一、简介 Spring早期是通过实现ApplicationListener接口来定义监听事件,在spring4.2的时候开始我们可以通过@EventListener注解来定义监听事件,ApplicationListener接口定义如下: @FunctionalInterface
public interface ApplicationListener < E extends ApplicationEvent > extends EventListener {
void onApplicationEvent ( E event) ;
}
Spring为我们提供的一个事件监听、订阅的实现,内部实现原理是观察者设计模式(拉模型);为的就是业务系统逻辑的解耦,提高可扩展性以及可维护性。事件发布者并不需要考虑谁去监听,监听具体的实现内容是什么,发布者的工作只是为了发布事件而已。 比如在我们的系统中,我们需要记录某一些比较重要方法的调用日志,我们就可以通过自定义注解+实现自定义监听事件即可。 本篇文章我们通过@EventListener注解来分析Spring的事件注册及监听流程 建立事件对象,当调用publishEvent方法是会通过这个bean对象找对应事件的监听。 package com. asiainfo. gridtask. event;
import com. asiainfo. gridtask. entity. log. SysLog;
import org. springframework. context. ApplicationEvent;
public class SysLogEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
public SysLogEvent ( SysLog sysLog) {
super ( sysLog) ;
}
}
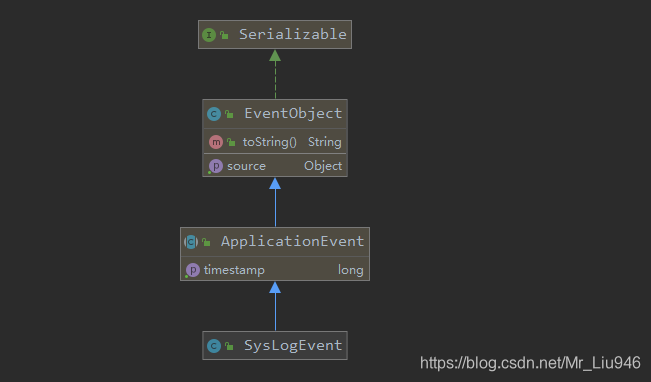
看一看SysLogEvent类的继承图,SysLogEvent继承至ApplicationEvent,ApplicationEvent 继承至EventObject,EventObject对象中定义了一个Object类型的source变量用于存放事件的消息。 新增对应的监听类 package com. asiainfo. gridtask. event;
import com. alibaba. fastjson. JSON;
import com. alibaba. fastjson. JSONObject;
import com. asiainfo. gridtask. common. constant. CommonConstant;
import lombok. extern. slf4j. Slf4j;
import org. springframework. beans. factory. annotation. Autowired;
import org. springframework. context. event. EventListener;
import org. springframework. core. annotation. Order;
import org. springframework. data. redis. core. StringRedisTemplate;
import org. springframework. scheduling. annotation. Async;
import org. springframework. stereotype. Component;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class SysLogListener {
@EventListener ( SysLogEvent. class )
public void saveSysLog ( SysLogEvent event) {
log. info ( "收到调用日志信息:info:{}" , JSON. toJSONString ( event) ) ;
}
}
package com. asiainfo. gridtask. controller;
import com. asiainfo. gridtask. entity. log. SysLog;
import com. asiainfo. gridtask. event. SysLogEvent;
import org. springframework. beans. factory. annotation. Autowired;
import org. springframework. context. ApplicationContext;
import org. springframework. web. bind. annotation. GetMapping;
import org. springframework. web. bind. annotation. RestController;
@RestController
public class TestController {
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@GetMapping ( "testEvent.do" )
public void testEvent ( ) {
SysLog sysLog = new SysLog ( ) ;
sysLog. setLogId ( "123456789" )
. setStaffCode ( "jack" )
. setPhoneNo ( "13378224441" ) ;
applicationContext. publishEvent ( new SysLogEvent ( sysLog) ) ;
}
}
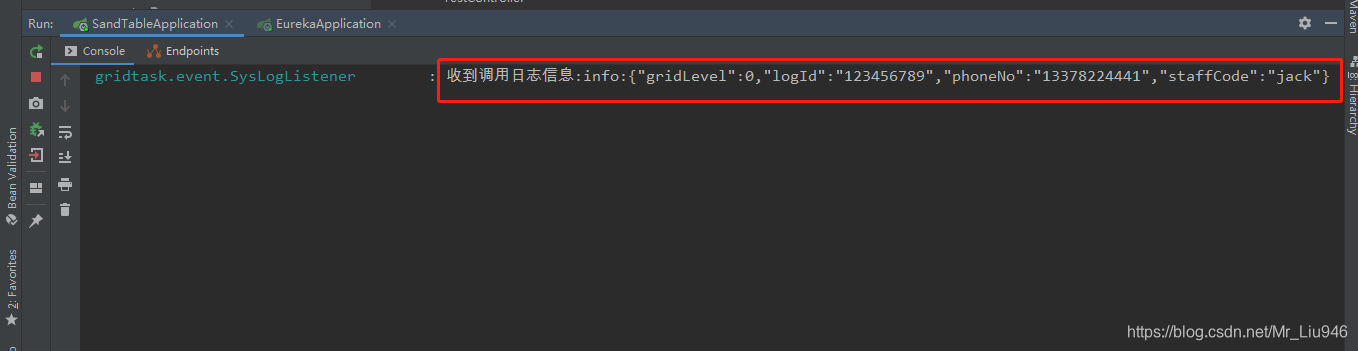
调用Restful接口后结果如下: 在AnnotationConfigUtils #registerAnnotationConfigProcessors注册了EventListenerMethodProcessor 的BeanDefinition信息, 初始化SpringIOC容器的时候会将EventListenerMethodProcessor 注册到容器中。 AnnotationConfigUtils是在AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext构造方法里被加载。AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext,他是spring boot启动入口的重要类(我这里用的是spring boot所以是这个类),可以相当于用xml的ClassPathXmlApplicationContext。 AnnotationConfigUtils类
public static final String EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME =
"org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor" ;
