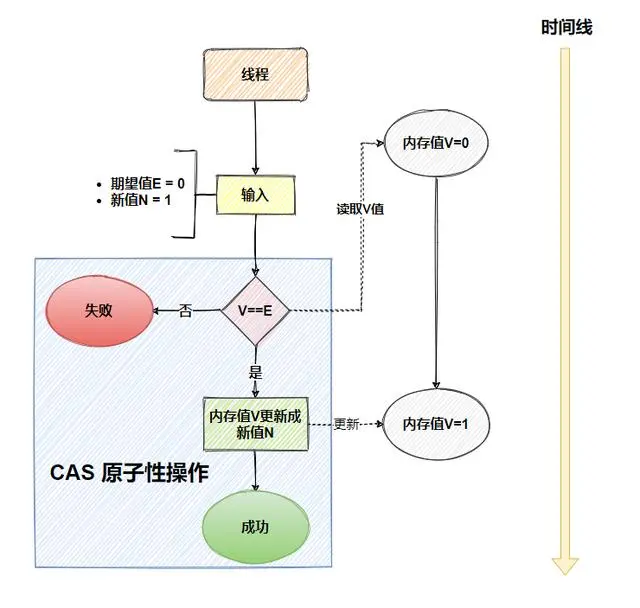
1.CAS介绍
什么是 CAS
public class CASDemo {
// 内存中当前的值
private volatile int ramAddress;
/**
* @param expectedValue 期望值
* @return newValue 更新的值
**/
public synchronized int compareAndSwap(int expectedValue, int newValue) {
//TODO 模拟直接从内存地址读取到内存中的值
int oldRamAddress = accessMemory(ramAddress);
//内存中的值和期望的值进行比较
if (oldRamAddress == expectedValue) {
ramAddress = newValue;
}
return oldRamAddress;
}
private int accessMemory(int ramAddress) {
//TODO 模拟直接从内存地址读取到内存中的值
return ramAddress;
}
}
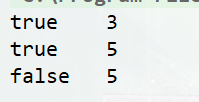
CAS使用

public class CASTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Entity entity = new Entity();
Unsafe unsafe = UnsafeFactory.getUnsafe();
long offset = UnsafeFactory.getFieldOffset(unsafe, Entity.class, "x");
boolean successful;
// 4个参数分别是:对象实例、字段的内存偏移量、字段期望值、字段新值
successful = unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(entity, offset, 0, 3);
System.out.println(successful + "\t" + entity.x);
successful = unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(entity, offset, 3, 5);
System.out.println(successful + "\t" + entity.x);
successful = unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(entity, offset, 3, 8);
System.out.println(successful + "\t" + entity.x);
}
}
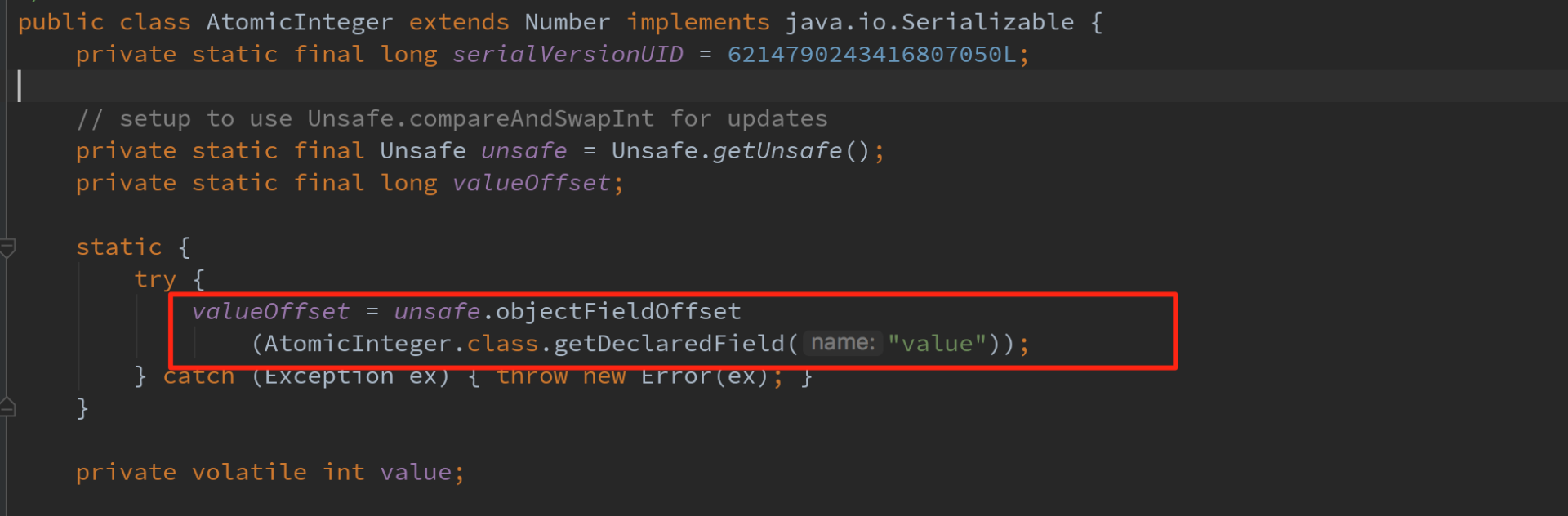
public class UnsafeFactory {
/**
* 获取 Unsafe 对象
* @return
*/
public static Unsafe getUnsafe() {
try {
Field field = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
field.setAccessible(true);
return (Unsafe) field.get(null);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 获取字段的内存偏移量
* @param unsafe
* @param clazz
* @param fieldName
* @return
*/
public static long getFieldOffset(Unsafe unsafe, Class clazz, String fieldName) {
try {
return unsafe.objectFieldOffset(clazz.getDeclaredField(fieldName));
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
throw new Error(e);
}
}
}
CAS应用场景
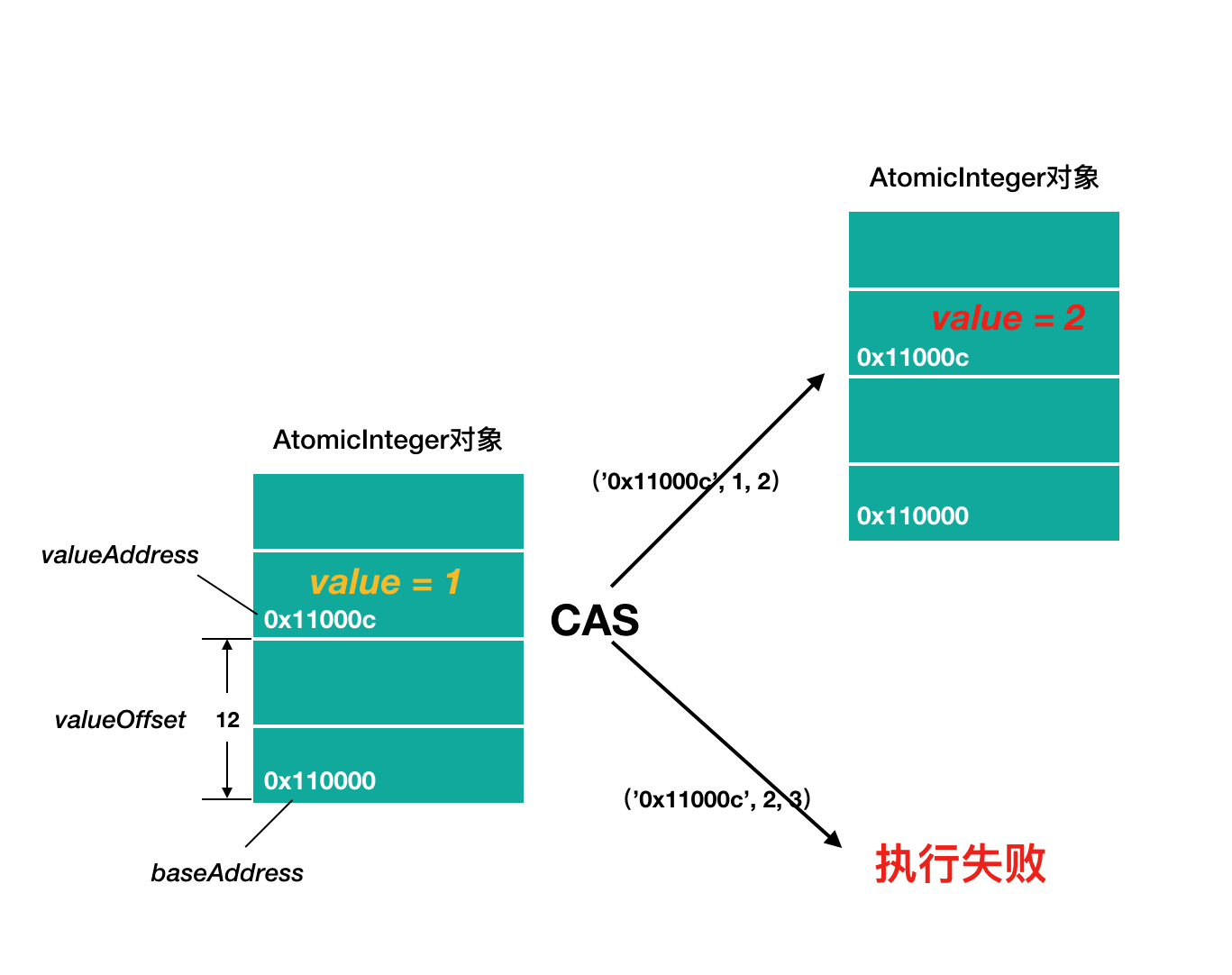
CAS源码分析
#unsafe.cpp
UNSAFE_ENTRY(jboolean, Unsafe_CompareAndSwapInt(JNIEnv *env, jobject unsafe, jobject obj, jlong offset, jint e, jint x))
