文章目录
AI五子棋所用到的库
tkinter
更多的见《Python GUI之tkinter窗口视窗教程(转载篇)》
Tkinter是使用python进行窗口视窗设计的模块。
Tkinter支持16个核心的窗口部件。
- Button 按钮
- Canvas 画布
- 可以用来绘制图表和图,创建图形编辑器,实现定制窗口部件。
- Checkbutton 复选框
- Entry 单行文本框
- Frame 框架
- Label 标签
- 用于显示不可编辑的文本或图标
- LabelFrame 容器控件
- Listbox 列表框
- Menu 菜单
- Menubutton 菜单按钮
- Message 消息框
- 类似于标签,但可以显示对行文本
- OptionMenu 选择菜单
- Panedwindow 窗口布局管理
- Radiobutton 单选框
- Scale 进度条
- 允许通过滑块设置一数字值
- Scrollbar 滚动条
- Spinbox 输入控件
- Text 多行文本框
- Toplevel 顶层
- messageBox 消息框
- 用于显示应用程序的消息框
os
os库提供通用的基本操作系统交互功能,常用路径操作、进程管理、环境参数等几类。
os.path子库以path为入口,用于操作和处理文件路径。
import os
路径操作
- os.path.abspath(path)
- 返回path在当前路径中的绝对路径
- os.path.normpath(path)
- 归一化path的表示形式,统一用\分隔路径
- os.path.relpath(path)
- 返回当前程序与文件之间的相对路径
- os.path.dirname(path)
- 返回path中目录名称
- os.path.basename
- 返回path中的最后的文件名称
- *os.path.join(path, paths)
- 组合path和paths,返回一个路径字符串
- os.path.exists(path)
- 判断path对应文件或目录是否存在,返回true或false
- os.path.isfile(path)
- 判断path所对应是否为已存在的文件,返回true或false
- os.path.isdir(path)
- 判断path所对应是否为已存在的目录,返回true或false
- os.path.getatime(path)
- 返回path对应文件或目录上一次的访问时间
- os.path.getmtime(path)
- 返回path对应文件或目录最近一次的修改时间
- os.path.getctime(path)
- 返回path对应文件或目录的创建时间
- os.path.getsize(path)
- 返回path对应文件的大小,以字节为单位
进程管理
os.system(command)
执行程序或命令command,在window系统中,返回值为cmd的调用返回信息。
环境参数
-
os.chdir(path)
- 修改当前程序操作的路径
-
os.getcwd()
- 返回程序的当前路径
-
os.getlogin()
- 获得当前系统登录用户名称
-
os.cpu_count()
- 获得当前系统的cpu数量
-
os.urandom(n)
- 获得n个字节长度的随机字符串,通常用于加解密运算
具体流程
建立棋盘
初始化棋盘
def __init__(self):
self.someoneWin = False
self.humanChessed = False
self.IsStart = False
self.player = 0
self.playmethod = 0
self.bla_start_pos = [235, 235]
self.whi_chessed = []
self.bla_chessed = []
self.board = self.init_board()
self.window = Tk()
self.var = IntVar()
self.var.set(0)
self.var1 = IntVar()
self.var1.set(0)
self.window.title("myGoBang")
self.window.geometry("600x470")
self.window.resizable(0, 0)
self.can = Canvas(self.window, bg="#EEE8AC", width=470, height=470)
self.draw_board() #调用draw_board函数绘制棋盘
self.can.grid(row=0, column=0)
self.net_board = self.get_net_board()#调用get_net_board函数获取棋盘上的点信息
self.robot = Robot(self.board)
self.sgf = SGFflie()
self.cnn = myCNN()
self.cnn.restore_save() #调用restore_save函数保存和读取模型
def init_board(self):
"""初始化棋盘"""
list1 = [[-1]*15 for i in range(15)]
return list1
参数说明:
- someoneWin:标识是否有人赢了
- humanChessed:人类玩家是否下了
- IsStart:是否开始游戏了
- player:玩家是哪一方(默认为黑棋)
- playmethod:模式,和robot下棋,还是和ai下棋
- bla_start_pos:黑棋开局时下在正中间的位置
- bla_chessed:保存黑棋已经下过的棋子
- whi_chessed:保存白棋已经下过的棋子
- board:棋盘
- window:窗口
- var:用于标记选择玩家颜色的一个变量
- var1:用于标记选择robot或者ai的一个变量
- can:画布,用于绘出棋盘
- net_board:棋盘的点信息
- robot:机器人
- sgf:处理棋谱
- cnn:cnn神经网络
- 初始化棋盘为15*15
部分代码详解:
self.window = Tk()
self.window.title("myGoBang")
self.window.geometry("600x470")
self.window.resizable(0, 0)
-
实例化,建立窗口window
-
给窗口的可视化设置title名字
-
geometry 设定窗口的大小(长*宽)
-
resizable()方法允许/禁止窗口根据用户需要进行更改其大小
- window.resizable(0, 0) 限制窗口更改大小(即设定固定大小的窗口)
- window.resizable(True, True) 允许更改窗口大小
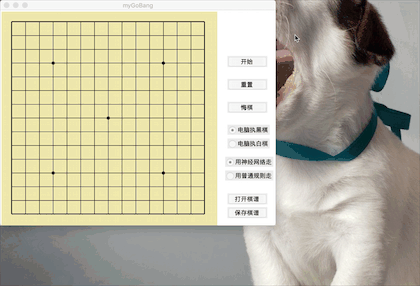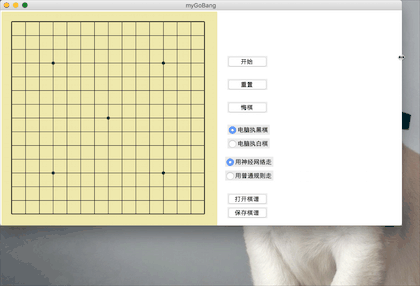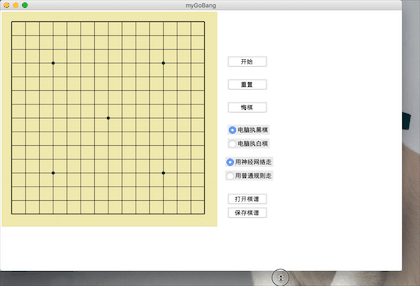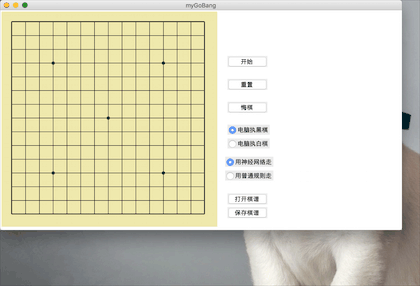
self.can = Canvas(self.window, bg="#EEE8AC", width=470, height=470)
self.can.grid(row=0, column=0)
- 在图形界面上创建470*470大小、#EEE8AC颜色的画布并放置各种元素
self.sgf = SGFflie()
- SGF文件
- sgf是Smart Game Format的简写,绝大多数棋谱文件都是用sgf格式的文件。主要用于读取棋谱并加载训练模型。
self.window.mainloop()
- 主窗口循环显示
self.net_board = self.get_net_board()#调用get_net_board函数
get_net_board函数
def get_net_board(self):
"""得到棋盘的点信息"""
net_list = []
for row in range(15):
for col in range(15):
point = pos_in_board(row, col)
net_list.append(point)
return net_list
遍历整个棋盘,调用pos_in_board函数查找棋子在棋盘上的位置,并添加到net_list中,返回整个棋盘信息。
布局棋盘
绘制棋盘线条及部分交点
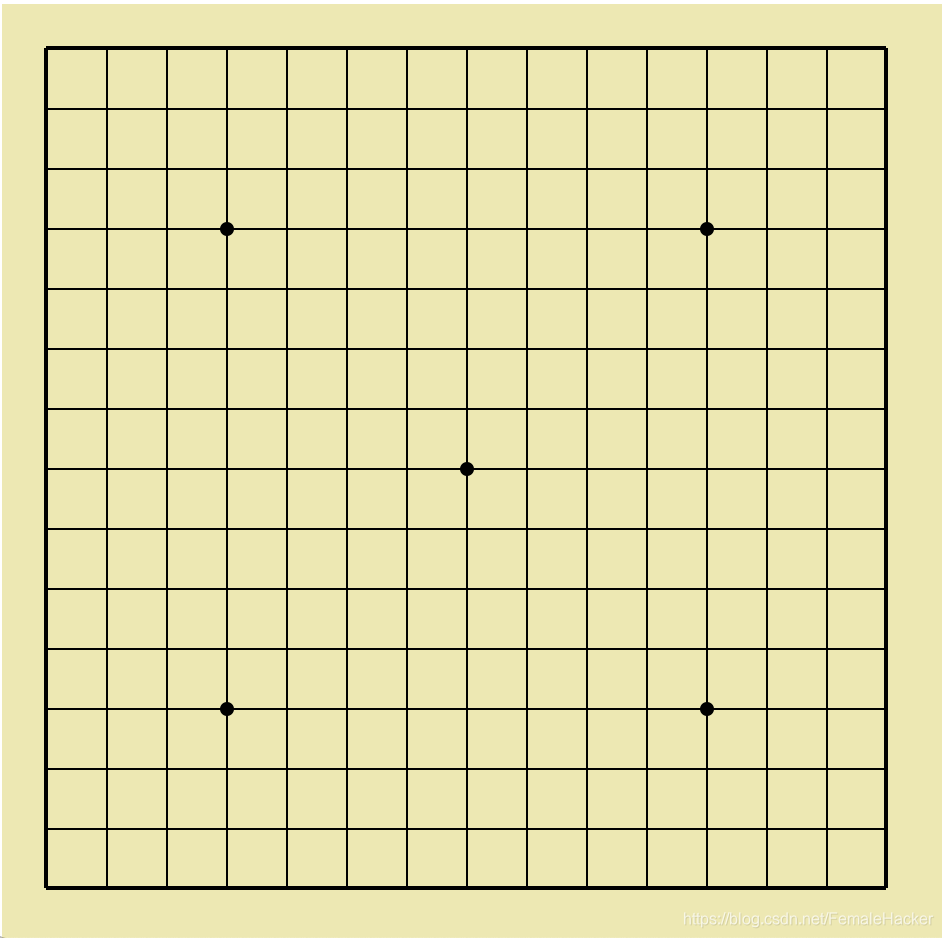
def draw_board(self):
"""画出棋盘"""
for row in range(15):
if row == 0 or row == 14:
self.can.create_line((25, 25 + row * 30), (445, 25 + row * 30), width=2)
else:
self.can.create_line((25, 25 + row * 30), (445, 25 + row * 30), width=1)
for col in range(15):
