
RT-DETR使用教程: RT-DETR使用教程
RT-DETR改进汇总贴:RT-DETR更新汇总贴
《LWGANet: A Lightweight Group Attention Backbone for Remote Sensing Visual Tasks》
一、 模块介绍
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.10040
代码链接:https://github.com/lwCVer/LWGANet
论文速览:
遥感 (RS) 视觉任务具有重要的学术和实践意义。然而,他们遇到了许多阻碍有效特征提取的挑战,包括检测和识别单个图像中比例差异很大的多个物体。虽然以前的双分支或多分支架构策略在管理这些对象差异方面是有效的,但它们同时导致了计算需求和参数数量的显着增加。因此,这些架构在资源受限的设备上部署的可行性降低。主要为自然图像设计的现代轻量级骨干网络在从多尺度物体中有效提取特征时经常遇到困难,这损害了它们在 RS 视觉任务中的功效。本文介绍了 LWGANet,这是一个专为 RS 视觉任务量身定制的专用轻量级骨干网络,它结合了一种新型的轻量级群体注意力 (LWGA) 模块,旨在应对这些特定挑战。LWGA 模块专为 RS 图像量身定制,可熟练地利用冗余特征来提取从局部尺度到全球尺度的各种空间信息,而不会引入额外的复杂性或计算开销。这有助于在高效的 http URL 中跨多个尺度进行精确特征提取,该 http URL 在 12 个数据集中进行了严格评估,这些数据集涵盖四个关键的 RS 视觉任务:场景分类、定向对象检测、语义分割和变化检测。
总结:本文更新其中LWGA模块的代码及使用方法
⭐⭐本文二创模块仅更新于付费群中,往期免费教程可看下方链接⭐⭐
二、二创融合模块
2.1 相关代码
# https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.10040
# https://blog.csdn.net/StopAndGoyyy?spm=1011.2124.3001.5343
class PA(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, norm_layer, act_layer):
super().__init__()
self.p_conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(dim, dim * 4, 1, bias=False),
norm_layer(dim * 4),
act_layer(),
nn.Conv2d(dim * 4, dim, 1, bias=False)
)
self.gate_fn = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
att = self.p_conv(x)
x = x * self.gate_fn(att)
return x
class LA(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, norm_layer, act_layer):
super().__init__()
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 3, 1, 1, bias=False),
norm_layer(dim),
act_layer()
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
return x
class MRA(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel, att_kernel, norm_layer):
super().__init__()
att_padding = att_kernel // 2
self.gate_fn = nn.Sigmoid()
self.channel = channel
self.max_m1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
self.max_m2 = antialiased_cnns.BlurPool(channel, stride=3)
self.H_att1 = nn.Conv2d(channel, channel, (att_kernel, 3), 1, (att_padding, 1), groups=channel, bias=False)
self.V_att1 = nn.Conv2d(channel, channel, (3, att_kernel), 1, (1, att_padding), groups=channel, bias=False)
self.H_att2 = nn.Conv2d(channel, channel, (att_kernel, 3), 1, (att_padding, 1), groups=channel, bias=False)
self.V_att2 = nn.Conv2d(channel, channel, (3, att_kernel), 1, (1, att_padding), groups=channel, bias=False)
self.norm = norm_layer(channel)
def forward(self, x):
x_tem = self.max_m1(x)
x_tem = self.max_m2(x_tem)
x_h1 = self.H_att1(x_tem)
x_w1 = self.V_att1(x_tem)
x_h2 = self.inv_h_transform(self.H_att2(self.h_transform(x_tem)))
x_w2 = self.inv_v_transform(self.V_att2(self.v_transform(x_tem)))
att = self.norm(x_h1 + x_w1 + x_h2 + x_w2)
out = x[:, :self.channel, :, :] * F.interpolate(self.gate_fn(att),
size=(x.shape[-2], x.shape[-1]),
mode='nearest')
return out
def h_transform(self, x):
shape = x.size()
x = torch.nn.functional.pad(x, (0, shape[-1]))
x = x.reshape(shape[0], shape[1], -1)[..., :-shape[-1]]
