1. String匹配算法
在一个文本或者较长的一段字符串中,找出一个指定字符串,并返回其位置。指定一个父类AbstractMatch,使用matchAtPosition(String, int)查看是否匹配。
public abstract class AbstractMatch {
protected final String pattern;
public AbstractMatch(String pattern) {
this.pattern = pattern;
}
public abstract int match(String text);
protected boolean matchAtPosition(String text, int position) {
for (int i = 0; i < pattern.length(); i++) {
if (pattern.charAt(i) != text.charAt(position + i)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
2. 简单算法
从初始位置开始,依次分别和pattern的各个文字的字符比较。
public class SimpleMatch extends AbstractMatch {
public SimpleMatch(String pattern) {
super(pattern);
}
public int match(String text) {
for (int position = 0;
position + pattern.length() <= text.length();
position++) {
if (matchAtPosition(text, position)) {
return position;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
3. KMP算法
利用匹配失败后的信息,减少匹配次数。例如模式ababc,文本ababdababc,匹配到position=4的时候,发生错误。
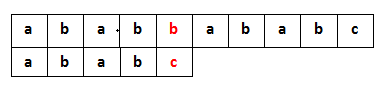
由于头部ab重复,匹配可以直接从position=2开始,还是匹配到position=4的时候,发生错误。
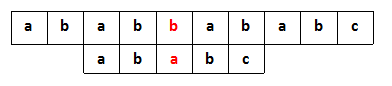
由于没有其他重复的地方,这次匹配从position=4开始
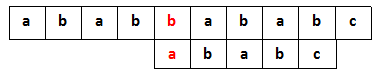
可以看到,在整个过程中,跳过了两次匹配,pattern里面重复的越多,节约的时间越多。
public class KMPMatch extends AbstractMatch {
private int[] prefixArray;
public KMPMatch(String pattern) {
super(pattern);
prefixArray = new int[pattern.length()];
prefixArray[0] = -1;
int matches = -1;
int index = 0;
while (index < pattern.length() - 1) {
if (matches == -1 || pattern.charAt(index) == pattern.charAt(matches)) {
++matches;
++index;
prefixArray[index] = matches;
} else {
matches = prefixArray[matches];
}
}
}
@Override
public int match(String text) {
int index = 0;
int matches = 0;
while (index < text.length() && matches < pattern.length()) {
if (matches == - 1 || text.charAt(index) == pattern.charAt(matches)) {
index++;
matches++;
} else {
matches = prefixArray[matches];
}
}
if (matches == pattern.length()) {
return index - matches;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
}
参考资料: https://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/7041827
相关文章
Java String匹配算法
Java String的intern方法
Java StringTokenizer用法
Java 中的String、StringBuilder以及StringBuffer























 951
951











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