public static Set< BeanDefinitionHolder> registerAnnotationConfigProcessors (
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Object source) {
. . . . . . . . . . . 省略. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
if ( ! registry. containsBeanDefinition ( EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME) ) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition ( EventListenerMethodProcessor. class ) ;
def. setSource ( source) ;
beanDefs. add ( registerPostProcessor ( registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME) ) ;
}
if ( ! registry. containsBeanDefinition ( EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME) ) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition ( DefaultEventListenerFactory. class ) ;
def. setSource ( source) ;
beanDefs. add ( registerPostProcessor ( registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME) ) ;
}
return beanDefs;
}
注册的EventListenerMethodProcessor 对象会在初始化非懒加载对象的时候执行它的afterSingletonsInstantiated 方法。这里通过AbstractApplicationContext类的refresh() 方法中的 finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory) 去做初始化。 AbstractApplicationContext#refresh() public void refresh ( ) throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized ( this . startupShutdownMonitor) {
prepareRefresh ( ) ;
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory ( ) ;
prepareBeanFactory ( beanFactory) ;
try {
postProcessBeanFactory ( beanFactory) ;
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors ( beanFactory) ;
registerBeanPostProcessors ( beanFactory) ;
initMessageSource ( ) ;
initApplicationEventMulticaster ( ) ;
onRefresh ( ) ;
registerListeners ( ) ;
finishBeanFactoryInitialization ( beanFactory) ;
finishRefresh ( ) ;
} catch ( BeansException ex) {
if ( logger. isWarnEnabled ( ) ) {
logger. warn ( "Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex) ;
}
destroyBeans ( ) ;
cancelRefresh ( ex) ;
throw ex;
} finally {
resetCommonCaches ( ) ;
}
}
}
这里我们重点关注refresh()#finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory)#preInstantiateSingletons() 方法 protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization ( ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
if ( beanFactory. containsBean ( CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) &&
beanFactory. isTypeMatch ( CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService. class ) ) {
beanFactory. setConversionService (
beanFactory. getBean ( CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService. class ) ) ;
}
if ( ! beanFactory. hasEmbeddedValueResolver ( ) ) {
beanFactory. addEmbeddedValueResolver ( strVal - > getEnvironment ( ) . resolvePlaceholders ( strVal) ) ;
}
String[ ] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory. getBeanNamesForType ( LoadTimeWeaverAware. class , false , false ) ;
for ( String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) {
getBean ( weaverAwareName) ;
}
beanFactory. setTempClassLoader ( null) ;
beanFactory. freezeConfiguration ( ) ;
beanFactory. preInstantiateSingletons ( ) ;
}
DefaultListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons() @Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons ( ) throws BeansException {
. . . . . . . . . . 省略非必要代码. . . . . . . . . . .
