I.idr机制
i.idr介绍
系统许多资源都用整数ID来标识,如进程ID、文件描述符ID、IPC ID等;资源信息通常存放在对应的数据结构中(如进程信息存放在task_struct中、ipc信息存放在ipc_perm中),id与数据结构的关联机制有不同的实现,idr机制是其中的一种。
idr,id radix的缩写。idr主要用于建立id与指针(指向对应的数据结构)之间的对应关系。idr用类基数树结构来构造一个稀疏数组,以id为索引找到对应数组元素,进而找到对应的数据结构指针。
用到idr机制的主要有:IPC id(消息队列id、信号量id、共享内存id等),磁盘分区id(sda中数字部分)等
ii.idr实现
1.idr结构
idr是由基数树构成,叶结点存储id对应的指针,树干结点用于叶结点与根结点的串联而不存储数据。每个结点有radix个子结点,每个叶结点可存储radix个指针。
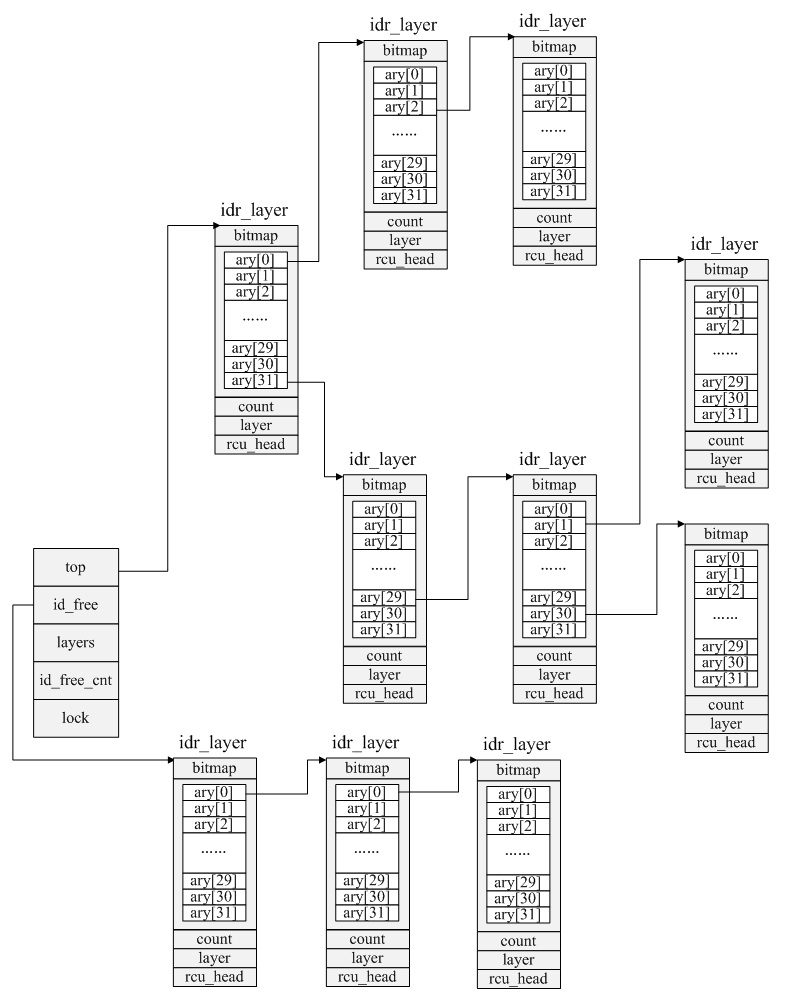
根结点、树干结点、叶结点均用idr_layer表示:
51 struct idr_layer {
52 unsigned long bitmap; /* A zero bit means "space here" */
53 struct idr_layer *ary[1<<IDR_BITS];
54 int count; /* When zero, we can release it */
55 int layer; /* distance from leaf */
56 struct rcu_head rcu_head;
57 };bitmap:用于标识子结点是否还有空闲空间,如果子结点对应位是0,则表示子结点还有空闲空间,否则表示子结点已满
ary:根或树干结点时存储子结点指针,叶结点时存储指针数据
count:ary中有效数据个数
layer:层数,即距叶结点的距离,如果时叶结点layer=0
rcu_head:用于idr_layer的内存释放
2.idr基数树
idr树用结构idr表示
59 struct idr {
60 struct idr_layer *top;
61 struct idr_layer *id_free;
62 int layers; /* only valid without concurrent changes */
63 int id_free_cnt;
64 spinlock_t lock;
65 };top:指向基数树根结点
id_free:指向idr_layer构成的缓存池链表
layers:基数树层数
id_free_cnt:缓存池大小
lock:idr锁,保护基数树
3.基数树结构图
3.宏定义
IDR_BITS:子结点索引位数,5或6;bitmap是long类型,表示子结点个数为sizeof(long)*8;long占32位时,可表示32个子结点,则需索引位数为5;long占64位时,则需索引位数为6
IDR_SIZE:子结点个数,(1 << IDR_BITS)
IDR_MASK:子结点索引掩码,((1 << IDR_BITS)-1)
MAX_ID_SHIFT:ID空间大小位数,(sizeof(int)*8 - 1);ID空间为0~0x7fffffff,即正整数
MAX_LEVEL:表示ID空间所需的层数,(MAX_ID_SHIFT + IDR_BITS - 1) / IDR_BITS;n层基数树表示id空间的个数=IDR_SIZE^n=1<<(n*IDR_BITS),则表示整个ID空间需要n=roundup(log2(1<<MAX_ID_SHIFT)/IDR_BITS)=(MAX_ID_SHIFT + IDR_BITS - 1) / IDR_BITS层
IDR_FREE_MAX:表示idr缓存在分配id过程中所需结点的最大值,MAX_LEVEL + MAX_LEVEL;分配id过程中,可能需要对树进行扩容,如果出现结点为空还要分配结点;比如空树情况,分配一个值为0x7fffffff的id,则首先要扩容MAX_LEVEL个结点,再添加MAX_LEVEL-1个结点后才能正确分配id
II.idr分配id
i.缓存预留
