一、前言
最近要求做系统的全局日志记录功能,要求把执行的完整SQL语句保存到数据库中,在实际开发中最终放弃了使用AOP的方法,改由使用mybatis的拦截器实现,这里简单记录一下实现过程。
系统数据库主要环境:
- 数据库:MySQL
- 数据源:DruidDataSource
二、创建数据库用表
这里只是简单演示一下实现过程,只用两张表模拟一下:
- 用户表(user)
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL,
`age` int(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
- 日志表(sys_log)
CREATE TABLE `sys_log` (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '主键',
`uri` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '调用的接口',
`daoMethodName` varchar(1000) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'DAO层执行的方法名称',
`ip` varchar(100) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'ip地址',
`wholeSql` mediumtext CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci NULL COMMENT '完整SQL语句',
`desc` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '描述',
`createDate` datetime(0) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '创建时间',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
注意:不要使用“SQL”关键字作为字段名称,否则后续系统执行SQL语句会报错。
三、创建演示项目
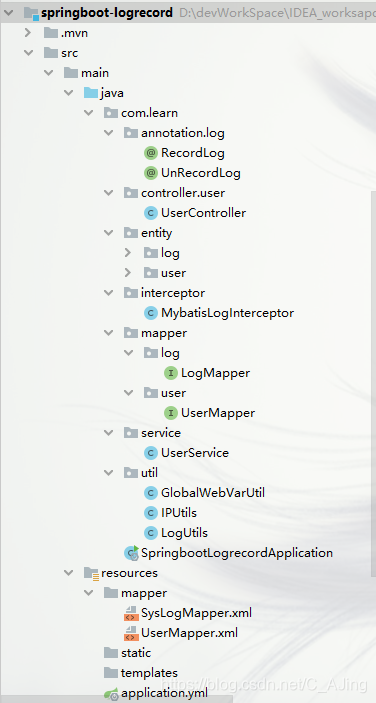
- 创建一个spring boot项目,项目结构如下:
2. 导入maven依赖:
<!--spring boot web-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--mybatis-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.4</version>
</dependency>
<!--druid-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
</dependency>
<!--apache工具类-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId>
<version>3.11</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!--lombok-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<!--spring boot test-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
- 修改application.yml配置文件:
server:
port: 8888
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/bg-learnsp?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false # 连接数据库的url
username: root # 连接数据库的用户名
password: root # 连接数据库的密码
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
mybatis:
mapper-locations: classpath:/mapper/*.xml
- 创建用户和日志的实体类:
- User类:
package com.learn.entity.user;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Setter;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Setter
@Getter
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class User implements Serializable {
private long id;
private Integer age;
private String name;
}
- SysLog类:
package com.learn.entity.log;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.Date;
@Data
public class SysLog {
private long id;
private String uri;
private String daoMethodName;
private String ip;
private String wholeSql;
private String desc;
private Date createDate;
}
- 创建用户和日志的mapper接口和xml文件:
- UserMapper:
package com.learn.mapper.user;
import com.learn.entity.user.User;
import java.util.List;
public interface UserMapper {
List<User> selectAllUsers();
int insert(User user);
}
- UserMapper.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.learn.mapper.user.UserMapper">
<select id="selectAllUsers" resultType="com.learn.entity.user.User">
select id,age,name from user
</select>
<insert id="insert" parameterType="com.learn.entity.user.User">
INSERT INTO USER(ID,NAME, AGE) VALUES(#{id},#{name}, #{age})
</insert>
</mapper>
- LogMapper:
package com.learn.mapper.log;
import com.learn.entity.log.SysLog;
public interface LogMapper {
int insertLog(SysLog sysLog);
}
- SysLogMapper.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.learn.mapper.log.LogMapper">
<insert id="insertLog" parameterType="com.learn.entity.log.SysLog">
INSERT INTO `sys_log`(`id`, `uri`,`daoMethodName`, `ip`, `wholeSql`,`desc`, `createDate`) VALUES (#{id}, #{uri}, #{daoMethodName}, #{ip}, #{wholeSql}, #{desc}, #{createDate})
</insert>
</mapper>
- 修改启动类,添加相关配置:
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("com.learn.mapper.user") //mapper包扫描
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class SpringbootLogrecordApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootLogrecordApplication.class, args);
