一、在说拆箱和装箱之前的准备知识
首先,我们需要知道C#中有两种类型:值类型和引用类型
| 名称 | 值类型 | 引用类型 |
|---|
| 表示类型 | 基本类型 | 类,数组,接口 ,C#特有的委托. |
| 存储内容 | 值 | 值的引用 |
| 存储位置 | 堆栈 | 托管堆 |
二、拆箱和装箱的概念
上面为什么要讲C#的两种类型呢,因为拆箱和装箱实质上就是两个类型之间的转换.
拆箱: 引用类型 —>值类型
装箱: 值类型—–>引用类型
三、拆箱和装箱实例
我们看下面一篇代码,非常简单,就三句代码,就完成了装箱和拆箱的一个过程。
namespace DR_HelloWorld
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int num = 12;
object numObj = num;
int num2 = (int)numObj;
}
}
}
1、分析:
首先我们这三句代码中,出现了三个变量,两个类型:
int类型 : num,num2
object类型:numObj
很明显我们知道int类型是值类型,object类型是引用类型,但是为什么int类型是值类型,object类型是引用类型呢?我们可以跳入两者的定义代码中一探究竟:
int: 本质上是一个结构体(struct),所以int是一个值类型
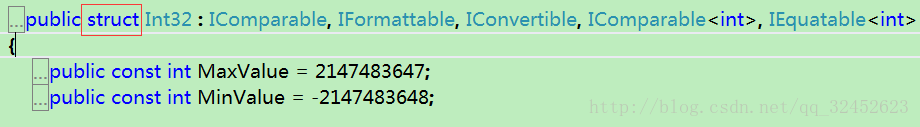
object: 本质上是一个类(class),类属于引用类型

那我们就可以很清楚的知道:
1、Int32—>Object 装箱 :
object numObj = num;
2、Object —>Int32 拆箱:
int num2 = (int)numObj;
2、通过C#代码的IL语言,查看装箱和拆箱:
这里我们要通过查看c#源码的IL语言来查看代码的执行过程.
IL,全称是 Intermediate
Language,是微软平台上的一门中间语言,我们平常开发写的c#语言,在编译器中都会自动转换为IL,然后由即时编译器(JIT
Compiler)转换为二进制机器码,最后被CPU执行.
如果小伙伴们不知道该怎么看IL代码的话,可以移步这里C# IL DASM 使用 PS:我感觉讲的特别好,我就是从那里学会的.
以下是我们上面实例代码的IL代码:
.method private hidebysig static void Main(string[] args) cil managed
{
.entrypoint
.maxstack 1
.locals init ([0] int32 num,
[1] object numObj,
[2] int32 num2)
IL_0000: nop
IL_0001: ldc.i4.s 12
IL_0003: stloc.0
IL_0004: ldloc.0
IL_0005: box [mscorlib]System.Int32
IL_000a: stloc.1
IL_000b: ldloc.1
IL_000c: unbox.any [mscorlib]System.Int32
IL_0011: stloc.2
IL_0012: ret
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
四、拆箱和装箱对于代码效率的影响:
装箱和拆箱因为多了个执行过程,肯定会对代码的执行速度产生影响,我们通过以下的代码,打印他们的运行时间,可以得出的我们的结论:
Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch()
watch.Start()
string s = "测试数据"
for (int i = 0
{
s = s + 1
}
watch.Stop()
Console.WriteLine("----直接添加---会执行装箱过程---" + watch.ElapsedMilliseconds)
watch.Restart()
string s1 = "测试数据"
for (int i = 0
{
s1 = s1 + 1.ToString()
}
watch.Stop()
Console.WriteLine("----ToString()添加---不会执行装箱---" + watch.ElapsedMilliseconds)
Console.ReadLine()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
运行结果:

很明显在循环100000次之后,因为装箱的操作,导致代码的执行速度变慢了.
五、如何优化拆箱和装箱:
1、警惕隐式类型转换–使用合理的方式进行类型转换
为什么要说使用合理的方式?
因为我们很容易就忽略了一些值类型隐式转换为System.Object的操作
例如:
string s = "测试数据";
s = s + 1;
1是值类型,s是string类型,为引用类型,这个”s +1”操作,虽然没有显式的类型转换,但是确实发生了装箱的操作
这个代码的IL语言如下:
.locals init ([0] string s)
IL_0000: nop
IL_0001: ldstr bytearray (4B 6D D5 8B 70 65 6E 63 ) // Km..penc
IL_0006: stloc.0
IL_0007: ldloc.0
IL_0008: ldc.i4.1
IL_0009: box [mscorlib]System.Int32 //装箱操作
IL_000e: call string [mscorlib]System.String::Concat(object,
object)
IL_0013: stloc.0
IL_0014: ret
那我们应该如下操作:
string s = "测试数据";
s = s + 1.ToString();
这个调用了Int32的ToString()方法,就变为两个string类型的数据添加,就不存在装箱操作了
这个代码的IL语言如下:
.locals init ([0] string s,
[1] int32 CS$0$0000)
IL_0000: nop
IL_0001: ldstr bytearray (4B 6D D5 8B 70 65 6E 63 )
IL_0006: stloc.0
IL_0007: ldloc.0
IL_0008: ldc.i4.1
IL_0009: stloc.1
IL_000a: ldloca.s CS$0$0000
IL_000c: call instance string [mscorlib]System.Int32::ToString()
IL_0011: call string [mscorlib]System.String::Concat(string,
string)
IL_0016: stloc.0
IL_0017: ret
2、使用泛型—运行时绑定数据类型,减少装箱与拆箱
首先我们需要知道什么是泛型?
泛型,简单的来说,是一种可以接收很多种类型的类型,具体是接收多少种,你可以自己去约束,默认是全部类型,一般是用”T”表示.
来个例子感受一下:
简单示例(一)—-泛型参数的使用
1、指定参数类型的方法:
public static void TestMethod(int s)
{
s.GetType();
}
因为GetType()是Object的方法,但是参数传的是Int32类型,肯定会有装箱操作.
这个代码的IL语言如下:
.method public hidebysig static void TestMethod(int32 s) cil managed
{
// 代码大小 14 (0xe)
.maxstack 8
IL_0000: nop
IL_0001: ldarg.0
IL_0002: box [mscorlib]System.Int32 //装箱
IL_0007: call instance class [mscorlib]System.Type [mscorlib]System.Object::GetType()
IL_000c: pop
IL_000d: ret
} // end of method Program::TestMethod
2、不指定参数类型,使用泛型接收的方法
public static void TestMethod2<T>(T t)
{
t.GetType();
}
这个方法,我们的参数定义的是泛型的参数,所以,虽然GetType()是Object的方法,但是不会进行装箱操作.
这个代码的IL语言如下:
.method public hidebysig static void TestMethod2<T>(!!T t) cil managed
{
.maxstack 8
IL_0000: nop
IL_0001: ldarga.s t
IL_0003: constrained. !!T
IL_0009: callvirt instance class [mscorlib]System.Type [mscorlib]System.Object::GetType()
IL_000e: pop
IL_000f: ret
}
很明显使用泛型的并没有装箱操作,但是执行了constrained指令,那到底是box指令执行快,还是constrained指令执行快,我们需要做个测试.
仍然是100000次循环:
Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch()
watch.Start()
string s = "测试数据"
for (int i = 0
{
TestMethod(1)
}
watch.Stop()
Console.WriteLine("---TestMethod--指定类型参数--会执行装箱过程---" + watch.ElapsedMilliseconds)
watch.Restart()
string s1 = "测试数据"
for (int i = 0
{
TestMethod2(1)
}
watch.Stop()
Console.WriteLine("----TestMethod2--泛型参数--不会执行装箱---" + watch.ElapsedMilliseconds)
Console.ReadLine()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
运行结果:

很明显,还是泛型方法执行的速度快一点.
简单示例(二)—ArrayList和List
上面那个例子是我自己想的,很简单,很容易理解,但是我们要知道在正常的使用过程中,最常涉及到拆箱/装箱 和泛型操作的就是列表操作,例如ArrayList和List:
ArrayList array = new ArrayList();
array.Add(1);
List<int> list = new List<int>();
list.Add(1);
其中,
ArrayList是来自System.Collections,是一个非泛型的集合—-存在装箱

List来源于System.Collections.Generic,是一个泛型集合—–不存在装箱

这个代码的IL语言如下:
.method private hidebysig static void Main(string[] args) cil managed
{
.entrypoint
.maxstack 2
.locals init ([0] class [mscorlib]System.Collections.ArrayList 'array',
[1] class [mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.List`1<int32> list)
IL_0000: nop
IL_0001: newobj instance void [mscorlib]System.Collections.ArrayList::.ctor()
IL_0006: stloc.0
IL_0007: ldloc.0
IL_0008: ldc.i4.1
IL_0009: box [mscorlib]System.Int32
IL_000e: callvirt instance int32 [mscorlib]System.Collections.ArrayList::Add(object)
IL_0013: pop
IL_0014: newobj instance void class [mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.List`1<int32>::.ctor()
IL_0019: stloc.1
IL_001a: ldloc.1
IL_001b: ldc.i4.1
IL_001c: callvirt instance void class [mscorlib]System.Collections.Generic.List`1<int32>::Add(!0)
IL_0021: nop
IL_0022: ret
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
五、总结:
1、拆箱和装箱的存在,让值类型和引用类型之间的转换变得方便
2、但是在大量的数据操作中,频繁的装箱和拆箱操作会大大消耗CPU的资源,降低代码的执行速率
3、为了解决这个问题,我们要合理的使用类型转换和泛型类与泛型方法来防止隐式的装箱和拆箱操作




























 99
99

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








