文章目录
JSON 对 Unicode 有完整的支持,遵循 UTF-8 编码标准,并提供多种方式来表示 Unicode 字符。
JSON转义规则
JSON 转义机制如下图:
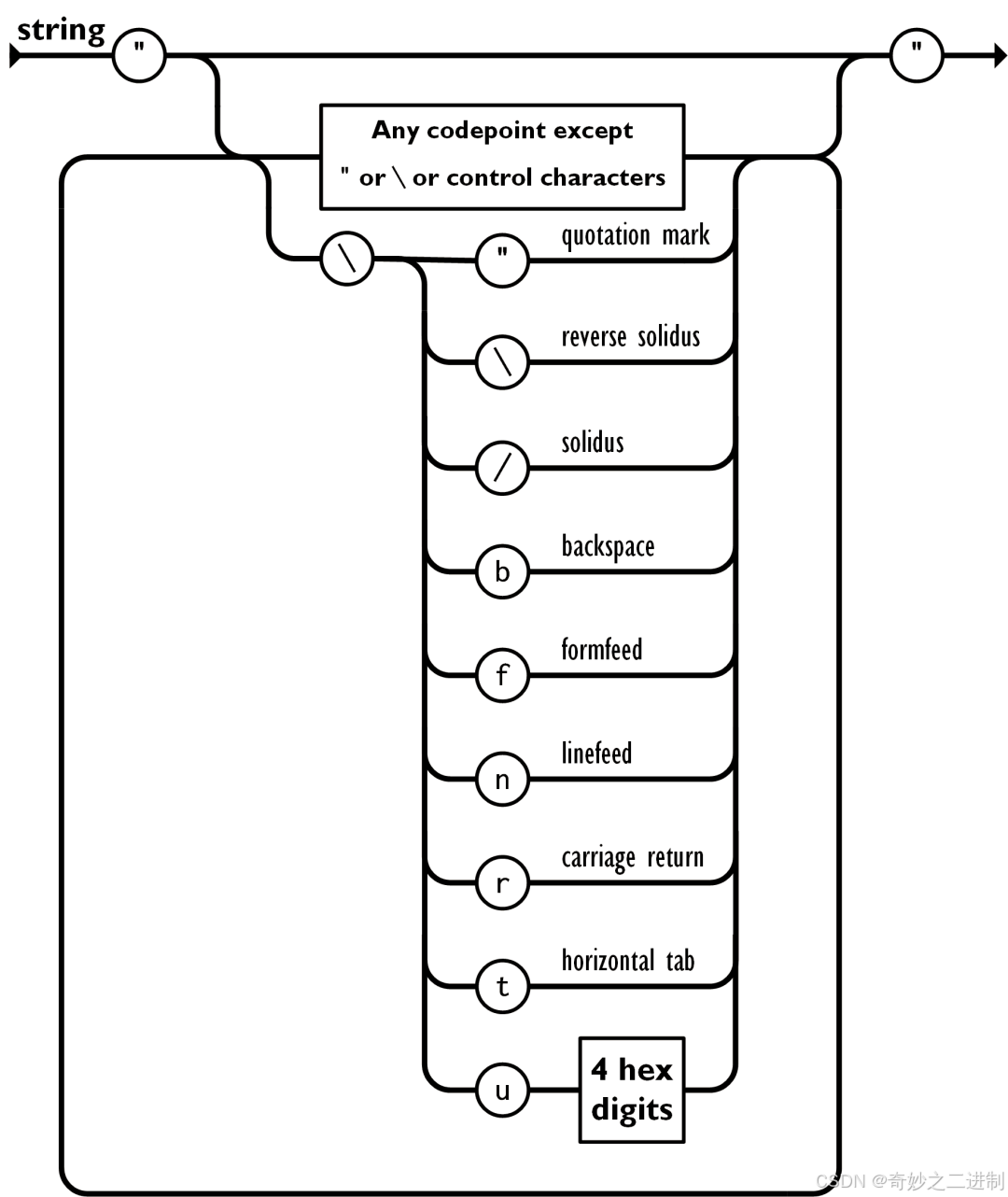
-
JSON 中字符串针对于特殊字符需要 JSON 转义,它使用反斜杠\进行转义
-
JSON 序列包括
“\\、\"、\/、\b、\f、\n、\r、\t,或者 Unicode16 进制转义字符(比如\uD83D\uDE02) -
JSON 字符串为 UTF-8 编码
JSON Unicode 基本规则
1. JSON 字符串必须是 Unicode
- JSON 文本默认使用 UTF-8 编码
- 所有字符串都是 Unicode 字符串
- 支持全球所有语言的字符
{
"english": "Hello",
"chinese": "中文",
"japanese": "日本語",
"emoji": "😀🎉",
"mixed": "Hello 中文 🎉"
}
Unicode 转义序列
2. \uXXXX 格式
JSON 使用 \uXXXX 格式表示 Unicode 字符,其中 XXXX 是 4 位十六进制数,不够的前面要补0
{
"basicLatin": "\u0041\u0042\u0043", // ABC
"chinese": "\u4E2D\u6587", // 中文
"mathSymbols": "\u221A\u221E", // √∞
"currency": "\u20AC\u00A5", // €¥
"controls": "\u000A\u000D", // \n\r
"emoji": "\uD83D\uDE00\uD83C\uDF89" // 😀🎉
}
3. 代理对(Surrogate Pairs)
对于超出基本多文种平面(BMP)的字符(U+10000 到 U+10FFFF),使用代理对:
// Unicode 代理对机制
// 高代理: U+D800 到 U+DBFF
// 低代理: U+DC00 到 U+DFFF
// 😀 = U+1F600
// 计算代理对:
// code = 0x1F600
// code -= 0x10000 → 0xF600
// high = (code >> 10) + 0xD800 → 0xD83D
// low = (code & 0x3FF) + 0xDC00 → 0xDE00
实际 JSON 表示:
{
"smile": "\uD83D\uDE00", // 😀 U+1F600
"rocket": "\uD83D\uDE80", // 🚀 U+1F680
"flag": "\uD83C\uDDE8\uD83C\uDDF3" // 🇨🇳 中国国旗
}
实际代码示例
C++ 中的 Unicode 处理
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <nlohmann/json.hpp>
using json = nlohmann::json;
// 验证解析结果
void verifyUnicodeParsing() {
std::string json_str = R"({
"ascii": "ABC",
"escape": "\"",
"chinese": "\u4E2D\u6587",
"emoji": "\uD83D\uDE00",
"mixed": "Hello \u4E16\u754C \uD83C\uDF89"
})";
std::cout << "原生字符串: " << json_str << std::endl;
json j = json::parse(json_str);
std::cout << "解析结果:" << std::endl;
std::cout << "escape: " << j["escape"] << std::endl;
std::cout << "chinese: " << j["chinese"] << std::endl;
std::cout << "emoji: " << j["emoji"] << std::endl;
std::cout << "mixed: " << j["mixed"] << std::endl;
// 检查字符串长度(UTF-8 码点)
std::string chinese = j["chinese"];
