哇 这次上了波分 开心
这次的题目,作为弱弱的我,感觉A题还是可以的,用到模拟
A:
Karen is getting ready for a new school day!

It is currently hh:mm, given in a 24-hour format. As you know, Karen loves palindromes, and she believes that it is good luck to wake up when the time is a palindrome.
What is the minimum number of minutes she should sleep, such that, when she wakes up, the time is a palindrome?
Remember that a palindrome is a string that reads the same forwards and backwards. For instance, 05:39 is not a palindrome, because 05:39 backwards is 93:50. On the other hand, 05:50 is a palindrome, because 05:50 backwards is 05:50.
The first and only line of input contains a single string in the format hh:mm (00 ≤ hh ≤ 23, 00 ≤ mm ≤ 59).
Output a single integer on a line by itself, the minimum number of minutes she should sleep, such that, when she wakes up, the time is a palindrome.
05:39
11
13:31
0
23:59
1
In the first test case, the minimum number of minutes Karen should sleep for is 11. She can wake up at 05:50, when the time is a palindrome.
In the second test case, Karen can wake up immediately, as the current time, 13:31, is already a palindrome.
In the third test case, the minimum number of minutes Karen should sleep for is 1 minute. She can wake up at 00:00, when the time is a palindrome.
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<memory.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
string x;
int a;
int b;
int dir;
int ans;
int x1[4];
bool cp()
{
if (x1[0] == x1[3] && x1[1] == x1[2])
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
int main()
{
cin >> x;
x1[0] = x[0] - '0';
x1[1] = x[1] - '0';
x1[2] = x[3] - '0';
x1[3] = x[4] - '0';
for (int i = 0; ;i++)
{
if (cp() == 1)
{
cout << i << endl;
break;
}
x1[3]++;
if (x1[3] == 10)
{
x1[3] = 0;
x1[2]++;
}
if (x1[2] == 6)
{
x1[2] = 0;
x1[1]++;
}
if (x1[1] == 10)
{
x1[1] = 0;
x1[0]++;
}
if (x1[1] == 4 && x1[0] == 2)
{
x1[1] = 0;
x1[0] = 0;
}
}
return 0;
}To stay woke and attentive during classes, Karen needs some coffee!

Karen, a coffee aficionado, wants to know the optimal temperature for brewing the perfect cup of coffee. Indeed, she has spent some time reading several recipe books, including the universally acclaimed "The Art of the Covfefe".
She knows n coffee recipes. The i-th recipe suggests that coffee should be brewed between li and ri degrees, inclusive, to achieve the optimal taste.
Karen thinks that a temperature is admissible if at least k recipes recommend it.
Karen has a rather fickle mind, and so she asks q questions. In each question, given that she only wants to prepare coffee with a temperature between a and b, inclusive, can you tell her how many admissible integer temperatures fall within the range?
The first line of input contains three integers, n, k (1 ≤ k ≤ n ≤ 200000), and q (1 ≤ q ≤ 200000), the number of recipes, the minimum number of recipes a certain temperature must be recommended by to be admissible, and the number of questions Karen has, respectively.
The next n lines describe the recipes. Specifically, the i-th line among these contains two integers li and ri (1 ≤ li ≤ ri ≤ 200000), describing that the i-th recipe suggests that the coffee be brewed between li and ri degrees, inclusive.
The next q lines describe the questions. Each of these lines contains a and b, (1 ≤ a ≤ b ≤ 200000), describing that she wants to know the number of admissible integer temperatures between a and b degrees, inclusive.
For each question, output a single integer on a line by itself, the number of admissible integer temperatures between a and b degrees, inclusive.
3 2 4 91 94 92 97 97 99 92 94 93 97 95 96 90 100
3 3 0 4
2 1 1 1 1 200000 200000 90 100
0
In the first test case, Karen knows 3 recipes.
- The first one recommends brewing the coffee between 91 and 94 degrees, inclusive.
- The second one recommends brewing the coffee between 92 and 97 degrees, inclusive.
- The third one recommends brewing the coffee between 97 and 99 degrees, inclusive.
A temperature is admissible if at least 2 recipes recommend it.
She asks 4 questions.
In her first question, she wants to know the number of admissible integer temperatures between 92 and 94 degrees, inclusive. There are 3: 92, 93 and 94 degrees are all admissible.
In her second question, she wants to know the number of admissible integer temperatures between 93 and 97 degrees, inclusive. There are 3: 93, 94 and 97 degrees are all admissible.
In her third question, she wants to know the number of admissible integer temperatures between 95 and 96 degrees, inclusive. There are none.
In her final question, she wants to know the number of admissible integer temperatures between 90 and 100 degrees, inclusive. There are 4: 92, 93, 94 and 97 degrees are all admissible.
In the second test case, Karen knows 2 recipes.
- The first one, "wikiHow to make Cold Brew Coffee", recommends brewing the coffee at exactly 1 degree.
- The second one, "What good is coffee that isn't brewed at at least 36.3306 times the temperature of the surface of the sun?", recommends brewing the coffee at exactly 200000 degrees.
A temperature is admissible if at least 1 recipe recommends it.
In her first and only question, she wants to know the number of admissible integer temperatures that are actually reasonable. There are none.
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<memory.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int da1[200010];
int ans[200010];
int main()
{
memset(da1, 0, sizeof da1);
int n;
int k;
int q;
int l;
int r;
scanf("%d %d %d", &n, &k, &q);
while (n--)
{
scanf("%d %d", &l, &r);
da1[l]++;
da1[r + 1]--;
}
for (int i = 1;i < 200010;i++)
da1[i] = da1[i - 1] + da1[i];
ans[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1;i < 200010;i++)
if (da1[i] >= k)
ans[i] = ans[i - 1] + 1;
else
ans[i] = ans[i - 1];
while (q--)
{
scanf("%d %d", &l, &r);
printf("%d\n", ans[r] - ans[l - 1]);
}
return 0;
}On the way to school, Karen became fixated on the puzzle game on her phone!

