android的API Demo提供了很多有趣+有用的Demo,本系列将学习基于4.4.2版本的API,其中涉及到的代码大部分是出于android 自带的Demo,本人根据自己的学习、理解,加以注释。
public class Rotate3DAnimation extends Animation {
private final float mFromDegrees;//开始角度
private final float mToDegrees;//结束角度
private final float mCenterX;//中心X点
private final float mCenterY;//中心Y点
private final float mDepthZ;//深度Z,越大缩放越明显
private final boolean mReverse;//是否相反,true:视角由近到远 false:视角由远到近(缩放效果)
private Camera mCamera;
public Rotate3DAnimation(float mFromDegrees, float mToDegrees,
float mCenterX, float mCenterY, float mDepthZ, boolean mReverse) {
super();
this.mFromDegrees = mFromDegrees;
this.mToDegrees = mToDegrees;
this.mCenterX = mCenterX;
this.mCenterY = mCenterY;
this.mDepthZ = mDepthZ;
this.mReverse = mReverse;
}
@Override
public void initialize(int width, int height, int parentWidth,
int parentHeight) {
super.initialize(width, height, parentWidth, parentHeight);
mCamera=new Camera();
// 动画时间
setDuration(500);
// 动画完成后保持完成的状态
setFillAfter(true);
}
//当动画开始时,会不断调用applyTransformation,这个过程是动态的,不断在变化
//interpolatedTime 代表当前方法掉用时,动画进行的一个时间点,这个值的范围是0到1,也就是说动画刚开始的时候
//传进来的interpolatedTime为0,动画进行中的时候,传进来的是0到1之间的小数,动画结束的时候传进来的是1。
@Override
protected void applyTransformation(float interpolatedTime, Transformation t) {
final float fromDegrees = mFromDegrees;
//计算每次变化的角度
float degrees = fromDegrees + ((mToDegrees - fromDegrees) * interpolatedTime);
final float centerX = mCenterX;
final float centerY = mCenterY;
final Camera camera = mCamera;
//获取原始矩阵
final Matrix matrix = t.getMatrix();
camera.save();
if(mReverse){//视图离镜头越来越远,即缩小视角
camera.translate(0.0f, 0.0f, mDepthZ*interpolatedTime);
}else{//视图离镜头越来越近,即放大视角
camera.translate(0.0f, 0.0f, mDepthZ*(1.0f-interpolatedTime));
}
//以Y轴为旋转中心轴,旋转degrees角度
camera.rotateY(degrees);
camera.getMatrix(matrix);
camera.restore();
//pre是前乘,参数给出的矩阵乘以当前的矩阵。在旋转之前,先平移(-centerX, -centerY)
matrix.preTranslate(-centerX, -centerY);
//post是后乘,当前的矩阵乘以参数给出的矩阵。旋转之后,在平移(centerX, centerY)
matrix.postTranslate(centerX, centerY);
//总的来说,就是在绕Y轴旋转之前,先把旋转中心点从(0,0)移到(centerX,centerY),然后以Y轴为轴线,
//(centerX,centerY)为轴心旋转degrees后,将中心点复原为(0,0),这样看起来就是以视图的中心,绕Y轴旋转了。
}
}Rotate3DAnimation是封装了3D旋转动画效果的类,注释是我对其的理解
public class Transition3dActivity extends Activity implements
OnItemClickListener, OnClickListener {
private ListView mPhotosList;
private ViewGroup mContainer;
private ImageView mImageView;
// Names of the photos we show in the list