std::cout << "中文长度(字节): " << chinese.length() << std::endl;
std::cout << "中文长度(字符): " << j["chinese"].get<std::string>().size() << std::endl;
}
执行结果:

使用等号对json对象进行赋值时,只会纯粹当字符串处理,并不会执行上面的转义解析规则:
void unicodeExamples() {
// 直接使用 Unicode 字符
json j1;
j1["direct"] = "中文 😀 🎉";
j1["escaped"] = "\\u4E2D\\u6587 \\uD83D\\uDE00 \\uD83C\\uDF89";
std::cout << "直接Unicode: " << j1["direct"] << std::endl;
std::cout << "转义形式: " << j1["escaped"] << std::endl;
std::cout << "JSON输出: " << j1.dump() << std::endl;
}

Unicode 字符分类处理
4. 不同范围的 Unicode 字符
void unicodeCategories() {
json j;
// 基本拉丁字符 (U+0000 - U+007F)
j["basic_latin"] = "Hello World!";
// 拉丁扩展 (U+0080 - U+02AF)
j["latin_extended"] = "Ñañé Café";
// 中日韩统一表意文字 (U+4E00 - U+9FFF)
j["cjk"] = "中文日本語한국어";
// 表情符号 (U+1F600 - U+1F64F)
j["emoticons"] = "😀😂🤔🎉❤️";
// 数学符号 (U+2200 - U+22FF)
j["math"] = "√∞∫∑";
// 货币符号 (U+20A0 - U+20CF)
j["currency"] = "€£¥$";
std::cout << j.dump(2) << std::endl;
}
编码转换工具函数
5. Unicode 工具函数
#include <iomanip>
#include <sstream>
// 将字符串转换为 Unicode 转义序列
std::string toUnicodeEscape(const std::string& input) {
std::ostringstream output;
for (size_t i = 0; i < input.length();) {
unsigned char c = input[i];
if (c < 128) {
// ASCII 字符
if (c == '"' || c == '\\') { // C里需要使用\\表示\
output << '\\' << c;
} else if (c < 32) {
// 控制字符转义为unicode编码
output << "\\u00" << std::hex << std::setw(2)
<< std::setfill('0') << static_cast<int>(c);
} else {
output << c;
}
i++;
} else {
// UTF-8 多字节字符
// 计算 Unicode 码点
unsigned int code_point = 0;
int num_bytes = 0;
if ((c & 0xF8) == 0xF0) {
// 4字节 UTF-8
code_point = (c & 0x07) << 18;
num_bytes = 4;
} else if ((c & 0xF0) == 0xE0) {
// 3字节 UTF-8
code_point = (c & 0x0F) << 12;
num_bytes = 3;
} else if ((c & 0xE0) == 0xC0) {
// 2字节 UTF-8
code_point = (c & 0x1F) << 6;
num_bytes = 2;
}
// 读取后续字节
for (int j = 1; j < num_bytes && i + j < input.length(); j++) {
unsigned char next = input[i + j];
