二叉堆,是一个满二叉树,满足堆的性质。即父节点大于等于子节点(max heap)或者是父节点小于等于子节点(min heap)。二叉堆的如上性质常用于优先队列(priority queue)或是用于堆排序。
由于max heap 与min heap类似,下文只针对min heap进行讨论和实现。
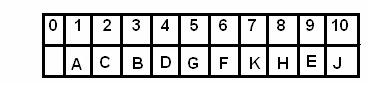
如上图,是根据字母的ASCII码建立的最小堆。
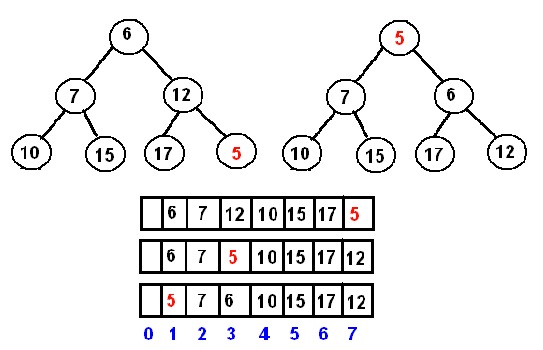
我们用数组对满二叉树采用宽度优先遍历存储堆结构,如下图所示:
从数组下标1开始存储堆,这样的处理方式可以得到如下性质:
1.堆中的每个父节点k,他的两个子节点为k*2和k*2+1
2.堆中的每个子节点k,他的父节点为k/2
堆的插入:当向堆中插入一个元素时,首先将新添加的元素放入数组的末尾,然后使用percolatingUp方法,将新添加的元素逐层向上移动至合适位置。如下图所示:
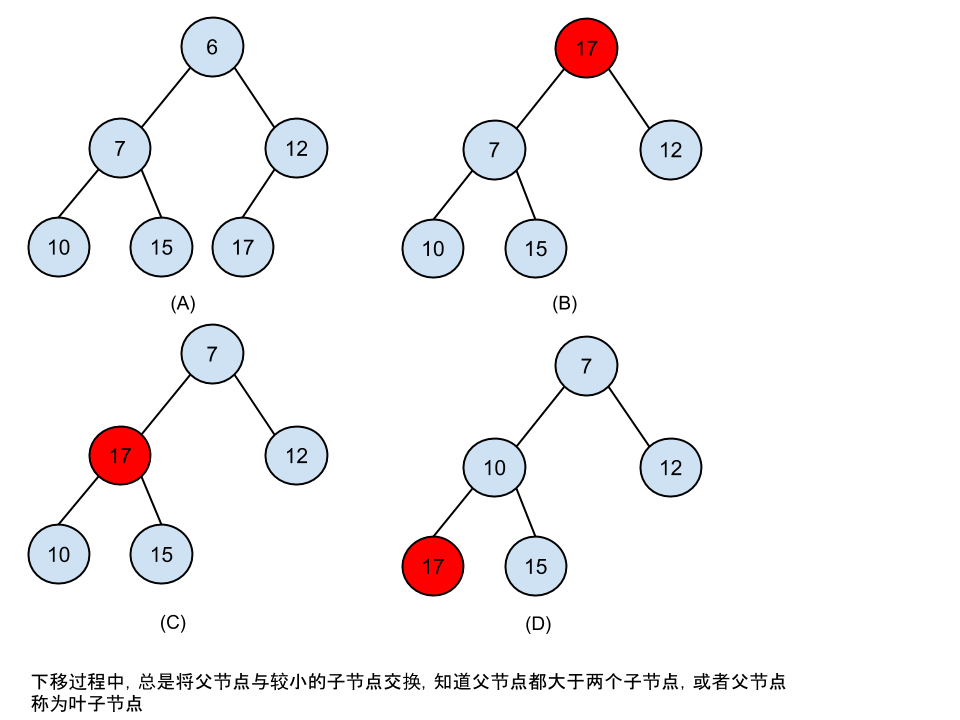
堆的删除:当将堆顶元素删除时,首先将数组中末尾的元素放入对顶,然后使用percolatingDown方法,将堆顶元素逐层向下移动至合适位置。如下图所示:
堆的构建:将对大小为k的数组,从第k/2个元素开始(第1个到第k/2个元素有子节点),依次使用porcelatingUp将元素向上调整,其时间复杂度O(k)。
堆排序的思想是:将待排序的数组转成堆(堆的构建),删除root节点(获取最小元素),重构(porcelatingDown),删除root节点(获取第二小元素),重构(porcelatingDown),...一直到堆中不再有元素。
堆操作的时间复杂度(N表示元素个数):
建堆:O(N)
添加:O(logN)
删除:O(logN)
堆排序:O(NlogN)
堆及堆排序的java实现:
/****************************************************************************
* This demonstrates binary heap operations along with the heapSort.