UnsafeWrapper("Unsafe_CompareAndSwapInt");
oop p = JNIHandles::resolve(obj);
// 根据偏移量,计算value的地址
jint* addr = (jint *) index_oop_from_field_offset_long(p, offset);
// Atomic::cmpxchg(x, addr, e) cas逻辑 x:要交换的值 e:要比较的值
//cas成功,返回期望值e,等于e,此方法返回true
//cas失败,返回内存中的value值,不等于e,此方法返回false
return (jint)(Atomic::cmpxchg(x, addr, e)) == e;
UNSAFE_END2
#atomic_linux_x86.inline.hpp
inline jint Atomic::cmpxchg (jint exchange_value, volatile jint* dest, jint compare_value) {
//判断当前执行环境是否为多处理器环境
int mp = os::is_MP();
//LOCK_IF_MP(%4) 在多处理器环境下,为 cmpxchgl 指令添加 lock 前缀,以达到内存屏障的效果
//cmpxchgl 指令是包含在 x86 架构及 IA-64 架构中的一个原子条件指令,
//它会首先比较 dest 指针指向的内存值是否和 compare_value 的值相等,
//如果相等,则双向交换 dest 与 exchange_value,否则就单方面地将 dest 指向的内存值交给exchange_value。
//这条指令完成了整个 CAS 操作,因此它也被称为 CAS 指令。
__asm__ volatile (LOCK_IF_MP(%4) "cmpxchgl %1,(%3)"
: "=a" (exchange_value)
: "r" (exchange_value), "a" (compare_value), "r" (dest), "r" (mp)
: "cc", "memory");
return exchange_value;
}
cmpxchgl的详细执行过程:
首先,输入是"r" (exchange_value), “a” (compare_value), “r” (dest), “r” (mp),表示compare_value存入eax寄存器,而exchange_value、dest、mp的值存入任意的通用寄存器。嵌入式汇编规定把输出和输入寄存器按统一顺序编号,顺序是从输出寄存器序列从左到右从上到下以“%0”开始,分别记为%0、%1···%9。也就是说,输出的eax是%0,输入的exchange_value、compare_value、dest、mp分别是%1、%2、%3、%4。
因此,cmpxchg %1,(%3)实际上表示cmpxchg exchange_value,(dest)
需要注意的是cmpxchg有个隐含操作数eax,其实际过程是先比较eax的值(也就是compare_value)和dest地址所存的值是否相等,
输出是"=a" (exchange_value),表示把eax中存的值写入exchange_value变量中。
Atomic::cmpxchg这个函数最终返回值是exchange_value,也就是说,如果cmpxchgl执行时compare_value和dest指针指向内存值相等则会使得dest指针指向内存值变成exchange_value,最终eax存的compare_value赋值给了exchange_value变量,即函数最终返回的值是原先的compare_value。此时Unsafe_CompareAndSwapInt的返回值(jint)(Atomic::cmpxchg(x, addr, e)) == e就是true,表明CAS成功。如果cmpxchgl执行时compare_value和(dest)不等则会把当前dest指针指向内存的值写入eax,最终输出时赋值给exchange_value变量作为返回值,导致(jint)(Atomic::cmpxchg(x, addr, e)) == e得到false,表明CAS失败。
CAS缺陷
- 自旋 CAS 长时间不成功,则会给 CPU 带来非常大的开销
- 只能保证一个共享变量原子操作
- ABA 问题
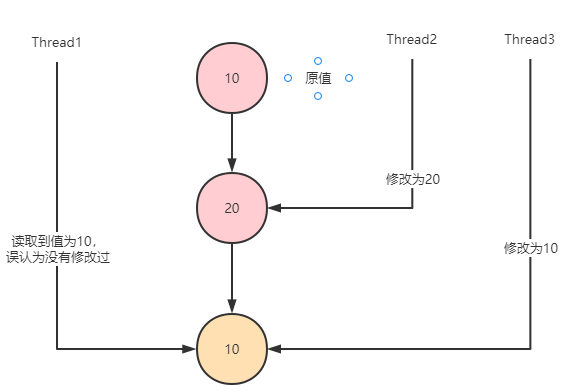
ABA问题及其解决方案
什么是ABA问题
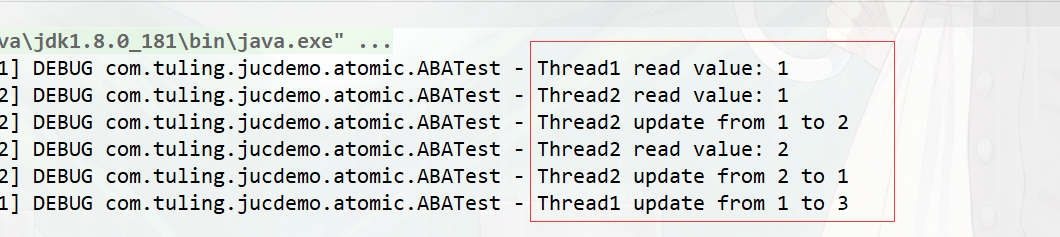
@Slf4j
public class ABATest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(1);
