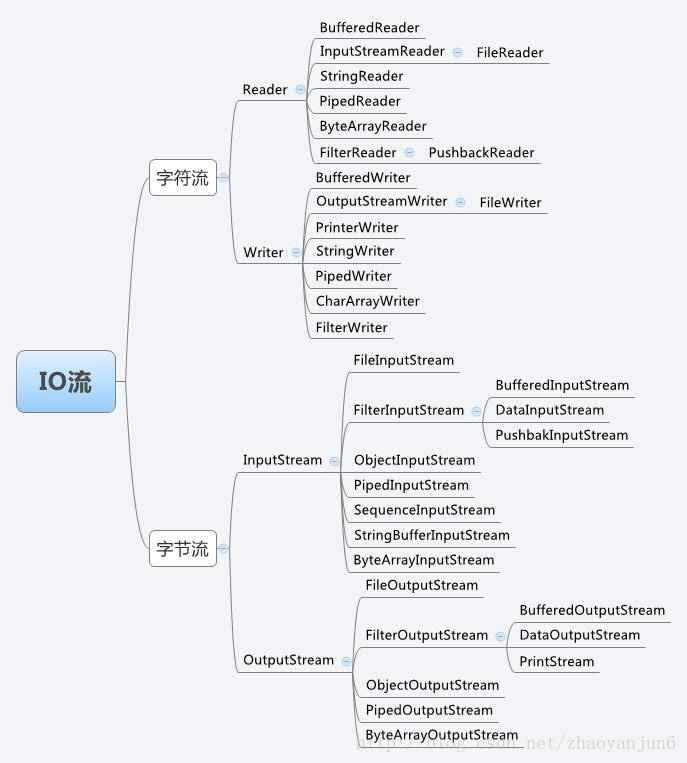
Java流类图结构:
流的概念和作用
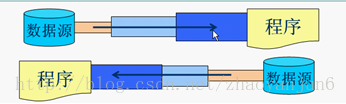
流是一组有顺序的,有起点和终点的字节集合,是对数据传输的总称或抽象。即数据在两设备间的传输称为流,流的本质是数据传输,根据数据传输特性将流抽象为各种类,方便更直观的进行数据操作。
IO流的分类
- 根据处理数据类型的不同分为:字符流和字节流
- 根据数据流向不同分为:输入流和输出流
字符流和字节流
字符流的由来: 因为数据编码的不同,而有了对字符进行高效操作的流对象。本质其实就是基于字节流读取时,去查了指定的码表。 字节流和字符流的区别:
- 读写单位不同:字节流以字节(8bit)为单位,字符流以字符为单位,根据码表映射字符,一次可能读多个字节。
处理对象不同:字节流能处理所有类型的数据(如图片、avi等),而字符流只能处理字符类型的数据。
- 字节流:一次读入或读出是8位二进制。
字符流:一次读入或读出是16位二进制。
设备上的数据无论是图片或者视频,文字,它们都以二进制存储的。二进制的最终都是以一个8位为数据单元进行体现,所以计算机中的最小数据单元就是字节。意味着,字节流可以处理设备上的所有数据,所以字节流一样可以处理字符数据。
结论:只要是处理纯文本数据,就优先考虑使用字符流。 除此之外都使用字节流。
输入流和输出流
输入流只能进行读操作,输出流只能进行写操作,程序中需要根据待传输数据的不同特性而使用不同的流。
输入字节流 InputStream
InputStream是所有的输入字节流的父类,它是一个抽象类。ByteArrayInputStream、StringBufferInputStream、FileInputStream是三种基本的介质流,它们分别从Byte 数组、StringBuffer、和本地文件中读取数据。PipedInputStream是从与其它线程共用的管道中读取数据,与Piped 相关的知识后续单独介绍。ObjectInputStream和所有FilterInputStream的子类都是装饰流(装饰器模式的主角)。
输出字节流 OutputStream
OutputStream是所有的输出字节流的父类,它是一个抽象类。ByteArrayOutputStream、FileOutputStream是两种基本的介质流,它们分别向Byte 数组、和本地文件中写入数据。PipedOutputStream是向与其它线程共用的管道中写入数据。ObjectOutputStream和所有FilterOutputStream的子类都是装饰流。
总结:
- 输入流:InputStream或者Reader:从文件中读到程序中;
- 输出流:OutputStream或者Writer:从程序中输出到文件中;
节点流
节点流:直接与数据源相连,读入或读出。
直接使用节点流,读写不方便,为了更快的读写文件,才有了处理流。
常用的节点流
- 父 类 :
InputStream、OutputStream、Reader、Writer - 文 件 :
FileInputStream、FileOutputStrean、FileReader、FileWriter文件进行处理的节点流 - 数 组 :
ByteArrayInputStream、ByteArrayOutputStream、CharArrayReader、CharArrayWriter对数组进行处理的节点流(对应的不再是文件,而是内存中的一个数组) - 字符串 :
StringReader、StringWriter对字符串进行处理的节点流 - 管 道 :
PipedInputStream、PipedOutputStream、PipedReader、PipedWriter对管道进行处理的节点流
处理流
处理流和节点流一块使用,在节点流的基础上,再套接一层,套接在节点流上的就是处理流。如BufferedReader.处理流的构造方法总是要带一个其他的流对象做参数。一个流对象经过其他流的多次包装,称为流的链接。
