思维导图

前言
算法和数据结构是一个程序员的内功,所以经常在一些笔试中都会要求手写一些简单的排序算法,以此考验面试者的编程水平!动图来源于今日头条、动图来源于今日头条、动图来源于今日头条!
1、冒泡排序
1-1 思路:
1、比较相邻的元素。如果第一个比第二个大,就交换它们两个;
2、对每一对相邻元素作同样的工作,从开始第一对到结尾的最后一对,这样在最后的元素就是最大的数;
3、排除最大的数,接着下一轮继续相同的操作,确定第二大的数…
4、重复步骤1-3,直到排序完成。
1-2 动画演示:

1-3实现代码
@Test
public void bubbleSort() throws Exception {
int[] a = {2, 7, 4, 6, 0, 8, 5, 1, 3, 9, 10};
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {//表示 n 次排序过程。
for (j = 1; j < a.length - i; j++) {
if (a[j - 1] > a[j]) {//前面的数字大于后面的数字就交换
//交换 a[j-1]和a[j]
int temp;
temp = a[j - 1];
a[j - 1] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}
}
for ( int v : a) {
System.out.print(v + " ");
}
}
结果:

1-4 总结
平均时间复杂度:O(n²)
空间复杂度:O(1)
算法稳定性:稳定
2 插入排序
2-1 思路
1、从第一个元素开始,该元素可以认为已经被排序;
2、取出下一个元素,在前面已排序的元素序列中,从后向前扫描;
3、如果该元素(已排序)大于新元素,将该元素移到下一位置;
4、重复步骤3,直到找到已排序的元素小于或者等于新元素的位置;
5、将新元素插入到该位置后;
6、重复步骤2~5。
2-2 动画演示

2-3 实现代码
@Test
public void insertSort() throws Exception {
int[] arr = {2, 7, 4, 6, 0, 8, 5, 1, 3, 9, 10};
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
//插入的数
int insertVal = arr[i];
//被插入的位置(准备和前一个数比较)
int index = i - 1;
//如果插入的数比被插入的数小
while (index >= 0 && insertVal < arr[index]) {
//将把arr[index] 向后移动
arr[index + 1] = arr[index];
//让 index 向前移动
index--;
}
//把插入的数放入合适位置
arr[index + 1] = insertVal;
}
for (int k : arr) {
System.out.print(k + " ");
}
}
结果:
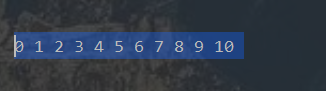
2-4 总结
平均时间复杂度:O(n²)
空间复杂度:O(1)
算法稳定性:稳定
3 选择排序
3-1 思路
1、第一轮,找到最小的元素,和数组第一个数交换位置。
2、第二轮,找到第二小的元素,和数组第二个数交换位置…
3、直到最后一个元素,排序完成。
3-2 动画演示

3-3 实现代码
public class SelectSort extends BaseSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SelectSort sort = new SelectSort();
sort.printNums(); } @Override
protected void sort(int[] nums) {
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int minIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
if (nums[j] < nums[minIndex]) {
minIndex = j; } } if (minIndex != i) {
int temp = nums[i];
nums[minIndex] = temp; nums[i] = nums[minIndex]; } } }}//10万个数的数组,耗时:8492毫秒
3-4 总结
平均时间复杂度:O(n²)
算法空间复杂度:O(1)
算法稳定性:不稳定
4 希尔排序
4-1 思路
把数组分割成若干(h)个小组(一般数组长度length/2),然后对每一个小组分别进行插入排序。每一轮分割的数组的个数逐步缩小,h/2->h/4->h/8,并且进行排序,保证有序。当h=1时,则数组排序完成。
4-2 动画演示