if col == 0 or col == 14:
self.can.create_line((25 + col * 30, 25), (25 + col * 30, 445), width=2)
else:
self.can.create_line((25 + col * 30, 25), (25 + col * 30, 445), width=1)
self.can.create_oval(112, 112, 118, 118, fill="black")
self.can.create_oval(352, 112, 358, 118, fill="black")
self.can.create_oval(112, 352, 118, 358, fill="black")
self.can.create_oval(232, 232, 238, 238, fill="black")
self.can.create_oval(352, 352, 358, 358, fill="black")
绘制出棋盘的所有线条以及突出某些交点。
棋盘格每个单元格为30*30。
知识点
-
.create_line(起始坐标,终点坐标,width=线宽,fill=颜色)
- 画线
-
.create_arc(起始坐标,终点坐标,width=线宽,fill=颜色)
- 画圆弧
-
.create_rectangle(起始坐标,终点坐标,width=线宽,fill=颜色,outline=边框颜色)
- 画矩形
-
.create_oval(四个坐标,fill=填充颜色,outline=边框的颜色)
- 画椭圆
-
.create_polygon(多个点的坐标,fill=颜色,outline=边框颜色)
- 画多边形
-
.create_text(text=“文字”)
- 显示文字
部分代码详解
self.can.create_line((25, 25 + row * 30), (445, 25 + row * 30), width=2)
- 根据坐标,画出行、列。边界处加粗,因此width=2。
self.can.create_oval(112, 112, 118, 118, fill="black")
- 根据椭圆的四个方向坐标来绘制部分交点(坐标顺序分别为左、下、右、上)
棋盘图
绘制棋子
def draw_a_chess(self, x, y, player=None):
"""在棋盘中画一个棋子"""
_x, _y = pos_in_qiju(x, y)
oval = pos_to_draw(x, y)
if player == 0:
self.can.create_oval(oval, fill="black")
self.bla_chessed.append([x, y, 0])
self.board[_x][_y] = 1
elif player == 1:
self.can.create_oval(oval, fill="white")
self.whi_chessed.append([x, y, 1])
self.board[_x][_y] = 0
return
def pos_in_qiju(x, y):
"""棋盘中的点计算在棋局中的位置"""
return int((x - 25) / 30), int((y - 25) / 30)
def pos_to_draw(*args):
"""计算棋子在棋盘的顶,底,左,右的位置"""
x, y = args
return x - 11, y - 11, x + 11, y + 11
-
先调用pos_in_qiju函数获取棋盘中的棋子落脚点
-
再调用pos_to_draw函数设置棋子(椭圆)四个方向的坐标
-
如果player为0,则代表黑棋;player为1,则代表白棋。
-
通过.create_oval()绘制棋子,分别保存在bla_chessed、whi_chessed
- bla_chessed:保存黑棋已经下过的棋子
- whi_chessed:保存白棋已经下过的棋子
下棋
下棋子
def chess(self, event):
"""下棋函数"""
if self.someoneWin == True or self.IsStart == False:
"""判断是否有人赢了或者是否按了开始键"""
return
ex = event.x
ey = event.y
if not click_in_board(ex, ey):# 调用click_in_board函数
"""检查鼠标点击的坐标是否在棋盘内"""
return
neibor_po = self.get_nearest_po(ex, ey)#调用get_nearest_po函数得到两点最近的位置
if self.no_in_chessed(neibor_po):#调用no_in_chessed函数
if self.player == 0:
self.draw_a_chess(*neibor_po, 1)
else:
self.draw_a_chess(*neibor_po, 0)
self.someoneWin = self.check_win()
if self.playmethod == 0:
self.AIrobotChess()#调用AIrobotChess函数AI机器人下棋
else:
self.robotChess()#调用robotChess函数普通机器人下棋
self.someoneWin = self.check_win()
-
先调用click_in_board函数判断鼠标点击位置是否在棋盘内,保证下的棋子有效
-
再调用get_nearest_po函数获取到两点距离最近的位置
-
如果该位置没有棋子,则调用draw_a_chess函数,根据玩家是黑/白棋进行落子。
-
根据玩家模式为AI或普通玩法,调用不同的下棋方式进行下棋。
-
AIrobotChess AI机器人下棋
-
def AIrobotChess(self): """ai机器人下棋""" cnn_predict = self.cnn.predition(self.board)#调用预测函数 if self.player % 2 == 0:#黑棋 """开局优化""" if len(self.bla_chessed) == 0 and len(self.whi_chessed) == 0: self.draw_a_chess(*self.bla_start_pos, 0) else: #机器人计算出全局价值最大的点 _x, _y, _ = self.robot.MaxValue_po(1, 0) newPoint = pos_in_board(_x, _y) if self.ai_no_in_chessed(cnn_predict, _): self.draw_a_chess(*cnn_predict, 0) else: self.draw_a_chess(*newPoint, 0) else: self.robotChess()-
根据预测函数返回某个点,计算出去全局价值最大的点
-
调用ai_no_in_chessed函数判断AI预测出来的点是否已有棋子,
-
def ai_no_in_chessed(self, pos, value): """ ai预测出来的点是否已经下过, 以及结合机器人计算出来的值, 如果ai的点没有下过,而且机器 人预测出来的最大值小于400 返回真 """ no_in_chessed = self.no_in_chessed(pos) return no_in_chessed and value < 4000
-
-
robotChess 普通机器人下棋
-
def robotChess(self): """机器人下棋""" if self.player == 0: if len(self.bla_chessed) == 0 and len(self.whi_chessed) == 0: '''电脑执黑棋,开局优化''' self.draw_a_chess(*self.bla_start_pos, player=0) return else: _x, _y, _ = self.robot.MaxValue_po(0, 1) newPoint = pos_in_board(_x, _y) self.draw_a_chess(*newPoint, player=0) else:#白棋下 _x, _y, _ = self.robot.MaxValue_po(1, 0) newPoint = pos_in_board(_x, _y) self.draw_a_chess(*newPoint, player=1)- 如果玩家为黑棋,当电脑执黑棋时,则开局优化,落下棋子;否则计算出价值最大的点,调用pos_in_board函数判断此点再棋盘中的位置,落下棋子。
-
-
最后检查是否有哪方获胜
click_in_board函数
def click_in_board(x, y):
"""判断鼠标是否点击到棋盘里面"""
return x > 10 and x < 460 and y > 10 and y < 460
click_in_board函数写好边界判断鼠标是否点击再棋盘内,防止棋子落在外面。
get_nearest_po函数