x = x.reshape(shape[0], shape[1], shape[2], 2 * shape[3] - 1)
return x
def inv_h_transform(self, x):
shape = x.size()
x = x.reshape(shape[0], shape[1], -1).contiguous()
x = torch.nn.functional.pad(x, (0, shape[-2]))
x = x.reshape(shape[0], shape[1], shape[-2], 2 * shape[-2])
x = x[..., 0: shape[-2]]
return x
def v_transform(self, x):
x = x.permute(0, 1, 3, 2)
shape = x.size()
x = torch.nn.functional.pad(x, (0, shape[-1]))
x = x.reshape(shape[0], shape[1], -1)[..., :-shape[-1]]
x = x.reshape(shape[0], shape[1], shape[2], 2 * shape[3] - 1)
return x.permute(0, 1, 3, 2)
def inv_v_transform(self, x):
x = x.permute(0, 1, 3, 2)
shape = x.size()
x = x.reshape(shape[0], shape[1], -1)
x = torch.nn.functional.pad(x, (0, shape[-2]))
x = x.reshape(shape[0], shape[1], shape[-2], 2 * shape[-2])
x = x[..., 0: shape[-2]]
return x.permute(0, 1, 3, 2)
class GA12(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, act_layer):
super().__init__()
self.downpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, return_indices=True)
self.uppool = nn.MaxUnpool2d((2, 2), 2, padding=0)
self.proj_1 = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 1)
self.activation = act_layer()
self.conv0 = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 5, padding=2, groups=dim)
self.conv_spatial = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 7, stride=1, padding=9, groups=dim, dilation=3)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim // 2, 1)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim // 2, 1)
self.conv_squeeze = nn.Conv2d(2, 2, 7, padding=3)
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(dim // 2, dim, 1)
self.proj_2 = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 1)
def forward(self, x):
x_, idx = self.downpool(x)
x_ = self.proj_1(x_)
x_ = self.activation(x_)
attn1 = self.conv0(x_)
attn2 = self.conv_spatial(attn1)
attn1 = self.conv1(attn1)
attn2 = self.conv2(attn2)
attn = torch.cat([attn1, attn2], dim=1)
avg_attn = torch.mean(attn, dim=1, keepdim=True)
max_attn, _ = torch.max(attn, dim=1, keepdim=True)
agg = torch.cat([avg_attn, max_attn], dim=1)
sig = self.conv_squeeze(agg).sigmoid()
attn = attn1 * sig[:, 0, :, :].unsqueeze(1) + attn2 * sig[:, 1, :, :].unsqueeze(1)
attn = self.conv(attn)
x_ = x_ * attn
x_ = self.proj_2(x_)
x = self.uppool(x_, indices=idx)
return x
class D_GA(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, norm_layer):
super().__init__()
self.norm = norm_layer(dim)
self.attn = GA(dim)
self.downpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, return_indices=True)
self.uppool = nn.MaxUnpool2d((2, 2), 2, padding=0)
def forward(self, x):
x_, idx = self.downpool(x)
x = self.norm(self.attn(x_))
x = self.uppool(x, indices=idx)
return x
class GA(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, head_dim=4, num_heads=None, qkv_bias=False,
attn_drop=0., proj_drop=0., proj_bias=False, **kwargs):