new Thread(()->{
int value = atomicInteger.get();
log.debug("Thread1 read value: " + value);
// 阻塞1s
LockSupport.parkNanos(1000000000L);
// Thread1通过CAS修改value值为3
if (atomicInteger.compareAndSet(value, 3)) {
log.debug("Thread1 update from " + value + " to 3");
} else {
log.debug("Thread1 update fail!");
}
},"Thread1").start();
new Thread(()->{
int value = atomicInteger.get();
log.debug("Thread2 read value: " + value);
// Thread2通过CAS修改value值为2
if (atomicInteger.compareAndSet(value, 2)) {
log.debug("Thread2 update from " + value + " to 2");
// do something
value = atomicInteger.get();
log.debug("Thread2 read value: " + value);
// Thread2通过CAS修改value值为1
if (atomicInteger.compareAndSet(value, 1)) {
log.debug("Thread2 update from " + value + " to 1");
}
}
},"Thread2").start();
}
}
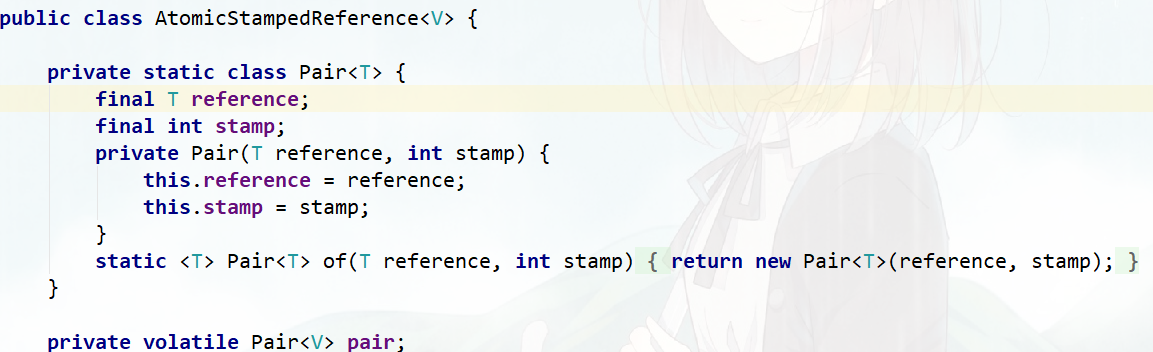
ABA问题的解决方案
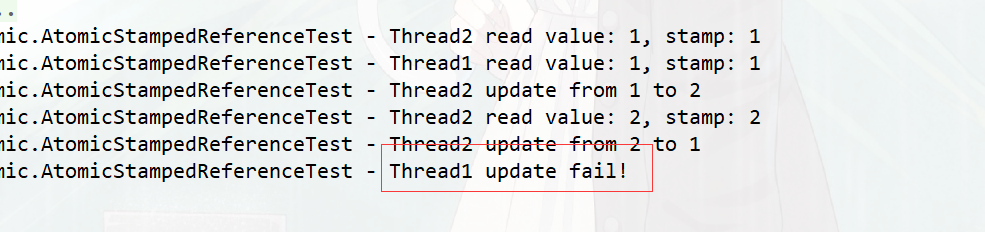
@Slf4j
public class AtomicStampedReferenceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义AtomicStampedReference Pair.reference值为1, Pair.stamp为1
AtomicStampedReference atomicStampedReference = new AtomicStampedReference(1,1);
new Thread(()->{
int[] stampHolder = new int[1];
int value = (int) atomicStampedReference.get(stampHolder);
int stamp = stampHolder[0];
log.debug("Thread1 read value: " + value + ", stamp: " + stamp);
// 阻塞1s
LockSupport.parkNanos(1000000000L);
// Thread1通过CAS修改value值为3
if (atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(value, 3,stamp,stamp+1)) {
log.debug("Thread1 update from " + value + " to 3");
} else {
log.debug("Thread1 update fail!");
}
},"Thread1").start();
new Thread(()->{
int[] stampHolder = new int[1];
int value = (int)atomicStampedReference.get(stampHolder);
int stamp = stampHolder[0];
log.debug("Thread2 read value: " + value+ ", stamp: " + stamp);
// Thread2通过CAS修改value值为2
if (atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(value, 2,stamp,stamp+1)) {
log.debug("Thread2 update from " + value + " to 2");
// do something
value = (int) atomicStampedReference.get(stampHolder);
stamp = stampHolder[0];