常用的处理流
- 缓冲流:
BufferedInputStrean、BufferedOutputStream、BufferedReader、BufferedWriter增加缓冲功能,避免频繁读写硬盘。 - 转换流:
InputStreamReader、OutputStreamReader实现字节流和字符流之间的转换。 - 数据流:
DataInputStream、DataOutputStream等-提供将基础数据类型写入到文件中,或者读取出来。
转换流
InputStreamReader 、OutputStreamWriter 要InputStream或OutputStream作为参数,实现从字节流到字符流的转换。
构造函数
实战演练
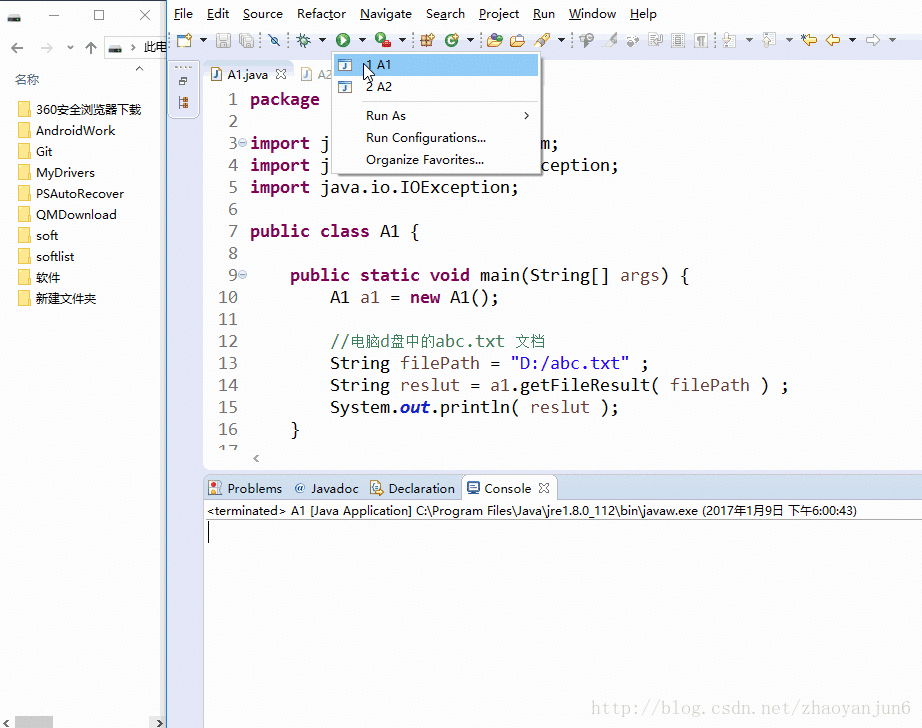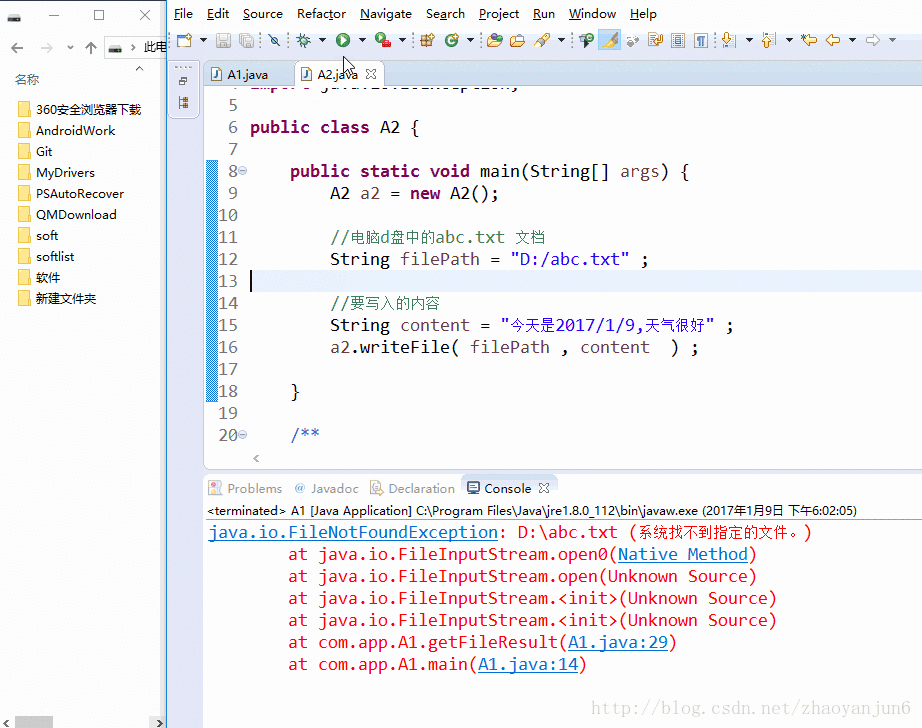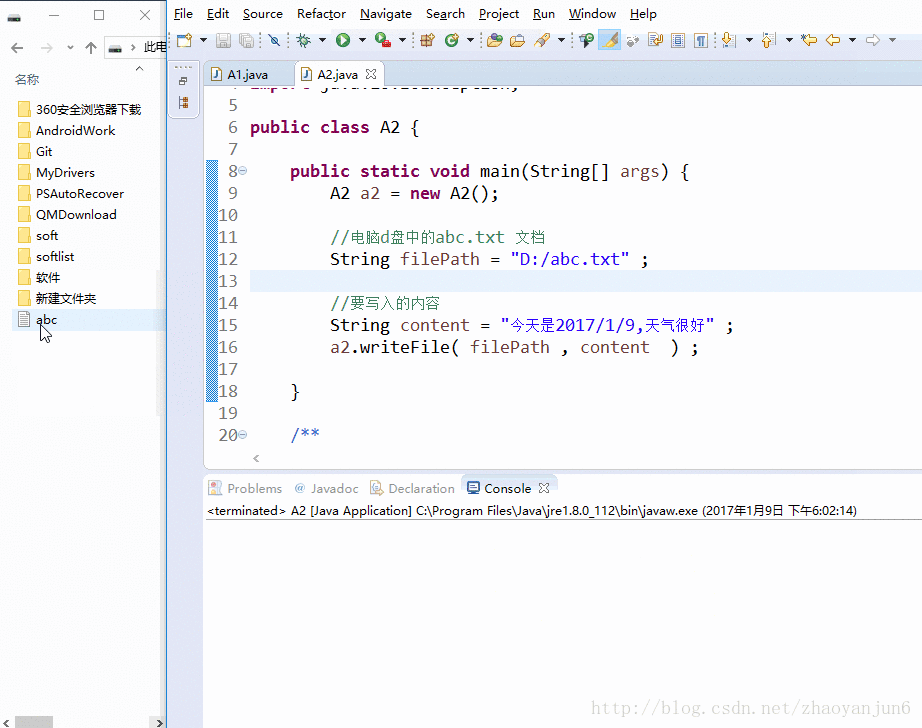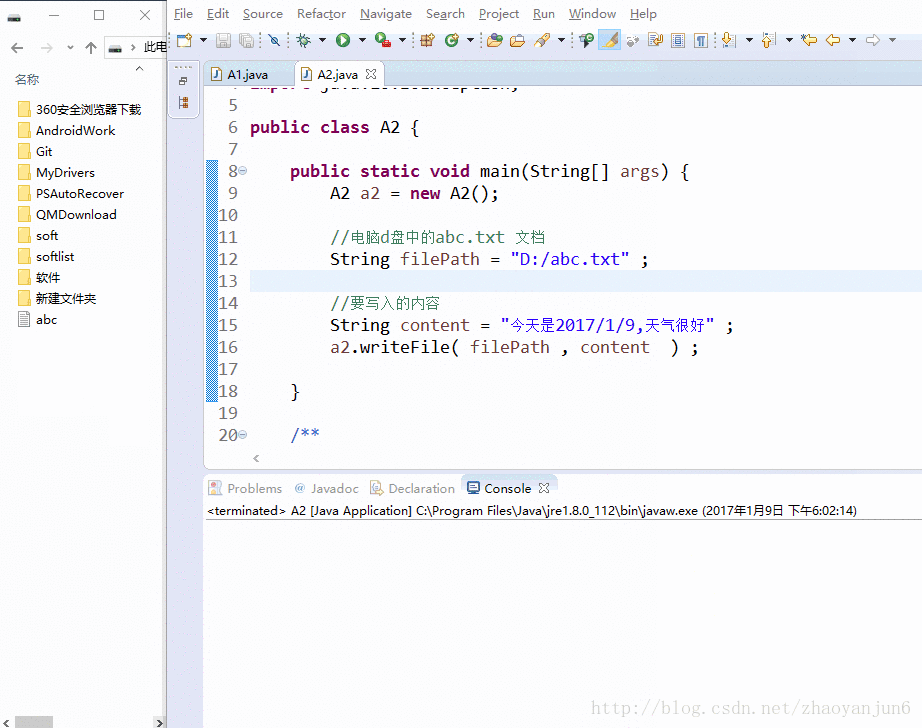
- FileInputStream类的使用:读取文件内容
1 package com.app; 2 3 import java.io.FileInputStream; 4 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 7 public class A1 { 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 A1 a1 = new A1(); 11 12 //电脑d盘中的abc.txt 文档 13 String filePath = "D:/abc.txt" ; 14 String reslut = a1.readFile( filePath ) ; 15 System.out.println( reslut ); 16 } 17 18 19 /** 20 * 读取指定文件的内容 21 * @param filePath : 文件的路径 22 * @return 返回的结果 23 */ 24 public String readFile( String filePath ){ 25 FileInputStream fis=null; 26 String result = "" ; 27 try { 28 // 根据path路径实例化一个输入流的对象 29 fis = new FileInputStream( filePath ); 30 31 //2. 返回这个输入流中可以被读的剩下的bytes字节的估计值; 32 int size = fis.available() ; 33 //3. 根据输入流中的字节数创建byte数组; 34 byte[] array = new byte[size]; 35 //4.把数据读取到数组中; 36 fis.read( array ) ; 37 38 //5.根据获取到的Byte数组新建一个字符串,然后输出; 39 result = new String(array); 40 41 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 42 e.printStackTrace(); 43 }catch (IOException e) { 44 e.printStackTrace(); 45 }finally{ 46 if ( fis != null) { 47 try { 48 fis.close(); 49 } catch (IOException e) { 50 e.printStackTrace(); 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 55 return result ; 56 } 57 58 59 } 60 61
