import java.awt.GridLayout;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class TestFigurePanel extends JFrame {
public TestFigurePanel()
{
setLayout(new GridLayout(2,3,5,5));
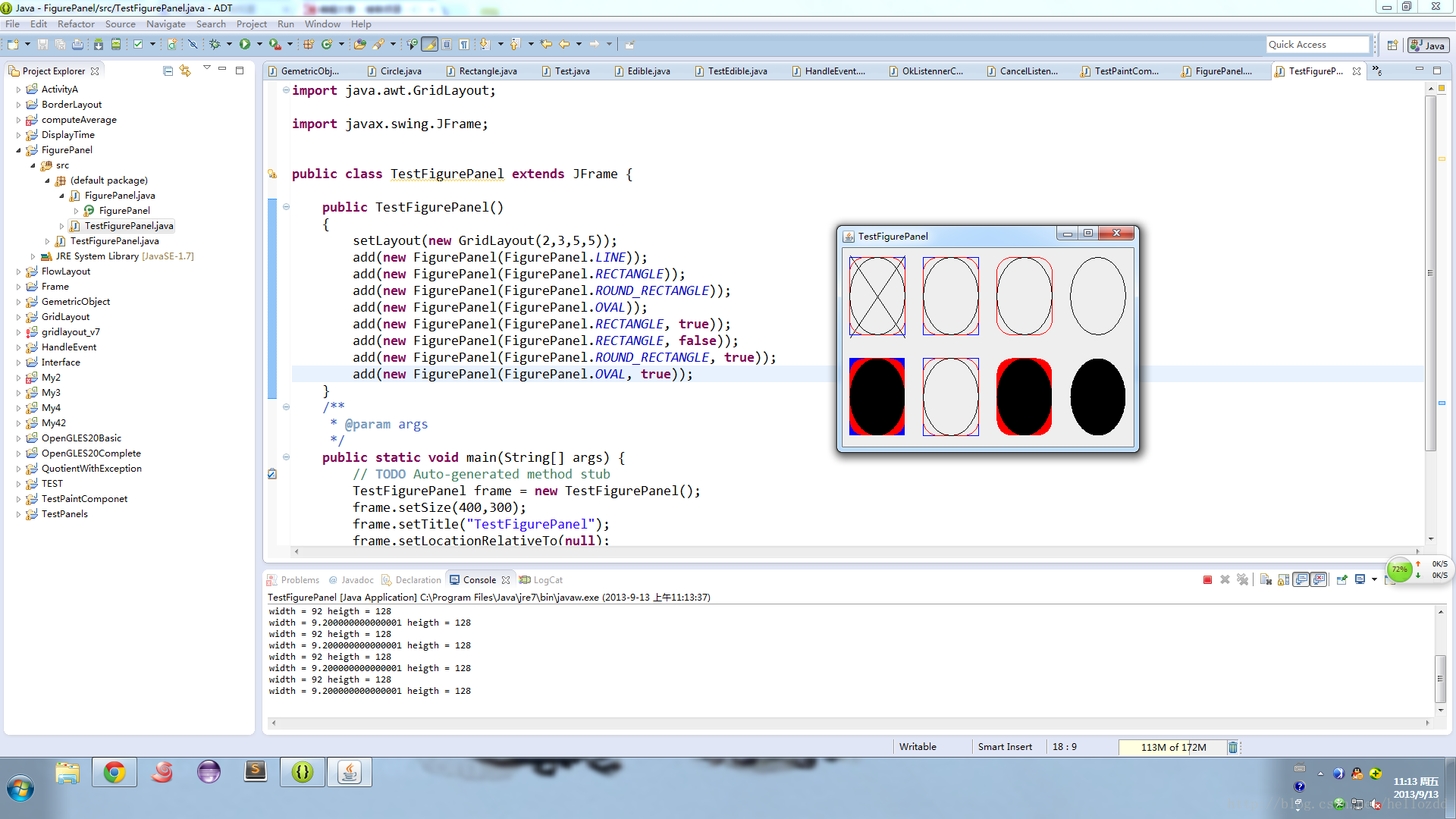
add(new FigurePanel(FigurePanel.LINE));
add(new FigurePanel(FigurePanel.RECTANGLE));
add(new FigurePanel(FigurePanel.ROUND_RECTANGLE));
add(new FigurePanel(FigurePanel.OVAL));
add(new FigurePanel(FigurePanel.RECTANGLE, true));
add(new FigurePanel(FigurePanel.RECTANGLE, false));
add(new FigurePanel(FigurePanel.ROUND_RECTANGLE, true));
add(new FigurePanel(FigurePanel.OVAL, true));
}
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
TestFigurePanel frame = new TestFigurePanel();
frame.setSize(400,300);
frame.setTitle("TestFigurePanel");
frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
public class FigurePanel extends JPanel {
// define constants
public static final int LINE = 1;
public static final int RECTANGLE = 2;
public static final int ROUND_RECTANGLE = 3;
public static final int OVAL = 4;
private int type = 1;
private boolean filled = false;
public FigurePanel()
{
}
public FigurePanel(int type)
{
this.type = type;
}
public FigurePanel(int type, boolean filled)
{
this.type = type;
this.filled = filled;
}
protected void paintComponent(Graphics g)
{
super.paintComponents(g);
int width = getWidth();
int height = getHeight();
System.out.println("width = " + width + " heigth = "+ height);
System.out.println("width = " + ((int)width*0.1) + " heigth = "+ height);
switch (type)
{
case LINE:
{
g.setColor(Color.BLACK);
g.drawLine(10, 10, width - 10, height - 10);
g.drawLine(width - 10, 10, 10, height - 10);
}
case RECTANGLE:
{
g.setColor(Color.BLUE);
if (filled)
{
g.fillRect((int)(0.1*width), (int)(0.1 * height), (int)(0.8 *width), (int)(0.8*height));
}
else
{
g.drawRect((int)(0.1*width), (int)(0.1 * height), (int)(0.8 *width), (int)(0.8*height));
}
}
case ROUND_RECTANGLE:
{
g.setColor(Color.RED);
if (filled)
{
g.fillRoundRect((int)(0.1*width), (int)(0.1 * height), (int)(0.8 *width), (int)(0.8*height), 40, 40);
}
else
{
g.drawRoundRect((int)(0.1*width), (int)(0.1 * height), (int)(0.8 *width), (int)(0.8*height), 40, 40);
}
}
case OVAL:
{
g.setColor(Color.BLACK);
if (filled)
{
g.fillOval((int)(0.1*width), (int)(0.1 * height), (int)(0.8 *width), (int)(0.8*height));
}
else
{
g.drawOval((int)(0.1*width), (int)(0.1 * height), (int)(0.8 *width), (int)(0.8*height));
}
}
}
}
public void setType(int type)
{
this.type = type;
}
public int getType()
{
return type;
}
public void setFilled(boolean filled)
{
this.filled = filled;
repaint();
}
public boolean isFilled()
{
return filled;
}
public Dimension getPreferredSize()
{
return new Dimension(80, 80);
}
}






















 1300
1300











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








