感谢文章作者整理分享:原文地址
1. 基本
1.1 概述
Java的IO操作中有面向字节(Byte)和面向字符(Character)两种方式。
- 面向字节的操作为以8位为单位对二进制的数据进行操作,对数据不进行转换,这些类都是InputStream和OutputStream的子类。面向字符的操作为以字符为单位对数据进行操作,在读的时候将二进制数据转为字符,在写的时候将字符转为二进制数据,这些类都是Reader和Writer的子类。
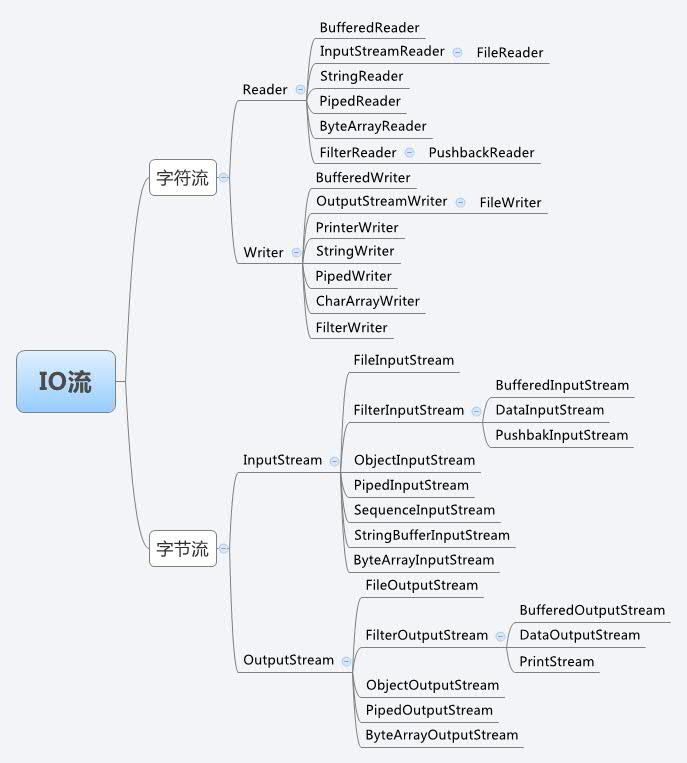
IO常用类的继承关系图如下:
使用系统路径标识来组建路径
@Test
// 使用系统路径标识来组建路径
public void testFileAttr() throws IOException {
System.out.println(File.separator);
System.out.println(File.pathSeparator);
// 这样组成的路径能实现在windows和linux中的通用性
String fileName = "D:" + File.separator + "hello_testFileAttr.txt";
File f = new File(fileName);
f.createNewFile();
}取得本地的默认编码
@Test
// 取得本地的默认编码
public void testGetLocalEncoding() {
System.out.println("系统默认编码为:" + System.getProperty("file.encoding"));
}创建文件夹
@Test
// File.mkdir() 创建文件夹
public void testCreateMkdir() {
String fileName = "D:" + File.separator + "hello";
File f = new File(fileName);
f.mkdir();
}创建文件
@Test
// 创建文件
public void testCreateFile() {
File f = new File("D:\\hello_testCreateFile.txt");// 参数为待创建[文件路径+文件名]组成的字符串
try {
f.createNewFile();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}判断文件是否存在、删除文件
@Test
// File.exists()、File.delete() 判断文件是否存在、删除文件
public void testDelFile() {
String fileName = "D:" + File.separator + "hello_testFileAttr.txt";
File f = new File(fileName);
if (f.exists()) {
f.delete();
System.out.println("文件已经删除");
} else {
System.out.println("文件不存在");
}
}列出全部文件
@Test
// File.list() 列出指定目录的全部文件(包括隐藏文件)
// File.listFiles() 列出指定目录下全部带完整路径的文件(包括隐藏文件)
public void testListAllFile() {
String fileName = "D:" + File.separator;
File f = new File(fileName);
String[] str = f.list();// 返回的是Sring数组
for (int i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
System.out.println(str[i]);
}
System.out.println("--------------");
File[] files = f.listFiles();// 返回的是File[]
for (int i = 0; i < files.length; i++) {
System.out.println(files[i]);
}
}判断一个指定的路径是否为目录
@Test
// 使用isDirectory判断一个指定的路径是否为目录,如果目录不存在也是返回NO
public void testIsDirectory() {
String fileName = "D:" + File.separator + "hello";
File f = new File(fileName);
if (f.isDirectory()) {
System.out.println("YES");
} else {
System.out.println("NO");
}
}打印出所有文件的路径
// 打印出所有文件的路径
public void print(File f) {
if (f != null) {
if (f.isDirectory()) {// 如果f是目录
File[] fileArray = f.listFiles();// 得到目录下的所有文件
if (fileArray != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < fileArray.length; i++) {
print(fileArray[i]);// 递归调用
}
}
} else {// 如果f是文件,直接输出文件路径
System.out.println(f);
}
}
}列出指定目录的全部内容
@Test
public void testListAll() {
String fileName = "D:" + File.separator;
File f = new File(fileName);
print(f);
}2. 读取写入流、转换流
字节流,向文件中写入字符串,会覆盖原来的内容!