- FileOutputStream 类的使用:将内容写入文件
1 package com.app;
2 import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
3 import java.io.FileOutputStream;
4 import java.io.IOException;
5
6 public class A2 {
7
8 public static void main(String[] args) {
9 A2 a2 = new A2();
10
11 //电脑d盘中的abc.txt 文档
12 String filePath = "D:/abc.txt" ;
13
14 //要写入的内容
15 String content = "今天是2017/1/9,天气很好" ;
16 a2.writeFile( filePath , content ) ;
17
18 }
19
1 /**
2 * 根据文件路径创建输出流
3 * @param filePath : 文件的路径
4 * @param content : 需要写入的内容
5 */
6 public void writeFile( String filePath , String content ){
7 FileOutputStream fos = null ;
8 try {
9 //1、根据文件路径创建输出流
10 fos = new FileOutputStream( filePath );
11
12 //2、把string转换为byte数组;
13 byte[] array = content.getBytes() ;
14 //3、把byte数组输出;
15 fos.write( array );
16
17 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
18 e.printStackTrace();
19 }catch (IOException e) {
20 e.printStackTrace();
21 }finally{
22 if ( fos != null) {
23 try {
24 fos.close();
25 } catch (IOException e) {
26 e.printStackTrace();
27 }
28 }
29 }
30 }
31
32
33 }
34 注意:
- 在实际的项目中,所有的IO操作都应该放到子线程中操作,避免堵住主线程。
FileInputStream在读取文件内容的时候,我们传入文件的路径("D:/abc.txt"), 如果这个路径下的文件不存在,那么在执行readFile()方法时会报FileNotFoundException异常。FileOutputStream在写入文件的时候,我们传入文件的路径("D:/abc.txt"), 如果这个路径下的文件不存在,那么在执行writeFile()方法时, 会默认给我们创建一个新的文件。还有重要的一点,不会报异常。
效果图:
- 综合练习,实现复制
1 package com.app; 2 import java.io.FileInputStream; 3 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 4 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 7 public class A3 { 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 A3 a2 = new A3(); 11 12 //电脑d盘中的cat.png 图片的路径 13 String