一:
关键参考:http://www.jianshu.com/p/847432c2cb3b
When a user-generated event occurs, UIKit creates an event object containing the information needed to process the event. Then it places the event object in the active app’s event queue.
An event travels along a specific path until it is delivered to an object that can handle it.
First, the singleton UIApplication object takes an event from the top of the queue and dispatches it for handling. Typically, it sends the event to the app’s key window object, which passes the event to an initial object for handling.
iOS系统检测到手指触摸(Touch)操作时会将其打包成一个UIEvent对象,并放入当前活动Application的事件队列,单例的UIApplication会从事件队列中取出触摸事件并传递给单例的UIWindow来处理,UIWindow对象首先会使用hitTest:withEvent:方法寻找此次Touch操作初始点所在的视图(View),即需要将触摸事件传递给其处理的视图,这个过程称之为hit-test view。
UIWindow实例对象会首先在它的内容视图上调用hitTest:withEvent:,此方法会在其视图层级结构中的每个视图上调用pointInside:withEvent:(该方法用来判断点击事件发生的位置是否处于当前视图范围内,以确定用户是不是点击了当前视图),如果pointInside:withEvent:返回YES,则继续逐级调用,直到找到touch操作发生的位置,这个视图也就是要找的hit-test view。
hitTest:withEvent:方法的处理流程如下:
首先调用当前视图的pointInside:withEvent:方法判断触摸点是否在当前视图内;
若返回NO,则hitTest:withEvent:返回nil;
若返回YES,则向当前视图的所有子视图(subviews)发送hitTest:withEvent:消息,所有子视图的遍历顺序是从最顶层视图一直到到最底层视图,即从subviews数组的末尾向前遍历,直到有子视图返回非空对象或者全部子视图遍历完毕;
若第一次有子视图返回非空对象,则hitTest:withEvent:方法返回此对象,处理结束;
如所有子视图都返回非,则hitTest:withEvent:方法返回自身(self)。
这是找第一响应者的过程
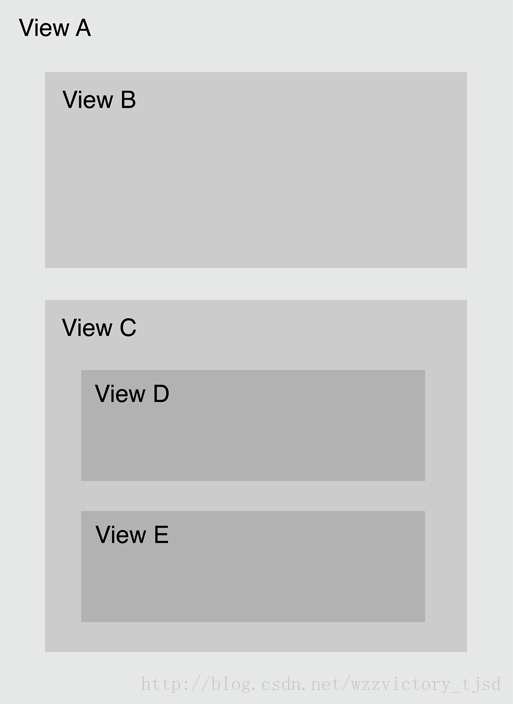
假如用户点击了View E,下面结合图二介绍hit-test view的流程:
1、A是UIWindow的根视图,因此,UIWindwo对象会首相对A进行hit-test;
2、显然用户点击的范围是在A的范围内,因此,pointInside:withEvent:返回了YES,这时会继续检查A的子视图;
3、这时候会有两个分支,B和C:
点击的范围不再B内,因此B分支的pointInside:withEvent:返回NO,对应的hitTest:withEvent:返回nil;
点击的范围在C内,即C的pointInside:withEvent:返回YES;
4、这时候有D和E两个分支:
点击的范围不再D内,因此D的pointInside:withEvent:返回NO,对应的hitTest:withEvent:返回nil;
点击的范围在E内,即E的pointInside:withEvent:返回YES,由于E没有子视图(也可以理解成对E的子视图进行hit-test时返回了nil),因此,E的hitTest:withEvent:会将E返回,再往回回溯,就是C的hitTest:withEvent:返回E--->>A的hitTest:withEvent:返回E。
至此,本次点击事件的第一响应者就通过响应者链的事件分发逻辑成功的找到了。
这是处理事件的过程
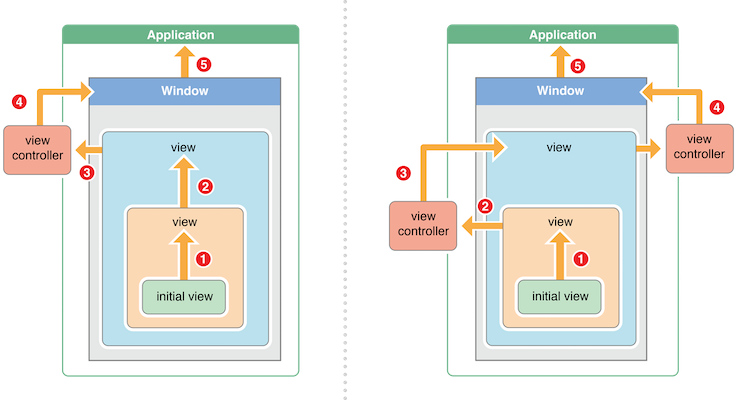
For the app on the left, the event follows this path:
-
The initial view attempts to handle the event or message. If it can’t handle the event, it passes the event to its superview, because the initial view is not the top most view in its view controller’s view hierarchy.