基数树是在分配id的过程中动态分配树结点的,如果结点不存在会从idr缓存中取出可用结点自动添加到树中;一次分配id过程中,最多会添加2*MAX_LEVEL-1个结点,所以缓存中必须保证存在2*MAX_LEVEL-1个结点,才能保证分配不出现无内存情况。
lib/idr.c:
108 /**
109 * idr_pre_get - reserver resources for idr allocation
110 * @idp: idr handle
111 * @gfp_mask: memory allocation flags
112 *
113 * This function should be called prior to locking and calling the
114 * idr_get_new* functions. It preallocates enough memory to satisfy
115 * the worst possible allocation.
116 *
117 * If the system is REALLY out of memory this function returns 0,
118 * otherwise 1.
119 */
120 int idr_pre_get(struct idr *idp, gfp_t gfp_mask)
121 {
122 while (idp->id_free_cnt < IDR_FREE_MAX) {
123 struct idr_layer *new;
124 new = kmem_cache_zalloc(idr_layer_cache, gfp_mask);
125 if (new == NULL)
126 return (0);
127 move_to_free_list(idp, new);
128 }
129 return 1;
130 }
ii.idr基数树扩容
当idr表示的id空间大小不满足要求时,会对idr树扩容,主要就是增加idr树的层数;树层数由n增加到n+1后,则n层树的根结点必属于n+1层的第一个结点的第个一元素。
idr基数是在分配id时自动扩容,实现代码是idr_get_empty_slot:
202 static int idr_get_empty_slot(struct idr *idp, int starting_id,
203 struct idr_layer **pa)
204 {
205 struct idr_layer *p, *new;
206 int layers, v, id;
207 unsigned long flags;
208
209 id = starting_id;
210 build_up:
211 p = idp->top;
212 layers = idp->layers;
213 if (unlikely(!p)) {
214 if (!(p = get_from_free_list(idp)))
215 return -1;
216 p->layer = 0;
217 layers = 1;
218 }
219 /*
220 * Add a new layer to the top of the tree if the requested
221 * id is larger than the currently allocated space.
222 */
223 while ((layers < (MAX_LEVEL - 1)) && (id >= (1 << (layers*IDR_BITS)))) {
224 layers++;
225 if (!p->count) {
226 /* special case: if the tree is currently empty,
227 * then we grow the tree by moving the top node
228 * upwards.
229 */
230 p->layer++;
231 continue;
232 }
233 if (!(new = get_from_free_list(idp))) {
234 /*
235 * The allocation failed. If we built part of
236 * the structure tear it down.