super().__init__()
self.head_dim = head_dim
self.scale = head_dim ** -0.5
self.num_heads = num_heads if num_heads else dim // head_dim
if self.num_heads == 0:
self.num_heads = 1
self.attention_dim = self.num_heads * self.head_dim
self.qkv = nn.Linear(dim, self.attention_dim * 3, bias=qkv_bias)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)
self.proj = nn.Linear(self.attention_dim, dim, bias=proj_bias)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)
def forward(self, x):
B, C, H, W = x.shape
x = x.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
N = H * W
qkv = self.qkv(x).reshape(B, N, 3, self.num_heads, self.head_dim).permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4)
q, k, v = qkv.unbind(0) # make torchscript happy (cannot use tensor as tuple)
attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1)) * self.scale
attn = attn.softmax(dim=-1)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
x = (attn @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B, H, W, self.attention_dim)
x = self.proj(x)
x = self.proj_drop(x)
x = x.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
return x
class LWGA_Block(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
dim,
stage=2,
att_kernel=3,
mlp_ratio=4.0,
drop_path=0.1,
act_layer=nn.GELU,
norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d
):
super().__init__()
self.stage = stage
self.dim_split = dim // 4
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity()
mlp_hidden_dim = int(dim * mlp_ratio)
mlp_layer: List[nn.Module] = [
nn.Conv2d(dim, mlp_hidden_dim, 1, bias=False),
norm_layer(mlp_hidden_dim),
act_layer(),
nn.Conv2d(mlp_hidden_dim, dim, 1, bias=False)
]
self.mlp = nn.Sequential(*mlp_layer)
self.PA = PA(self.dim_split, norm_layer, act_layer) # PA is point attention
self.LA = LA(self.dim_split, norm_layer, act_layer) # LA is local attention
self.MRA = MRA(self.dim_split, att_kernel, norm_layer) # MRA is medium-range attention
if stage == 2:
self.GA3 = D_GA(self.dim_split, norm_layer) # GA3 is global attention (stage of 3)
elif stage == 3:
self.GA4 = GA(self.dim_split) # GA4 is global attention (stage of 4)
self.norm = norm_layer(self.dim_split)
else:
self.GA12 = GA12(self.dim_split, act_layer) # GA12 is global attention (stages of 1 and 2)
self.norm = norm_layer(self.dim_split)
self.norm1 = norm_layer(dim)
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path)
def forward(self, x):
# for training/inference
shortcut = x.clone()
x1, x2, x3, x4 = torch.split(x, [self.dim_split, self.dim_split, self.dim_split, self.dim_split], dim=1)
x1 = x1 + self.PA(x1)
x2 = self.LA(x2)
x3 = self.MRA(x3)
if self.stage == 2:
x4 = x4 + self.GA3(x4)
elif self.stage == 3:
x4 = self.norm(x4 + self.GA4(x4))
else:
x4 = self.norm(x4 + self.GA12(x4))
x_att = torch.cat((x1, x2, x3, x4), 1)
x = shortcut + self.norm1(self.drop_path(self.mlp(x_att)))
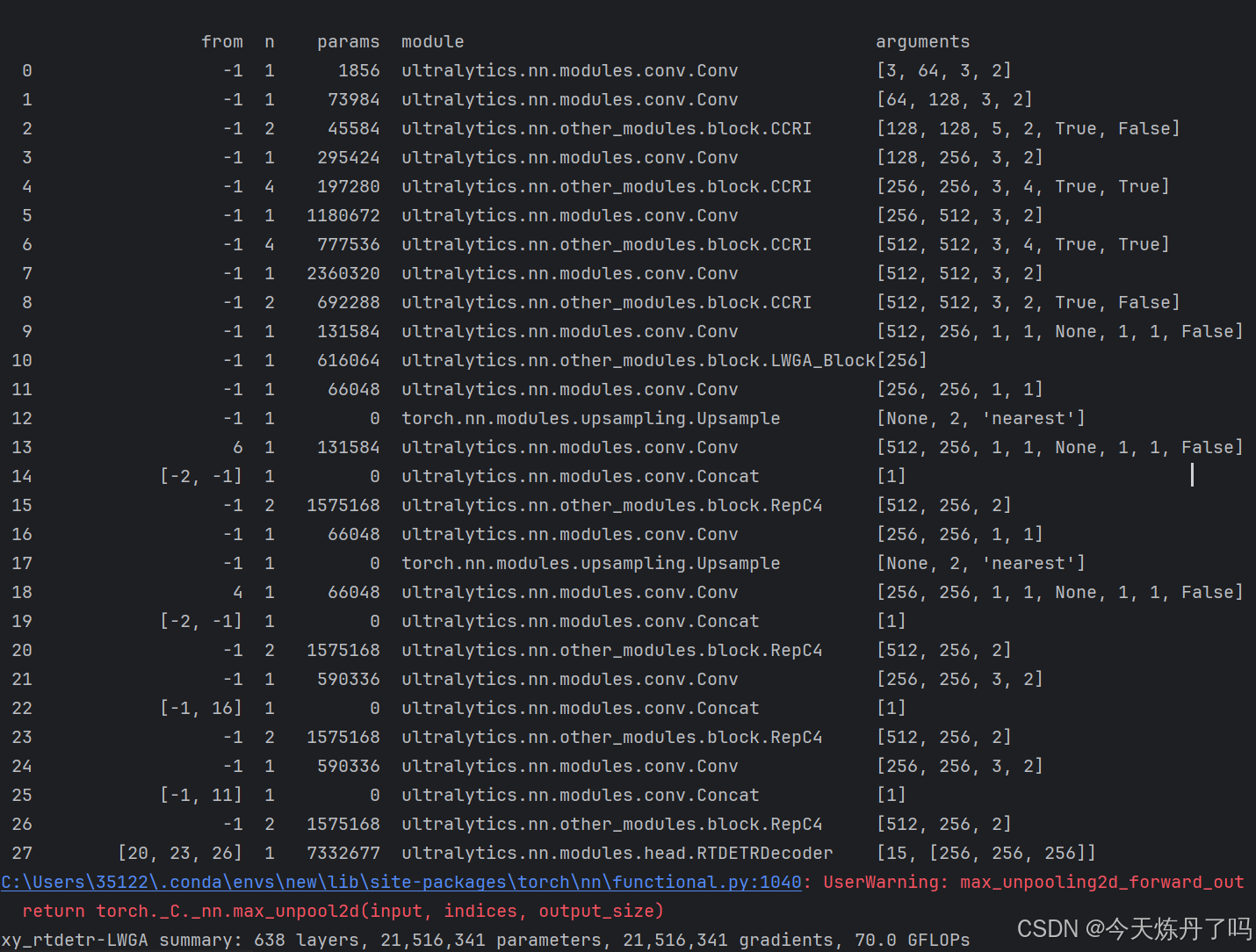