log.debug("Thread2 read value: " + value+ ", stamp: " + stamp);
// Thread2通过CAS修改value值为1
if (atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(value, 1,stamp,stamp+1)) {
log.debug("Thread2 update from " + value + " to 1");
}
}
},"Thread2").start();
}
}
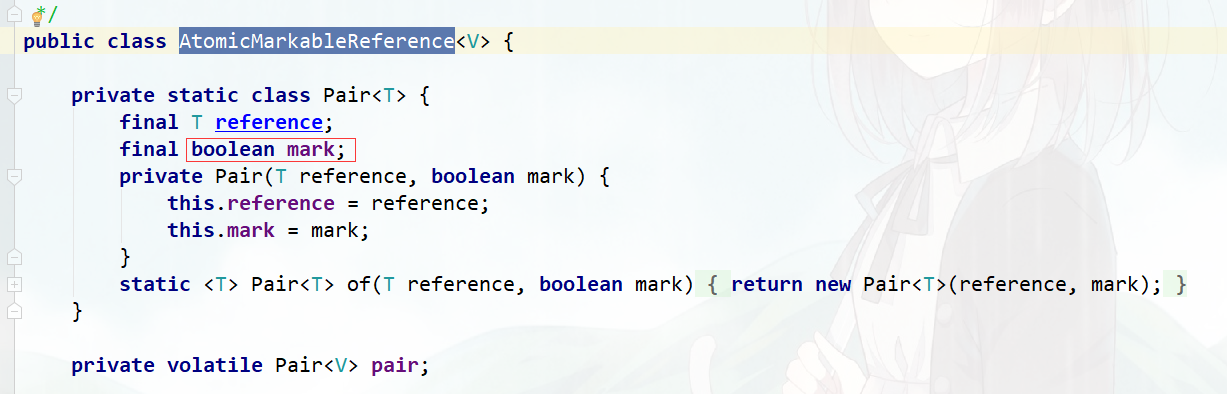
2.Atomic原子操作类介绍
原子更新基本类型
//以原子的方式将实例中的原值加1,返回的是自增前的旧值;
public final int getAndIncrement() {
return unsafe.getAndAddInt(this, valueOffset, 1);
}
//getAndSet(int newValue):将实例中的值更新为新值,并返回旧值;
public final boolean getAndSet(boolean newValue) {
boolean prev;
do {
prev = get();
} while (!compareAndSet(prev, newValue));
return prev;
}
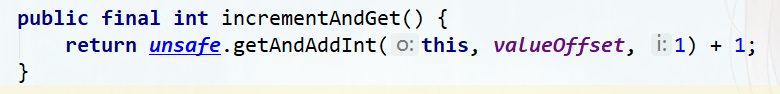
//incrementAndGet() :以原子的方式将实例中的原值进行加1操作,并返回最终相加后的结果;
public final int incrementAndGet() {
return unsafe.getAndAddInt(this, valueOffset, 1) + 1;
}
//addAndGet(int delta) :以原子方式将输入的数值与实例中原本的值相加,并返回最后的结果;
public final int addAndGet(int delta) {
return unsafe.getAndAddInt(this, valueOffset, delta) + delta;
public class AtomicIntegerTest {
static AtomicInteger sum = new AtomicInteger(0);
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
for (int j = 0; j < 10000; j++) {
// 原子自增 CAS
sum.incrementAndGet();
//TODO
}
});
thread.start();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(sum.get());
}
}

原子更新数组类型
//addAndGet(int i, int delta):以原子更新的方式将数组中索引为i的元素与输入值相加;
public final int addAndGet(int i, int delta) {
return getAndAdd(i, delta) + delta;
}
//getAndIncrement(int i):以原子更新的方式将数组中索引为i的元素自增加1;
public final int getAndIncrement(int i) {
return getAndAdd(i, 1);
}
//compareAndSet(int i, int expect, int update):将数组中索引为i的位置的元素进行更新
public final boolean compareAndSet(int i, int expect, int update) {
return compareAndSetRaw(checkedByteOffset(i), expect, update);
}
public class AtomicIntegerArrayTest {
static int[] value = new int[]{ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
static AtomicIntegerArray atomicIntegerArray = new AtomicIntegerArray(value);
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//设置索引0的元素为100
atomicIntegerArray.set(0, 100);
System.out.println(atomicIntegerArray.get(0));