237 */
238 spin_lock_irqsave(&idp->lock, flags);
239 for (new = p; p && p != idp->top; new = p) {
240 p = p->ary[0];
241 new->ary[0] = NULL;
242 new->bitmap = new->count = 0;
243 __move_to_free_list(idp, new);
244 }
245 spin_unlock_irqrestore(&idp->lock, flags);
246 return -1;
247 }
248 new->ary[0] = p;
249 new->count = 1;
250 new->layer = layers-1;
251 if (p->bitmap == IDR_FULL)
252 __set_bit(0, &new->bitmap);
253 p = new;
254 }
255 rcu_assign_pointer(idp->top, p);
256 idp->layers = layers;
257 v = sub_alloc(idp, &id, pa);
258 if (v == IDR_NEED_TO_GROW)
259 goto build_up;
260 return(v);
261 }
分配步骤如下:
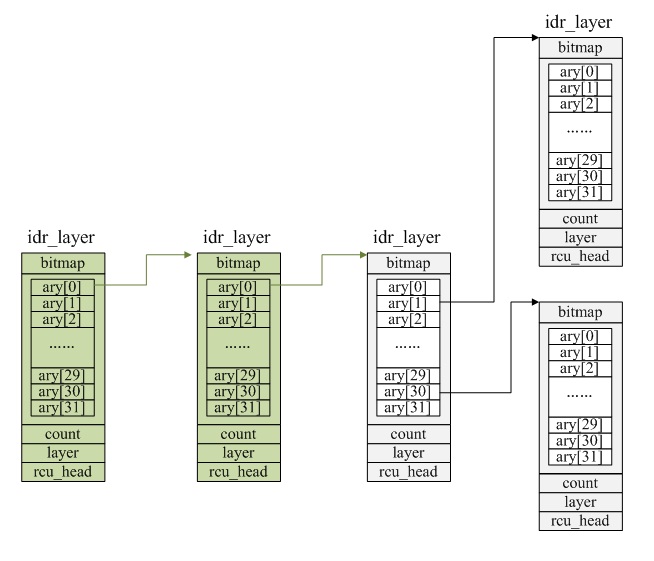
1.由于idr初始化后,基数树没有任何树结点;如果没有根结点,则创建根结点,且layer=0,表示根结点也是叶结点
2.如果查找起始id已经超过基数树的大小空间,则会对基数树进行扩容;
a.如果当前树是空树,则直接修改树的层数及根结点的层级
b.否则,将原树的根结点作为新树根结点的第一个元素,循环添加根结点直到满足扩容要求;在扩容过程中如果失败,则会删除前面添加的结点
3.修改树的根结点级层信息
4.从基数树中分配空闲id,如果树需要扩容,则根据id大小对树进行扩容。
基数树扩容过程如下图所示,其中绿色部分是扩容的结点:
iii.idr分配id
idr分配id,此过程可能会添加树的新结点,实现为sub_alloc
133 static int sub_alloc(struct idr *idp, int *starting_id, struct idr_layer **pa)
134 {
135 int n, m, sh;
136 struct idr_layer *p, *new;
137 int l, id, oid;
138 unsigned long bm;
139
140 id = *starting_id;
141 restart:
142 p = idp->top;
143 l = idp->layers;
144 pa[l--] = NULL;
145 while (1) {
146 /*
147 * We run around this while until we reach the leaf node...
148 */
149 n = (id >> (IDR_BITS*l)) & IDR_MASK;
150 bm = ~p->bitmap;
151 m = find_next_bit(&bm, IDR_SIZE, n);
152 if (m == IDR_SIZE) {
153 /* no space available go back to previous layer. */
154 l++;
155 oid = id;
156 id = (id | ((1 << (IDR_BITS * l)) - 1)) + 1;
158 /* if already at the top layer, we need to grow */
159 if (id >= 1 << (idp->layers * IDR_BITS)) {
160 *starting_id = id;
161 return IDR_NEED_TO_GROW;
162 }
163 p = pa[l];
164 BUG_ON(!p);
165
166 /* If we need to go up one layer, continue the
167 * loop; otherwise, restart from the top.
168 */
169 sh = IDR_BITS * (l + 1);
170 if (oid >> sh == id >> sh)
171 continue;
172 else
173 goto restart;
174 }
175 if (m != n) {
176 sh = IDR_BITS*l;
177 id = ((id >> sh) ^ n ^ m) << sh;
178 }
179 if ((id >= MAX_ID_BIT) || (id < 0))
180 return IDR_NOMORE_SPACE;
181 if (l == 0)
182 break;
183 /*
184 * Create the layer below if it is missing.