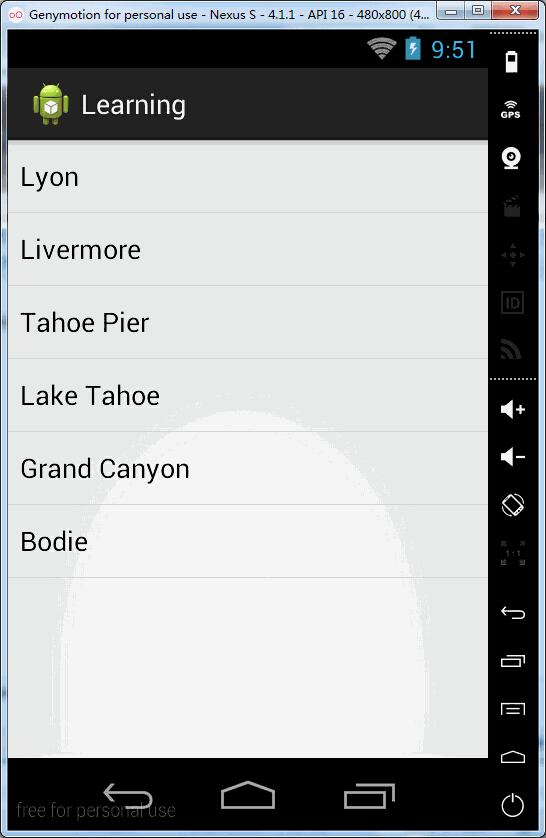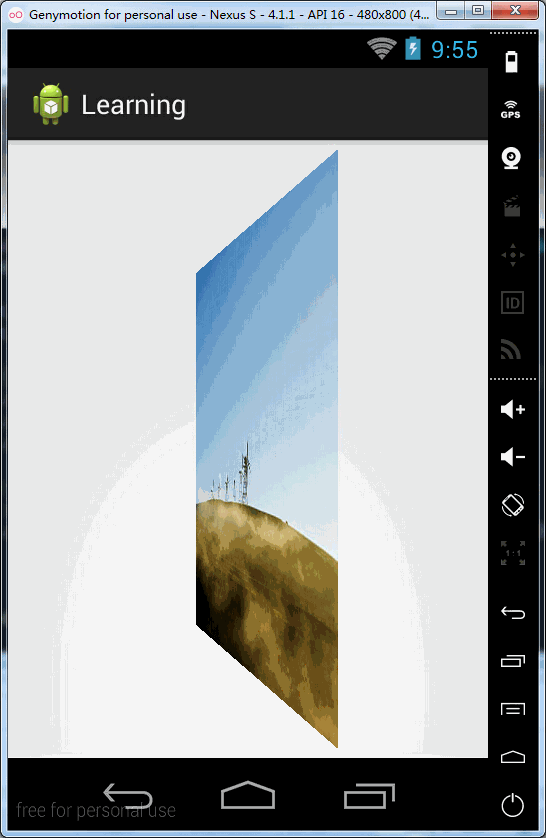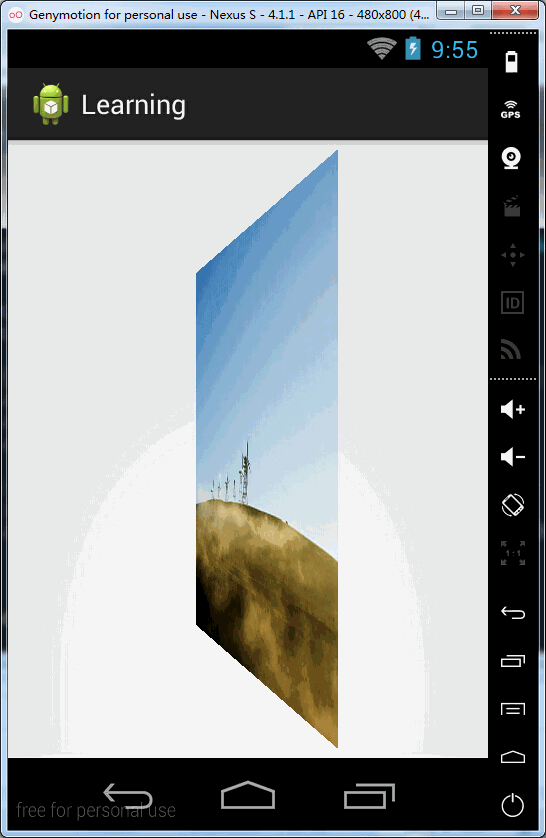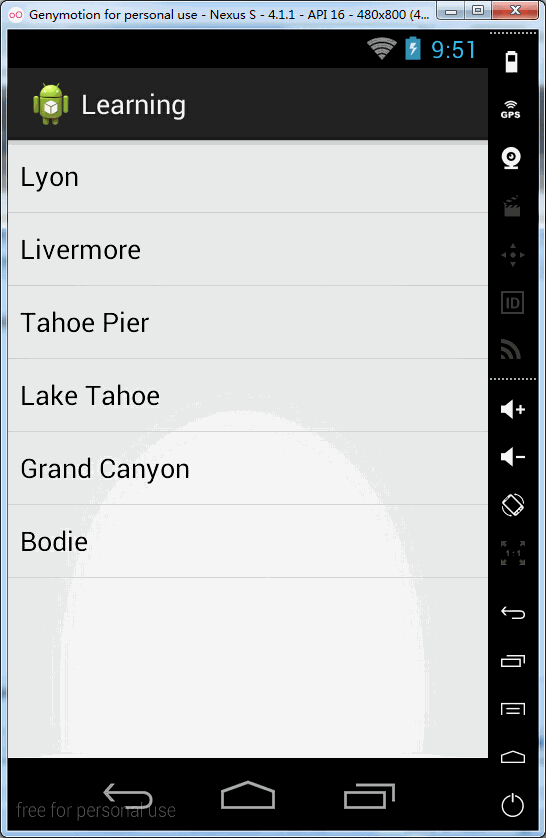
private static final String[] PHOTOS_NAMES = new String[] { "Lyon",
"Livermore", "Tahoe Pier", "Lake Tahoe", "Grand Canyon", "Bodie" };
// 显示的图片资源
private static final int[] PHOTOS_RESOURCES = new int[] {
R.drawable.photo1, R.drawable.photo2, R.drawable.photo3,
R.drawable.photo4, R.drawable.photo5, R.drawable.photo6 };
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.animations_main_screen);
mPhotosList = (ListView) findViewById(android.R.id.list);
mImageView = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.picture);
mContainer = (ViewGroup) findViewById(R.id.container);
// Prepare the ListView
final ArrayAdapter<String> adapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>(this,
android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, PHOTOS_NAMES);
mPhotosList.setAdapter(adapter);
mPhotosList.setOnItemClickListener(this);
// Prepare the ImageView
mImageView.setClickable(true);
mImageView.setFocusable(true);
mImageView.setOnClickListener(this);
// Since we are caching large views, we want to keep their cache
// between each animation(缓存)
mContainer.setPersistentDrawingCache(ViewGroup.PERSISTENT_ANIMATION_CACHE);
}
/**
* 3D旋转视图 2014-11-13 下午1:31:06
*
* @param position
* item位置
* @param start
* 开始角度
* @param end
* 结束角度
* @TODO
*/
private void applyRotation(int position, float start, float end) {
// 获取视图中心点
float centerX = mContainer.getWidth() / 2.0f;
float centerY = mContainer.getHeight() / 2.0f;
// 构建3D旋转动画对象
final Rotate3DAnimation rotation = new Rotate3DAnimation(start, end,
centerX, centerY, 310.0f, true);
// 设置动画速度变化曲线为加速
rotation.setInterpolator(new AccelerateInterpolator());
// 动画监听
rotation.setAnimationListener(new DisplayNextView(position));
mContainer.startAnimation(rotation);
}
@Override
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position,
long id) {
mImageView.setImageResource(PHOTOS_RESOURCES[position]);
// 每次点击item时,将mContainer根布局旋转角度从0到90(可将自己的左手正面朝上当作mContainer容器,逆时针旋转90度的过程)---①
applyRotation(position, 0, 90);
}
/**
* This class listens for the end of the first half of the animation. It
* then posts a new action that effectively swaps the views when the
* container is rotated 90 degrees and thus invisible.
*/
private final class DisplayNextView implements Animation.AnimationListener {