@Test
// 字节流,向文件中写入字符串,会覆盖原来的内容!【FileOutputStream->write()】
public void testWriteString() throws IOException {
String fileName = "D:" + File.separator + "hello.txt";
File f = new File(fileName);
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(f);// ★参数文件
String str = "你好";
byte[] b = str.getBytes();
out.write(b);
out.close();
}一个字节一个字节的写入字符串,会覆盖原来的内容!
@Test
// 第二种方式:一个字节一个字节的写入字符串,会覆盖原来的内容!
public void testWriteStringOneByOne() throws IOException {
String fileName = "D:" + File.separator + "hello.txt";
File f = new File(fileName);
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(f);
String str = "妹子,我喜欢你!";
byte[] b = str.getBytes();
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
out.write(b[i]);
}
out.close();
}字节流:向文件中追加新内容:
@Test
// 字节流:向文件中追加新内容:
public void testAppendString() throws IOException {
String fileName = "D:" + File.separator + "hello.txt";
File f = new File(fileName);
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(f, true);
String str = "亲爱的,嫁给我吧!";// 可以用\r\n换行,如:String str="\r\n你好";
byte[] b = str.getBytes();
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
out.write(b[i]);
}
out.close();
}使用RandomAccessFile写入文
@Test
// 使用RandomAccessFile写入文件,打开文件后会发现那是乱码。
public void testRandomAccessFile() throws IOException {
String fileName = "D:" + File.separator + "hello.txt";
File f = new File(fileName);
RandomAccessFile demo = new RandomAccessFile(f, "rw");// 设置文件读写权限
demo.writeBytes("Hewei I love you!");
demo.writeInt(12);
demo.writeBoolean(true);
demo.writeChar('A');
demo.writeFloat(1.21f);
demo.writeDouble(12.123);
demo.close();
}
字节流:读文件内容
@Test
// ★字节流:读文件内容【FileInputStream->read()】
public void testReadFileString() throws IOException {
String fileName = "D:" + File.separator + "hello.txt";
File f = new File(fileName);
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(f);
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
in.read(b);
in.close();
System.out.println(new String(b));
}字节流:读文件内容
@Test
// ★字节流:读文件内容,一个个的读以节省空间
public void testReadFileStringOneByOne() throws IOException {
String fileName = "D:" + File.separator + "hello.txt";
File f = new File(fileName);
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(f);
byte[] b = new byte[(int) f.length()];
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
b[i] = (byte) in.read();
}
in.close();
System.out.println(new String(b));
}不知道文件有多大读取文件内容
@Test
// 在知道文件的内容多大,然后才展开的,有时候我们不知道文件有多大,这种情况下用下面这种方法
public void testReadFileStringBySureEnd() throws IOException {
String fileName = "D:" + File.separator + "hello.txt";
File f = new File(fileName);
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(f);
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int count = 0, temp = 0;
while ((temp = in.read()) != (-1)) {// ★当独到文件末尾的时候会返回-1,用此判断是否独到文件的末尾。
b[count++] = (byte) temp;
}
in.close();
System.out.println(new String(b));
}字符流:向文件中写入数据
@Test
//★★字符流:向文件中写入数据【FileWriter->write】
public void testWriteFileStringByCharStream() throws Exception {
String fileName = "D:" + File.separator + "hello.txt";
File f = new File(fileName);
Writer out = new FileWriter(f);
String str = "妹子,我又来了";// 把以前的内容覆盖了
out.write(str);
out.close();
}字符流:从文件中读出内容
@Test
// ★★字符流:从文件中读出内容
public void testReadFileStringByCharStream() throws IOException {
String fileName = "D:" + File.separator + "hello.txt";
File f = new File(fileName);
Reader read = new FileReader(f);
read.close();
}循环读取文件内容
@Test
// ★采用循环读取的方式,因为我们有时候不知道文件到底有多大
public void testReadFileStringBySureEndInCharStream() throws IOException {
String fileName = "D:" + File.separator + "hello.txt";
File f = new File(fileName);
char[] ch = new char[100];
Reader read = new FileReader(f);
int temp = 0;
int count = 0;
while ((temp = read.read()) != (-1)) {
ch[count++] = (char) temp;
}
read.close();
System.out.println(new String(ch, 0, count));
}文件内容拷贝
@Test
// ★★★将hello.txt中的内容拷贝被到world.txt中(覆盖原来有的内容),如果world.txt中不存在,则创建该文件,
public void testCopyFile() throws IOException {
String file1 = "D:" + File.separator + "hello.txt";
String file2 = "D:" + File.separator + "world.txt";
InputStream input = new FileInputStream(file1);
OutputStream output = new FileOutputStream(file2);
if ((input != null) && (output != null)) {
int temp = 0;
