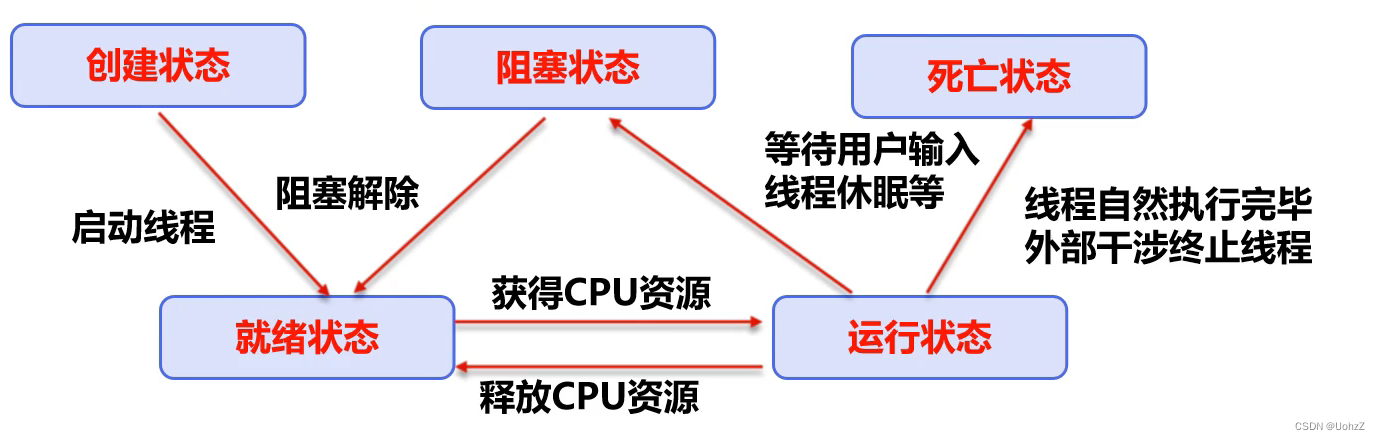
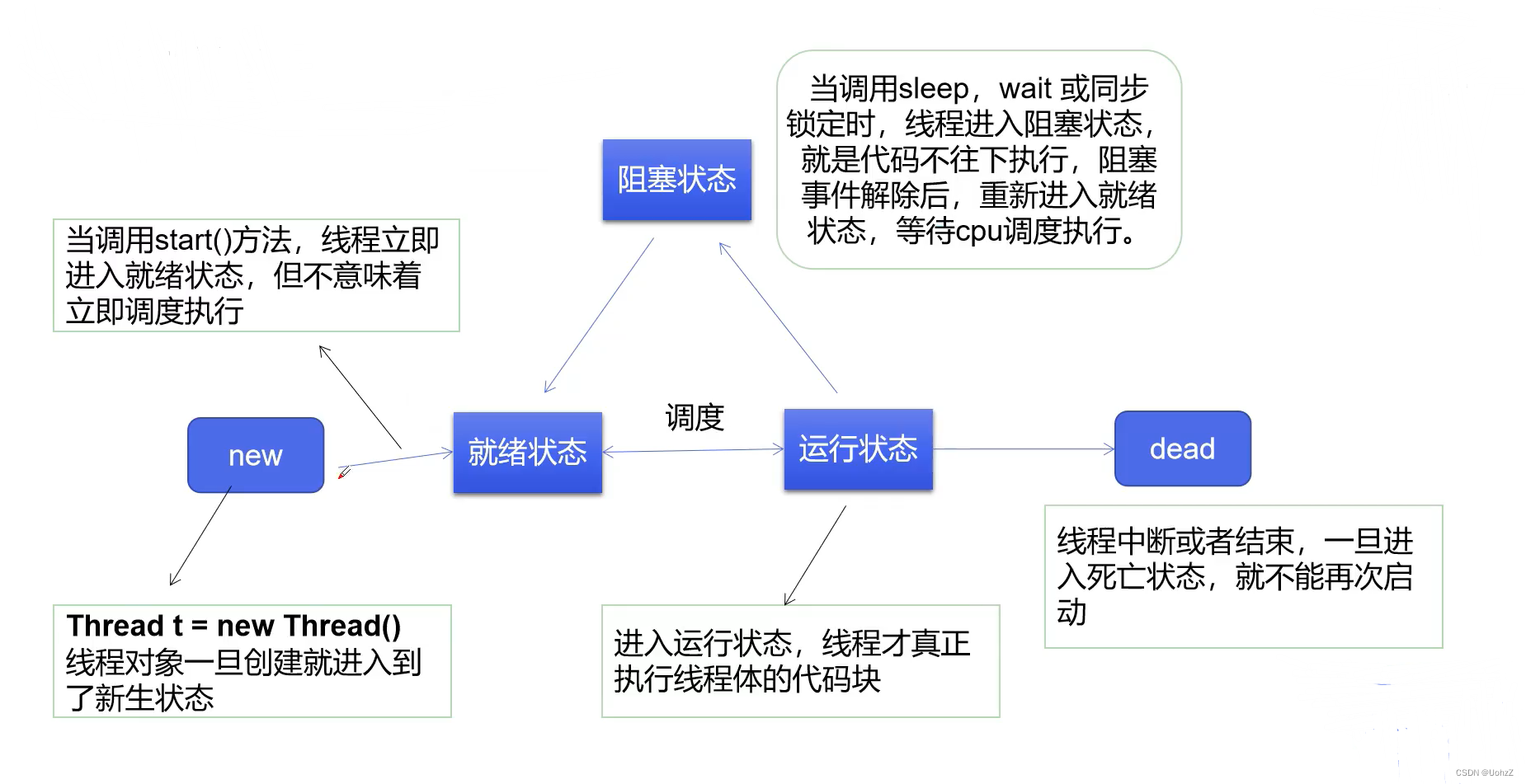
线程状态
线程方法