-
The superview attempts to handle the event. If the superview can’t handle the event, it passes the event to its superview, because it is still not the top most view in the view hierarchy.
-
The topmost view in the view controller’s view hierarchy attempts to handle the event. If the topmost view can’t handle the event, it passes the event to its view controller.
-
The view controller attempts to handle the event, and if it can’t, passes the event to the window.
-
If the window object can’t handle the event, it passes the event to the singleton app object.
-
If the app object can’t handle the event, it discards the event.
The app on the right follows a slightly different path, but all event delivery paths follow these heuristics:
-
A view passes an event up its view controller’s view hierarchy until it reaches the topmost view.
-
The topmost view passes the event to its view controller.
-
The view controller passes the event to its topmost view’s superview.
Steps 1-3 repeat until the event reaches the root view controller.
-
The root view controller passes the event to the window object.
-
The window passes the event to the app object.
说明:
1、如果最终hit-test没有找到第一响应者,或者第一响应者没有处理该事件,则该事件会沿着响应者链向上回溯,如果UIWindow实例和UIApplication实例都不能处理该事件,则该事件会被丢弃;
2、hitTest:withEvent:方法将会忽略隐藏(hidden=YES)的视图,禁止用户操作(userInteractionEnabled=YES)的视图,以及alpha级别小于0.01(alpha<0.01)的视图。如果一个子视图的区域超过父视图的bound区域(父视图的clipsToBounds 属性为NO,这样超过父视图bound区域的子视图内容也会显示),那么正常情况下对子视图在父视图之外区域的触摸操作不会被识别,因为父视图的pointInside:withEvent:方法会返回NO,这样就不会继续向下遍历子视图了。当然,也可以重写pointInside:withEvent:方法来处理这种情况。
3、我们可以重写hitTest:withEvent:来达到某些特定的目的,下面的链接就是一个有趣的应用举例,当然实际应用中很少用到这些。
参考文档:
https://developer.apple.com/library/ios/#documentation/EventHandling/Conceptual/
EventHandlingiPhoneOS/event_delivery_responder_chain/event_delivery_responder_chain.html#//
apple_ref/doc/uid/TP40009541-CH4-SW1
http://www.jianshu.com/p/9179e5d780c8 简书
二:
通俗理解:
响应者链条概念: iOS系统检测到手指触摸(Touch)操作时会将其打包成一个UIEvent对象,并放入当前活动Application的事件队列,单例的UIApplication会从事件队列中取出触摸事件并传递给单例的UIWindow来处理,UIWindow对象首先会使用hitTest:withEvent:方法寻找此次Touch操作初始点所在的视图(View),即需要将触摸事件传递给其处理的视图,这个过程称之为hit-test view。
响应者对象(Responder Object) 指的是 有响应和处理事件能力的对象。 响应者链就是由一系列的响应者对象 构成的一个层次结构。
UIResponder 是所有响应对象的基类,在UIResponder类中定义了处理上述各种事件的接口。我们熟悉的 UIApplication、 UIViewController、 UIWindow 和所有继承自UIView的UIKit类都直接或间接的继承自UIResponder,所以它们的实例都是可以构成响应者链的响应者对象。
UIWindow实例对象会首先在它的内容视图上调用hitTest:withEvent:,此方法会在其视图层级结构中的每个视图上调用pointInside:withEvent:(该方法用来判断点击事件发生的位置是否处于当前视图范围内,以确定用户是不是点击了当前视图),如果pointInside:withEvent:返回YES,则继续逐级调用,直到找到touch操作发生的位置,这个视图也就是要找的hit-test view。
hitTest:withEvent:方法的处理流程如下:
首先调用当前视图的pointInside:withEvent:方法判断触摸点是否在当前视图内;
若返回NO,则hitTest:withEvent:返回nil;
若返回YES,则向当前视图的所有子视图(subviews)发送hitTest:withEvent:消息,所有子视图的遍历顺序是从最顶层视图一直到到最底层视图,即从subviews数组的末尾向前遍历,直到有子视图返回非空对象或者全部子视图遍历完毕;
若第一次有子视图返回非空对象,则hitTest:withEvent:方法返回此对象,处理结束;
如所有子视图都返回非,则hitTest:withEvent:方法返回自身(self)。
























 1897
1897

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