185 */
186 if (!p->ary[m]) {
187 new = get_from_free_list(idp);
188 if (!new)
189 return -1;
190 new->layer = l-1;
191 rcu_assign_pointer(p->ary[m], new);
192 p->count++;
193 }
194 pa[l--] = p;
195 p = p->ary[m];
196 }
197
198 pa[l] = p;
199 return id;
200 }分配id过程如下:
1.查找starting_id开始的id空间,如果没有可用空间,则需要对基数树进行扩容
2.根据starting_id递归子结点,如果子结点无空间,则回退到上级或顶级并根据增大后的starting_id继续查找空闲id
注:递归过程中,需要父结点bitmap中标识子结点有空闲空间,但是子结点的空闲区间可能会出现在id之前,id之后无空闲空间,所以会出现回退上级或顶级的情况
注:一个结点有32或64个区间,分别对应ary的每个元素
如果该结点没有空闲id,则回退到上层,并向后偏移一个区间继续查找空闲ID;如果父区间是该结点的最后一个区间,则回退到根结点重新开始查找。
回退上层与根的两种情况如下:
layer = 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
id = 00 00000 00000 00000 11111 00001 00000时
a.在查找第0层第0(00000)区间时,由于该区间没有空闲id,则回退上级,并向后偏移一个区间即第2(00001+1)区间;由于上层两个区间属于同一节点,则可以继续查找
b.在查找第1层第1(00001)区间时,由于该区间没有空闲id,则回退上级,并向后偏移一个区间即第0(11111+1)区间;由于上层两个区间不属于同一节点,则回到根结点继续查找
3.递归子结点过程中,如果结点不存在,则添加结点
4.递归到叶结点,则循环结束,并返回叶结点的空闲id
注:
156行:id = (id | ((1 << (IDR_BITS * l)) - 1)) + 1;表示回退到上层,并偏移一个区间;
169行:sh = IDR_BITS * (l + 1);用来判断偏移后的区间与原区间是否在同一结点
176行:sh = IDR_BITS*l; id = ((id >> sh) ^ n ^ m) << sh;将id中代表l级的域值由n修改成m,可以看成id=id>>(sh+IDR_BITS)<<(sh+IDR_BITS)+n^n^m<<sh=id>>(sh+IDR_BITS)<<(sh+IDR_BITS)+m<<sh
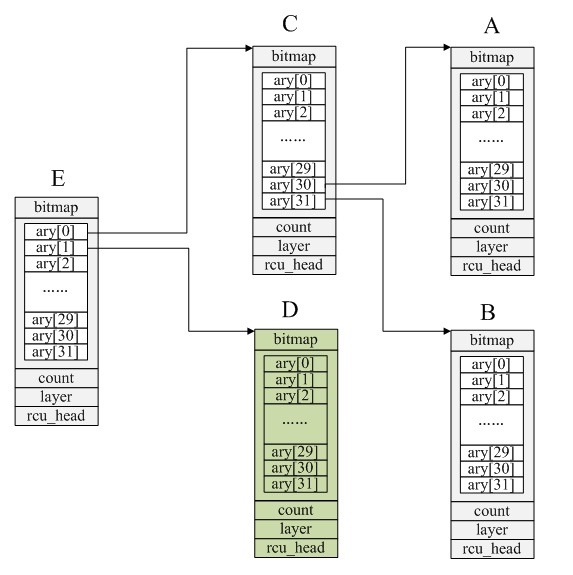
回退到上层或顶层情况如下图:
A结点bitmap=0x0000FFFF,B结点bitmap=0x0000FFFF,D结点bitmap=0x00000000
当从977开始查找空闲id时,会查找到A结点,但A结点没有空闲id,会回退到上层C.ary[30],并编移一个区间C.ary[31],由于C.ary[30]与C.ary[31]在同一结点即E.ary[0]=E.ary[0];继续从C.ary[31]开始查找,会在B结点找到空闲id=992
当从1009开始查找空闲id时,会查找到B结点,但B结点没有空闲id,会回退到上层C.ary[31],并统称一个区间D.ary[0],由于C.ary[31]与D.ary[0]不在同一结点即E.ary[0]!=E.ary[1];则回到顶层结点E,并从id=1024重新再查找空闲ID,则会在D结点找到空闲id=1024
III.idr释放id
i.删除id
idr释放id实现为:
353 static void sub_remove(struct idr *idp, int shift, int id)
354 {
355 struct idr_layer *p = idp->top;
356 struct idr_layer **pa[MAX_LEVEL];
357 struct idr_layer ***paa = &pa[0];
358 struct idr_layer *to_free;
359 int n;
360
361 *paa = NULL;
362 *++paa = &idp->top;
363
364 while ((shift > 0) && p) {
365 n = (id >> shift) & IDR_MASK;
366 __clear_bit(n, &p->bitmap);
367 *++paa = &p->ary[n];
368 p = p->ary[n];
369 shift -= IDR_BITS;
370 }
371 n = id & IDR_MASK;
372 if (likely(p != NULL && test_bit(n, &p->bitmap))){
373 __clear_bit(n, &p->bitmap);
374 rcu_assign_pointer(p->ary[n], NULL);
375 to_free = NULL;
376 while(*paa && ! --((**paa)->count)){
377 if (to_free)
378 free_layer(to_free);
379 to_free = **paa;
380 **paa-- = NULL;
381 }
382 if (!*paa)
383 idp->layers = 0;
384 if (to_free)
385 free_layer(to_free);