}
}
四、自定义日志注解和增加工具类
为了增加日记记录的灵活性,增加两个自定义日志注解:
- RecordLog注解:
package com.learn.annotation.log;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
/**
* 使用此注解标识DAO层需要日记记录的方法
*
*/
public @interface RecordLog {
/**
* 日志记录描述
*
* @return
*/
String desc() default "";
}
- UnRecordLog注解:
package com.learn.annotation.log;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
/**
* 使用此注解标识DAO层不需要日记记录的方法
*
*/
public @interface UnRecordLog {
}
为了方便开发,增加几个工具类:
- GlobalWebVarUtil工具类主要用于获取HttpServletRequest对象:
public class GlobalWebVarUtil {
/**
* 得到HttpServletRequest对象
*
* @return
*/
public static HttpServletRequest getRequest() {
RequestAttributes requestAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
return requestAttributes != null ? ((ServletRequestAttributes) requestAttributes).getRequest() : null;
}
/**
* 设置父线程requestAttributes共享 当异步执行的DAO方法需要记录日志时,需要先调用此方法设置
*/
public static void setParentRequestShare() {
RequestAttributes requestAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
if (requestAttributes != null) {
RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributes(requestAttributes, true);
}
}
}
- IPUtils工具类主要用于获取ip地址:
@Slf4j
public class IPUtils {
/**
* 获取请求主机IP地址,如果通过代理进来,则透过防火墙获取真实IP地址;
*
* @param request
* @return
*/
public static String getIpAddress(HttpServletRequest request) {
// 获取请求主机IP地址,如果通过代理进来,则透过防火墙获取真实IP地址
String ip = request.getHeader("X-Forwarded-For");
if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(ip)) {
if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(ip)) {
ip = request.getHeader("Proxy-Client-IP");
}
if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(ip)) {
ip = request.getHeader("WL-Proxy-Client-IP");
}
if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(ip)) {
ip = request.getHeader("HTTP_CLIENT_IP");
}
if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(ip)) {
ip = request.getHeader("HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR");
}
if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(ip)) {
ip = request.getRemoteAddr();
}
} else if (ip.length() > 15) {
String[] ips = ip.split(",");
for (int index = 0; index < ips.length; index++) {
String strIp = (String) ips[index];
if (!("unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(strIp))) {
ip = strIp;
break;
}
}
}
if ("127.0.0.1".equals(ip) || "0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1".equals(ip)) {
// 根据网卡取本机配置的IP
try {
ip = getLocalIp();
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
log.error("获取请求主机IP地址异常!", e);
ip = "UNIP";
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return ip;
}
/**
* 获取本机IP
*/
public static String getLocalIp() throws UnknownHostException {
InetAddress inetAddress = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
String ip = inetAddress.getHostAddress().toString();// 获得本机Ip
return ip;
}
}
接下来重点介绍一下LogUtils工具类:
@Component
@Slf4j
public class LogUtils {
/**
* 默认记录操作日志的DAO层方法名开头
*/
public static final String[] DEFAULT_RECORD_METHOD_START = {"insert", "update", "delete", "remove"};
/**
* 默认不记录的操作方法(记录日志的方法)
*/
public static final String[] DEFAULT_NOT_RECORED_METHOD = new String[]{"com.learn.mapper.log.LogMapper.insertLog"};
private static LogUtils logUtils;
/**
* 注入SqlSessionFactory对象
*/
@Autowired
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
/**
* 注入DataSource对象
*/
@Autowired
private DataSource mysqlDataSource;
private LogUtils() {
}
/**
* 给logUtils对象赋值
*/
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
logUtils = this;
logUtils.sqlSessionFactory = this.sqlSessionFactory;
logUtils.mysqlDataSource = this.mysqlDataSource;
}
/**
* 判断方法名是否满足日志记录格式
*
* @param methodName
* @return
*/
public static boolean verifyMethodName(String methodName) {
boolean methodNameFlag = false;
for (int i = 0; i < DEFAULT_RECORD_METHOD_START.length; i++) {
if (methodName.startsWith(DEFAULT_RECORD_METHOD_START[i])) {