def get_nearest_po(self, x, y):
"""得到坐标(x, y)在棋盘各点中最近的一个点"""
flag = 600
position = ()
for point in self.net_board: #遍历棋盘上的点
distance = get_distance([x, y], point)#调用get_distance函数
if distance < flag:
flag = distance
position = point
return position
调用**下面get_distance函数计算出距离。如果计算出的距离比原标签小,则替换,并获取且返回最近的距离位置**。
get_distance函数
def get_distance(p0, p1):
"""计算两个点之间的距离"""
return math.sqrt((p0[0] - p1[0]) ** 2 + (p0[1] - p1[1]) ** 2)
根据公式 ( x 1 − x 2 ) 2 + ( y 1 − y 2 ) 2 \sqrt{(x1-x2)^2+(y1-y2)^2} (x1−x2)2+(y1−y2)2 计算点距离。
no_in_chessed函数
def no_in_chessed(self, pos):
"""pos 没有下过"""
whi_chess = self.check_chessed(pos, self.whi_chessed)
bla_chess = self.check_chessed(pos, self.bla_chessed)
return whi_chess == False and bla_chess == False
判断该位置没有棋子。
pos_in_board函数
def pos_in_board(x, y):
"""棋局中的点计算在棋盘中的位置"""
return x * 30 + 25, y * 30 + 25
根据点计算该落点在棋盘中的位置。
显示下过的棋子
def draw_chessed(self):
"""在棋盘中画出已经下过的棋子"""
if len(self.whi_chessed) != 0:
for tmp in self.whi_chessed:
oval = pos_to_draw(*tmp[0:2])
self.can.create_oval(oval, fill="white")
if len(self.bla_chessed) != 0:
for tmp in self.bla_chessed:
oval = pos_to_draw(*tmp[0:2])
self.can.create_oval(oval, fill="black")
只要存放白棋的数组(whi_chessed)不为空,则画出其白棋。
只要存放黑棋的数组(bla_chessed)不为空,则画出其黑棋。
判断胜负
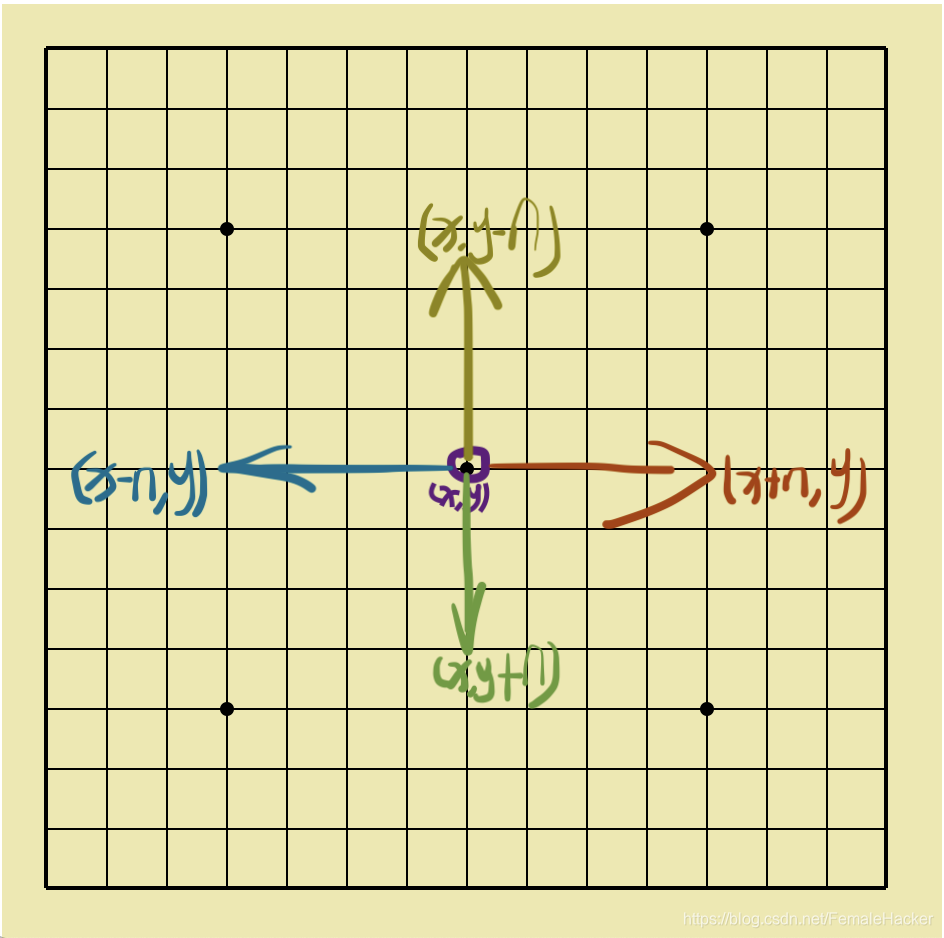
判断五子是否连成一线(4个方向均可)断定输赢.
检测是否连五
def have_five(self, chessed):
"""检测是否存在连五了"""
if len(chessed) == 0:
return False
for row in range(15):
for col in range(15):
x = 25 + row * 30
y = 25 + col * 30
if self.check_chessed((x, y), chessed) == True and \
self.check_chessed((x, y + 30), chessed) == True and \
self.check_chessed((x, y + 60), chessed) == True and \
self.check_chessed((x, y + 90), chessed) == True and \
self.check_chessed((x, y + 120), chessed) == True:
return True
elif self.check_chessed((x, y), chessed) == True and \
self.check_chessed((x + 30, y), chessed) == True and \
self.check_chessed((x + 60, y), chessed) == True and \
self.check_chessed((x + 90, y), chessed) == True and \
self.check_chessed((x + 120, y), chessed) == True:
return True
elif self.check_chessed((x, y), chessed) == True and \
self.check_chessed((x + 30, y + 30), chessed) == True and \
self.check_chessed((x + 60, y + 60), chessed) == True and \
self.check_chessed((x + 90, y + 90), chessed) == True and \
self.check_chessed((x + 120, y + 120), chessed) == True:
return True
elif self.check_chessed((x, y), chessed) == True and \
self.check_chessed((x + 30, y - 30), chessed) == True and \
self.check_chessed((x + 60, y - 60), chessed) == True and \
self.check_chessed((x + 90, y - 90), chessed) == True and \
self.check_chessed((x + 120, y - 120), chessed) == True:
return True
else:
pass
return False
调用**下面**check_chessed函数,检测此处是否有棋子。
- have_five函数分别检测四个方向是否五子连成一条线
- (x,y+n) 向下检测
- (x+n,y) 向右检测
- (x,y-n) 向上检测
- (x-n,y) 向左检测
def check_chessed(self, point, chessed):
"""检测是否已经下过了"""
if len(chessed) == 0:
return False
flag = 0
for p in chessed:
if point[0] == p[0] and point[1] == p[1]:
flag = 1
if flag == 1:
return True
else:
return False
-
创建flag标签,且初始化为0
-
如果没下过,则下棋,并将flag更新为1
-
如果flag为1,则表示此处已有棋子
检测哪方棋子赢
def check_win(self):
"""检测哪方棋子赢了"""
if self.have_five(self.whi_chessed) == True:
label = Label(self.window, text="White Win!", background='#FFF8DC', font=("宋体", 15, "bold"))
label.place(relx=0, rely=0, x=480, y=40)
return True
elif self.have_five(self.bla_chessed) == True:
label = Label(self.window, text="Black Win!", background='#FFF8DC', font=("宋体", 15, "bsold"))
label.place(relx=0, rely=0, x=480, y=40)
return True
else:
return False
调用have_five函数判断是哪方棋子先连五,则显示哪方赢。
知识点
label = Label(self.window, text="White Win!", background='#FFF8DC', font=("宋体", 15, "bold"))
label.place(relx=0, rely=0, x=480, y=40)
- Label(win,text=‘文本显示内容’,background=‘背景颜色’,font=(“字体名”,字体大小))
- 设置显示内容
- 设置此文本内容显示位置
定义按钮实现各个功能
"""开始,主要实现一些按钮与按键"""
b3 = Button(self.window, text="开始", command=self.startButton)
b3.place(relx=0, rely=0, x=495, y=100)
b1 = Button(self.window, text="重置", command=self.resetButton)
b1.place(relx=0, rely=0, x=495, y=150)
