在多线程开发中停止线程是很重要的技术点。停止线程在Java语言中并不像break语句那样干脆,需要一些技巧性的处理。
一、 异常法
采用异常法来停止一个线程,首先我们需要了解一下两个方法的用法:
1、interrupt()方法
public class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++) {
System.out.println("i="+i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
MyThread thread=new MyThread();
thread.start();
thread.sleep(10);
thread.interrupt();
}
}上面的例子调用interrupt()方法来停止线程,但interrupt()方法的使用效果并不像for+break语句那样,马上就能停止循环。调用interrupt()方法仅仅是在当前线程打了一个停止的标记,并不是真的停止。那么如果停止线程了?我们接着往下面看。
2、判断线程是否是停止状态
1)、 interrupted()
public class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++) {
System.out.println("i="+i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
try{
MyThread thread=new MyThread();
thread.start();
thread.sleep(100);
thread.interrupt();
System.out.println("线程停止了吗1?--->"+thread.interrupted());
System.out.println("线程停止了吗2?--->"+thread.interrupted());
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}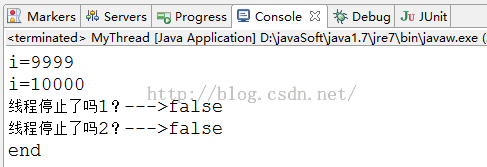
从控制台打印的结果来看,线程没有停止,这就是说,interrupted()测试当前线程是否中断,因为这个当前线程就是main,它没有中断过,所以打印的结果是两个false。
如何使main线程产生中断效果了。我们在看下,下面的例子:
public class MyThread{
public static void main(String[] args){
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
System.out.println("线程停止了吗1?---->"+Thread.interrupted());
System.out.println("线程停止了吗2?---->"+Thread.interrupted());
System.out.println("end");
}
}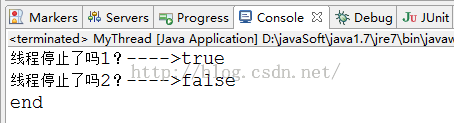
从上面的结果来看,interrupted()方法的确判断当前线程是否是停止状态。但是为什么第2个值是false。原来,连续两次调用该方法第一次会清除中断状态后,第二次调用所以返回flase。
2)、 isInterrupted()
public class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++) {
System.out.println("i="+i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
MyThread thread=new MyThread();
thread.start();
thread.sleep(10);
thread.interrupt();
System.out.println("线程停止了吗1?--->"+thread.isInterrupted());
System.out.println("线程停止了吗2?--->"+thread.isInterrupted());
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}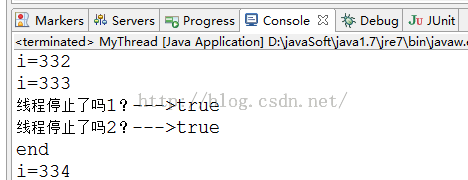
从结果看出方法isInterrupted()并未清除,所以打印出了两个true.
3、停止线程
public class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++) {
if(this.interrupted()){
System.out.println("线程是停止状态了,我要退出了.");
break;
}
System.out.println("i="+i);
}
System.out.println("如果此处还是循环,那么我就会继续执行.线程并没有停止");
}
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
MyThread thread=new MyThread();
thread.start();
thread.sleep(10);
thread.interrupt();
System.out.println("end");
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}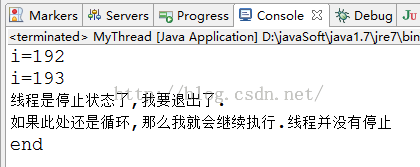
如果这么写的话,线程并没有停止。现在我们在修改下代码,也就是所谓的异常法停止线程。
public class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
try{
for (int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++) {
if(this.interrupted()){
System.out.println("线程是停止状态了,我要退出了.");
throw new InterruptedException();
}
System.out.println("i="+i);
}
System.out.println("我被执行了吗?");
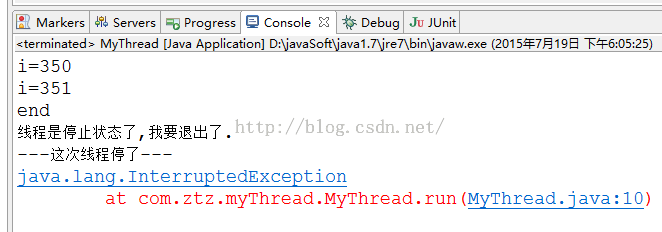
}catch(InterruptedException e){
System.out.println("---这次线程停了---");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
MyThread thread=new MyThread();
thread.start();
thread.sleep(10);
thread.interrupt();
System.out.println("end");
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
二、 在沉睡中停止
如果线程在sleep()状态下停止线程会有什么效果了?