4-3 实现代码
public class ShellSort extends BaseSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShellSort sort = new ShellSort();
sort.printNums(); } @Override
protected void sort(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length < 2) {
return;
} int length = nums.length;
int temp;
//步长
int gap = length / 2;
while (gap > 0) {
for (int i = gap; i < length; i++) {
temp = nums[i];
int preIndex = i - gap;
while (preIndex >= 0 && nums[preIndex] > temp) {
nums[preIndex + gap] = nums[preIndex];
preIndex -= gap;
}
nums[preIndex + gap] = temp;
}
gap /= 2;
}
}
}
//10万个数的数组,耗时:261毫秒
4-4 总结
平均时间复杂度:O(nlog2n)
算法空间复杂度:O(1)
算法稳定性:稳定
5 快速排序
快排,面试最喜欢问的排序算法。这是运用分治法的一种排序算法。
5-1 思路
1、从数组中选一个数做为基准值,一般选第一个数,或者最后一个数。
2、采用双指针(头尾两端)遍历,从左往右找到比基准值大的第一个数,从右往左找到比基准值小的第一个数,交换两数位置,直到头尾指针相等或头指针大于尾指针,把基准值与头指针的数交换。这样一轮之后,左边的数就比基准值小,右边的数就比基准值大。
3、对左边的数列,重复上面1,2步骤。对右边重复1,2步骤。
4、左右两边数列递归结束后,排序完成。
5-2 动画演示

5-3 实现代码
public class QuickSort extends BaseSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
QuickSort sort = new QuickSort();
sort.printNums(); } @Override
protected void sort(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length < 2) {
return;
} quickSort(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
} private void quickSort(int[] nums, int star, int end) {
if (star > end) {
return;
} int i = star;
int j = end;
int key = nums[star];
while (i < j) {
while (i < j && nums[j] > key) {
j--; } while (i < j && nums[i] <= key) {
i++; } if (i < j) {
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j]; nums[j] = temp; } } nums[star] = nums[i]; nums[i] = key; quickSort(nums, star, i - 1);
quickSort(nums, i + 1, end);
}}//10万个数的数组,耗时:50毫秒
5-4 总结
平均时间复杂度:O(nlogn)
算法空间复杂度:O(1)
算法稳定性:不稳定
6 归并排序
6-1 思路
归并排序是采用分治法的典型应用,而且是一种稳定的排序方式,不过需要使用到额外的空间。
1、把数组不断划分成子序列,划成长度只有2或者1的子序列。
2、然后利用临时数组,对子序列进行排序,合并,再把临时数组的值复制回原数组。
3、反复操作1~2步骤,直到排序完成。
归并排序的优点在于最好情况和最坏的情况的时间复杂度都是O(nlogn),所以是比较稳定的排序方式。
6-2 动画演示

6-3 实现代码
public class MergeSort extends BaseSort {
public static void main(String[] args) { MergeSort sort = new MergeSort();
sort.printNums(); } @Override protected void sort(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length < 2) {
return;
} //归并排序 mergeSort(0, nums.length - 1, nums, new int[nums.length]);
} private void mergeSort(int star, int end, int[] nums, int[] temp) {
//递归终止条件
if (star >= end) {
return;
} int mid = star + (end - star) / 2;
//左边进行归并排序
mergeSort(star, mid, nums, temp); //右边进行归并排序
mergeSort(mid + 1, end, nums, temp);
//合并左右
merge(star, end, mid, nums, temp); } private void merge(int star, int end, int mid, int[] nums, int[] temp) {
int index = 0;
int i = star;
int j = mid + 1;
while (i <= mid && j <= end) {
if (nums[i] > nums[j]) {
temp[index++] = nums[j++];
} else {
temp[index++] = nums[i++];
} } while (i <= mid) {
temp[index++] = nums[i++];
} while (j <= end) {
temp[index++] = nums[j++];
} //把临时数组中已排序的数复制到nums数组中 if (index >= 0) System.arraycopy(temp, 0, nums, star, index);
}}//10万个数的数组,耗时:26毫秒
6-4 总结
平均时间复杂度:O(nlogn)
算法空间复杂度:O(n)
算法稳定性:稳定
7 堆排序
7-1 思路
大顶堆概念:每个节点的值都大于或者等于它的左右子节点的值,所以顶点的数就是最大值。
7-2 动画演示