b2 = Button(self.window, text="悔棋", command=self.BakcAChess)
b2.place(relx=0, rely=0, x=495, y=200)
b4 = Radiobutton(self.window, text="电脑执黑棋", variable=self.var, value=0, command=self.selectColor)
b4.place(relx=0, rely=0, x=495, y=250)
b5 = Radiobutton(self.window, text="电脑执白棋", variable=self.var, value=1, command=self.selectColor)
b5.place(relx=0, rely=0, x=495, y=280)
b6 = Button(self.window, text="打开棋谱", command=self.OpenFile)
b6.place(relx=0, rely=0, x=495, y=400)
b7 = Button(self.window, text="保存棋谱", command=self.SaveFile)
b7.place(relx=0, rely=0, x=495, y=430)
b8 = Radiobutton(self.window, text="用神经网络走", variable=self.var1, value=0, command=self.selectMathod)
b8.place(relx=0, rely=0, x=490, y=320)
b9 = Radiobutton(self.window, text="用普通规则走", variable=self.var1, value=1, command=self.selectMathod)
b9.place(relx=0, rely=0, x=490, y=350)
-
tk.Button(win,text=’’,command=功能函数)
- 按钮
-
tk.Radiobutton(win,text=’’,command=功能函数)
- 单选按钮
-
place()方法 place(relx,rely,x,y)
-
b6.place(relx=0, rely=0, x=495, y=400)- 先设置相对坐标(0,0),再使用(495,400)将坐标作偏移(495,400)
开始函数(startButton)
def startButton(self):
"""开始按钮的回调函数"""
if self.IsStart == False:
self.IsStart = True
if self.player % 2 == 0:
if self.playmethod == 0:
self.AIrobotChess()
elif self.playmethod == 1:
self.robotChess()
self.draw_chessed()
-
点击开始按钮,如果开始状态IsStart为false,则改为true。
-
选择玩家颜色和下棋模式后开始
重置函数(resetButton)
def resetButton(self):
"""重置按钮的回调函数,实现了整个棋盘重置"""
self.someoneWin = False
self.IsStart = False
self.whi_chessed.clear()
self.bla_chessed.clear()
self.board = self.init_board()
self.robot = Robot(self.board)
label = Label(self.window, text=" ", background="#F0F0F0", font=("宋体", 15, "bold"))
label.place(relx=0, rely=0, x=480, y=40)
self.can.delete("all")
self.draw_board()
self.can.grid(row=0, column=0)
- 清除黑/白棋数组
- 重新初始化棋盘
- 清空画布
- 重新绘制棋盘
知识点
self.can.delete("all")
canvas.delete(“all”)
- 清空画布
如若删除部分内容,则在创建内容时加入标签tags,删除时将“all”更改为设定的标签即可。
悔棋函数(BakcAChess)
def BakcAChess(self):
"""悔棋按钮的回调函数"""
if self.someoneWin == False:
if len(self.whi_chessed) != 0:
p = self.whi_chessed.pop()
x, y = pos_in_qiju(*p[0:2])
self.board[x][y] = -1
if self.player == 0 and len(self.bla_chessed) != 1:
p = self.bla_chessed.pop()
x, y = pos_in_qiju(*p[0:2])
self.board[x][y] = -1
elif self.player == 1 and len(self.bla_chessed) != 0:
p = self.bla_chessed.pop()
x, y = pos_in_qiju(*p[0:2])
self.board[x][y] = -1
else:
pass
self.can.delete("all")
self.draw_board()
self.draw_chessed()
- 悔棋的前提是当前没有任何一方赢得比赛。
- 当黑/白棋数组不为null,则将最后下的棋子出栈,然后获取到此位置,修改棋盘中此位置变为无棋子。
选择执棋颜色(selectColor)
def selectColor(self):
"""选择执棋的颜色"""
if self.IsStart == False:
if self.var.get() == 0:
self.player = 0
elif self.var.get() == 1:
self.player = 1
else:
pass
return
在点击开始前选择玩家执棋颜色。
**注:**已经开始后,再点击执棋颜色按钮无效。
选择下棋方式(selectMathod)
def selectMathod(self):
"""选择下棋的方式,与robot下还是与ai下,0:跟ai,1:跟robot"""
if self.IsStart == False:
if self.var1.get() == 0:
self.playmethod = 0
elif self.var1.get() == 1:
self.playmethod = 1
else:
pass
return
在点击开始前选择下棋方式。
**注:**已经开始后,再选择下棋方式无效。
棋盘处理
生成棋谱
def createqipu(self):
"""将棋盘中的棋局生成棋盘"""
qipu = [] #存放棋谱的数组
step = 0
totalstep = len(self.whi_chessed) + len(self.bla_chessed)
while step < totalstep:
if totalstep == 0:
break
flag = int(step / 2)
if step % 2 == 0:
pos = pos_in_qiju(*self.bla_chessed[flag][0:2])
qipu.append([*pos, 0, step + 1])
else:
pos = pos_in_qiju(*self.whi_chessed[flag][0:2])
qipu.append([*pos, 1, step + 1])
step += 1
return qipu
-
定义存放棋谱的数组 qipu=[]
-
获取该局棋盘总步数totalstep
- 黑/白棋数组中的步数相加
-
获取到棋子在棋盘中的位置并加入到qipu数组中
-
最后返回qipu数组,方便保存棋谱
保存棋谱
def SaveFile(self, method=1):
"""保存棋谱"""
qipu = self.createqipu()#调用createqipu函数获得qipu数组
if method == 0:
try:
file = asksaveasfile(filetypes=(('sgf file', '*.sgf'),
('All File', '*.*')))
file.close()
except AttributeError:
return
pathName = file.name
newName = pathName + '.sgf'
os.rename(pathName, newName)
f = open(newName, 'w')
data = self.sgf.createdata(qipu)#调用createdata函数
f.write(data)
f.close()
elif method == 1:
self.sgf.savefile(qipu)#调用savefile函数
- 先获取到生成的棋谱数组
- 设置文件名,获取存储数据
