一、原理
(1)最常用到的轮廓匹配就是字符的匹配,而两个轮廓最最简洁的方式就是比较它们的轮廓矩。
矩就是通过对轮廓上所有点进行积分运算活求和运算而得到一个粗略的特征,对一幅图像I(x,y)
求普通矩公式为:
其中p对应x维度上的矩,q对应y维度上的矩,阶数表示对应的部分的指数,该计算是对轮廓边界上
所有像素(数目为n)进行求和。
各阶矩的物理意义:0阶矩(m00)表示目标区域的质量,m00实际上对应轮廓边界上点的数目。
1阶矩(m01,m10)表示目标区域质心
2阶矩(m02,m20,m11)表示旋转半径
3阶矩(m03,m30,m12,m21,)表示描述目标的方位和斜度,反应目标的扭曲程度
但矩要能够作为一种特征描述方法得到应用,其要与目标空间变换(平移、尺度、旋转)无关。因此在几何
矩的基本定义基础上,进一步构造平移不变。尺度不变和旋转不变矩。
(2)中心矩:构造平移不变性
质心坐标为:

为了使矩具有平移不变性,利用质心坐标构造中心矩:
(3)归一化中心矩;构造尺度不变性。为抵消尺度变化对中心矩的影响,用零阶中心矩u00对其余各个中心矩
进行归一化处理,得到归一化中心矩为:
其中r=(p+q)/2+1。
(4)hu矩:构造旋转不变性.hu矩是归一化中心矩的线性组合。hu矩是从中心矩中计算得到,其计算公式如下:
根据公式可以看到,每个图像对应7个hu矩。通过观察可以发现当阶数变高时,hu矩一般会变小。根据定义,高阶hu矩
由多个归一化矩的高阶幂计算得到,而归一化矩都是小于1的,所以指数越大,计算所得的值越小。
很自然,使用hu矩就可以比较两个物体判断他们的相似性。









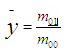
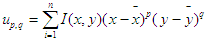
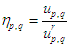















 9899
9899

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








