GAN定义的生成器和判别器网络结构:

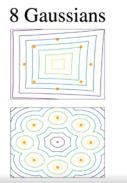
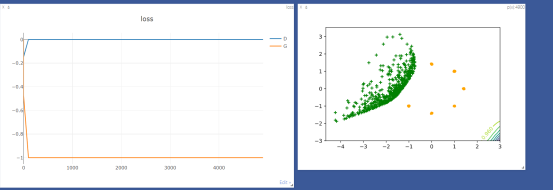
GAN训练:首先训练D,每迭代训练5次D再迭代训练一次G,总训练5000次,批次为512。数据集为8个高斯混合模型,使得GAN去拟合一个圆上的8个分布点。
根据GAN的loss函数,使得D尽可能的大,G尽可能的小,所以D取负数。
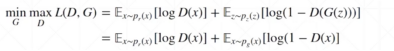
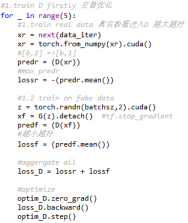
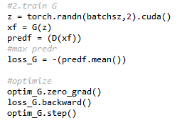
过程中用到了visdom可视化工具。
import visdom
viz = visdom.Visdom()
viz.line([[loss_D.item(),loss_G.item()]],[epoch],win = 'loss',update = 'append')
需要在终端中打开visdom,激活visdom所在的环境(python -m visdom.server),然后再执行visdom。打开浏览器,输入localhost:8097即可。
优化器:

代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Tue Jan 14 16:37:46 2020
@author: ZM
"""
import torch
#自动求导函数
from torch import nn,optim,autograd
import numpy as np
#visdom可视化数据
import visdom
import random
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
h_dim = 400
batchsz = 512
viz = visdom.Visdom()
#Generator结构
class Generator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Generator,self).__init__()
self.net = nn.Sequential(
# 输入z:[b,2] => 2 ; 4层
nn.Linear(2, h_dim),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Linear(h_dim,h_dim),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Linear(h_dim,h_dim),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Linear(h_dim,2),
)
def forward(self,z):
output = self.net(z)
return output
class Discriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Discriminator,self).__init__()
# 输入z:[b,2] => 2 2维的x分布
self.net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(2, h_dim),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Linear(h_dim,h_dim),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Linear(h_dim,h_dim),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Linear(h_dim,1),
nn.Sigmoid() # [0,1]分布内
)
def forward(self,x):
output = self.net(x)
return output.view(-1)
def data_generator():
# 数据分布已知 8个高斯混合模型 生成数据集
scale = 2.
centers = [
(1,0),
(-1,0),
(0,1),
(0,-1),
(1./np.sqrt(2), 1./np.sqrt(2)),
(1./np.sqrt(2),-1./np.sqrt(2)),
(-1./np.sqrt(2),1./np.sqrt(2)),
(-1./np.sqrt(2),-1./np.sqrt(2))]
centers = [(scale * x,scale * y) for x,y in centers]
while True:
dataset = []
for i in range(batchsz):
#从center 8个高斯均值点中选择一个
point = np.random.randn(2) * 0.02
center = random.choice(centers)
#N(0.1) + center_x1/x2
point[0] += center[0]
point[1] += center[1]
dataset.append(point)
dataset = np.array(dataset).astype(np.float32)
dataset /=1.414
#yield 数据返回并保存状态
yield dataset
def generate_image(D, G, xr, epoch):
"""
Generates and saves a plot of the true distribution, the generator, and the
critic.
"""
N_POINTS = 128
RANGE = 3
plt.clf()
points = np.zeros((N_POINTS, N_POINTS, 2), dtype='float32')
points[:, :, 0] = np.linspace(-RANGE, RANGE, N_POINTS)[:, None]
points[:, :, 1] = np.linspace(-RANGE, RANGE, N_POINTS)[None, :]
points = points.reshape((-1, 2))
# (16384, 2)
# print('p:', points.shape)
# draw contour
with torch.no_grad():
points = torch.Tensor(points).cuda() # [16384, 2]
disc_map = D(points).cpu().numpy() # [16384]
x = y = np.linspace(-RANGE, RANGE, N_POINTS)
cs = plt.contour(x, y, disc_map.reshape((len(x), len(y))).transpose())
plt.clabel(cs, inline=1, fontsize=10)
# plt.colorbar()
# draw samples
with torch.no_grad():
z = torch.randn(batchsz, 2).cuda() # [b, 2]
samples = G(z).cpu().numpy() # [b, 2]
plt.scatter(xr[:, 0], xr[:, 1], c='orange', marker='.')
plt.scatter(samples[:, 0], samples[:, 1], c='green', marker='+')
viz.matplot(plt, win='contour', opts=dict(title='p(x):%d'%epoch))
def main():
#设置种子,seed固定住
torch.manual_seed(23)
np.random.seed(23)
data_iter = data_generator()
x = next(data_iter)
# x = next(data_iter)
# print(x.shape)
G = Generator().cuda()
D = Discriminator().cuda()
# print(G)
# print(D)
optim_G = optim.Adam(G.parameters(), lr=5e-4,betas=(0.5,0.9))
optim_D = optim.Adam(D.parameters(), lr=5e-4,betas=(0.5,0.9))
viz.line([[0,0]],[0],win = 'loss',opts = dict(title = 'loss',legend=['D','G']))
for epoch in range(5000):
#1.train D firstly 交替优化
for _ in range(5):
#1.train real data 真实数据送入D 越大越好
xr = next(data_iter)
xr = torch.from_numpy(xr).cuda()
#[b,2] =>[b,1]
predr = (D(xr))
#max predr
lossr = -(predr.mean())
#1.2 train on fake data
z = torch.randn(batchsz,2).cuda()
xf = G(z).detach() #tf.stop_gradient
predf = (D(xf))
#越小越好
lossf = (predf.mean())
#aggergate all
loss_D = lossr + lossf
#optimize
optim_D.zero_grad()
loss_D.backward()
optim_D.step()
#2.train G
z = torch.randn(batchsz,2).cuda()
xf = G(z)
predf = (D(xf))
#max predr
loss_G = -(predf.mean())
#optimize
optim_G.zero_grad()
loss_G.backward()
optim_G.step()
if epoch % 100 == 0:
viz.line([[loss_D.item(),loss_G.item()]],[epoch],win = 'loss',update = 'append')
print(loss_D.item(), loss_G.item())
generate_image(D,G,xr.cpu(),epoch)
if __name__=='__main__':
main()5000的GAN训练的效果:训练并不稳定,没有趋近于想要的点。























 1254
1254











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