//以原子更新的方式将数组中索引为1的元素与输入值相加
atomicIntegerArray.getAndAdd(1,5);
System.out.println(atomicIntegerArray);
}
}
原子更新引用类型
public class AtomicReferenceTest {
public static void main( String[] args ) {
User user1 = new User("张三", 23);
User user2 = new User("李四", 25);
User user3 = new User("王五", 20);
//初始化为 user1
AtomicReference<User> atomicReference = new AtomicReference<>();
atomicReference.set(user1);
//把 user2 赋给 atomicReference
atomicReference.compareAndSet(user1, user2);
System.out.println(atomicReference.get());
//把 user3 赋给 atomicReference
atomicReference.compareAndSet(user1, user3);
System.out.println(atomicReference.get());
}
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
class User {
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
对象属性原子修改器
public class AtomicIntegerFieldUpdaterTest {
public static class Candidate {
volatile int score = 0;
AtomicInteger score2 = new AtomicInteger();
}
public static final AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<Candidate> scoreUpdater =
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(Candidate.class, "score");
public static AtomicInteger realScore = new AtomicInteger(0);
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
final Candidate candidate = new Candidate();
Thread[] t = new Thread[10000];
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
t[i] = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (Math.random() > 0.4) {
candidate.score2.incrementAndGet();
scoreUpdater.incrementAndGet(candidate);
realScore.incrementAndGet();
}
}
});
t[i].start();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
t[i].join();
}
System.out.println("AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater Score=" + candidate.score);
System.out.println("AtomicInteger Score=" + candidate.score2.get());
System.out.println("realScore=" + realScore.get());
}
}
LongAdder/DoubleAdder详解

性能测试
public class LongAdderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
testAtomicLongVSLongAdder(10, 10000);
System.out.println("==================");
testAtomicLongVSLongAdder(10, 200000);