7-3 实现代码
public class HeapSort extends BaseSort {
public static void main(String[] args) { HeapSort sort = new HeapSort();
sort.printNums(); } @Override protected void sort(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length < 2) {
return;
} heapSort(nums); } private void heapSort(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length < 2) {
return;
} //构建大根堆 createTopHeap(nums); int size = nums.length;
while (size > 1) {
//大根堆的交换头尾值,固定最大值在末尾
swap(nums, 0, size - 1);
//末尾的索引值往左减1
size--; //重新构建大根堆
updateHeap(nums, size); } } private void createTopHeap(int[] nums) {
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
//当前插入的索引
int currIndex = i;
//父节点的索引
int parentIndex = (currIndex - 1) / 2;
//如果当前遍历的值比父节点大的话,就交换值。然后继续往上层比较
while (nums[currIndex] > nums[parentIndex]) {
//交换当前遍历的值与父节点的值
swap(nums, currIndex, parentIndex); //把父节点的索引指向当前遍历的索引
currIndex = parentIndex; //往上计算父节点索引
parentIndex = (currIndex - 1) / 2;
} } } private void updateHeap(int[] nums, int size) {
int index = 0;
//左节点索引
int left = 2 * index + 1;
//右节点索引
int right = 2 * index + 2;
while (left < size) {
//最大值的索引
int largestIndex;
//如果右节点大于左节点,则最大值索引指向右子节点索引
if (right < size && nums[left] < nums[right]) {
largestIndex = right; } else {
largestIndex = left; } //如果父节点大于最大值,则把父节点索引指向最大值索引 if (nums[index] > nums[largestIndex]) {
largestIndex = index;
} //如果父节点索引指向最大值索引,证明已经是大根堆,退出循环 if (largestIndex == index) {
break;
} //如果不是大根堆,则交换父节点的值 swap(nums, largestIndex, index);
//把最大值的索引变成父节点索引
index = largestIndex;
//重新计算左节点索引
left = 2 * index + 1;
//重新计算右节点索引
right = 2 * index + 2;
} } private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j]; nums[j] = temp; }}//10万个数的数组,耗时:38毫秒
7-4 总结
平均时间复杂度:O(nlogn)
算法空间复杂度:O(1)
算法稳定性:不稳定
8 桶排序
8-1 思路
1、找出最大值,最小值。
2、根据数组的长度,创建出若干个桶。
3、遍历数组的元素,根据元素的值放入到对应的桶中。
4、对每个桶的元素进行排序(可使用快排,插入排序等)。
5、按顺序合并每个桶的元素,排序完成。
对于数组中的元素分布均匀的情况,排序效率较高。相反的,如果分布不均匀,则会导致大部分的数落入到同一个桶中,使效率降低。
8-2 动画演示

8-3 实现代码
public class BucketSort extends BaseSort {
public static void main(String[] args) { BucketSort sort = new BucketSort();
sort.printNums(); } @Override protected void sort(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length < 2) {
return;
} bucketSort(nums); } public void bucketSort(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length < 2) {
return;
} //找出最大值,最小值 int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int num : nums) {
min = Math.min(min, num); max = Math.max(max, num); } int length = nums.length;
//桶的数量
int bucketCount = (max - min) / length + 1;
int[][] bucketArrays = new int[bucketCount][];
//遍历数组,放入桶内
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
//找到桶的下标
int index = (nums[i] - min) / length;
//添加到指定下标的桶里,并且使用插入排序排序
bucketArrays[index] = insertSortArrays(bucketArrays[index], nums[i]);
} int k = 0;
//合并全部桶的
for (int[] bucketArray : bucketArrays) {
if (bucketArray == null || bucketArray.length == 0) {
continue;
} for (int i : bucketArray) {
//把值放回到nums数组中
nums[k++] = i; } } } //每个桶使用插入排序进行排序 private int[] insertSortArrays(int[] arr, int num) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
return new int[]{num};
} //创建一个temp数组,长度是arr数组的长度+1
int[] temp = new int[arr.length + 1];
//把传进来的arr数组,复制到temp数组
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
temp[i] = arr[i]; } //找到一个位置,插入,形成新的有序的数组 int i;
for (i = temp.length - 2; i >= 0 && temp[i] > num; i--) {
temp[i + 1] = temp[i];
} //插入需要添加的值 temp[i + 1] = num;
//返回
return temp;
}}//10万个数的数组,耗时:8750毫秒
8-4 总结
平均时间复杂度:O(M+N)
算法空间复杂度:O(M+N)
算法稳定性:稳定(取决于桶内的排序算法,这里使用的是插入排序所以是稳定的)。
八种排序算法总结

























 1177
1177











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








