一、例子
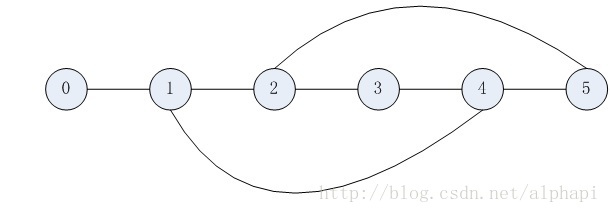
如上图,节点0到节点5的最短路径长度为3,有两条最短路径:
路径1:0 — 1 — 4— 5
路径2:0 — 1 — 2— 5
二、相关名称
tempLadder: 存储当前正在计算的路径
canditStack: 存储备选结点的栈
shortestLength: 最短路径长度
startNode: 开始节点
endNode: 终止节点
allShortestPath: 存储startNod与endNode之间的所有的最短路径。
三、约束条件:
1、如果节点node_a在路径tempLadder中,从startNode起,node_a之前的各节点与node_a的距离分别是i,i-1,i-2....1,node_a与终结点的距离为shortestLength-i。
2、遍历与node_a相邻的各个节点,如果结点node_i已经在当前路径tempLadder或者在canditStack中,或者与endNode的距离大于node_a与endNode的距离,则应该过滤掉node_i。
四:算法过程:
step1、使用floyd计算结点间的最短距离
step2、输入起点和终点的结点序号
step3、计算起点到终点间的所有最短距离
step3.1
将startNode加入到tempLadder中,再将所有与startNode距离为1,与终结点距离为shortestLength-1的结点加入canditStack中,然后进入step3.2。
step3.2
当canditStack为空时,进入step4。
当canditStack不为空时,从canditStack中取出栈顶元素node,然后进入step3.3。
step3.3
如果node满足条件1,则加入到tempLadder中,如果node与endNode距离为1,则同时将tempLadder加入到allShortestPath,tempLadder进行出栈,然后进入step3.4。
如果node不满足条件1,tempLadder出栈,直到node满足条件1为止,然后将node压入tempLadder中,然后进入step3.4。
step3.4
遍历与node距离为1的节点,如果满足条件2,则过滤掉,否则,加入到canditStack中,进入step3.2。
step4
算法终止。
五、程序
allshortpath.h
#ifndef H_FLOYD
#define H_FLOYD
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 1000
#define NODECOUNT 6 //结点数
typedef char VexType;
struct GraphMatrix
{
int n; //图的顶点个数
VexType *vexs;//顶点信息
int arcs[NODECOUNT][NODECOUNT];//边信息
};
struct ShortPath
{
int a[NODECOUNT][NODECOUNT];
int nextvex[NODECOUNT][NODECOUNT];
};
void floyd(GraphMatrix * pgraph, ShortPath * ppath);
void show_GraphMatirx(GraphMatrix * pgraph, int nodeCount);
void show_path(ShortPath * ppath, int nodeCount);
int shortestPath_2Nodes(int startNode, int endNode, ShortPath *ppath);
//判断结点是否已经存在当前路径中
int inVector(int nodeNum, vector<int> & tempvector, ShortPath *ppath);
int isPostNode(int nodeNum, int endNode, vector<int> & tempvector, ShortPath *ppath);
vector<vector<int>> getAllShortestPath(int startNode, int endNode, ShortPath *ppath, int nodeCount);
#endif
/allshortpath.cpp//
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "allshortpath.h"
void floyd(GraphMatrix * pgraph, ShortPath * ppath)
{
int i,j,k;
for ( i=0; i<pgraph->n; i++ )
{
for ( j=0; j<pgraph->n; j++ )
{
ppath->a[i][j] = pgraph->arcs[i][j];
}
}
for ( k=0; k<pgraph->n; k++ )
{
for ( i=0; i<pgraph->n; i++ )
{
for ( j=0; j<pgraph->n; j++ )
{
if ( (ppath->a[i][k]>=MAX)||(ppath->a[k][j]>=MAX) )
continue;
if ( ppath->a[i][j] > (ppath->a[i][k] + ppath->a[k][j]) )
{
ppath->a[i][j] = ppath->a[i][k] + ppath->a[k][j];
}
}
}
}
}
void show_GraphMatirx(GraphMatrix *pgraph, int nodeCount)
{
int i,j;
for ( i=0; i<nodeCount; i++ )
{
for ( j=0; j<nodeCount; j++ )
{
printf("%5d ",pgraph->arcs[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
void show_path(ShortPath *ppath, int nodeCount)
{
int i, j;
for ( i=0; i<nodeCount; i++ )
{
for ( j=0; j<nodeCount; j++ )
{
printf("%5d ", ppath->a[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
int shortestPath_2Nodes(int startNode, int endNode, ShortPath *ppath)
{
int distance = ppath->a[startNode][endNode];
return distance;
}
vector<vector<int>> getAllShortestPath(int startNode, int endNode, ShortPath *ppath, int nodeCount)
{
int nodeNum = 0;
int tempFromStack;
int tempFromLadder;
int shortestLength;
vector<int> canditNodeStack;
vector<int> tempLadder;
vector<vector<int>> resultvector;
if ( startNode == endNode )
{
return resultvector;
}
tempLadder.push_back(startNode);
if ( ppath->a[startNode][endNode] == 1 )
{
tempLadder.push_back(endNode);
resultvector.push_back(tempLadder);
return resultvector;
}
shortestLength = shortestPath_2Nodes(startNode, endNode, ppath);
for ( nodeNum = 0; nodeNum < nodeCount; nodeNum++ )