- 打开文件,写入数据,保存棋谱
知识点
-
asksaveasfile(filetypes=((‘sgf file’, ‘.sgf’),(‘All File’, '.*’)))
- 支持保存的文件类型
-
file.close()
- 关闭文件
-
file.name
- 文件名
-
os.rename(src,dst )
-
重命名文件
- src:要修改的目录名
- dst:修改后的目录名
-
f = open(filename, ‘w’)
-
打开文件,并设置可写
-
f.write()
- 写文件
createdata函数
def createdata(self, board):
"""将棋盘中的数据进行处理,生成能够保存为棋谱的数据形式"""
now = time.localtime(time.time())
_time = ''
for index in range(6):
_time = _time + str(now[index])
data = '(;' + _time + ";"
for it in board:
if it[2] == 0:
data = data + 'B[' + self.POS[it[0]] + self.POS[it[1]] + "];"
else:
data = data + 'W[' + self.POS[it[0]] + self.POS[it[1]] + "];"
data = data + ')'
return data
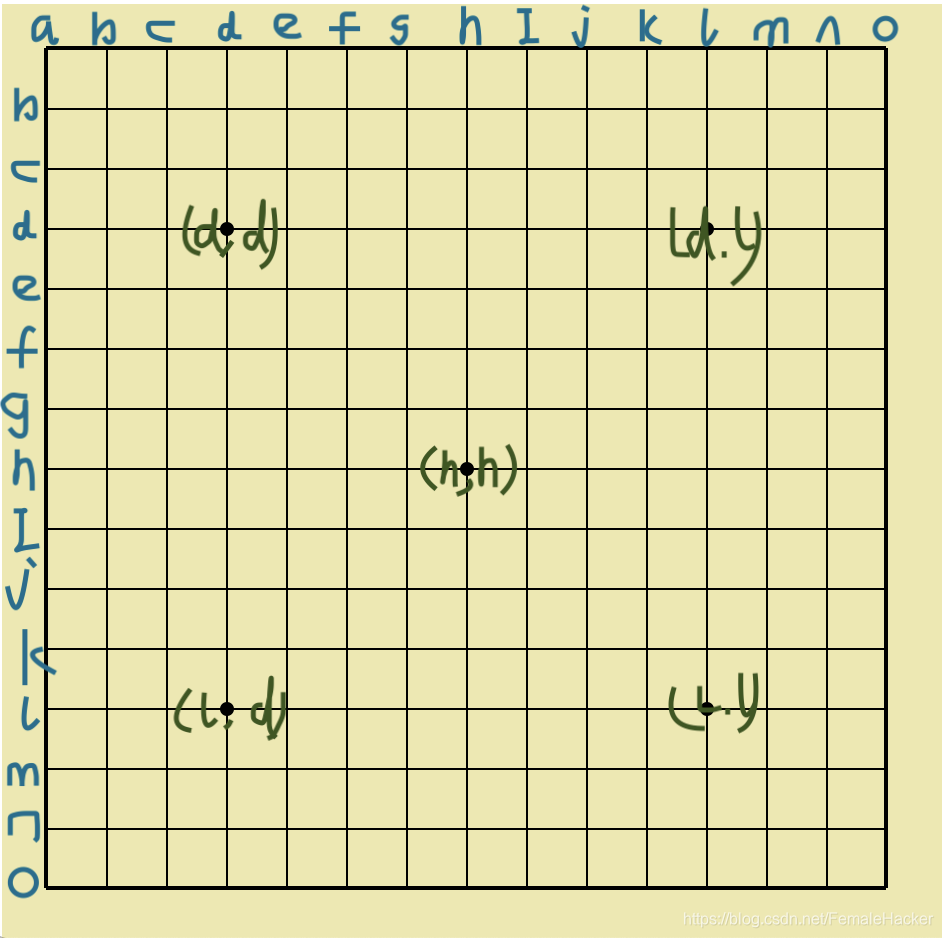
生成的data数据为:(;time;B[];W[];…😉
例:(;202086135756;B[hh];W[gf];B[ig];W[ij];B[fh];W[ki];B[gi];W[hi];B[fj];W[hm];B[ek]😉
self.POS = 'abcdefghijklmno'#棋盘坐标的对应字母顺序
savefile函数
def savefile(self, board):
"""将棋盘中的数据保存成棋谱"""
data = self.createdata(board)
filepath = self.savepath + data.split(';')[1] + ".sgf"
f = open(filepath, 'w')
f.write(data)
f.close()
return
打开棋谱
def OpenFile(self):
"""打开保存好的棋谱"""
file_path = askopenfilename(filetypes=(('sgf file', '*.sgf'),
('All File', '*.*')))
if len(file_path) == 0:
return
qipu = self.sgf.openfile(file_path)#调用openfile函数
self.whi_chessed.clear()
self.bla_chessed.clear()
for point in qipu:
pos = pos_in_board(*point[0:2])
if point[2] == 0:
self.bla_chessed.append([*pos, 0])
else:
self.whi_chessed.append([*pos, 1])
self.can.delete("all")
self.draw_board()
self.draw_chessed()
- 先清除当前棋盘上的棋子,再根据打开的文件再棋盘上画出棋子
知识点
askopenfilename(filetypes=((‘sgf file’, ‘.sgf’),(‘All File’, '.*’)))
- 支持打开的文件类型
openfile函数
def openfile(self, filepath):
"""打开文件,读取棋谱"""
f = open(filepath, 'r')
data = f.read()
f.close()
#分割数据
effective_data = data.split(';')
s = effective_data[2:-1]
board = []
step = 0
for point in s:
x = self.POS.index(point[2])
y = self.POS.index(point[3])
color = step % 2
step += 1
board.append([x, y, color, step])
return board
-
保存数据时的data为**(;time;B[];W[];…😉**
-
打开文件时根据==;==进行分割,获取**[2:-1]**中见的数据
-
根据棋盘坐标的对应字母顺序,得到在棋盘中的位置
电脑落子
五子棋的几种基本棋形
五子棋的几种基本棋形:连五、活四、眠四、活三、眠三、活二、眠二。
连五
- 五颗同色棋子连在一起。
def willbefive(self, player, checklist):
"""下在这个点将会得到连五"""
if checklist[0] == player and checklist[1] == player and \
checklist[2] == player and checklist[3] == player:
return 10000
elif checklist[5] == player and checklist[6] == player and \
checklist[7] == player and checklist[8] == player:
return 10000
elif checklist[2] == player and checklist[3] == player and \
checklist[5] == player and checklist[6] == player:
return 10000
elif checklist[1] == player and checklist[2] == player and \
checklist[3] == player and checklist[5] == player:
return 10000
elif checklist[3] == player and checklist[5] == player and \
checklist[6] == player and checklist[7] == player:
return 10000
else:
return 0
活四
-
四颗同色棋子连在一起,并且左右两边都没有对方棋子阻挡。
-
有两个连五点
def willbealive4(self, player, checklist):
"""下在这个点将会形成活四"""
if checklist[0] == -1 and checklist[1] == player and \
checklist[2] == player and checklist[3] == player \
and checklist[5] == -1:
return 5000
elif checklist[3] == -1 and checklist[5] == player and \
checklist[6] == player and checklist[7] == player \
and checklist[8] == -1:
return 5000
elif checklist[1] == -1 and checklist[2] == player and \
checklist[3] == player and checklist[5] == player \
and checklist[6] == -1:
return 5000
elif checklist[2] == -1 and checklist[3] == player and \
checklist[5] == player and checklist[6] == player \
and checklist[7] == -1:
return 5000
else:
return 0
眠四
-
四颗同色棋子连在一起,并且一边有对方棋子阻挡
-
或者四颗棋子不是连着的,当中有空档
-
只有一个连五点
def willbesleep4(self, player, enemy, checklist):
"""下在这个点会形成眠四"""
if checklist[0] == enemy and checklist[1] == player and \
checklist[2] == player and checklist[3] == player \
and checklist[5] == -1:
return 1700
elif checklist[1] == enemy and checklist[2] == player and \
checklist[3] == player and checklist[5] == player \
and checklist[6] == -1:
return 1700
elif checklist[2] == enemy and checklist[3] == player and \