filePath1 = "D:/cat.png" ; 14 15 //电脑e盘中的cat.png 图片的路径 16 String filePath2 = "E:/cat.png" ; 17 18 //复制文件 19 a2.copyFile( filePath1 , filePath2 ); 20 21 } 22 23 /** 24 * 文件复制 25 * @param filePath_old : 需要复制文件的路径 26 * @param filePath_new : 复制文件存放的路径 27 */ 28 public void copyFile( String filePath_old , String filePath_new){ 29 FileInputStream fis=null ; 30 FileOutputStream fout = null ; 31 try { 32 // 根据path路径实例化一个输入流的对象 33 fis = new FileInputStream( filePath_old ); 34 35 //2. 返回这个输入流中可以被读的剩下的bytes字节的估计值; 36 int size = fis.available() ; 37 //3. 根据输入流中的字节数创建byte数组; 38 byte[] array = new byte[size]; 39 //4.把数据读取到数组中; 40 fis.read( array ) ; 41 42 //5、根据文件路径创建输出流 43 fout = new FileOutputStream( filePath_new ) ; 44 45 //5、把byte数组输出; 46 fout.write( array ); 47 48 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 49 e.printStackTrace(); 50 }catch (IOException e) { 51 e.printStackTrace(); 52 }finally{ 53 if ( fis != null) { 54 try { 55 fis.close(); 56 } catch (IOException e) { 57 e.printStackTrace(); 58 } 59 } 60 if ( fout != null ) { 61 try { 62 fout.close(); 63 } catch (IOException e) { 64 e.printStackTrace(); 65 } 66 } 67 } 68 } 69 } 70
补充:
1 package 文件的删除与地址; 2 3 import java.io.File; 4 import java.io.FileInputStream; 5 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 6 import java.io.FileReader; 7 import java.io.IOException; 8 9 public class Test { 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ 12 // boolean nfl=true; 13 // // TODO Auto-generated method stub 14 File file new File("."); 15 //File nfl1=new File("E:/1.txt"); 16 //if(nfl1.exists()) { 17 // nfl1.delete(); 18 //}else { 19 // nfl1.createNewFile(); 20 //} 21 // 22 //System.out.println("获取文件名"+nfl1.getName()); 