[root@k8s6 proc]# ps aux|grep -v PID|sort -rn -k +3|head -5 root 921 0.4 0.9 582140 38532 ? Ssl 17:19 0:29 /usr/bin/dockerd root 691 0.2 0.1 305296 6308 ? Ssl 17:19 0:16 /usr/bin/vmtoolsd root 1206 0.1 0.1 357556 6368 ? Ssl 17:19 0:12 docker-containerd -l unix:///var/run/docker/libcontainerd/docker-containerd.sock --metrics-interval=0 --start-timeout 2m --state-dir /var/run/docker/libcontainerd/containerd --shim docker-containerd-shim --runtime docker-runc root 920 0.0 0.4 562388 18616 ? Ssl 17:19 0:01 /usr/bin/python -Es /usr/sbin/tuned -l -P root 919 0.0 0.1 106000 4076 ? Ss 17:19 0:00 /usr/sbin/sshd -D [root@k8s6 proc]# [root@k8s6 proc]# [root@k8s6 proc]# ps aux|head -1 USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
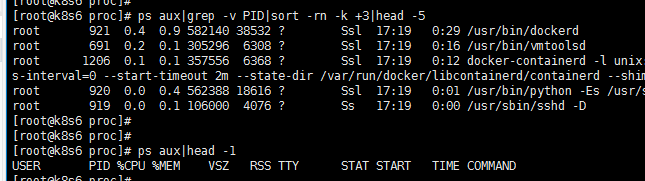
一、用python实现前5个进程的监控
1)用该命令把内容实时更新推送至该文件
ps aux|grep -v PID|sort -rn -k +3|head -5 > test.txt
2)用python获取该文件的内容


status = [] with open('test.txt',mode='r',encoding='utf-8') as f: for line in f: line = line.split('\n')[0].split(' ') for li in line: if len(li) != 0: pass else: line.remove(li) status.append(line) for i in status: print(i)
3)利用传值的方式获取每个进程的cpu


import sys run = sys.argv cmd = int(run[1]) - 1 status = [] with open('test.txt',mode='r',encoding='utf-8') as f: for line in f: line = line.split('\n')[0].split(' ') for li in line: if len(li) != 0: pass else: line.remove(li) status.append(line) print(status[cmd][2])
指定获取每行的cpu进程
python cpu_test.py 1 # 第1高进程 python cpu_test.py 2 # 第2高进程 python cpu_test.py 3 # 第3高进程 python cpu_test.py 4 # 第4高进程 python cpu_test.py 5 # 第5高进程
4)修改脚本文件,也可以实现获取到每个进程所占用的内存空间


import sys run = sys.argv cmd = int(run[1]) - 1 status = [] with open('test.txt',mode='r',encoding='utf-8') as f: for line in f: line = line.split('\n')[0].split(' ') for li in line: if len(li) != 0: pass else: line.remove(li) status.append(line) print(status[cmd][3])
获取每行的所占用的内存
python cpu_test.py 1 # 第1高进程 python cpu_test.py 2 # 第2高进程 python cpu_test.py 3 # 第3高进程 python cpu_test.py 4 # 第4高进程 python cpu_test.py 5 # 第5高进程
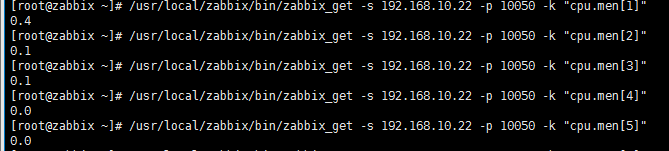
二、完善脚本,直接获取结果至内存
1) 针对cpu


import sys import subprocess run = sys.argv cmd=int(run[1]) - 1 status = [] obj=subprocess.Popen('ps aux|grep -v PID|sort -rn -k +3|head -3', shell=True, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE ) result = obj.stdout status = [] for line in result: line = line.split('\n')[0].split(' ') for li in line: if len(li) != 0: pass else: line.remove(li) status.append(line) result= float(status[cmd][2]) * 100 print(result)
执行 python cpu.py 1 到 3
2)针对men


import sys import subprocess run = sys.argv cmd=int(run[1]) - 1 status = [] obj=subprocess.Popen('ps aux|grep -v PID|sort -rn -k +3|head -3', shell=True, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE ) result = obj.stdout status = [] for line in result: line = line.split('\n')[0].split(' ') for li in line: if len(li) != 0: pass else: line.remove(li) status.append(line) result= float(status[cmd][3]) * 100 print(result)
执行 python men.py 1 到 3
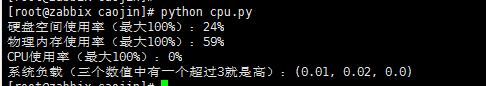
三、监控cpu,内存


#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- - import os, time last_worktime=0 last_idletime=0 def get_cpu(): global last_worktime, last_idletime f=open("/proc/stat","r") line="" while not "cpu " in line: line=f.readline() f.close() spl=line.split(" ") worktime=int(spl[2])+int(spl[3])+int(spl[4]) idletime=int(spl[5]) dworktime=(worktime-last_worktime) didletime=(idletime-last_idletime) rate=float(dworktime)/(didletime+dworktime) last_worktime=worktime last_idletime=idletime if(last_worktime==0): return 0 return rate def get_mem_usage_percent(): try: f = open('/proc/meminfo', 'r') for line in f: if line.startswith('MemTotal:'): mem_total = int(line.split()[1]) elif line.startswith('MemFree:'): mem_free = int(line.split()[1]) elif line.startswith('Buffers:'): mem_buffer = int(line.split()[1]) elif line.startswith('Cached:'): mem_cache = int(line.split()[1]) elif line.startswith('SwapTotal:'): vmem_total = int(line.split()[1]) elif line.startswith('SwapFree:'): vmem_free = int(line.split()[1]) else: continue f.close() except: return None physical_percent = usage_percent(mem_total - (mem_free + mem_buffer + mem_cache), mem_total) virtual_percent = 0 if vmem_total > 0: virtual_percent = usage_percent((vmem_total - vmem_free), vmem_total) return physical_percent, virtual_percent def usage_percent(use, total): try: ret = (float(use) / total) * 100 except ZeroDivisionError: raise Exception("ERROR - zero division error") return ret statvfs = os.statvfs('/') total_disk_space = statvfs.f_frsize * statvfs.f_blocks free_disk_space = statvfs.f_frsize * statvfs.f_bfree disk_usage = (total_disk_space - free_disk_space) * 100.0 / total_disk_space disk_usage = int(disk_usage) disk_tip = "硬盘空间使用率(最大100%):"+str(disk_usage)+"%" print(disk_tip) mem_usage = get_mem_usage_percent() mem_usage = int(mem_usage[0]) mem_tip = "物理内存使用率(最大100%):"+str(mem_usage)+"%" print(mem_tip) cpu_usage = int(get_cpu()*100) cpu_tip = "CPU使用率(最大100%):"+str(cpu_usage)+"%" print(cpu_tip) load_average = os.getloadavg() load_tip = "系统负载(三个数值中有一个超过3就是高):"+str(load_average) print(load_tip)





















 430
430











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