The game is played as follows. In each level, you have a grid with n rows and m columns. Each cell originally contains the number 0.
One move consists of choosing one row or column, and adding 1 to all of the cells in that row or column.
To win the level, after all the moves, the number in the cell at the i-th row and j-th column should be equal to gi, j.
Karen is stuck on one level, and wants to know a way to beat this level using the minimum number of moves. Please, help her with this task!
The first line of input contains two integers, n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 100), the number of rows and the number of columns in the grid, respectively.
The next n lines each contain m integers. In particular, the j-th integer in the i-th of these rows contains gi, j (0 ≤ gi, j ≤ 500).
If there is an error and it is actually not possible to beat the level, output a single integer -1.
Otherwise, on the first line, output a single integer k, the minimum number of moves necessary to beat the level.
The next k lines should each contain one of the following, describing the moves in the order they must be done:
- row x, (1 ≤ x ≤ n) describing a move of the form "choose the x-th row".
- col x, (1 ≤ x ≤ m) describing a move of the form "choose the x-th column".
If there are multiple optimal solutions, output any one of them.
3 5 2 2 2 3 2 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 2 1
4 row 1 row 1 col 4 row 3
3 3 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
-1
3 3 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
3 row 1 row 2 row 3
In the first test case, Karen has a grid with 3 rows and 5 columns. She can perform the following 4 moves to beat the level:
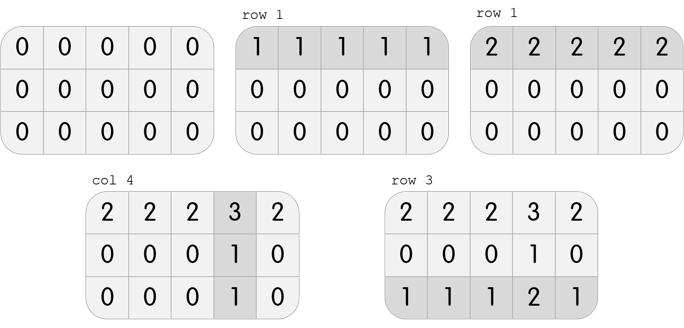
In the second test case, Karen has a grid with 3 rows and 3 columns. It is clear that it is impossible to beat the level; performing any move will create three 1s on the grid, but it is required to only have one 1 in the center.
In the third test case, Karen has a grid with 3 rows and 3 columns. She can perform the following 3 moves to beat the level:
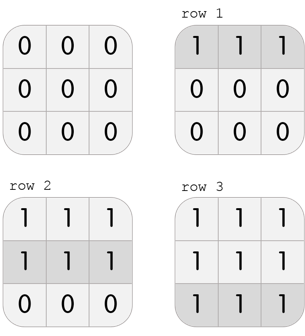
Note that this is not the only solution; another solution, among others, is col 1, col 2, col 3.
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<memory.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int x;
int y;
int da[110][110];
int da2[110][110];
int minx[110];
int waysx[110];
int waysy[110];
int main()
{
memset(waysx, 0, sizeof waysx);
memset(waysy, 0, sizeof waysy);
scanf("%d %d ", &x, &y);
for (int i = 0;i < x;i++)
for (int j = 0;j < y;j++)
{
scanf("%d", &da[i][j]);
da2[j][i] = da[i][j];
}
int ans = 0;
if (y >= x)
{
for (int i = 0;i < x;i++)
{
int min = 10000000;
for (int j = 0;j < y;j++)
if (da[i][j] < min)
min = da[i][j];
ans += min;
waysx[i]+=min;
for (int j = 0;j < y;j++)
da[i][j] -= min;
}
for (int j = 0;j < y;j++)
{
int dir = da[0][j];
for (int i = 0;i < x;i++)
{
if (da[i][j] != da[0][j])
{
printf("-1\n");
return 0;
}
}
waysy[j] += da[0][j];
ans += da[0][j];
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
for (int i = 0;i < x;i++)
{
while (waysx[i] > 0)
{
printf("row %d\n", i+1);
waysx[i]--;
}
}
for (int j = 0;j < y;j++)
{
while (waysy[j] > 0)
{
printf("col %d\n", j+1);
waysy[j]--;
}
}
}
else
{
int c = x;
x = y;
y = c;
for (int i = 0;i < x;i++)
{
int min = 10000000;
for (int j = 0;j < y;j++)
if (da2[i][j] < min)
min = da2[i][j];
ans += min;
waysy[i] += min;
for (int j = 0;j < y;j++)
da2[i][j] -= min;
}
for (int j = 0;j < y;j++)
{
int dir = da2[0][j];
for (int i = 0;i < x;i++)
{
if (da2[i][j] != da2[0][j])
{
printf("-1\n");
return 0;
}
}
waysx[j] += da2[0][j];
ans += da2[0][j];
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
for (int i = 0;i < y;i++)
{
while (waysx[i] > 0)
{
printf("row %d\n", i+1);
waysx[i]--;
}
}
for (int j = 0;j < x;j++)
{
while (waysy[j] > 0)
{
printf("col %d\n", j+1);
waysy[j]--;
}
}
}
//printf("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
}






















 295
295

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