checklist[5] == player and checklist[6] == player \
and checklist[7] == -1:
return 1700
elif checklist[3] == enemy and checklist[5] == player and \
checklist[6] == player and checklist[7] == player \
and checklist[8] == -1:
return 1700
elif checklist[0] == -1 and checklist[1] == player and \
checklist[2] == player and checklist[3] == player \
and checklist[5] == enemy:
return 1700
elif checklist[1] == -1 and checklist[2] == player and \
checklist[3] == player and checklist[5] == player \
and checklist[6] == enemy:
return 1700
elif checklist[2] == -1 and checklist[3] == player and \
checklist[5] == player and checklist[6] == player \
and checklist[7] == enemy:
return 1700
elif checklist[3] == -1 and checklist[5] == player and \
checklist[6] == player and checklist[7] == player \
and checklist[8] == enemy:
return 1700
else:
return 0
活三
- 三颗同色棋子连在一起
def willbealive3(self, player, checklist):
"""下在这个点会形成活三"""
if checklist[0] == -1 and checklist[1] == -1 and \
checklist[2] == player and checklist[3] == player \
and checklist[5] == -1:
return 1900
elif checklist[1] == -1 and checklist[2] == -1 and \
checklist[3] == player and checklist[5] == player \
and checklist[6] == -1:
return 1900
elif checklist[2] == -1 and checklist[3] == -1 and \
checklist[5] == player and checklist[6] == player \
and checklist[7] == -1:
return 1900
elif checklist[1] == -1 and checklist[2] == player and \
checklist[3] == player and checklist[5] == -1 \
and checklist[6] == -1:
return 1900
elif checklist[2] == -1 and checklist[3] == player and \
checklist[5] == player and checklist[6] == -1 \
and checklist[7] == -1:
return 1900
elif checklist[3] == -1 and checklist[5] == player and \
checklist[6] == player and checklist[7] == -1 \
and checklist[8] == -1:
return 1900
elif checklist[0] == -1 and checklist[1] == player and \
checklist[2] == player and checklist[3] == -1 \
and checklist[5] == -1:
return 1600
elif checklist[2] == -1 and checklist[3] == player and \
checklist[6] == player and checklist[5] == -1 \
and checklist[7] == -1:
return 1600
elif checklist[3] == -1 and checklist[5] == player and \
checklist[7] == player and checklist[6] == -1 \
and checklist[8] == -1:
return 1600
elif checklist[3] == -1 and checklist[5] == -1 and \
checklist[7] == player and checklist[6] == player \
and checklist[8] == -1:
return 1600
elif checklist[0] == -1 and checklist[1] == player and \
checklist[2] == player and checklist[3] == -1 \
and checklist[6] == -1:
return 1600
elif checklist[0] == -1 and checklist[1] == player and \
checklist[2] == player and checklist[3] == -1 \
and checklist[6] == -1:
return 1600
else:
return 0
眠三
- 一边被对方棋子阻挡
- 当中有两个空格
def willbesleep3(self, player, enemy, checklist):
"""下在这个点会形成眠三"""
if checklist[1] == enemy and checklist[2] == player and \
checklist[3] == player and checklist[5] == -1 \
and checklist[6] == -1:
return 350
elif checklist[2] == enemy and checklist[3] == player and \
checklist[5] == player and checklist[6] == -1 \
and checklist[7] == -1:
return 350
elif checklist[3] == enemy and checklist[5] == player and \
checklist[6] == player and checklist[7] == -1 \
and checklist[8] == -1:
return 350
elif checklist[0] == -1 and checklist[1] == -1 and \
checklist[2] == player and checklist[3] == player \
and checklist[5] == enemy:
return 350
elif checklist[1] == -1 and checklist[2] == -1 and \
checklist[3] == player and checklist[5] == player \
and checklist[6] == enemy:
return 350
elif checklist[2] == -1 and checklist[3] == -1 and \
checklist[5] == player and checklist[6] == player \
and checklist[7] == enemy:
return 350
elif checklist[0] == enemy and checklist[1] == -1 and \
checklist[2] == player and checklist[3] == player \
and checklist[5] == -1 and checklist[6] == enemy:
return 300
elif checklist[1] == enemy and checklist[2] == -1 and \
checklist[3] == player and checklist[5] == player \
and checklist[6] == -1 and checklist[7] == enemy:
return 300
elif checklist[2] == enemy and checklist[3] == -1 and \
checklist[5] == player and checklist[6] == player \