List< String> = new ArrayList < String> ( this . beanDefinitionNames) ;
. . . . . . . . . . 省略非必要代码. . . . . . . . . . .
for ( String beanName : beanNames) {
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton ( beanName) ;
if ( singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton ) {
final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = ( SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if ( System. getSecurityManager ( ) != null) {
AccessController. doPrivileged ( ( PrivilegedAction< Object> ) ( ) - > {
smartSingleton. afterSingletonsInstantiated ( ) ;
return null;
} , getAccessControlContext ( ) ) ;
}
else {
smartSingleton. afterSingletonsInstantiated ( ) ;
}
}
}
}
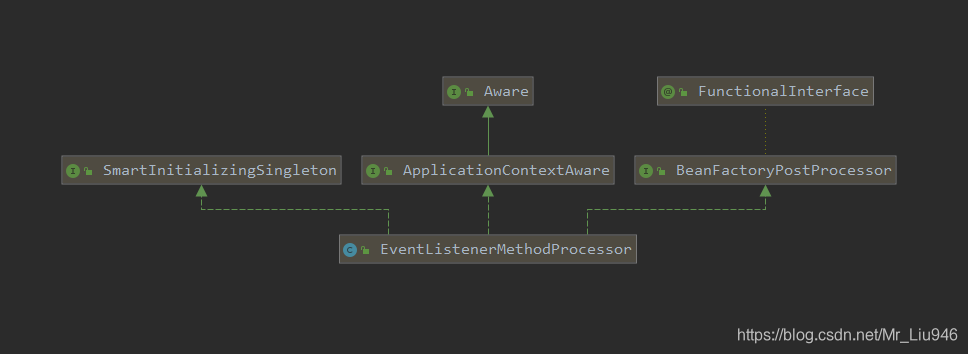
EventListenerMethodProcessor类图如下,这里可以看到其实现了SmartInitializingSingleton接口 EventListenerMethodProcessor#afterSingletonsInstantiated,敲黑板,这里开始注册带有@EventListener注解的方法了 @Override
public void afterSingletonsInstantiated ( ) {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this . beanFactory;
Assert. state ( this . beanFactory != null, "No ConfigurableListableBeanFactory set" ) ;
String[ ] beanNames = beanFactory. getBeanNamesForType ( Object. class ) ;
for ( String beanName : beanNames) {
if ( ! ScopedProxyUtils. isScopedTarget ( beanName) ) {
Class< ? > type = null;
try {
type = AutoProxyUtils. determineTargetClass ( beanFactory, beanName) ;
}
catch ( Throwable ex) {
if ( logger. isDebugEnabled ( ) ) {
logger. debug ( "Could not resolve target class for bean with name '" + beanName + "'" , ex) ;
}
}
if ( type != null) {
if ( ScopedObject. class . isAssignableFrom ( type) ) {
try {
Class< ? > targetClass = AutoProxyUtils. determineTargetClass (
beanFactory, ScopedProxyUtils. getTargetBeanName ( beanName) ) ;
if ( targetClass != null) {
type = targetClass;
}
}
catch ( Throwable ex) {
if ( logger. isDebugEnabled ( ) ) {
logger. debug ( "Could not resolve target bean for scoped proxy '" + beanName + "'" , ex) ;
}
}
}
try {
processBean ( beanName, type) ;
}
catch ( Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException ( "Failed to process @EventListener " +
"annotation on bean with name '" + beanName + "'" , ex) ;
}
}
}
}
}
EventListenerMethodProcessor#processBean ,这里会将带有EventListener注解的方法包装为ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter类,Spring容器在发布事件后会通过多播器触发调用这个类的onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event)方法,这个方法最终会通过反射的方式对应的调用我们加了EventListener注解的方法,最终完成整个事件的发布调用流程。private void processBean ( final String beanName, final Class< ? > targetType) {
if ( ! this . nonAnnotatedClasses. contains ( targetType) && ! isSpringContainerClass ( targetType) ) {
Map< Method, EventListener> = null;
try {