private final int mPosition;
private DisplayNextView(int position) {
mPosition = position;
}
public void onAnimationStart(Animation animation) {
}
public void onAnimationEnd(Animation animation) {
// 当ListView动画结束时,ListView隐藏,不显示,此时图片开始显示
mContainer.post(new SwapViews(mPosition));
}
public void onAnimationRepeat(Animation animation) {
}
}
/**
* This class is responsible for swapping the views and start the second
* half of the animation.
*/
private final class SwapViews implements Runnable {
private final int mPosition;
public SwapViews(int position) {
mPosition = position;
}
public void run() {
final float centerX = mContainer.getWidth() / 2.0f;
final float centerY = mContainer.getHeight() / 2.0f;
Rotate3DAnimation rotation;
if (mPosition > -1) {// 点击的是item
mPhotosList.setVisibility(View.GONE);
mImageView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
mImageView.requestFocus();
// 由于第①步的旋转,此时mContainer是处于90度的,再次旋转90度,从90到180,
// 等于此时的mContainer已经旋转了180度,处于“背面”向上-----②
// (相当于左手手心起始向右,向下转动的过程,直至手心向下,手背在上面,而这个过程正是图片从无到有,ListView从有到无的过程)
rotation = new Rotate3DAnimation(90, 180, centerX, centerY,
310.0f, false);
} else {// 点击的是ImageView(mPosition=-1)
mImageView.setVisibility(View.GONE);
mPhotosList.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
mPhotosList.requestFocus();
// 由于第③步,此时的mContainer处于90度,然后再次旋转90度,从90到0,复原了初始状态(左手手心向右顺时针旋转90度至手心向上的原始状态)
rotation = new Rotate3DAnimation(90, 0, centerX, centerY,
310.0f, false);
}
// 设置动画速度变化曲线为减速
rotation.setInterpolator(new DecelerateInterpolator());
mContainer.startAnimation(rotation);
}
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// 由于第②步的结果,使mContainer处于旋转了180的状态,当点击ImageView时,使mContainer状态复原回去
// 从180到旋转到90-----③(当点击图片时,左手旋转的动作是一个相反的过程,即从左手手心向下,手背在上的状态,顺时针旋转90度至手心向右)
applyRotation(-1, 180, 90);
}
}xml布局animations_main_screen.xml
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/container"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<ListView
android:id="@android:id/list"
android:persistentDrawingCache="animation|scrolling"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
/>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/picture"
android:scaleType="fitCenter"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:visibility="gone" />
</FrameLayout>效果图:






















 2187
2187

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