{
if ( shortestPath_2Nodes(nodeNum, startNode, ppath) == 1 )
{
canditNodeStack.push_back(nodeNum);
}
}
while ( canditNodeStack.size() > 0 )
{
tempFromStack = canditNodeStack.back();
canditNodeStack.pop_back();
int d_temp_end = shortestPath_2Nodes(tempFromStack, endNode, ppath);
if ( d_temp_end == 0 && tempLadder.size() == shortestLength )
{
tempLadder.push_back(tempFromStack);
resultvector.push_back(tempLadder);
tempLadder.pop_back();
}
else
{
if ( isPostNode(tempFromStack, endNode, tempLadder, ppath) == 1 )
{
if ( tempLadder.size() <= shortestLength )
{
tempLadder.push_back(tempFromStack);
}
}
else
{
while ( tempLadder.size() > 0 && tempLadder.back() != startNode )
{
tempLadder.pop_back();
if ( isPostNode(tempFromStack, endNode, tempLadder, ppath) == 1 )
{
tempLadder.push_back(tempFromStack);
break;
}
}
}
}
for ( nodeNum = 0; nodeNum < nodeCount; nodeNum++ )
{
int i2 = shortestPath_2Nodes(tempFromStack, nodeNum, ppath);
int i3 = shortestPath_2Nodes(endNode, nodeNum, ppath);
if ( i2 == 1 && d_temp_end > i3 && !inVector(nodeNum, canditNodeStack, ppath) && !inVector(nodeNum, tempLadder, ppath))
{
canditNodeStack.push_back(nodeNum);
}
}
}
return resultvector;
}
int inVector(int nodeNum, vector<int> & tempvector, ShortPath *ppath)
{
int exist = 0;
vector<int>::iterator it;
for ( it=tempvector.begin(); it!=tempvector.end(); it++ )
{
if(shortestPath_2Nodes(*it, nodeNum, ppath)==0)
{
exist = 1;
break;
}
}
return exist;
}
int isPostNode(int nodeNum, int endNode, vector<int> & tempvector, ShortPath *ppath)
{
if ( nodeNum == tempvector.back() )
{
return 0;
}
int flag = 1;
int d_temp_end = shortestPath_2Nodes(nodeNum, endNode, ppath);
int d_back_end = shortestPath_2Nodes(tempvector.back(), endNode, ppath);
if ( d_temp_end >= d_back_end )
{
return 0;
}
for ( int i = tempvector.size() - 1; i >= 0; i-- )
{
if ( shortestPath_2Nodes(nodeNum, tempvector.at(i), ppath) != (tempvector.size() - i) )
{
flag = 0;
}
}
return flag;
}
main.cpp
#include <set>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include "allshortpath.h"
using namespace std;
void CalAllShortestPath()
{
int i=0;
int j=0;
GraphMatrix *pgraph = (GraphMatrix *)malloc(sizeof(struct GraphMatrix));
ShortPath *ppath = (ShortPath *)malloc(sizeof(struct ShortPath));
if ( pgraph==NULL || ppath==NULL )
{
return;
}
pgraph->n = NODECOUNT;
初始化无向无权图的邻接矩阵///
int arcs[NODECOUNT][NODECOUNT]={0,1,MAX,MAX,MAX,MAX, 1,0,1,MAX,1,MAX, MAX,1,0,1,MAX,1, MAX,MAX,1,0,1,MAX, MAX,1,MAX,1,0,1, MAX,MAX,1,MAX,1,0};
//int arcs[POINTNUM][POINTNUM]={0,1,1,MAX,1,MAX,MAX,MAX, 1,0,1,1,MAX,MAX,MAX,MAX, 1,1,0,1,MAX,MAX,MAX,MAX, MAX,1,1,0,MAX,1,MAX,MAX, 1,MAX,MAX,MAX,0,MAX,1,1, MAX,MAX,MAX,1,MAX,0,1,1, MAX,MAX,MAX,MAX,1,1,0,1, MAX,MAX,MAX,MAX,1,1,1,0};
for ( i = 0; i < NODECOUNT; i++ )
{
for ( j = 0; j < NODECOUNT; j++ )
{
pgraph->arcs[i][j] = arcs[i][j];
}
}
show_GraphMatirx(pgraph, NODECOUNT);
floyd(pgraph, ppath);
show_path(ppath, NODECOUNT);
int startNode = 5;
int endNod = 0;
vector<vector<int>> result = getAllShortestPath(startNode, endNod, ppath, NODECOUNT);
vector<int> eachone;
vector<int>::iterator eachI;
set<int>::iterator it;
vector<vector<int>>::iterator resultIt;
for ( resultIt=result.begin(); resultIt!=result.end(); resultIt++ )
{
eachone = *resultIt;
for ( eachI=eachone.begin(); eachI!=eachone.end(); eachI++ )
{
cout<<*eachI<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
int main()
{
CalAllShortestPath();
system("pause");
return 0;
}




















 1901
1901











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