23 //System.out.println("获取相对路径"+nfl1.getParent()); 24 //System.out.println("获取绝对路径"+nfl1.getAbsolutePath()); 25 //System.out.println("获取上一级路径"+nfl1.getAbsoluteFile().getParent()); 26 //字节流 27 // FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(new File("E:/1.txt")); 28 // byte[] buf=new byte[10]; 29 // int rd=0; 30 // String ret=""; 31 // fis.read(buf,0,5); 32 // ret+=new String (buf,0,5); 33 // System.out.println(buf[0]); 34 // 35 // } 36 //字符流 37 // FileReader fis=new FileReader(new File("E:/1.txt")); 38 // char[] buf=new char[10]; 39 // int rd=0; 40 // String ret=""; 41 // while((rd=fis.read(buf))>0) { 42 fis.read(buf,0,5); 43 // ret+=new String (buf,0,5); 44 // System.out.println(buf[0]); 45 // System.out.println(buf[]); 46 // 47 //} 48 //写入文件 49 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("E:/2.txt"); 50 for(int i=90;i<120;i++) { 51 fos.write(i);//写入 52 } 53 for(int i=2000;i<20000;i++) { 54 fos.write(i); 55 } 56 57 System.out.println(fos); 58 } 59 } 60
日志:
1 Random rnd=new Random(); 2 FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("E:/2.txt"); 3 SimpleDateFormat sdb=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH-mm-ss"); 4 for(int i=0;i<10;i++) { 5 Thread.currentThread().sleep(rnd.nextInt(1000)); 6 String s=sdb.format(new Date())+"张三准备第"+i+"次"; 7 fw.write(s); 8 } 9 fw.close(); 10 }
结果:
1 2019-08-15 19-41-58张三准备第0次2019-08-15 19-41-59张三准备第1次2019-08-15 19-42-00张三准备第2次2019-08-15 19-42-00张三准备第3次2019-08-15 19-42-00张三准备第4次2019-08-15 19-42-01张三准备第5次2019-08-15 19-42-02张三准备第6次2019-08-15 19-42-03张三准备第7次2019-08-15 19-42-03张三准备第8次2019-08-15 19-42-03张三准备第9次






















 802
802

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