while ((temp = input.read()) != (-1)) {
output.write(temp);
}
}
input.close();
output.close();
}流转换:字节输出流转化为字符输出流
@Test
// ★★将字节输出流转化为字符输出流
public void testByteOutStream2CharOutStream() throws Exception {
String fileName = "d:" + File.separator + "hello.txt";
File file = new File(fileName);
Writer out = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(file));
out.write("hello");
out.close();
}流转换:字节输入流变为字符输入流
@Test
// ★★将字节输入流变为字符输入流
public void testByteInStream2CharInStream() throws Exception {
String fileName = "d:" + File.separator + "hello.txt";
File file = new File(fileName);
Reader read = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file));
char[] b = new char[100];
int len = read.read(b);
System.out.println(new String(b, 0, len));
read.close();
}[内存操作流内]ByteArrayInputStream
@Test
// ★★[内存操作流内]ByteArrayInputStream:内存操作流内一般使用来生成一些临时信息,这样可以避免删除的麻烦
public void testByteArrayInputStream() throws IOException {
String str = "ILOVEYOU";
ByteArrayInputStream input = new ByteArrayInputStream(str.getBytes());
ByteArrayOutputStream output = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
int temp = 0;
while ((temp = input.read()) != -1) {
char ch = (char) temp;
output.write(Character.toLowerCase(ch));
}
String outStr = output.toString();
input.close();
output.close();
System.out.println(outStr);
}PipedOutputStream 管道输出流
@Test
// PipedOutputStream 管道输出流;PipedInputStream 管道输入流
public void testPipeStreamSend() {
Send_PipedStreamTest send = new Send_PipedStreamTest();
Recive_PipedStreamTest recive = new Recive_PipedStreamTest();
try {// 管道连接
send.getOut().connect(recive.getInput());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(send).start();
new Thread(recive).start();
}打印流PrintStream进行输出
@Test
// 使用PrintStream进行输出
public void testPrintStreamOut() throws Exception {
PrintStream print = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream(new File("d:"
+ File.separator + "hello.txt")));
print.println(true);// 输入到hello.txt文件中
print.println("Rollen");
print.close();
}PrintStream进行格式化输出
@Test
// 使用PrintStream进行输出,并进行格式化
public void testFormatPrintOut() throws Exception {
PrintStream print = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream(new File("d:"
+ File.separator + "hello.txt")));
String name = "Rollen";
int age = 20;
print.printf("姓名:%s. 年龄:%d.", name, age);
print.close();
}字符流的缓冲区:BufferedReader
@Test
// BufferedReader:只能接受字符流的缓冲区,为每一个中文需要占据两个字节,所以需要将System.in这个字节输入流变为字符输入流
// 采用:BufferedReader buf = new BufferedReader(new
// InputStreamReader(System.in));
// 使用缓冲区从键盘上读入内容
public void testBufferedReader() {
BufferedReader buf = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String str = null;
System.out.println("请输入内容:");
try {
str = buf.readLine();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("你输入的内容是:" + str);
}Scanner类:可以接受任何的输入流
@Test
// ★★Scanner类:从键盘读数据,可以接受任何的输入流。使用Scanner类从文件中读出内容
public void testScanner() {
File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.txt");
Scanner sca = null;
try {
sca = new Scanner(file);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
String str = sca.next();
System.out.println("从文件中读取的内容是:" + str);
}数据操作流DataOutputStream、DataInputStream类
@Test
public void testData() throws Exception {
File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.txt");
char[] ch = { 'A', 'B', 'C' };
DataOutputStream out = null;
out = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file));
for (char temp : ch) {
out.writeChar(temp);
}
out.close();
}3. 流合并、文件压缩与解压
合并流 SequenceInputStream
@Test
// 合并流 SequenceInputStream:将2个流合并在一起,比如将两个txt中的内容合并为另外一个txt
// 下面结果会在hello.txt文件中包含hello1.txt和hello2.txt文件中的内容。
public void testSequenceInputStream() throws Exception {
File file1 = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello1.txt");
File file2 = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello2.txt");
File file3 = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.txt");
InputStream input1 = new FileInputStream(file1);// 如果文件不存在,报系统找不到指定的文件
InputStream input2 = new FileInputStream(file2);
OutputStream output = new FileOutputStream(file3);
// 合并流
SequenceInputStream sis = new SequenceInputStream(input1, input2);
int temp = 0;
while ((temp = sis.read()) != -1) {
output.write(temp);
}
input1.close();