return x2.2 更改yaml文件 (以自研模型加入为例)
打开更改ultralytics/cfg/models/rt-detr路径下的rtdetr-l.yaml文件,替换原有模块。

# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# RT-DETR-l object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For details see https://docs.ultralytics.com/models/rtdetr
# ⭐⭐Powered by https://blog.csdn.net/StopAndGoyyy, 技术指导QQ:2668825911⭐⭐
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n-cls.yaml' will call yolov8-cls.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512]
# n: [ 0.33, 0.25, 1024 ]
# s: [ 0.33, 0.50, 1024 ]
# m: [ 0.67, 0.75, 768 ]
# l: [ 1.00, 1.00, 512 ]
# x: [ 1.00, 1.25, 512 ]
# ⭐⭐Powered by https://blog.csdn.net/StopAndGoyyy, 技术指导QQ:2668825911⭐⭐
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 2, CCRI, [128, 5, True, False]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 4, CCRI, [256, 3, True, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 4, CCRI, [512, 3, True, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 2, CCRI, [1024, 3, True, False]]
head:
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1, None, 1, 1, False]] # 9 input_proj.2
- [-1, 1, LWGA_Block, []]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]] # 11, Y5, lateral_convs.0
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]
- [6, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1, None, 1, 1, False]] # 13 input_proj.1
- [[-2, -1], 1, Concat, [1]]
- [-1, 2, RepC4, [256]] # 15, fpn_blocks.0
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]] # 16, Y4, lateral_convs.1
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]
- [4, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1, None, 1, 1, False]] # 18 input_proj.0
- [[-2, -1], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 2, RepC4, [256]] # X3 (20), fpn_blocks.1
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 22, downsample_convs.0
- [[-1, 16], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat Y4
- [-1, 2, RepC4, [256]] # F4 (23), pan_blocks.0
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 24, downsample_convs.1
- [[-1, 11], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat Y5
- [-1, 2, RepC4, [256]] # F5 (26), pan_blocks.1
- [[20, 23, 26], 1, RTDETRDecoder, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
# ⭐⭐Powered by https://blog.csdn.net/StopAndGoyyy, 技术指导QQ:2668825911⭐⭐
2.2 修改train.py文件
创建Train_RT脚本用于训练。
from ultralytics.models import RTDETR
import os
os.environ['KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK'] = 'True'
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = RTDETR(model='ultralytics/cfg/models/rt-detr/rtdetr-l.yaml')
# model.load('yolov8n.pt')
model.train(data='./data.yaml', epochs=2, batch=1, device='0', imgsz=640, workers=2, cache=False,
amp=True, mosaic=False, project='runs/train', name='exp')

在train.py脚本中填入修改好的yaml路径,运行即可训。






















 6970
6970

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