methodNameFlag = true;
break;
}
}
return methodNameFlag;
}
/**
* 验证方法是否需要日志记录
*
* @param methodFullName
* @return
*/
public static Map<String, Object> verifyRecordLog(String methodFullName) {
Map<String, Object> resultMap = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < DEFAULT_NOT_RECORED_METHOD.length; i++) {
if (methodFullName.equals(DEFAULT_NOT_RECORED_METHOD[i])) {
return resultMap;
}
}
boolean isRecord = false;
String desc = StringUtils.EMPTY;
int flag = methodFullName.lastIndexOf(".");
String classPath = methodFullName.substring(0, flag);
String methodName = methodFullName.substring(flag + 1);
Class<?> clazz = null;
try {
clazz = Class.forName(classPath);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
log.error("判断是否需要记录日志异常!", e);
}
if (clazz != null) {
Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for (int i = 0; i < methods.length; i++) {
Method method = methods[i];
if (methodName.equals(method.getName())) { // 找到当前方法
RecordLog rl = method.getAnnotation(RecordLog.class); // 判断是否有RecordLog注解
if (rl != null) { // 有RecordLog注解,直接进行记录
isRecord = true;
desc = rl.desc();
} else {
// 没有UnRecordLog注解,并且方法满足记录格式则进行记录
if (method.getAnnotation(UnRecordLog.class) == null && verifyMethodName(methodName)) {
isRecord = true;
}
}
break;
}
}
}
resultMap.put("isRecord", isRecord); // 是否记录
resultMap.put("desc", desc); // 方法描述
return resultMap;
}
/**
* 填充日记记录SQL参数
*
* @param methodFullName
* @param desc
* @param originalSql
* @return
*/
private static List<Object> getParamList(String methodFullName, String desc, String originalSql) {
List<Object> paramList = new ArrayList<>();
String unknownFlag = "UNKNOWN";
// 获取Request对象
HttpServletRequest request = GlobalWebVarUtil.getRequest();
String uri;
String ip;
if (request == null) {
uri = unknownFlag;
ip = unknownFlag;
} else {
uri = request.getRequestURI();
ip = IPUtils.getIpAddress(request);
}
// id
paramList.add(System.currentTimeMillis());
// 调用的接口
paramList.add(uri);
//DAO层执行的方法名称
paramList.add(methodFullName);
// ip地址
paramList.add(ip);
// 完整SQL语句
paramList.add(handlerSql(originalSql));
// 描述
paramList.add(desc);
// 创建时间
paramList.add(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()));
return paramList;
}
/**
* 处理SQL语句
*
* @param originalSql
* @return
*/
private static String handlerSql(String originalSql) {
String sql = originalSql.substring(originalSql.indexOf(":") + 1);
// 将原始sql中的空白字符(\s包括换行符,制表符,空格符)替换为" "
return sql.replaceAll("[\\s]+", " ");
}
/**
* 获取日志保存SQL
*
* @param methodFullName
* @param desc
* @param originalSql
* @return
*/
public static String getSaveLogSql(String methodFullName, String desc, String originalSql) {
String sql = logUtils.sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration()
.getMappedStatement(DEFAULT_NOT_RECORED_METHOD[0]).getBoundSql(null).getSql();
List<Object> paramList = getParamList(methodFullName, desc, originalSql);
sql = paramList != null && !paramList.isEmpty() ? SQLUtils.format(sql, JdbcConstants.MYSQL, paramList) : null;
return sql;
}
/**
* 获取mysql Connection对象
*
* @return
*/
public static Connection getMysqlConnection() {
Connection conn = null;
try {
conn = logUtils.mysqlDataSource.getConnection();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
log.error("保存日志时获取Connection对象异常!", e);
}
return conn;
}
}
工具类的代码注释写的很清晰了,主要就是判断一下DAO层的方法是否需要记录(默认记录DAO层以"insert", “update”, “delete”, "remove"开头的方法),以及填充日志记录SQL进行记录保存到数据库,代码中使用的SQLUtils工具类,是druid自带的工具类。
五、日志记录拦截器实现
自己实现一个mybatis的拦截器,然后进行判断是否需要日志记录,核心代码:
package com.learn.interceptor;
import com.learn.util.LogUtils;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.apache.ibatis.executor.statement.StatementHandler;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.MappedStatement;