input2.close();
output.close();
sis.close();
}文件压缩 ZipOutputStream
@Test
public void testZipStream() throws Exception {
File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.txt");
File zipFile = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.zip");
InputStream input = new FileInputStream(file);
ZipOutputStream zipOut = new ZipOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(
zipFile));
zipOut.putNextEntry(new ZipEntry(file.getName()));
// 设置注释
zipOut.setComment("hello");
int temp = 0;
while ((temp = input.read()) != -1) {
zipOut.write(temp);
}
input.close();
zipOut.close();
}压缩多个文件
@Test
public void testZipMutilFile() throws Exception {
// 要被压缩的文件夹
File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "temp");
File zipFile = new File("d:" + File.separator + "zipFile.zip");// 压缩后的文件名
InputStream input = null;
ZipOutputStream zipOut = new ZipOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(
zipFile));
zipOut.setComment("hello");
if (file.isDirectory()) {// 压缩temp问文件夹下的所有文件
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (int i = 0; i < files.length; ++i) {
input = new FileInputStream(files[i]);
zipOut.putNextEntry(new ZipEntry(file.getName()
+ File.separator + files[i].getName()));
int temp = 0;
while ((temp = input.read()) != -1) {
zipOut.write(temp);
}
input.close();
}
}
zipOut.close();
}ZipFile类getName()
@Test
public void testUnderStandZipFile() throws Exception {
File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "zipFile.zip");
ZipFile zipFile = new ZipFile(file);
System.out.println("压缩文件的名称为:" + zipFile.getName());
}解压缩文件:ZipEntry(压缩文件中只有一个文件的情况)
@Test
public void testZipFile() throws Exception {
File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.zip");
File outFile = new File("d:" + File.separator + "unZipFile.txt");
ZipFile zipFile = new ZipFile(file);
ZipEntry entry = zipFile.getEntry("hello.txt");
InputStream input = zipFile.getInputStream(entry);
OutputStream output = new FileOutputStream(outFile);
int temp = 0;
while ((temp = input.read()) != -1) {
output.write(temp);
}
input.close();
output.close();
}解压缩多个文件
@Test
// 解压缩多个文件的时候,ZipEntry就无法使用了,如果想操作更加复杂的压缩文件,我们就必须使用ZipInputStream类
public void testUnZipMutilFile() throws Exception {
File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "zipFile.zip");
File outFile = null;
ZipFile zipFile = new ZipFile(file);
ZipInputStream zipInput = new ZipInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
ZipEntry entry = null;
InputStream input = null;
OutputStream output = null;
while ((entry = zipInput.getNextEntry()) != null) {
System.out.println("解压缩" + entry.getName() + "文件");
outFile = new File("d:" + File.separator + entry.getName());
if (!outFile.getParentFile().exists()) {
outFile.getParentFile().mkdir();
}
if (!outFile.exists()) {
outFile.createNewFile();
}
input = zipFile.getInputStream(entry);
output = new FileOutputStream(outFile);
int temp = 0;
while ((temp = input.read()) != -1) {
output.write(temp);
}
input.close();
output.close();
}
}4. 其它
PushBackInputStream回退流
@Test
public void testPushBackInputStream() throws IOException {
String str = "hello,rollenholt";
PushbackInputStream push = null;
ByteArrayInputStream bat = null;
bat = new ByteArrayInputStream(str.getBytes());
push = new PushbackInputStream(bat);
int temp = 0;
while ((temp = push.read()) != -1) {
if (temp == ',') {
push.unread(temp);
temp = push.read();
System.out.print("(回退" + (char) temp + ") ");
} else {
System.out.print((char) temp);
}
}
}
ObjectInputStream
@Test
// 示范:查看hello.txt二进制文件里面的内容
public void testObjectInputStream() throws Exception {
File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.txt");
ObjectInputStream input = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
Object obj = input.readObject();
input.close();
System.out.println(obj);
}序列化
@Test
//被Serializable接口声明的类的对象的属性都将被序列化,但是如果想自定义序列化的内容的时候,就需要实现Externalizable接口
public void test() throws Exception {
File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "hello.txt");
ObjectInputStream input = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
Object obj = input.readObject();
input.close();
System.out.println(obj);
}






















 1733
1733

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