annotatedMethods = MethodIntrospector. selectMethods ( targetType,
( MethodIntrospector. MetadataLookup< EventListener> ) method - >
AnnotatedElementUtils. findMergedAnnotation ( method, EventListener. class ) ) ;
}
catch ( Throwable ex) {
if ( logger. isDebugEnabled ( ) ) {
logger. debug ( "Could not resolve methods for bean with name '" + beanName + "'" , ex) ;
}
}
if ( CollectionUtils. isEmpty ( annotatedMethods) ) {
this . nonAnnotatedClasses. add ( targetType) ;
if ( logger. isTraceEnabled ( ) ) {
logger. trace ( "No @EventListener annotations found on bean class: " + targetType. getName ( ) ) ;
}
}
else {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = this . applicationContext;
Assert. state ( context != null, "No ApplicationContext set" ) ;
List< EventListenerFactory> = this . eventListenerFactories;
Assert. state ( factories != null, "EventListenerFactory List not initialized" ) ;
for ( Method method : annotatedMethods. keySet ( ) ) {
for ( EventListenerFactory factory : factories) {
if ( factory. supportsMethod ( method) ) {
Method methodToUse = AopUtils. selectInvocableMethod ( method, context. getType ( beanName) ) ;
ApplicationListener< ? > applicationListener = factory. createApplicationListener ( beanName, targetType, methodToUse) ;
if ( applicationListener instanceof ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter ) {
( ( ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter) applicationListener) . init ( context, this . evaluator) ;
}
context. addApplicationListener ( applicationListener) ;
break ;
}
}
}
if ( logger. isDebugEnabled ( ) ) {
logger. debug ( annotatedMethods. size ( ) + " @EventListener methods processed on bean '" +
beanName + "': " + annotatedMethods) ;
}
}
}
}
public ApplicationListener< ? > createApplicationListener ( String beanName, Class< ? > type, Method method) {
return new ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter ( beanName, type, method) ;
}
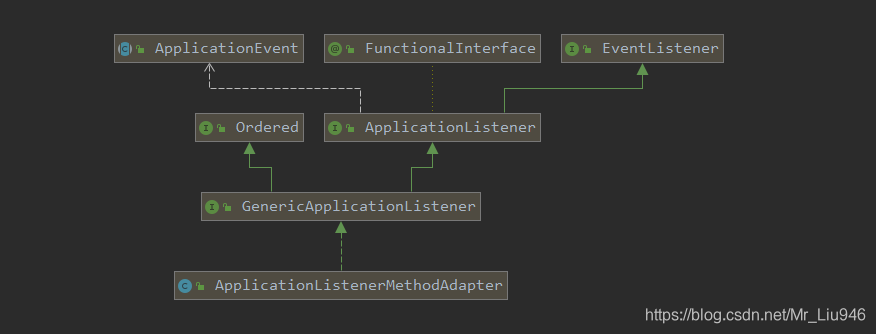
ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter类的UML图 ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter类的属性及部分关键方法。 public class ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter implements GenericApplicationListener {
protected final Log logger = LogFactory. getLog ( getClass ( ) ) ;
private final String beanName;
private final Method method;
private final Method targetMethod;
private final AnnotatedElementKey methodKey;
private final List< ResolvableType> ;
@Nullable
private final String condition;
private final int order;
@Nullable
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Nullable
private EventExpressionEvaluator evaluator;
. . . . . . . . . 省略不相关方法. . . . . . . . . . .