and checklist[7] == -1 and checklist[8] == enemy:
return 300
elif checklist[0] == enemy and checklist[1] == player and \
checklist[2] == -1 and checklist[3] == player \
and checklist[5] == -1 and checklist[6] == enemy:
return 300
elif checklist[1] == enemy and checklist[2] == player and \
checklist[3] == -1 and checklist[5] == player \
and checklist[6] == -1 and checklist[7] == enemy:
return 300
elif checklist[2] == enemy and checklist[3] == player and \
checklist[5] == -1 and checklist[6] == player \
and checklist[7] == -1 and checklist[8] == enemy:
return 300
elif checklist[0] == enemy and checklist[1] == player and \
checklist[2] == -1 and checklist[3] == player \
and checklist[5] == -1 and checklist[6] == enemy:
return 300
elif checklist[1] == enemy and checklist[2] == player and \
checklist[3] == -1 and checklist[5] == player \
and checklist[6] == -1 and checklist[7] == enemy:
return 300
elif checklist[3] == enemy and checklist[5] == -1 and \
checklist[6] == player and checklist[7] == player \
and checklist[8] == -1:
return 300
elif checklist[0] == enemy and checklist[1] == player and \
checklist[2] == player and checklist[3] == -1 \
and checklist[5] == -1:
return 300
elif checklist[2] == enemy and checklist[3] == player and \
checklist[5] == -1 and checklist[6] == player \
and checklist[7] == -1:
return 300
elif checklist[3] == enemy and checklist[5] == player and \
checklist[6] == -1 and checklist[7] == player \
and checklist[8] == -1:
return 300
elif checklist[0] == player and checklist[1] == player and \
checklist[2] == -1 and checklist[3] == -1 \
and checklist[5] == enemy:
return 300
elif checklist[2] == enemy and checklist[3] == player and \
checklist[5] == -1 and checklist[6] == -1 \
and checklist[7] == player:
return 300
elif checklist[3] == enemy and checklist[5] == player and \
checklist[6] == -1 and checklist[7] == -1 \
and checklist[8] == player:
return 300
elif checklist[0] == player and checklist[1] == -1 and \
checklist[2] == -1 and checklist[3] == player \
and checklist[5] == enemy:
return 300
elif checklist[1] == player and checklist[2] == -1 and \
checklist[3] == -1 and checklist[5] == player \
and checklist[6] == enemy:
return 300
elif checklist[3] == enemy and checklist[5] == -1 and \
checklist[6] == -1 and checklist[7] == player \
and checklist[8] == player:
return 300
elif checklist[0] == -1 and checklist[1] == player and \
checklist[2] == player and checklist[3] == -1 \
and checklist[5] == enemy:
return 30
elif checklist[2] == -1 and checklist[3] == player and \
checklist[5] == -1 and checklist[6] == player \
and checklist[7] == enemy:
return 300
elif checklist[3] == -1 and checklist[5] == player and \
checklist[6] == -1 and checklist[7] == player \
and checklist[8] == enemy:
return 300
elif checklist[0] == -1 and checklist[1] == player and \
checklist[2] == -1 and checklist[3] == player \
and checklist[5] == enemy:
return 300
elif checklist[1] == -1 and checklist[2] == player and \
checklist[3] == -1 and checklist[5] == player \
and checklist[6] == enemy:
return 300
elif checklist[3] == -1 and checklist[5] == -1 and \
checklist[6] == player and checklist[7] == player \
and checklist[8] == enemy:
return 300
elif checklist[0] == player and checklist[1] == -1 and \
checklist[2] == player and checklist[3] == -1 \
and checklist[5] == enemy:
return 300
elif checklist[1] == enemy and checklist[2] == player and \
checklist[3] == -1 and checklist[5] == -1 \
and checklist[6] == player:
return 300
elif checklist[2] == player and checklist[3] == -1 and \
checklist[5]== -1 and checklist[6] == player \
and checklist[7] == enemy:
return 300
elif checklist[3] == enemy and checklist[5] == -1 and \
checklist[6] == player and checklist[7] == -1 \
and checklist[8] == player:
return 300
else:
return 0
活二
def willbealive2(self, player, enemy, checklist):
"""下在这个点会形成活二"""
if checklist[1] == -1 and checklist[2] == -1 and \
checklist[3] == player and checklist[5] == -1 \
and checklist[6] == -1:
return 99
