Specification
class MyFirstSpec extend Specification{
// ...
}
Field
实例字段在feature方法中不共享,每个feature方法中都会重复创建。如果需要共享实例对象,使用@Share注解。
Fixture Methods
def setupSpec() {} // 只执行一次,在第一个`feature`方法前执行
def setup() {} // 在每个`feature`方法前执行
def cleanup() {} // 在每个`feature`方法后执行
def cleanupSpec() {} // 只执行一次,在最后一个`feature`方法执行完后
Feature Methods
def "here is some descriptive info"() {
// blocks
}
组成:
- 设置约束
- 在特定约定下给系统提供激励
- 描述期望来自系统的响应
- 清理约束
Blocks
即feature方法中每一个步骤对应的代码块和标签。包括:given, when, then', expect, cleanup, where
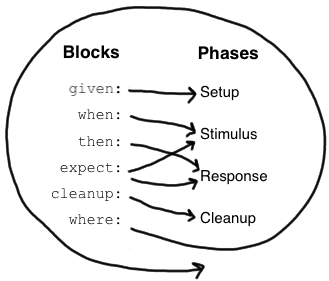
Given Blocks
given:
def stack = new Stack()
def elem = 'push me'
When and Then Blocks
when:
then:
Conditions
when:
stack.push(elem)
then:
!stack.empty
stack.size() == 1
stack.peak() == elem
Exception Conditions
when:
stack.pop()
then:
thron(EmptyStackException)
stack.empty
when:
stack.pop()
then:
def e = thrown(EmptyStackException)
e.cause == null
when:
stack.pop()
then:
EmptyStackException e = thrown()
e.cause == null
def "HashMap accepts null key"() {
given:
def map = new HashMap()
when:
map.put(null, "elem")
then:
notThrown(NullPointerException)
}
Expect Blocks
expect从语义上来说,比then的限定要强,如下两段代码是等价的。
when:
def x = Math.max(1, 2)
then:
x == 2
expect:
Math.max(1, 2) == 2
Cleanup Blocks
given:
def file = new File("/some/path")
file.createNewFile()
//...
cleanup:
file?.delete()
Where Blocks
where块通常处于方法的最后,不可重复执行,用于数据驱动测试
def "computing the maximum of two numbers"() {
expect:
Math.max(a, b) == c
where:
a << [5, 3]
b << [1, 9]
c << [5, 9]
}
Helper Methods
没什么好写的。。。
Using with for expecations
``与用Helper方法不同,使用with语句块不需要显式断言。
def "offered PC matches preferred configuration"() {
when:
def pc = shop.buyPc()
then:
with(pc) {
vendor == "Sunny"
clockRate >= 2333
ram >= 406
os == "Linux"
}
}
Using verifyAll to assert multiple expectations together
可以使用verifyAll对每一个语句做断言检查,即不会因为中途某一个断言失败而直接退出,也叫软断言。
def "offered PC matches preferred configuration"() {
when:
def pc = shop.buyPc()
then:
verifyAll(pc) {
vendor == "Sunny"
clockRate >= 2333
ram >= 406
os == "Linux"
}
}
Specifications as Documentation
规格说明即文档
given: "open a database connection"
// code goes here
Extensions
-[] TODO
Data Driven Testing
Data Tables
class MathSpec extends Specification {
def "maximum of two numbers"() {
expect:
Math.max(a, b) == c
where:
a | b || c
1 | 3 || 3
7 | 4 || 7
0 | 0 || 0
}
}
使用@Unroll注解让每一条数据都有测试报告
Data Pipes
...
where:
a << [1, 7, 0]
b << [3, 4, 0]
c << [3, 7, 0]
使用数据管道, <<右侧接收一个实现了Iterable接口的类型作为data provider
Multi-Variable Data Pipes
@Shared sql = Sql.newInstance("jdbc:h2:mem:", "org.h2.Driver")
def "maximum of two numbers"() {
expect:
Math.max(a, b) == c
where:
[a, b, c] << sql.rows("select a, b, c from maxdata")
}
Interaction Based Testing
基于交互的测试着重于对象的行为,而不是对象的状态。 通过特定的交互动作,如方法调用来观察对象的行为,以及它们协作的表现。
基于交互的测试会依赖mock对象来完成测试工作。
def "should send messages to all subscribers"() {
when:
publisher.send("hello")
then:
1 * subscriber.receive("hello")
1 * subscriber2.receive("hello")
}





















 2097
2097











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