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent ( ApplicationEvent event) {
processEvent ( event) ;
}
public void processEvent ( ApplicationEvent event) {
Object[ ] args = resolveArguments ( event) ;
if ( shouldHandle ( event, args) ) {
Object result = doInvoke ( args) ;
if ( result != null) {
handleResult ( result) ;
}
else {
logger. trace ( "No result object given - no result to handle" ) ;
}
}
}
@Nullable
protected Object doInvoke ( Object. . . args) {
Object bean = getTargetBean ( ) ;
ReflectionUtils. makeAccessible ( this . method) ;
try {
return this . method. invoke ( bean, args) ;
}
catch ( IllegalArgumentException ex) {
assertTargetBean ( this . method, bean, args) ;
throw new IllegalStateException ( getInvocationErrorMessage ( bean, ex. getMessage ( ) , args) , ex) ;
}
catch ( IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException ( getInvocationErrorMessage ( bean, ex. getMessage ( ) , args) , ex) ;
}
catch ( InvocationTargetException ex) {
Throwable targetException = ex. getTargetException ( ) ;
if ( targetException instanceof RuntimeException ) {
throw ( RuntimeException) targetException;
}
else {
String msg = getInvocationErrorMessage ( bean, "Failed to invoke event listener method" , args) ;
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException ( targetException, msg) ;
}
}
}
protected Object getTargetBean ( ) {
Assert. notNull ( this . applicationContext, "ApplicationContext must no be null" ) ;
return this . applicationContext. getBean ( this . beanName) ;
}
}
最后面就是触发事件监听了AbstractApplicationContext#publishEvent public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader
implements ConfigurableApplicationContext {
. . . . . . . . . 省略非必要代码. . . . . . . .
@Override
public void publishEvent ( ApplicationEvent event) {
publishEvent ( event, null) ;
}
protected void publishEvent ( Object event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
Assert. notNull ( event, "Event must not be null" ) ;
ApplicationEvent applicationEvent;
if ( event instanceof ApplicationEvent ) {
applicationEvent = ( ApplicationEvent) event;
}
else {
applicationEvent = new PayloadApplicationEvent < > ( this , event) ;
if ( eventType == null) {
eventType = ( ( PayloadApplicationEvent) applicationEvent) . getResolvableType ( ) ;
}
}
if ( this . earlyApplicationEvents != null) {
this . earlyApplicationEvents. add ( applicationEvent) ;
} else {
getApplicationEventMulticaster ( ) . multicastEvent ( applicationEvent, eventType) ;
}
if ( this . parent != null) {
if ( this . parent instanceof AbstractApplicationContext ) {
( ( AbstractApplicationContext) this . parent) . publishEvent ( event, eventType) ;
}
else {
this . parent. publishEvent ( event) ;
}
}
}
}
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster#multicastEvent->invokeListener->doInvokeListener @Override
public void multicastEvent ( final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = ( eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType ( event) ) ;
for ( final ApplicationListener< ? > listener : getApplicationListeners ( event, type) ) {
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor ( ) ;
if ( executor != null) {
executor. execute ( ( ) - > invokeListener ( listener, event) ) ;
}
else {
invokeListener ( listener, event) ;
}
}
}
protected void invokeListener ( ApplicationListener< ? > listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
ErrorHandler errorHandler = getErrorHandler ( ) ;
if ( errorHandler != null) {
try {
doInvokeListener ( listener, event) ;
}
catch ( Throwable err) {
errorHandler. handleError ( err) ;
}
}
else {
doInvokeListener ( listener, event) ;
}
}
@SuppressWarnings ( { "unchecked" , "rawtypes" } )
private void doInvokeListener ( ApplicationListener listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
try {
listener. onApplicationEvent ( event) ;
}
catch ( ClassCastException ex) {
String msg = ex. getMessage ( ) ;
if ( msg == null || matchesClassCastMessage ( msg, event. getClass ( ) ) ) {
Log logger = LogFactory. getLog ( getClass ( ) ) ;
if ( logger. isDebugEnabled ( ) ) {
logger. debug ( "Non-matching event type for listener: " + listener, ex) ;
}
}
else {
throw ex;
}
}
}
到这里整个事件监听的方法都已执行完毕,本篇内容为博主的第一篇博客,限于博主知识水平有限,如有错误欢迎大家及时指正,谢谢大家。





 本文深入解析Spring框架中事件监听机制的实现,从@EventListener注解的使用,到事件注册及监听流程的源码分析,全面阐述Spring如何通过观察者模式进行事件的发布与订阅。
本文深入解析Spring框架中事件监听机制的实现,从@EventListener注解的使用,到事件注册及监听流程的源码分析,全面阐述Spring如何通过观察者模式进行事件的发布与订阅。
















 1万+
1万+










