、 参数封装,也就是在命令行下启动应用带的参数,如--server.port=9000
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
args);
// 6、根据运行监听器和应用参数来准备 Spring 环境(本文重点)
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,
applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
// 7、创建 Banner 打印类
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
// 8、创建应用上下文
context = createApplicationContext();
// 9、准备异常报告器
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(
SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
// 10、准备应用上下文
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,
printedBanner);
// 11、刷新应用上下文
refreshContext(context);
// 12、应用上下文刷新后置处理
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
// 13、停止计时监控类
stopWatch.stop();
// 14、输出日志记录执行主类名、时间信息
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
.logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
// 15、发布应用上下文启动完成事件
listeners.started(context);
// 16、执行所有 Runner 运行器
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
// 17、发布应用上下文就绪事件
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
// 18、返回应用上下文
return context;
}
实现逻辑
让我们来看看这个方法callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
逻辑比较简单分为三部分
- 首先分别获取ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner的bean放入List中
- 根据实现类上面的Order值进行排序
- 分别执行它们的run方法
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
List<Object> runners = new ArrayList<>();
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values());
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners);
for (Object runner : new LinkedHashSet<>(runners)) {
if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner) {
callRunner((ApplicationRunner) runner, args);
}
if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner) {
callRunner((CommandLineRunner) runner, args);
}
}
}
那么如果是ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner的order是相同的谁会先执行呢?
- 准备两个ApplicationRunner实现类的Order值为1,2
- 准备两个CommandLineRunner实现类的Order值为1,2
测试结果
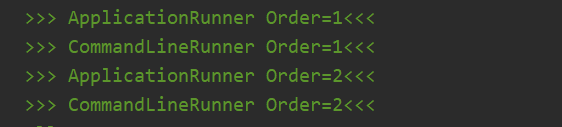
Order值相同的话ApplicationRunner先执行
在callRunner中发现ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner的run方法args用的不一样
private void callRunner(ApplicationRunner runner, ApplicationArguments args) {
try {
(runner).run(args);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to execute ApplicationRunner", ex);
}
}
private void callRunner(CommandLineRunner runner, ApplicationArguments args) {
try {
(runner).run(args.getSourceArgs());
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to execute CommandLineRunner", ex);
}
}
ApplicationArguments args是什么
- 传递参数的一种方式; 例如启动的时候
java -jar --spring.profiles.active=prod - 使用方式是 --key=value
它的配置优先于项目里面的配置;
在run方法里面我们跟踪这个看
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
找到解析args的类
class SimpleCommandLineArgsParser {
/**
* Parse the given {@code String} array based on the rules described {@linkplain
* SimpleCommandLineArgsParser above}, returning a fully-populated
* {@link CommandLineArgs} object.
* @param args command line arguments, typically from a {@code main()} method
*/
public CommandLineArgs parse(String... args) {
CommandLineArgs commandLineArgs = new CommandLineArgs();
for (String arg : args) {
if (arg.startsWith("--")) {
String optionText = arg.substring(2, arg.length());
String optionName;
String optionValue = null;
if (optionText.contains("=")) {
optionName = optionText.substring(0, optionText.indexOf('='));
optionValue = optionText.substring(optionText.indexOf('=')+1, optionText.length());
}
else {
optionName = optionText;
}
if (optionName.isEmpty() || (optionValue != null && optionValue.isEmpty())) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid argument syntax: " + arg);
}
commandLineArgs.addOptionArg(optionName, optionValue);
}
else {
commandLineArgs.addNonOptionArg(arg);
}
}
return commandLineArgs;
}
}
就是解析--key=value的格式。
我们在启动的时候加上参数
通过断点可以清楚的看到,上面是ApplicationRunner,下面是CommandLineRunner的入参
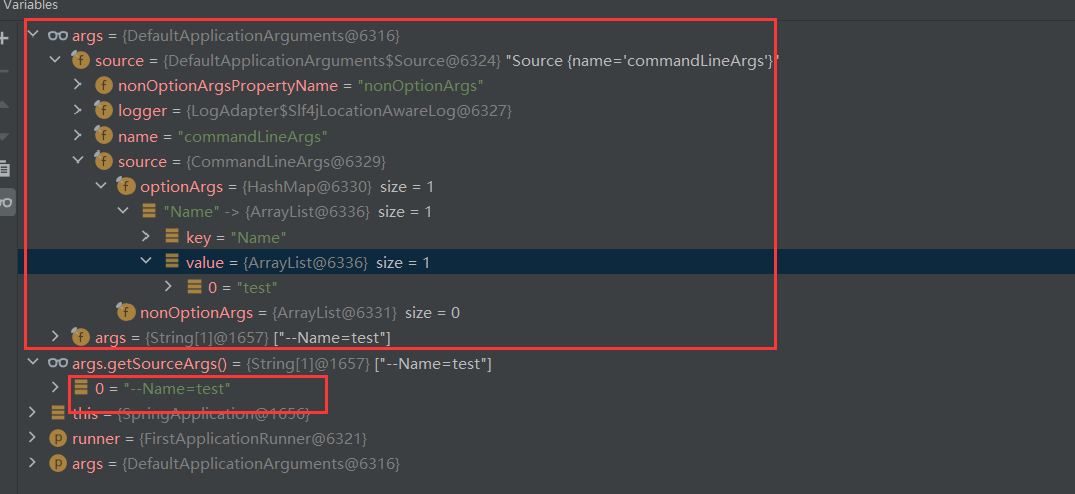
区别
- ApplicationRunner优先于CommandLineRunner执行,在Order相同的情况下
- ApplicationRunner的入参是解析过的,CommandLineRunner的入参没有处理





 本文详细介绍了SpringBoot的启动过程,特别是`SpringApplication.run`方法的内部逻辑。它首先获取`ApplicationRunner`和`CommandLineRunner`的Bean并按`Order`值排序,然后执行它们的`run`方法。当`Order`相同,`ApplicationRunner`会先于`CommandLineRunner`执行。`ApplicationArguments`用于接收启动参数,其值优于项目内配置。不同之处在于,`ApplicationRunner`的参数已经解析,而`CommandLineRunner`的参数未经处理。
本文详细介绍了SpringBoot的启动过程,特别是`SpringApplication.run`方法的内部逻辑。它首先获取`ApplicationRunner`和`CommandLineRunner`的Bean并按`Order`值排序,然后执行它们的`run`方法。当`Order`相同,`ApplicationRunner`会先于`CommandLineRunner`执行。`ApplicationArguments`用于接收启动参数,其值优于项目内配置。不同之处在于,`ApplicationRunner`的参数已经解析,而`CommandLineRunner`的参数未经处理。





