线程停止
不建议使用JDK提供的stop(),destroy()方法
推荐线程自己停下来
建议使用一个标志位进行终止变量,当flag=false时,线程终止运行
package thread.state;
//测试stop
//1.建议线程正常停止 利用次数,不建议使用死循环
// 2.建议使用标志位 设置一个标志位
// 3.不要使用stop和destroy等过时或JDK不建议使用的方法
public class TestStop implements Runnable{
private boolean flag = true;//1.设置标志位
@Override
public void run() {//重写run方法
int i = 0;
while (flag){
System.out.println("run......Thread"+i++);
}
}
//2.设置一个公开的方法停止线程,转换标志位
public void stop(){//自己写一个stop方法
this.flag = false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestStop testStop = new TestStop();//创建runnable接口的实现类对象
new Thread(testStop).start();//调用start()方法开启线程
for (int i = 0; i < 200; i++) {
System.out.println("main...."+i);
if (i==155){
testStop.stop();//调用stop方法切换标志位,让线程停止
System.out.println("线程该停止了");
}
}
}
}
线程休眠(sleep)
- sleep(时间)指定当前线程阻塞的毫秒数
- sleep存在异常InterruptedException,使用时需要抛出
- sleep时间达到后,线程进入就绪状态
- sleep可以模拟网络延时、倒计时等。
- 每一个对象都有一个锁,sleep不会释放锁
1.模拟延时
package thread.state;
//模拟网络延时
public class TestSleep01 implements Runnable {
private int ticketNums = 20;
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
if (ticketNums<= 0){
break;
}
//模拟延时
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"拿到了第"+ticketNums--+"张票");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestSleep01 testSleep01 = new TestSleep01();
new Thread(testSleep01,"小明").start();
new Thread(testSleep01,"小红").start();
new Thread(testSleep01,"小张").start();
}
}
2.模拟倒计时
package thread.state;
//模拟倒计时
public class TestSleep02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
tenDown();
}
//模拟倒计时
public static void tenDown(){
int nums = 10;
while (true){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(nums--);
if (nums == 0 ){
break;
}
}
}
}
3.打印系统当前时间
package thread.state;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.logging.SimpleFormatter;
//打印当前系统时间
public class TestSleep03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date starTime = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());//获取系统当前时间
while (true){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(starTime));//打印系统当前时间
starTime = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());//更新系统当前时间
}
}
}
线程礼让(yield)
礼让线程,让当前正在执行的线程暂停,但不阻塞
将线程从运行状态转为就绪状态
让CPU重新调度,礼让不一定成功,看CPU心情
package thread.state;
//测试礼让线程
//礼让不一定成功
public class TestYield implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程开始执行");
Thread.yield();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程结束执行");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestYield testYield = new TestYield();
new Thread(testYield,"a").start();
new Thread(testYield,"b").start();
}
}
线程强制执行(join)
join合并线程,待次线程执行完成后,再执行其他线程,其他线程阻塞
可以理解为插队
package thread.state;
//join强制执行 插队
public class TestJoin implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("vip来了"+i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//启动线程
TestJoin testJoin = new TestJoin();
Thread thread = new Thread(testJoin);//此时需要创建对象,不能两行代码简写为一行
thread.start();
//主线程
for (int i = 0; i < 500; ++i) {
if (i == 50){
try {
thread.join();//插队
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("main"+i);
}
}
}
观测线程状态
代码实现:
package thread.state;
//观察测试线程的状态
public class TestState {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
System.out.println("00000000");
});
//1.观察状态
Thread.State state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);//New
//2.观察启动后
thread.start();//启动线程
state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);//Run
while (state != Thread.State.TERMINATED){//只要线程不终止,就一直输出状态
Thread.sleep(100);
state = thread.getState();//更新线程状态
System.out.println(state);//输出状态
}
}
}






















 2868
2868











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