386 } else
387 idr_remove_warning(id);
388 }1.将id所表示的基数树路径上结点对应的位图置0
2.如果路径上结点为空结点,同时删除结点
ii.基数树缩小
基数树shrink实现是idr_remove:
390 /**
391 * idr_remove - remove the given id and free it's slot
392 * @idp: idr handle
393 * @id: unique key
394 */
395 void idr_remove(struct idr *idp, int id)
396 {
397 struct idr_layer *p;
398 struct idr_layer *to_free;
399
400 /* Mask off upper bits we don't use for the search. */
401 id &= MAX_ID_MASK;
402
403 sub_remove(idp, (idp->layers - 1) * IDR_BITS, id);
404 if (idp->top && idp->top->count == 1 && (idp->layers > 1) &&
405 idp->top->ary[0]) {
406 /*
407 * Single child at leftmost slot: we can shrink the tree.
408 * This level is not needed anymore since when layers are
409 * inserted, they are inserted at the top of the existing
410 * tree.
411 */
412 to_free = idp->top;
413 p = idp->top->ary[0];
414 rcu_assign_pointer(idp->top, p);
415 --idp->layers;
416 to_free->bitmap = to_free->count = 0;
417 free_layer(to_free);
418 }
419 while (idp->id_free_cnt >= IDR_FREE_MAX) {
420 p = get_from_free_list(idp);
421 /*
422 * Note: we don't call the rcu callback here, since the only
423 * layers that fall into the freelist are those that have been
424 * preallocated.
425 */
426 kmem_cache_free(idr_layer_cache, p);
427 }
428 return;
429 }1.如果根结点只使用了0区间,则删除根结点,将0区间表示的结点作为根结点
2.释放idr缓存中多余的结点
IV.idr查找id对应指针
id的查找即根据id值找到叶子结点中存储的指针值
查找过程由idr_find实现:
490 /**
491 * idr_find - return pointer for given id
492 * @idp: idr handle
493 * @id: lookup key
494 *
495 * Return the pointer given the id it has been registered with. A %NULL
496 * return indicates that @id is not valid or you passed %NULL in
497 * idr_get_new().
498 *
499 * This function can be called under rcu_read_lock(), given that the leaf
500 * pointers lifetimes are correctly managed.
501 */
502 void *idr_find(struct idr *idp, int id)
503 {
504 int n;
505 struct idr_layer *p;
506
507 p = rcu_dereference(idp->top);
508 if (!p)
509 return NULL;
510 n = (p->layer+1) * IDR_BITS;
511
512 /* Mask off upper bits we don't use for the search. */
513 id &= MAX_ID_MASK;
514
515 if (id >= (1 << n))
516 return NULL;
517 BUG_ON(n == 0);
518
519 while (n > 0 && p) {
520 n -= IDR_BITS;
521 BUG_ON(n != p->layer*IDR_BITS);
522 p = rcu_dereference(p->ary[(id >> n) & IDR_MASK]);
523 }
524 return((void *)p);
525 }注:以id中对应的域值作为结点的区间索引,找到对应的子结点,直到叶结点为止;





















 612
612











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