public class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
try{
System.out.println("run start");
Thread.sleep(1000000);
System.out.println("run end");
}catch(InterruptedException e){
System.out.println("sleep被停止,状态:--->"+this.isInterrupted());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
MyThread thread=new MyThread();
thread.start();
thread.interrupt();
thread.sleep(1000);
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("main catch");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}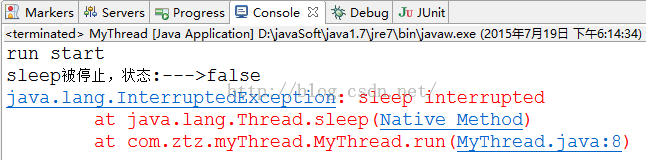
从结果我们可以看出,在线程睡眠时候停止某一线程,会异常,并且清除停止状态。我们前面异常停止线程,都是先睡眠,在停止线程,与之相反的操作,我写代码的时候需要注意下。
public class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
try{
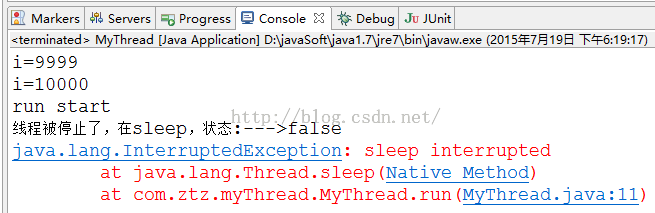
for (int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++) {
System.out.println("i="+i);
}
System.out.println("run start");
Thread.sleep(1000000);
System.out.println("run end");
}catch(InterruptedException e){
System.out.println("线程被停止了,在sleep,状态:--->"+this.isInterrupted());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
MyThread thread=new MyThread();
thread.start();
thread.interrupt();
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("main catch");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
三、 暴力停止
public class MyThread extends Thread{
private int i=0;
@Override
public void run() {
try{
while (true) {
i++;
System.out.println("i="+i);
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
MyThread thread=new MyThread();
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(6000);
thread.stop();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
stop()方法已经被弃用,如果强制让线程停止,可以会有一些清理工作没得到完成,还有就是对锁定的对象进行了解锁,导致数据不同步的现象,所以开发时候禁止使用该方法去暴力停止线程。
四、 使用return停止线程
public class MyThread extends Thread{
private int i=0;
@Override
public void run() {
try{
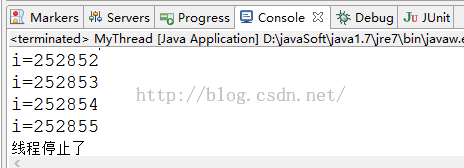
while (true) {
i++;
if(this.interrupted()){
System.out.println("线程停止了");
return;
}
System.out.println("i="+i);
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
MyThread thread=new MyThread();
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(2000);
thread.interrupt();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
PS:不过还是建议使用异常法来停止线程,因为在catch块中还可以将异常向上抛,使线程停止事件得到传播。
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。





















 8724
8724











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