if ((next & 0xC0) == 0x80) {
code_point |= (next & 0x3F) << (6 * (num_bytes - j - 1));
}
}
if (code_point <= 0xFFFF) {
// 基本多文种平面
output << "\\u" << std::hex << std::setw(4)
<< std::setfill('0') << code_point;
} else {
// 辅助平面,使用代理对
code_point -= 0x10000;
unsigned int high_surrogate = (code_point >> 10) + 0xD800;
unsigned int low_surrogate = (code_point & 0x3FF) + 0xDC00;
output << "\\u" << std::hex << std::setw(4) << high_surrogate;
output << "\\u" << std::hex << std::setw(4) << low_surrogate;
}
i += num_bytes;
}
}
return output.str();
}
实际应用场景
6. 处理包含 Unicode 的 JSON
void handleUnicodeJson() {
// 场景1: 包含各种 Unicode 字符的数据
json data;
data["user"] = "张三";
data["message"] = "Hello 世界! 🎉";
data["timestamp"] = "2024-01-01";
// 序列化时自动处理 Unicode
std::string json_str = data.dump();
std::cout << "序列化: " << json_str << std::endl;
// 反序列化
try {
json parsed = json::parse(json_str);
std::cout << "用户: " << parsed["user"] << std::endl;
std::cout << "消息: " << parsed["message"] << std::endl;
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
std::cout << "解析错误: " << e.what() << std::endl;
}
}
// 处理来自前端的 Unicode 数据
void handleWebData() {
// 模拟来自网页的 JSON 数据
std::string web_json = R"({
"name": "\u5F20\u4E09",
"comment": "Great product! \uD83D\uDC4D",
"rating": 5
})";
json j = json::parse(web_json);
std::cout << "姓名: " << j["name"] << std::endl; // 输出: 张三
std::cout << "评论: " << j["comment"] << std::endl; // 输出: Great product! 👍
}
重要注意事项
7. Unicode 处理最佳实践
- 始终使用 UTF-8 编码
- 验证代理对的完整性
- 注意字符串长度计算(字节数 vs 字符数)
- 处理无效的 UTF-8 序列
- 考虑 Unicode 规范化
// 检查字符串是否为有效 UTF-8
bool isValidUTF8(const std::string& str) {
try {
json j;
j["test"] = str;
std::string serialized = j.dump();
json parsed = json::parse(serialized);
return true;
} catch (...) {
return false;
}
}
JSON 的 Unicode 支持使得它成为处理国际化数据的理想格式,只要遵循正确的编码和转义规则,就可以安全地处理全球任何语言的文本数据。





















 8984
8984

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








