问题描述
在给定的有向有环图中,输入给定source和target所有的连通路径,例如下图中的 2 -> 3。本文提供 python / c++ / scala 实现步骤;
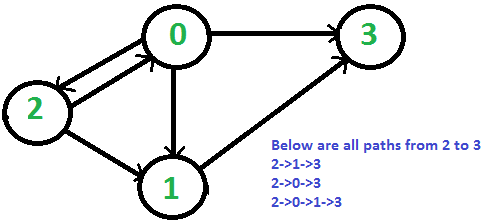
DFS 策略
Python 实现:
from collections import defaultdict
# This class represents a directed graph
# using adjacency list representation
class Graph:
def __init__(self, vertices):
# No. of vertices
self.V = vertices
# default dictionary to store graph
self.graph = defaultdict(list)
# function to add an edge to graph
def addEdge(self, u, v):
self.graph[u].append(v)
'''A recursive function to print all paths from 'u' to 'd'.
visited[] keeps track of vertices in current path.
path[] stores actual vertices and path_index is current
index in path[]'''
def printAllPathsUtil(self, u, d, visited, path):
# Mark the current node as visited and store in path
visited[u]= True
path.append(u)
# If current vertex is same as destination, then print
# current path[]
if u == d:
print path
else:
# If current vertex is not destination
# Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
for i in self.graph[u]:
if visited[i]== False:
self.printAllPathsUtil(i, d, visited, path)
# Remove current vertex from path[] and mark it as unvisited
path.pop()
visited[u]= False
# Prints all paths from 's' to 'd'
def printAllPaths(self, s, d):
# Mark all the vertices as not visited
visited =[False]*(self.V)
# Create an array to store paths
path = []
# Call the recursive helper function to print all paths
self.printAllPathsUtil(s, d, visited, path)
# Create a graph given in the above diagram
g = Graph(4)
g.addEdge(0, 1)
g.addEdge(0, 2)
g.addEdge(0, 3)
g.addEdge(2, 0)
g.addEdge(2, 1)
g.addEdge(1, 3)
s = 2 ; d = 3
print ("Following are all different paths from % d to % d :" %(s, d))
g.printAllPaths(s, d)
BFS 策略
C++ 实现:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// utility function for printing
// the found path in graph
void printpath(vector<int>& path)
{
int size = path.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout << path[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
// utility function to check if current
// vertex is already present in path
int isNotVisited(int x, vector<int>& path)
{
int size = path.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (path[i] == x)
return 0;
return 1;
}
// utility function for finding paths in graph
// from source to destination
void findpaths(vector<vector<int> >&g, int src,
int dst, int v)
{
// create a queue which stores
// the paths
queue<vector<int> > q;
// path vector to store the current path
vector<int> path;
path.push_back(src);
q.push(path);
while (!q.empty()) {
path = q.front();
q.pop();
int last = path[path.size() - 1];
// if last vertex is the desired destination
// then print the path
if (last == dst)
printpath(path);
// traverse to all the nodes connected to
// current vertex and push new path to queue
for (int i = 0; i < g[last].size(); i++) {
if (isNotVisited(g[last][i], path)) {
vector<int> newpath(path);
newpath.push_back(g[last][i]);
q.push(newpath);
}
}
}
}
// driver program
int main()
{
vector<vector<int> > g;
// number of vertices
int v = 4;
g.resize(4);
// construct a graph
g[0].push_back(3);
g[0].push_back(1);
g[0].push_back(2);
g[1].push_back(3);
g[2].push_back(0);
g[2].push_back(1);
int src = 2, dst = 3;
cout << "path from src " << src
<< " to dst " << dst << " are \n";
// function for finding the paths
findpaths(g, src, dst, v);
return 0;
}
Scala 实现:
def allPaths(graph: ConnectedGraph, alertNode: String, rootCauseNode: String): Seq[Seq[String]] = {
val logical_graph = graph.logical_error_digraph
var path = mutable.ArrayBuffer[String]()
val pathQueue: mutable.Queue[mutable.ArrayBuffer[String]] = mutable.Queue[mutable.ArrayBuffer[String]]()
val paths = mutable.ArrayBuffer[mutable.ArrayBuffer[String]]()
path.append(alertNode)
pathQueue.enqueue(path)
while (pathQueue.nonEmpty) {
path = pathQueue.dequeue()
val last = path.last
if (last == rootCauseNode) paths.append(path)
for (i <- logical_graph.out_edges(last).map(_._2)) {
if (!path.contains(i)) {
pathQueue.enqueue(path :+ i)
}
}
}





















 2094
2094











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








