ABOUT THESE VIDEOS
These demo videos show how to configure and test a Standard ACL on a network. You will be able to perform these tasks in a simulated network.
During the videos, you may want to refer to these illustrations:
Lab Topology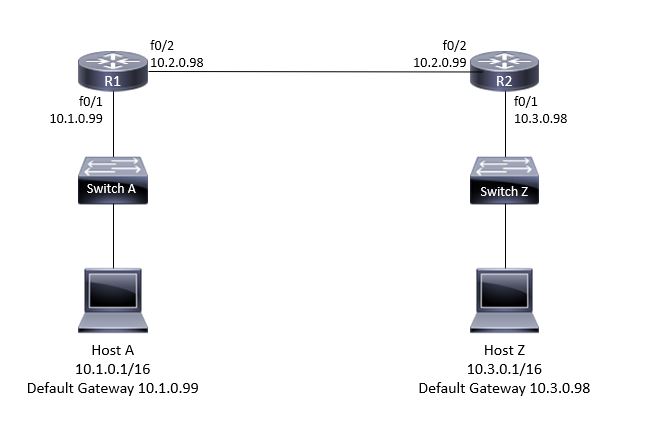
Router 1 Routing Table
Router 2 Routing Table
Pinging Without an ACL
Let's take a look at host A's configuration.
Host A has an IP address of ten one zero one, a subnet mask of slash sixteen,
and the default gateway of ten one zero ninety-nine.
Let's clear host A's ARP cache, and send a ping to host Z.
[silence]
Host A ARPs, looking for the Mac address of its gateway,
host A's default gateway sends its MAC address back to host A,
and the ICMP echo requests are now sent with the destination IP address of host Z,
but the destination MAC address of host A's default gateway.
The replies have the source MAC address of the default gateway of host A,
but the source IP address of host Z.
Let's take a look at the path the packets are taking from host A
to host Z, with a trace route utility.
The first hop is host A's default gateway of ten one zero ninety-nine,
the next hop is ten two zero ninety-nine on a different router,
and then finally after those two hops,
we reach the actual destination host Z. There are no ACLs,
Access Control Lists, on either of the routers.
So, the packets going through the routers in either direction are not filtered.
We're going to start off with a standard ACL that blocks all traffic from any host
on the ten one zero zero slash sixteen subnet,
to any host on the ten three zero zero slash sixteen subnet.
Standard ACLs should be placed as close as possible to the destination,
to prevent unnecessary filtering.
So, we're going to make this an outbound ACL on ten three zero ninety-eight.
I've established a console connection to R two, and I'm in the router,
using Putty, as my terminal emulator.
From user exec mode, I'm going to go into privileged exec mode.
I need to be in this mode to get to the next mode, global configuration mode.
This is where Access Control Lists are configured on Cisco routers.
Configuring and Testing a Standard ACL
>> Let's configure our ACL.
[silence]
Access dash list one, which identifies this as a standard ACL, deny, which is the action,
ten one zero zero, with the wildcard mask
of zero zero two fifty-five two fifty-five means any packets that match this pattern,
starting with the first octet of ten, and the second octet of one,
we don't care about the third or fourth octets.
Let's go ahead and execute this statement.
With just this statement, in the ACL, what will be blocked?
At this point, nothing, since we haven't applied the ACL to an interface,
but let's say we apply it as an outbound ACL on int F zero one
of router two, what will be blocked?
If you're thinking traffic from ten one zero zero slash sixteen, that's not all.
Actually, all traffic from any network will be blocked.
There is an implicit deny any at the bottom of every standard ACL,
blocking traffic not met by any ACL statement.
In this case, all traffic not meeting my explicitly configured statement,
will match the implicit deny any at the bottom of the ACL.
I'm going to add one more line to our ACL.
Now packets that don't meet the first statement will match the second statement,
and will be allowed to exit the F zero slash one interface of router two
into the ten three zero zero slash sixteen subnet.
Now it's time to apply the ACL to an interface.
[silence]
I'm applying it as an outbound ACL on interface F zero slash one,
outbound meaning from the router's perspective,
which is actually inbound, as far as the network goes.
You'll notice the syntax is a little bit different when applying the access control list
to an interface, but the number must match the number of the actual access control list.
Let's verify that the ACL has been properly applied to the interface.
[silence]
It has.
And now for the moment you've all been waiting for, from host A,
let's once again attempt a ping to host Z, this time, with the access control list in place.
Uh oh, destination unreachable, communication administratively filtered.
This ICMP error message comes from ten two zero ninety-nine,
which is interface F zero slash two, on router two, for closer interface
to host A. The access control list we wrote and applied
on router two denied the ping from host A to host Z. Success!




















 1343
1343











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








