学习一下linux kernel namespace的代码还是很有必要的,让你对docker容器的namespace隔离有更深的认识。我的源码分析,是基于Linux Kernel 4.4.19 (https://www.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v4.x/patch-4.4.19.gz)版本的,由于namespace模块更新很少,因此其他相近版本之间雷同。User namespace由于与其他namespaces耦合在一起,比较难分析,我将在后续再作分析。
Kernel,Namespace,Process
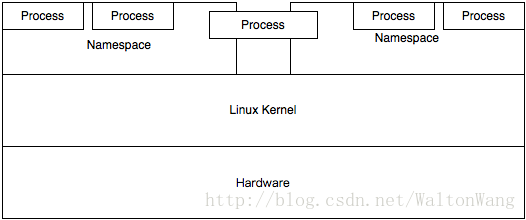
Linux Namespace是一种Linux Kernel提供的资源隔离方案,提供Pid,Network,Ipc,Uts,Mount等资源的隔离,每个Namespace下的这些资源对于其他Namespace是不可见的。
注意,一个进程可以同时属于多个Namespace。Linux Kernel、Namespace、Process之间的关系可以用下图描述。
Begin with “task_struct”
As u know, Linux Namespace是用来做进程资源隔离的,那么在进程描述符中,一定有对应的Namespaces Info。
在linux-4.4.19/include/linux/sched.h #1380 定义task_struct结构体,该结构体是Linux Process完整信息的集合,其中就包含了一个指向Namespace结构体的指针nsproxy。
struct task_struct {
...
/* namespaces */
struct nsproxy *nsproxy;
...
}nsproxy结构体的定义在linux-4.4.6/include/linux/nsproxy.h #29
/*
* A structure to contain pointers to all per-process
* namespaces - fs (mount), uts, network, sysvipc, etc.
*
* The pid namespace is an exception -- it's accessed using
* task_active_pid_ns. The pid namespace here is the
* namespace that children will use.
*
* 'count' is the number of tasks holding a reference.
* The count for each namespace, then, will be the number
* of nsproxies pointing to it, not the number of tasks.
*
* The nsproxy is shared by tasks which share all namespaces.
* As soon as a single namespace is cloned or unshared, the
* nsproxy is copied.
*/
struct nsproxy {
atomic_t count;
struct uts_namespace *uts_ns;
struct ipc_namespace *ipc_ns;
struct mnt_namespace *mnt_ns;
struct pid_namespace *pid_ns_for_children;
struct net *net_ns;
};注意:正如如上代码注释写到,只要namespace被clone了,那么nsproxy就会跟着被clone。
同时,nsproxy.h中定义了一些对namespace的操作,包括copy_namespaces等。
int copy_namespaces(unsigned long flags, struct task_struct *tsk);
void exit_task_namespaces(struct task_struct *tsk);
void switch_task_namespaces(struct task_struct *tsk, struct nsproxy *new);
void free_nsproxy(struct nsproxy *ns);
int unshare_nsproxy_namespaces(unsigned long, struct nsproxy **, struct cred *, struct fs_struct *);
int __init nsproxy_cache_init(void);
static inline void put_nsproxy(struct nsproxy *ns) { … }
static inline void get_nsproxy(struct nsproxy *ns) { … }uts_namespace
linux-4.4.19/include/linux/utsname.h #12
struct uts_namespace {
struct kref kref;
struct new_utsname name;
struct user_namespace *user_ns;
struct ns_common ns;
};ipc_namespace
linux-4.4.19/include/linux/ipc_namespace.h #21
struct ipc_namespace {
atomic_t count;
struct ipc_ids ids[3];
int sem_ctls[4];
int used_sems;
unsigned int msg_ctlmax;
unsigned int msg_ctlmnb;
unsigned int msg_ctlmni;
atomic_t msg_bytes;
atomic_t msg_hdrs;
size_t shm_ctlmax;
size_t shm_ctlall;
unsigned long shm_tot;
int shm_ctlmni;
/*
* Defines whether IPC_RMID is forced for _all_ shm segments regardless
* of shmctl()
*/
int shm_rmid_forced;
struct notifier_block ipcns_nb;
/* The kern_mount of the mqueuefs sb. We take a ref on it */
struct vfsmount *mq_mnt;
/* # queues in this ns, protected by mq_lock */
unsigned int mq_queues_count;
/* next fields are set through sysctl */
unsigned int mq_queues_max; /* initialized to DFLT_QUEUESMAX */
unsigned int mq_msg_max; /* initialized to DFLT_MSGMAX */
unsigned int mq_msgsize_max; /* initialized to DFLT_MSGSIZEMAX */
unsigned int mq_msg_default;
unsigned int mq_msgsize_default;
/* user_ns which owns the ipc ns */
struct user_namespace *user_ns;
struct ns_common ns;
};mnt_namespace
linux-4.4.19/fs/mount.h #7
struct mnt_namespace {
atomic_t count;
struct ns_common ns;
struct mount * root;
struct list_head list;
struct user_namespace *user_ns;
u64 seq; /* Sequence number to prevent loops */
wait_queue_head_t poll;
u64 event;
};pid_namespace
linux-4.4.19/include/linux/pid_namespace.h #24
struct pid_namespace {
struct kref kref;
struct pidmap pidmap[PIDMAP_ENTRIES];
struct rcu_head rcu;
int last_pid;
unsigned int nr_hashed;
struct task_struct *child_reaper;
struct kmem_cache *pid_cachep;
unsigned int level;
struct pid_namespace *parent;
#ifdef CONFIG_PROC_FS
struct vfsmount *proc_mnt;
struct dentry *proc_self;
struct dentry *proc_thread_self;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_BSD_PROCESS_ACCT
struct fs_pin *bacct;
#endif
struct user_namespace *user_ns;
struct work_struct proc_work;
kgid_t pid_gid;
int hide_pid;
int reboot; /* group exit code if this pidns was rebooted */
struct ns_common ns;
};net_namespace
linux-4.4.19/include/net/net_namespace.h #47
struct net {
atomic_t passive; /* To decided when the network
* namespace should be freed.
*/
atomic_t count; /* To decided when the network
* namespace should be shut down.
*/
spinlock_t rules_mod_lock;
atomic64_t cookie_gen;
struct list_head list; /* list of network namespace







 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章














 3873
3873











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