*
*****************************************************************************/
import java.util.*;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public class Heap<AnyType extends Comparable<AnyType>>
{
private static final int CAPACITY = 2;
private int size; // Number of elements in heap
private AnyType[] heap; // The heap array
public Heap()
{
size = 0;
heap = (AnyType[]) new Comparable[CAPACITY];
}
/**
* Construct the binary heap given an array of items.
*/
public Heap(AnyType[] array)
{
size = array.length;
heap = (AnyType[]) new Comparable[array.length+1];
System.arraycopy(array, 0, heap, 1, array.length);//we do not use 0 index
buildHeap();
}
/**
* runs at O(size)
*/
private void buildHeap()
{
for (int k = size/2; k > 0; k--)
{
percolatingDown(k);
}
}
private void percolatingDown(int k)
{
AnyType tmp = heap[k];
int child;
for(; 2*k <= size; k = child)
{
child = 2*k;
if(child != size &&
heap[child].compareTo(heap[child + 1]) > 0) child++;
if(tmp.compareTo(heap[child]) > 0) heap[k] = heap[child];
else
break;
}
heap[k] = tmp;
}
/**
* Sorts a given array of items.
*/
public void heapSort(AnyType[] array)
{
size = array.length;
heap = (AnyType[]) new Comparable[size+1];
System.arraycopy(array, 0, heap, 1, size);
buildHeap();
for (int i = size; i > 0; i--)
{
AnyType tmp = heap[i]; //move top item to the end of the heap array
heap[i] = heap[1];
heap[1] = tmp;
size--;
percolatingDown(1);
}
for(int k = 0; k < heap.length-1; k++)
array[k] = heap[heap.length - 1 - k];
}
/**
* Deletes the top item
*/
public AnyType deleteMin() throws RuntimeException
{
if (size == 0) throw new RuntimeException();
AnyType min = heap[1];
heap[1] = heap[size--];
percolatingDown(1);
return min;
}
/**
* Inserts a new item
*/
public void insert(AnyType x)
{
if(size == heap.length - 1) doubleSize();
//Insert a new item to the end of the array
int pos = ++size;
//Percolate up
for(; pos > 1 && x.compareTo(heap[pos/2]) < 0; pos = pos/2 )
heap[pos] = heap[pos/2];
heap[pos] = x;
}
private void doubleSize()
{
AnyType [] old = heap;
heap = (AnyType []) new Comparable[heap.length * 2];
System.arraycopy(old, 1, heap, 1, size);
}
public String toString()
{
String out = "";
for(int k = 1; k <= size; k++) out += heap[k]+" ";
return out;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Heap<String> h = new Heap<String>();
h.insert("p");
h.insert("r");
h.insert("i");
h.insert("o");
System.out.println(h);
h.deleteMin();
System.out.println(h);
Heap<Integer> tmp = new Heap<Integer>();
Integer[] a = {4,7,7,7,5,0,2,3,5,1};
tmp.heapSort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
}参考:
1.http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~adamchik/15-121/lectures/Binary%20Heaps/heaps.html

























 2380
2380

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