System.out.println("==================");
testAtomicLongVSLongAdder(100, 200000);
}
static void testAtomicLongVSLongAdder(final int threadCount, final int times) {
try {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
testLongAdder(threadCount, times);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
System.out.println("条件>>>>>>线程数:" + threadCount + ", 单线程操作计数" + times);
System.out.println("结果>>>>>>LongAdder方式增加计数" + (threadCount * times) + "次,共计耗时:" + end);
long start2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
testAtomicLong(threadCount, times);
long end2 = System.currentTimeMillis() - start2;
System.out.println("条件>>>>>>线程数:" + threadCount + ", 单线程操作计数" + times);
System.out.println("结果>>>>>>AtomicLong方式增加计数" + (threadCount * times) + "次,共计耗时:" + end2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
static void testAtomicLong(final int threadCount, final int times) throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(threadCount);
AtomicLong atomicLong = new AtomicLong();
for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int j = 0; j < times; j++) {
atomicLong.incrementAndGet();
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
}, "my-thread" + i).start();
}
countDownLatch.await();
}
static void testLongAdder(final int threadCount, final int times) throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(threadCount);
LongAdder longAdder = new LongAdder();
for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int j = 0; j < times; j++) {
longAdder.add(1);
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
}, "my-thread" + i).start();
}
countDownLatch.await();
}
}

LongAdder原理
设计思路
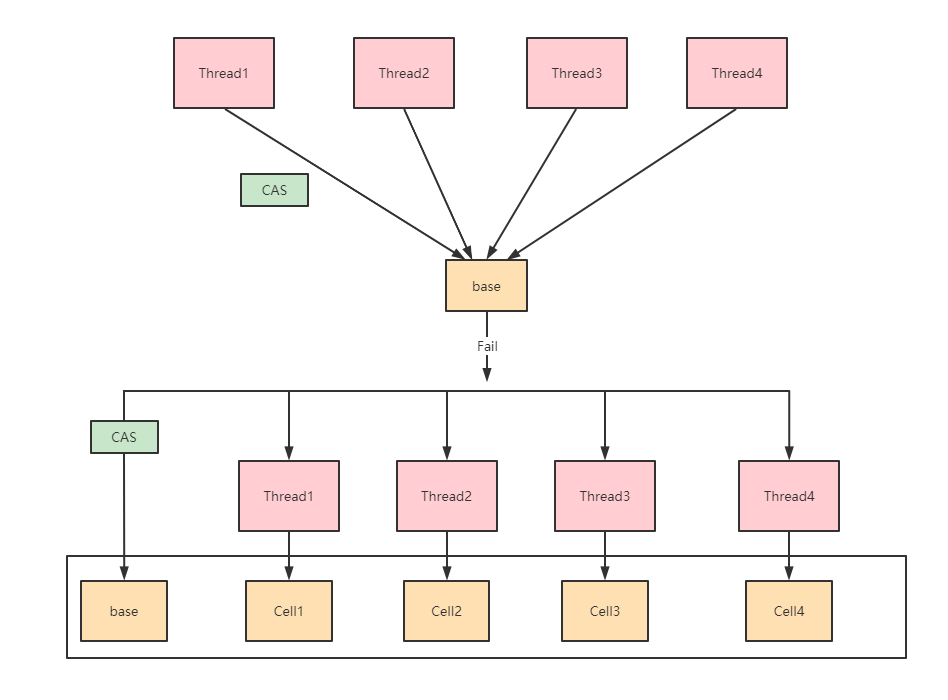
LongAdder的内部结构
/** Number of CPUS, to place bound on table size */
// CPU核数,用来决定槽数组的大小
static final int NCPU = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
/**
* Table of cells. When non-null, size is a power of 2.
*/
// 数组槽,大小为2的次幂
transient volatile Cell[] cells;
/**
* Base value, used mainly when there is no contention, but also as
* a fallback during table initialization races. Updated via CAS.