elif checklist[2] == -1 and checklist[3] == -1 and \
checklist[5] == player and checklist[6] == -1 \
and checklist[7] == -1:
return 99
elif checklist[0] == -1 and checklist[1] == -1 and \
checklist[2] == -1 and checklist[3] == player \
and checklist[5] == -1 and checklist[6] == enemy:
return 99
elif checklist[1] == -1 and checklist[2] == -1 and \
checklist[3] == -1 and checklist[5] == player \
and checklist[6] == -1 and checklist[7] == enemy:
return 99
elif checklist[1] == enemy and checklist[2] == -1 and \
checklist[3] == player and checklist[5] == -1 \
and checklist[6] == -1 and checklist[7] == -1:
return 99
elif checklist[2] == enemy and checklist[3] == -1 and \
checklist[5] == player and checklist[6] == -1 \
and checklist[7] == -1 and checklist[8] == -1:
return 99
else:
return 0
眠二
def willbesleep2(self, player, enemy, checklist):
"""下在这个点会形成眠二"""
if checklist[2] == enemy and checklist[3] == player and \
checklist[5] == -1 and checklist[6] == -1 \
and checklist[7] == -1:
return 5
elif checklist[3] == enemy and checklist[5] == player and \
checklist[6] == -1 and checklist[7] == -1 \
and checklist[8] == -1:
return 5
elif checklist[0] == -1 and checklist[1] == -1 and \
checklist[2] == -1 and checklist[3] == player \
and checklist[5] == enemy:
return 5
elif checklist[1] == -1 and checklist[2] == -1 and \
checklist[3] == -1 and checklist[5] == player \
and checklist[6] == enemy:
return 5
elif checklist[1] == enemy and checklist[2] == -1 and \
checklist[3] == player and checklist[5] == -1 \
and checklist[6] == -1 and checklist[7] == enemy:
return 5
elif checklist[2] == enemy and checklist[3] == -1 and \
checklist[5] == player and checklist[6] == -1 \
and checklist[7] == -1 and checklist[8] == enemy:
return 5
elif checklist[0] == enemy and checklist[1] == -1 and \
checklist[2] == player and checklist[3] == -1 \
and checklist[5] == -1 and checklist[6] == enemy:
return 5
elif checklist[2] == enemy and checklist[3] == -1 and \
checklist[5] == -1 and checklist[6] == player \
and checklist[7] == -1 and checklist[8] == enemy:
return 5
elif checklist[0] == enemy and checklist[1] == -1 and \
checklist[2] == -1 and checklist[3] == player \
and checklist[5] == -1 and checklist[6] == enemy:
return 5
elif checklist[1] == enemy and checklist[2] == -1 and \
checklist[3] == -1 and checklist[5] == player \
and checklist[6] == -1 and checklist[7] == enemy:
return 5
elif checklist[0] == -1 and checklist[1] == player and \
checklist[2] == -1 and checklist[3] == -1 \
and checklist[5] == enemy:
return 5
elif checklist[3] == -1 and checklist[5] == -1 and \
checklist[6] == -1 and checklist[7] == player \
and checklist[8] == enemy:
return 5
elif checklist[0] == -1 and checklist[1] == -1 and \
checklist[2] == player and checklist[3] == -1 \
and checklist[5] == enemy:
return 5
elif checklist[2] == -1 and checklist[3] == -1 and \
checklist[5] == -1 and checklist[6] == player \
and checklist[7] == enemy:
return 5
elif checklist[1] == enemy and checklist[2] == player and \
checklist[3] == -1 and checklist[5] == -1 \
and checklist[6] == -1:
return 5
elif checklist[3] == enemy and checklist[5] == -1 and \
checklist[6] == player and checklist[7] == -1 \
and checklist[8] == -1:
return 5
elif checklist[0] == enemy and checklist[1] == player and \
checklist[2] == -1 and checklist[3] == -1 \
and checklist[5] == -1:
return 5
elif checklist[3] == enemy and checklist[5] == -1 and \
checklist[6] == -1 and checklist[7] == player \
and checklist[8] == -1:
return 5
else:
return 0
其余知识点
(1)placeholder()函数是在神经网络构建graph的时候在模型中的占位,此时并没有把要输入的数据传入模型,它只会分配必要的内存
tf.placeholder(
dtype,
shape=None,
name=None
)
- dtype:数据类型。常用tf.float32,tf.float64等数值类型
- shape:数据形状。默认为None,就是一维值。
- name:名称
(2)tf.nn.relu(features, name = None) 激活函数
(3)saver.restore(sess,路径)
- restore是将训练好的参数提取出来
(4)saver = tf.train.Saver() saver.save(sess, ‘路径 + 模型文件名’)
- 保存和加载模型
saver类训练完后,是以checkpoints文件形式保存。提取时也是从checkpoints文件中恢复变量





















 4603
4603











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