import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.*;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.MetaObject;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.SystemMetaObject;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.ResultHandler;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = StatementHandler.class, method = "query", args = {Statement.class, ResultHandler.class}),
@Signature(type = StatementHandler.class, method = "update", args = {Statement.class}),
@Signature(type = StatementHandler.class, method = "batch", args = {Statement.class})
})
@Slf4j
@Component
public class MybatisLogInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// 执行方法
Object result = invocation.proceed();
// 获取MapperStatement对象,获取到sql的详细信息
Object realTarget = realTarget(invocation.getTarget());
// 获取metaObject对象
MetaObject metaObject = SystemMetaObject.forObject(realTarget);
// 获取MappedStatement对象
MappedStatement ms = (MappedStatement) metaObject.getValue("delegate.mappedStatement");
// 获取方法的全类名称
String methodFullName = ms.getId();
// 判断是否是需要日志记录的方法
Map<String, Object> map = LogUtils.verifyRecordLog(methodFullName);
if (!map.isEmpty() && (boolean) map.get("isRecord")) {
Statement statement;
// 获取方法参数
Object[] args = invocation.getArgs();
Object firstArg = args[0];
if (Proxy.isProxyClass(firstArg.getClass())) {
statement = (Statement) SystemMetaObject.forObject(firstArg).getValue("h.statement");
} else {
statement = (Statement) firstArg;
}
MetaObject stmtMetaObj = SystemMetaObject.forObject(statement);
// 获取Statement对象(sql语法已经构建完毕)
statement = (Statement) stmtMetaObj.getOriginalObject();
// 获取sql语句
String originalSql = statement.toString();
String saveLogSql = LogUtils.getSaveLogSql(methodFullName, (String) map.get("desc"), originalSql);
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(saveLogSql)) {
Connection connection = statement.getConnection();
if (connection.isReadOnly()) { // 当前事务是只读事务,则重新用不同的Connection对象
Connection mysqlConnection = LogUtils.getMysqlConnection();
if (mysqlConnection != null) {
try {
mysqlConnection.createStatement().execute(saveLogSql);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
log.error("拦截器记录日志出错!", e);
} finally {
mysqlConnection.close();//关闭连接
}
}
} else {
connection.createStatement().execute(saveLogSql);
}
}
}
return result;
}
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {
if (target instanceof StatementHandler) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
return target;
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties prop) {
}
/**
* <p>
* 获得真正的处理对象,可能多层代理.
* </p>
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> T realTarget(Object target) {
if (Proxy.isProxyClass(target.getClass())) {
MetaObject metaObject = SystemMetaObject.forObject(target);
return realTarget(metaObject.getValue("h.target"));
}
return (T) target;
}
}
拦截器的核心代码已经全都注释的很清晰了,思路如下:
- 判断该DAO层的方法是否需要记录日志;
- 如果需要记录,则获取日志记录的完整SQL;
- 获取当前Connection对象,执行日志记录SQL(如果当前Connection对象是只读的,则重新从数据源获取一个新的Connection对象)。
六、测试
为了简单,创建一个UserController类进行测试:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
@Slf4j
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
/**
* 查询所有user
*
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("listAll")
public List<User> listAllUsers() {
return userService.listAllUsers();
}
@GetMapping("saveDefaultUser")
public int saveDefaultUser() {
log.info("保存了默认用户");
return userService.saveDefaultUser(new User(System.currentTimeMillis(), 23, "admin"));
}
}
运行程序,分别访问:
查询数据库sys_log表:

可以看到成功记录了com.learn.mapper.user.UserMapper#insert方法执行的完整SQL。
下面,使用一下 @RecordLog注解和@UnRecordLog注解:
public interface UserMapper {
@RecordLog(desc="查询所有用户")
List<User> selectAllUsers();
@UnRecordLog
int insert(User user);
}
先删除sys_log中的数据,再次访问上面两个链接地址,查询数据库sys_log表:

可以看到,这次只记录了selectAllUsers方法执行的SQL,没有记录insert方法执行的SQL。
到此,spring boot 2.x 使用mybatis拦截器实现系统日志记录(将完整参数的SQL语句记录到数据库中)就简单实现了。

























 841
841











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