*/
/**
* 基数,在两种情况下会使用:
* 1. 没有遇到并发竞争时,直接使用base累加数值
* 2. 初始化cells数组时,必须要保证cells数组只能被初始化一次(即只有一个线程能对cells初始化),
* 其他竞争失败的线程会将数值累加到base上
*/
transient volatile long base;
/**
* Spinlock (locked via CAS) used when resizing and/or creating Cells.
*/
transient volatile int cellsBusy;
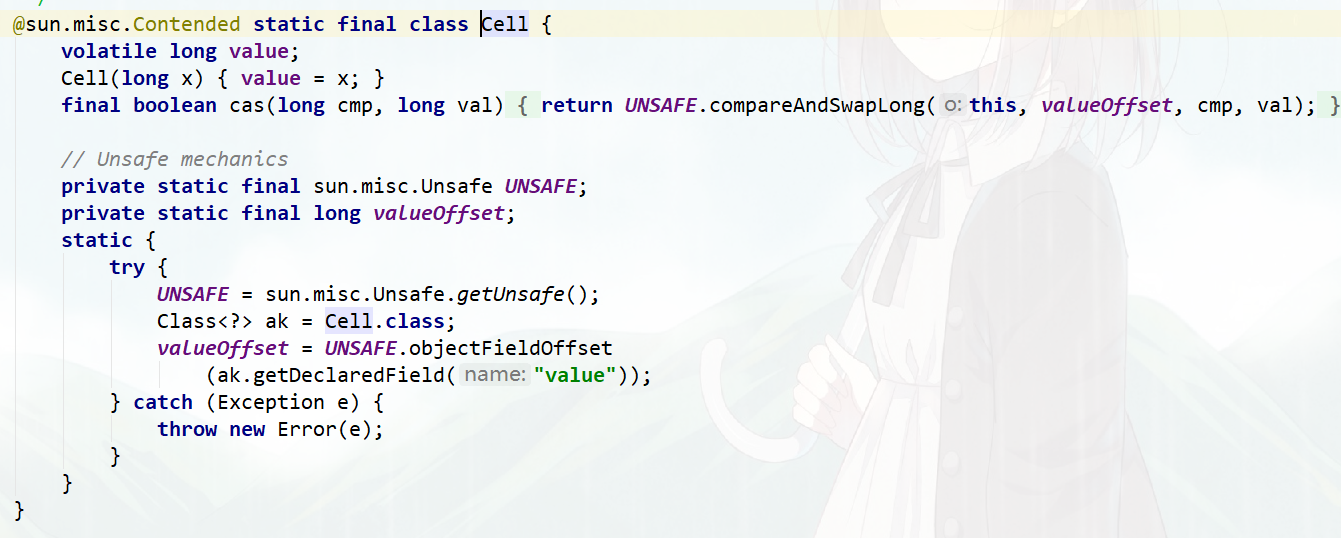
LongAdder#add方法
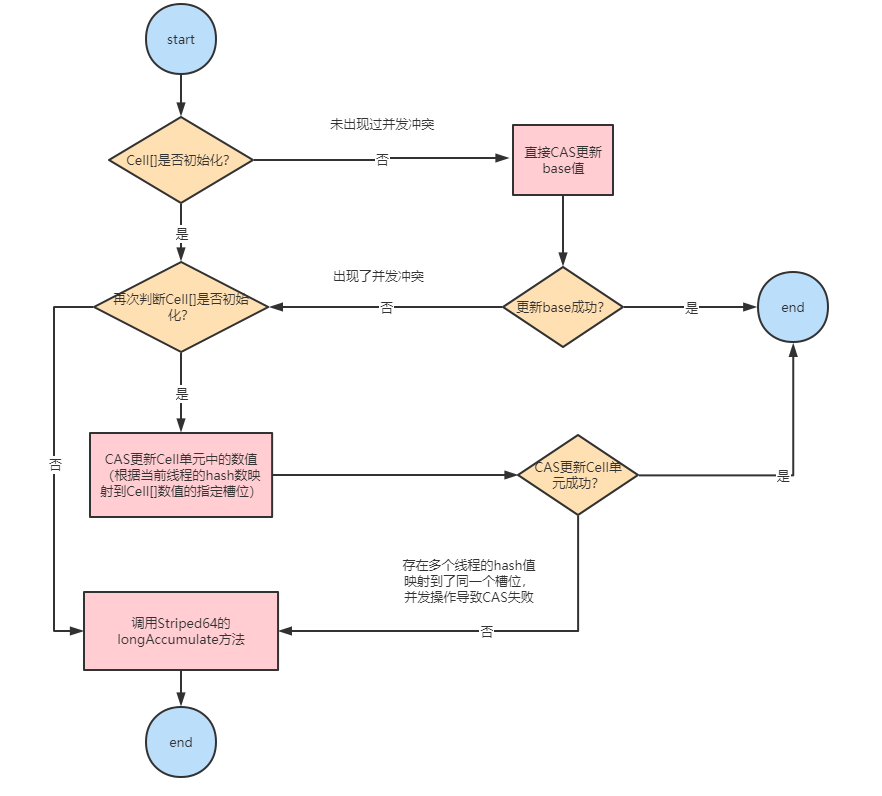
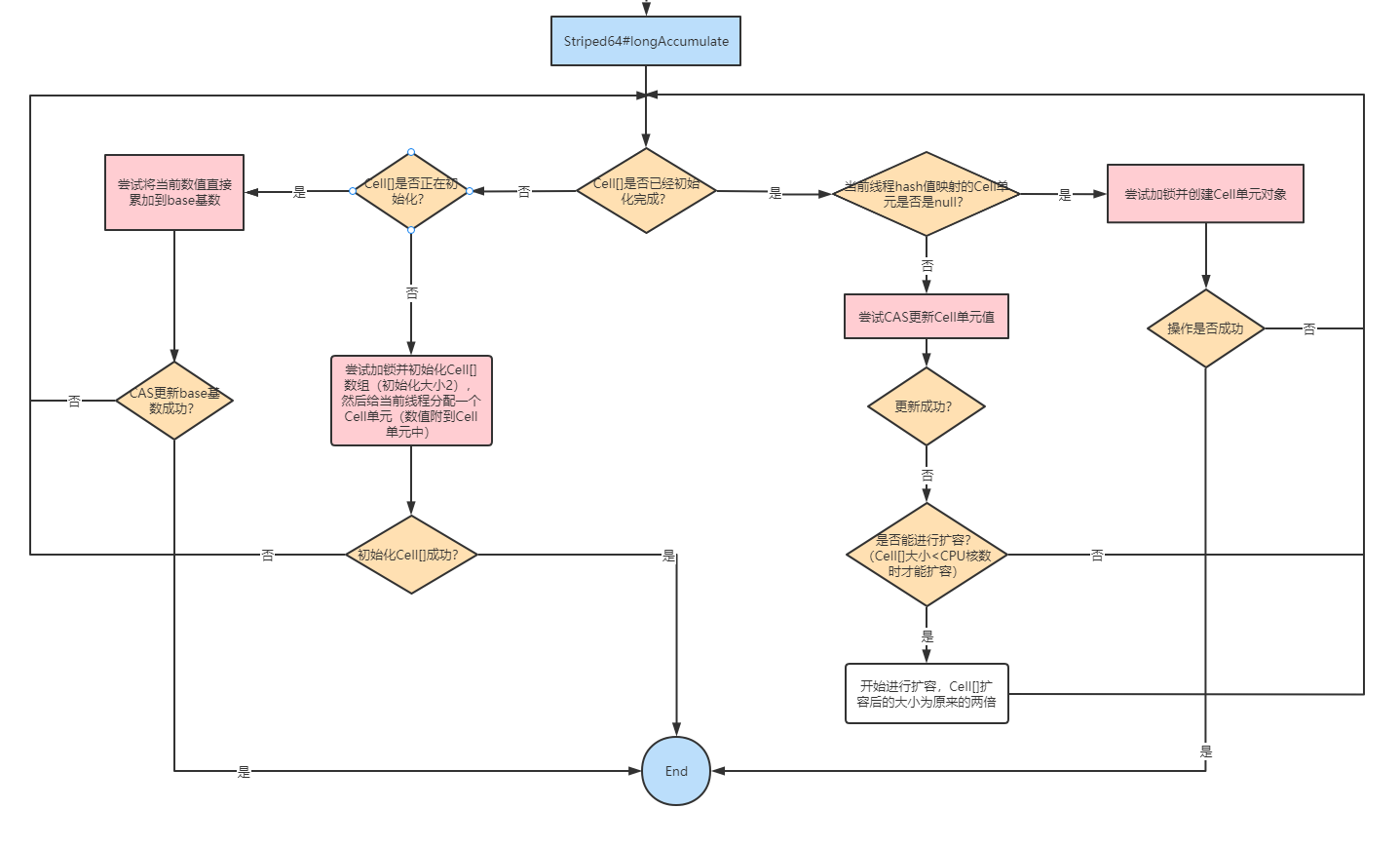
Striped64#longAccumulate方法
LongAdder#sum方法
/**
* 返回累加的和,也就是"当前时刻"的计数值
* 注意: 高并发时,除非全局加锁,否则得不到程序运行中某个时刻绝对准确的值
* 此返回值可能不是绝对准确的,因为调用这个方法时还有其他线程可能正在进行计数累加,
* 方法的返回时刻和调用时刻不是同一个点,在有并发的情况下,这个值只是近似准确的计数值
*/
public long sum() {
Cell[] as = cells; Cell a;
long sum = base;
if (as != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < as.length; ++i) {
if ((a = as[i]) != null)
sum += a.value;
}
}
return sum;
}




















 839
839

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








